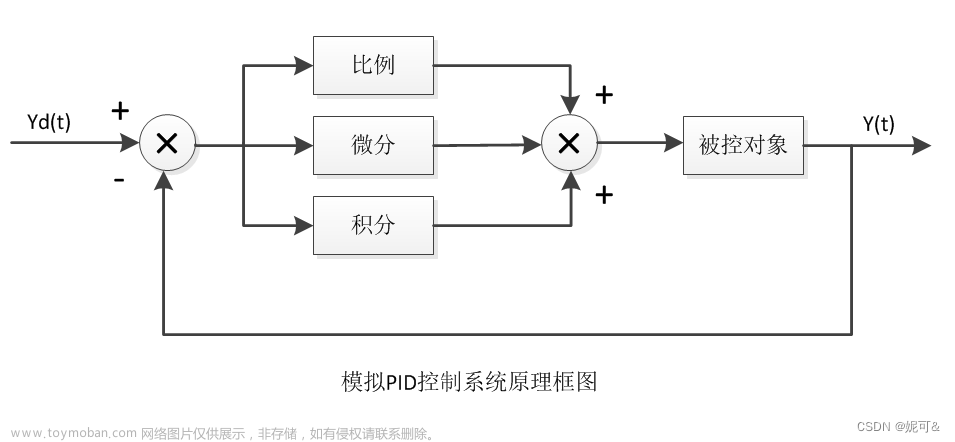
简介
在系统上存在外部干扰的情况下反馈是最好的选择否则使用前馈网络。为扭矩、通量和速度实施的调节器实际上是比例(P Proportional )、积分(I Integral)、微分 (D Derivative ) 调节器。 STM32中实际提供了3种,但是实际上我们常用的电机反馈调节使用的是PI反馈控制就够了。
PID的理解
带动图非常清晰
基维百科很好的资料
综上所述,
P—比例控制系统的响应快速性,快速作用于输出,好比"现在"(现在就起作用,快);
I—积分控制系统的准确性,消除过去的累积误差,好比"过去"(清除过去积怨,回到准确轨道);
D—微分控制系统的稳定性,具有超前控制作用,好比"未来"提前根据预测调整状态(放眼未来,未雨绸缪,稳定才能发展)。
当然这个结论也不可一概而论,只是想让初学者更加快速的理解PID的作用。

其中
Kp:比例增益,是调适参数
Ki:积分增益,也是调适参数
Kd:微分增益,也是调适参数
e:误差=设定值(SP)- 回授值(PV)
t:目前时间
τ:积分变数(dτ 的符号),数值从0到目前时间τ
用更专业的话来讲,PID控制器可以视为是频域系统的滤波器。在计算控制器最终是否会达到稳定结果时,此性质很有用。如果数值挑选不当,控制系统的输入值会反复振荡,这导致系统可能永远无法达到预设值。
PID控制器的一般转移函数是:
其中C是一个取决于系统带宽的常数。

参考《STM32F PMSM single/dual FOC SDK》文档
PID原理
文档章节4
并联:
我们平时使用到并联的PI的示意图,不过该图对于不同频率的时候的响应有缺陷。
串联:

并行模式Ki Kp变化的时候的0点对于频率的位置是变化的,即闭环的频率响应中实现极点0点消除。
使用串行模式可以避免频率变化0点对应位置不变。相关的参数变为了Ka和Kb,Ka=Kp ,Kb=Ki/Kp。

