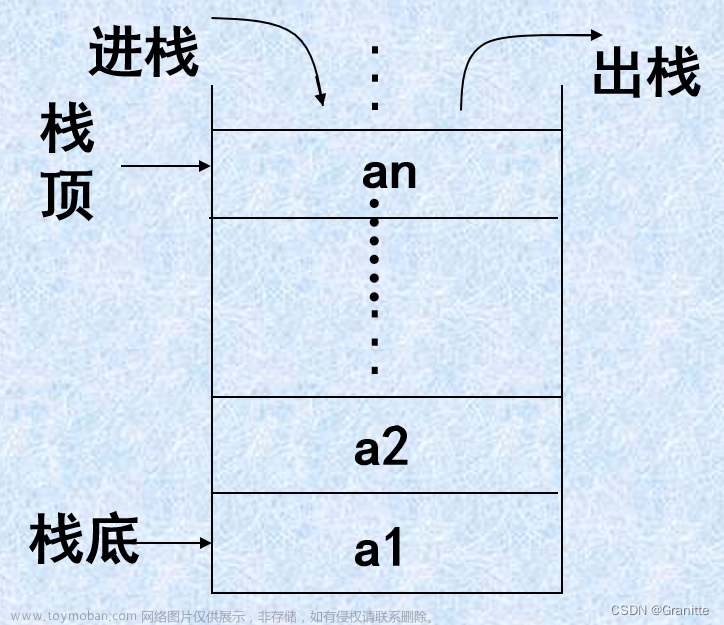
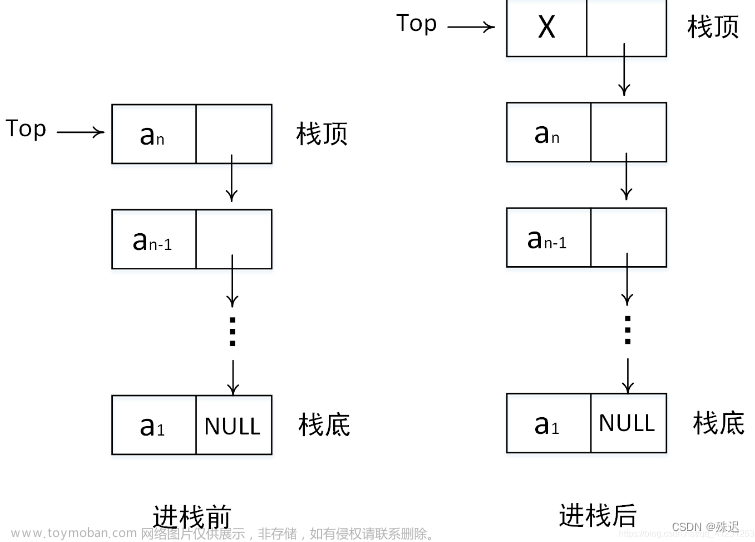
一、链栈概述
1.为什么要用链栈?
链式存储结构可以更好的避免栈上溢,因为顺序栈在定义结构体时需要定义最大值。
2.什么是链栈
栈的链式存储结构就是链栈,栈底就是链表的最后一个结点,而栈顶是链表的第一个结点,一个链栈可以由栈顶指针top唯一确定。
结构体的定义:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct Stack{
int data;
struct Stack *next;
}*LStack;
二、基本操作
//初始化链栈
int Init(LStack &top){
top=(Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
if(top==NULL){
printf("申请内存失败\n");
return -1;
}
top->next=NULL;
return 1;
}
//入栈
int pushLstack(LStack &top,int e){
LStack s;
s=(Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack)); //申请结点
if(s==NULL){
printf("申请失败!");
return -1;
}
s->data=e; //接收数据
s->next=top->next; //类似尾插链表
top->next=s;
return 1;
}
//出栈
int popLstack(LStack &top){
LStack p;
if(top->next==NULL){
printf("栈空!");
return 0;
}
p=top->next;
top->next=p->next;
printf("%d出栈\n",p->data);
free(p);
return 1;
}
//打印栈
int printLstack(LStack top){
if(top==NULL){
printf("栈空!\n");
return 0;
}
LStack p=top->next;
while(p){
printf("%d ",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
}
int main(){
LStack L;
Init(L); //初始化
int n,a;
printf("请输入进栈元素总数:");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
printf("请输入第%d个元素:",i);
scanf("%d",&a);
pushLstack(L,a); //for循环进栈
}
printf("此时栈序列为:");
printLstack(L); //打印
printf("\n");
popLstack(L); //出栈
popLstack(L); //出栈
printf("\n此时栈序列为:");
printLstack(L); //打印
}运行结果:

三、多重链栈
多重链栈用到结构体数组这一个点。
结构体数组的定义:
1.先声明结构体,再去定义结构体数组
struct 结构体名{
成员列表;
};
struct 结构体名 数组名[长度] ;
2.声明结构体的同时去定义结构体数组(结构体名可以省略).
struct 结构体名{
成员列表;
}数组名[长度];结构体数组的引用:
1.变量类型引用。
通过:结构数组名[ ].成员变量 来进行操作。
struct Day{
int year;
int mouth;
int day;
}stu[2];
Day[1].year=2022;
Day[1].mouth=2;
Day[1].day=7;
2.指针类型。
通过:结构数组名[ ]->成员变量来操作
typedef struct Stack{
int data;
struct Stack *next;
}*LStack;
struct Stack *top[3];
top[?]->next=?
top[?]->data=?多重链表操作:
//多重入栈
void pushs( Stack *top[3],int i,int x){ //i 代表要对哪一个栈进行入栈,x 是输入的值
Stack *p=(Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
p->data=x;
p->next=top[i]->next;
top[i]->next=p;
}
//多重出栈
void pops( Stack *top[3],int i){
if(top[i]->next==NULL){
printf("栈空!");
}
Stack *p=top[i]->next;
top[i]->next=p->next;
printf("%d出栈 ",p->data);
free(p);
}
//打印栈
int prints( Stack *top[3],int i){
if(top[i]==NULL){
printf("栈空!\n");
return 0;
}
LStack p=top[i]->next;
while(p){
printf("%d ",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
}
//main函数执行对于【1】栈的操作,其他的同理
int main(){
LStack top[3]; //声明
Init(top[3]); //初始化
pushs(&top[3],1,1); //1栈进 1-3
pushs(&top[3],1,2);
pushs(&top[3],1,3);
printf("\n此时1栈的序列为:");
prints(&top[3],1); //输出
printf("\n");
pops(&top[3],1); //1栈出栈
printf("\n此时1栈的序列为:");
prints(&top[3],1); //输出
}运行结果:(说明问题即可)文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-734665.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-734665.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-734665.html
到了这里,关于链栈(入栈,出栈,遍历)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!