对应设置:
总结:
- 两种拓扑结构,在书本上并联PI的结构可能要比串联的常见。
- 并联拓扑,kp和ki并不解耦,都影响着系统的零点。
- 串联拓扑,kp影响系统增益,ki影响系统带宽,相互独立的。
- 两种拓扑的软件复杂度是相同的
- 实际工程中,工程师可能更倾向使用串联拓扑,工程的角度,kp和ki直接和系统参数相关联。
ST例子的PI实现
下面代码的实现:OUT=(erroKp)/KpPow+(erroKi)/KpPow 和保存 sum_Ki*erro其中做了一些范围限定。
/**
* @brief This function compute the output of a PI regulator sum of its
* proportional and integral terms
* @param pHandle: handler of the current instance of the PID component
* @param wProcessVarError: current process variable error, intended as the reference
* value minus the present process variable value
* @retval computed PI output
*/
__weak int16_t PI_Controller( PID_Handle_t * pHandle, int32_t wProcessVarError )
{
int32_t wProportional_Term, wIntegral_Term, wOutput_32, wIntegral_sum_temp;
int32_t wDischarge = 0;
int16_t hUpperOutputLimit = pHandle->hUpperOutputLimit;
int16_t hLowerOutputLimit = pHandle->hLowerOutputLimit;
/* Proportional term computation*/
wProportional_Term = pHandle->hKpGain * wProcessVarError;//输入误差首先Kp比例调整
/* Integral term computation */
if ( pHandle->hKiGain == 0 )//判断I的积分是否为0p
{
pHandle->wIntegralTerm = 0;
}
else
{
wIntegral_Term = pHandle->hKiGain * wProcessVarError;//误差乘以Ki积分比例
wIntegral_sum_temp = pHandle->wIntegralTerm + wIntegral_Term;//将本次值加入到积分内容
if ( wIntegral_sum_temp < 0 )//如果最新的积分值小于0(判断是否超出INT32的界限)不过由于后面有最大最小的限制,如果能保证wIntegral_sum_temp 的范围这个界限判断应该可以忽略
{ //如果正+正=负肯定是超界了需要纠正为正最大
if ( pHandle->wIntegralTerm > 0 )
{
if ( wIntegral_Term > 0 )
{
wIntegral_sum_temp = INT32_MAX;
}
}
}
else//如果最新的积分值大于0
{ //如果负+负=正肯定是超界了需要纠正为负最大
if ( pHandle->wIntegralTerm < 0 )
{
if ( wIntegral_Term < 0 )
{
wIntegral_sum_temp = -INT32_MAX;
}
}
}
//限制最大最小值,其实有这个模块我认为上面的限制应该可以简化
if ( wIntegral_sum_temp > pHandle->wUpperIntegralLimit )
{
pHandle->wIntegralTerm = pHandle->wUpperIntegralLimit;
}
else if ( wIntegral_sum_temp < pHandle->wLowerIntegralLimit )
{
pHandle->wIntegralTerm = pHandle->wLowerIntegralLimit;
}
else
{
pHandle->wIntegralTerm = wIntegral_sum_temp;
}
}
//根据硬件选择较优的计算方式(注意的是P是除hKpDivisor ,I是除hKiDivisor 代码中定义的是2的14次方) ,为何要除或者位移2的N次方,是因为避免使用小数计算。所有值进行了整数放大后在对应缩小
//MISRA_C 是一种汽车级的C语言编程标准,设置该模式不能使用2位移的方式。
#ifdef FULL_MISRA_C_COMPLIANCY
wOutput_32 = ( wProportional_Term / ( int32_t )pHandle->hKpDivisor ) + ( pHandle->wIntegralTerm /
( int32_t )pHandle->hKiDivisor );
#else
/* WARNING: the below instruction is not MISRA compliant, user should verify
that Cortex-M3 assembly instruction ASR (arithmetic shift right)
wProportional_Term is used by the compiler to perform the shifts (instead of LSR
logical shift right)*/
wOutput_32 = ( wProportional_Term >> pHandle->hKpDivisorPOW2 ) + ( pHandle->wIntegralTerm >> pHandle->hKiDivisorPOW2 );
#endif
if ( wOutput_32 > hUpperOutputLimit )//判断输出是否超界限如果超界限,那么I的积分部分需要减去超界值
{
wDischarge = hUpperOutputLimit - wOutput_32;
wOutput_32 = hUpperOutputLimit;
}
else if ( wOutput_32 < hLowerOutputLimit )
{
wDischarge = hLowerOutputLimit - wOutput_32;
wOutput_32 = hLowerOutputLimit;
}
else { /* Nothing to do here */ }
pHandle->wIntegralTerm += wDischarge;
return ( ( int16_t )( wOutput_32 ) );
}
ST例子的使用理解
//由于处理器浮点运算能力较弱,所以使用了整数运算的方式来处理,值*KP/KPDiviser这样的方式。为了进一步的提高效率,对应M3的处理器还使用了2的N次位移的方式处理,当然也可以选择使用整数除的方式。(还有个原因是PID函数返回的是16位的INT类型数据,不进行位移或者除可能会导致超界),STM32还是太弱了如果直接用浮点哪有这么多倒腾?
register_interface.c(251) : PID_SetKP(pPIDIq[motorID], (int16_t)regdata16); //设置Kp参数
register_interface.c(257) : PID_SetKI(pPIDIq[motorID], (int16_t)regdata16); //设置Ki参数
register_interface.c(263) : PID_SetKD(pPIDIq[motorID], (int16_t)regdata16); //设置Kd参数
register_interface.c(429) : PID_SetKPDivisorPOW2(pPIDIq[motorID], regdata16); //设置Kp参数除以2的n次方表示
register_interface.c(435) : PID_SetKIDivisorPOW2(pPIDIq[motorID], regdata16); //设置Ki参数除以2的n次方表示
register_interface.c(441) : PID_SetKDDivisorPOW2(pPIDIq[motorID], regdata16); //设置Kd参数除以2的n次方表示
/*
在前面代码中的部分,位了提高效率使用位移代替除法加速
#ifdef FULL_MISRA_C_COMPLIANCY
wOutput_32 = ( wProportional_Term / ( int32_t )pHandle->hKpDivisor ) + ( pHandle->wIntegralTerm /
( int32_t )pHandle->hKiDivisor );
#else
/* WARNING: the below instruction is not MISRA compliant, user should verify
that Cortex-M3 assembly instruction ASR (arithmetic shift right)
wProportional_Term is used by the compiler to perform the shifts (instead of LSR
logical shift right)*/
wOutput_32 = ( wProportional_Term >> pHandle->hKpDivisorPOW2 ) + ( pHandle->wIntegralTerm >> pHandle->hKiDivisorPOW2 );
#endif
*/
register_interface.c(714) : *regdata16 = PID_GetKP(pPIDIq[motorID]);//获取Kp设置值
register_interface.c(720) : *regdata16 = PID_GetKI(pPIDIq[motorID]);//获取Ki设置值
register_interface.c(726) : *regdata16 = PID_GetKD(pPIDIq[motorID]);//获取Kd设置值
register_interface.c(958) : *regdataU16 = PID_GetKPDivisorPOW2(pPIDIq[motorID]);//获取Kp的除以2n次模式设置值
register_interface.c(964) : *regdataU16 = PID_GetKIDivisorPOW2(pPIDIq[motorID]);//获取Ki的除以2n次模式设置值
register_interface.c(970) : *regdataU16 = PID_GetKDDivisorPOW2(pPIDIq[motorID]);//获取Kd的除以2n次模式设置值
//wIntegral_Term 积分相
mc_tasks.c(667) : PID_SetIntegralTerm(pPIDIq[bMotor], ((int32_t)0));//设置启动积分相部分(一般初始化的时候)
mc_tasks.c(903) : Vqd.q = PI_Controller(pPIDIq[M1], (int32_t)(FOCVars[M1].Iqdref.q) - Iqd.q);//调用PI算法输入最近的差值,获取PI算法计算后的值
mc_config.c(346) : PID_Handle_t *pPIDIq[NBR_OF_MOTORS] = {&PIDIqHandle_M1};
mc_config.h(65) : extern PID_Handle_t *pPIDIq[NBR_OF_MOTORS];
void PID_SetLowerIntegralTermLimit(PID_Handle_t *pHandle, int32_t wLowerLimit) //设置积分部分下限
void PID_SetUpperIntegralTermLimit(PID_Handle_t *pHandle, int32_t wUpperLimit) //设置积分部分上限
void PID_SetLowerOutputLimit(PID_Handle_t *pHandle, int16_t hLowerLimit) //设置输出的下限
void PID_SetUpperOutputLimit(PID_Handle_t *pHandle, int16_t hUpperLimit) //设置输出的上限
PID时需要注意的事项
由于PID时有个d的微分项目。
void PID_SetPrevError(PID_Handle_t *pHandle, int32_t wPrevProcessVarError); //设置上一次的微分差值(微分初始化)
wDeltaError = wProcessVarError - pHandle->wPrevProcessVarError;//记录上一次的误差和当前的误差比较,获取差值
wDifferential_Term = pHandle->hKdGain * wDeltaError;//微分项目乘以微分增益
#ifndef FULL_MISRA_C_COMPLIANCY_PID_REGULATOR
wDifferential_Term >>= pHandle->hKdDivisorPOW2;//微分除
#else
wDifferential_Term /= ((int32_t)pHandle->hKdDivisor);
#endif
pHandle->wPrevProcessVarError = wProcessVarError;//保存本次值等下异次使用微分项目
wTemp_output = PI_Controller(pHandle, wProcessVarError) + wDifferential_Term;//PI项加上微分项即为PID值
PID使用例子
使用时设置的Divisor 都是为了不让PID最终结果不超过int16使用的。
/* Gains values for position control loops */
#define PID_POSIT_KP_DEFAULT 256
#define PID_POSIT_KI_DEFAULT 0
#define PID_POSIT_KD_DEFAULT 0
/*control loop gains dividers*/
#define POSIT_KPDIV 1024//16384
#define POSIT_KIDIV 8192//16384
#define POSIT_KDDIV 256//8192
#define POSIT_KPDIV_LOG LOG2((POSIT_KPDIV))
#define POSIT_KIDIV_LOG LOG2((POSIT_KIDIV))
#define POSIT_KDDIV_LOG LOG2((POSIT_KDDIV))
/* USER CODE BEGIN PID_SPEED_INTEGRAL_INIT_DIV */
#define PID_POSIT_INTEGRAL_INIT_DIV 1 /* */
/* USER CODE END PID_SPEED_INTEGRAL_INIT_DIV */
PID_Handle_t PIDHandle_POSITION_SPEED =
{
.hDefKpGain = (int16_t)PID_POSIT_KP_DEFAULT,
.hDefKiGain = (int16_t)PID_POSIT_KI_DEFAULT,
.wUpperIntegralLimit = (int32_t)INT16_MAX * POSIT_KIDIV,//return result is int16 so mast limit
.wLowerIntegralLimit = (int32_t)-INT16_MAX * POSIT_KIDIV,
.hUpperOutputLimit = INT16_MAX,//return result is int16 so mast limit
.hLowerOutputLimit = -INT16_MAX,
.hKpDivisor = (uint16_t)POSIT_KPDIV,
.hKiDivisor = (uint16_t)POSIT_KIDIV,
.hKpDivisorPOW2 = (uint16_t)POSIT_KPDIV_LOG,
.hKiDivisorPOW2 = (uint16_t)POSIT_KIDIV_LOG,
.hDefKdGain = (int16_t)PID_POSIT_KD_DEFAULT,
.hKdDivisor = POSIT_KDDIV,
.hKdDivisorPOW2 = POSIT_KDDIV_LOG,
};
int position_speed=1000;
int now_speed=0;
void test_position(void){
int i;
PID_HandleInit(&PIDHandle_POSITION_SPEED);//init the
PID_SetIntegralTerm(&PIDHandle_POSITION_SPEED, ((int32_t)0));
while(1){
now_speed=PID_Controller(&PIDHandle_POSITION_SPEED,position_speed-now_speed);
for(i=0;i<1000;i++);
}
}
设置与曲线状态
PI
/* Gains values for position control loops */
#define PID_POSIT_KP_DEFAULT 256
#define PID_POSIT_KI_DEFAULT 0
#define PID_POSIT_KD_DEFAULT 0
#define POSIT_KPDIV 1024
#define POSIT_KIDIV 1024
#define POSIT_KDDIV 256
只有比例误差将被固定
修改PID_POSIT_KP_DEFAULT 为1000时
#define PID_POSIT_KP_DEFAULT 256
#define PID_POSIT_KI_DEFAULT 256
PID
/* Gains values for position control loops */
#define PID_POSIT_KP_DEFAULT 256
#define PID_POSIT_KI_DEFAULT 512
#define PID_POSIT_KD_DEFAULT 64
/* control loop gains dividers*/
#define POSIT_KPDIV 1024//16384
#define POSIT_KIDIV 1024//16384
#define POSIT_KDDIV 8192//8192

/* Gains values for position control loops */
#define PID_POSIT_KP_DEFAULT 256
#define PID_POSIT_KI_DEFAULT 512
#define PID_POSIT_KD_DEFAULT 128
/* control loop gains dividers*/
#define POSIT_KPDIV 1024//16384
#define POSIT_KIDIV 1024//16384
#define POSIT_KDDIV 8192//8192

/* Gains values for position control loops */
#define PID_POSIT_KP_DEFAULT 256
#define PID_POSIT_KI_DEFAULT 512
#define PID_POSIT_KD_DEFAULT 2048
/* control loop gains dividers*/
#define POSIT_KPDIV 1024//16384
#define POSIT_KIDIV 1024//16384
#define POSIT_KDDIV 8192//8192

使用 /* Gains values for torque and flux control loops */ 参数的效果
/* Gains values for position control loops */
#define PID_POSIT_KP_DEFAULT 965
#define PID_POSIT_KI_DEFAULT 197
#define PID_POSIT_KD_DEFAULT 100
/* control loop gains dividers*/
#define POSIT_KPDIV 16384
#define POSIT_KIDIV 16384
#define POSIT_KDDIV 8192
参数的PID效果

SPEED 的PI

PID_FLUX_KP_DEFAULT 参数


PIDSpeedHandle_M1
调用积分项初始化的状态STO_ExecutePLL函数中调用,其中错误是比较小的量比如0XFFFFFFC1。
hTorqueReference = PI_Controller(pHandle->PISpeed, (int32_t)hError);

测试发现对于该PID 不能使用太大的数值查,容易形成震旦的效果,使用下面设置可以较为稳定的进入到设定值。
now_speed=PI_Controller(&PIDHandle_POSITION_SPEED,erro);
if(now_speed>position_speed)
erro=-5;
else
erro=4;
需要注意的事项
在FOC_CurrControllerM1的PI_Controller(pPIDIq[M1]
Vqd.q = PI_Controller(pPIDIq[M1], (int32_t)(FOCVars[M1].Iqdref.q) - Iqd.q);
需要除一个比例值,因为中间是有个比例转换,从I电流的范围转到了V电压范围。而且电流是根据采样电阻和最大AD值比例来处理的。 电机最大电流值对应着输出V最大值,那么他们间就有个比例值转换。
I 电机 0- 最大Imax 对应着输出 V 0 -最大值 0X7FFF
vss = PI_Controller(pPIDIq[M1], (int32_t)(100 - vss))/0x100;//需要除个比例值否则不正常。
从ST的文档获取算法上的状态
I和V对应的原理关系图:
本身I转V,V又转回I ,其中又部分电压电流转换关系可以抵消去除
最终的关系图:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-735982.html

 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-735982.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-735982.html
到了这里,关于STM32 FOC电机PID学习笔记的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!






![[FOC-Simulink]使用Simulink代码生成工具基于STM32开发板对永磁同步电机进行开环控制](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/648307-1.png)