6 最短路径
最短路径,对于图来说,是两顶点之间经过的边数最少的路径;对于网来说,是指两顶点之间经过的边上权值之和最小的路径。路径上第一个顶点为源点,最后一个顶点是终点。
6.1 迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法
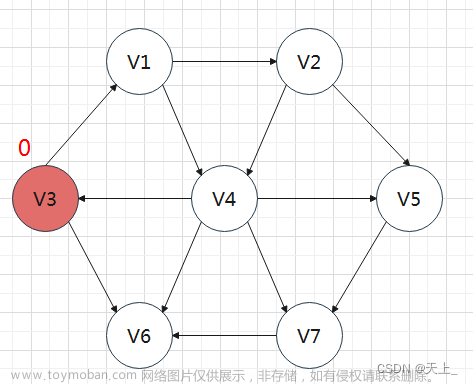
以如下无向图为例:

我们来计算下标为0的顶点,到其他顶点的最短路径,首先定义三个数组,calculated[j]表示0->j的最短路径是否已计算出来,pathVal[j]表示0->j的最短路径,目前还未进行计算,我们设置所有元素值均为无穷大,pre[j]表示0->j中经历的顶点,例如pre[1]=3、pre[3]=2、pre[2]=0,表示的:
(1) pre[1]=3表示0->1需要经过3;
(2) pre[3]=2表示0->3需要经过2;
(3) pre[2]=0表示0->2可以直达;
(4) 因此可以得出结论,0->1的路径是:0->2->3->1;
再定义一个变量min,表示“0->上一个顶点的最小权值”,k表示min对应的顶点的下标,因此初始情况如下所示:

接下来来看0到第0个顶点的最短路径,这个不需要计算,肯定是0,且不需要经过其他顶点,因此有如下情况:

到目前为止,min仍然为0,k仍然为0,接下来看0到其他顶点的最短路径,我们把arc[0][j]与现有的pathVal[j]比较,规则是:
(1) calculated[j]=1表示已找到最短路径,不进行任何处理;
(2) 如果arc[0][j]+min<pathVal[j],则令pathVal[j]=arc[0][j]+min,令pre[j]=k,表示0->j至少要经过顶点k;
(3) 如果arc[0][j]+min>=pathVal[j],则pathVal[j]不变,pre[j]也不变,表示0->j不会经过顶点k;
那么,有以下结果:
(1) calculated[0]=1,不进行任何处理;
(2) arc[0][1]+min=16+0<pathVal[1]=无穷大,令pathVal[1]=arc[0][1]+min=16,令pre[j]=k=0;
(3) arc[0][2]、arc[0][3]与arc[0][1]处理方式一致;
(4) arc[0][4]和arc[0][5]都为无穷大,加上min后等于pathVal[4]和pathVal[5],因此pathVal[4]、pathVal[5]和pre[4]、pre[5]不进行处理;
(5) 这时来看最新的pathVal[j],发现最小的权是pathVal[3],于是令min=pathVal[3]=12,令k=3,这也表示0->3的最短路径已找到,因此令calculated[3]=1,如下:

k=3,即其他未计算出的最短路径,都有可能会经过顶点3,因此我们把arc[3][j]与现有pathVal[j]比较,规则仍与arc[0][j]时一致,特别的,arc[3][2]+min=10+12=26>pathVal[2]=15,因此pathVal[2]和pre[2]不进行变更,当然,arc[3][1]也是同样的:

这时,min=15,k=2,因此处理arc[2][j],如下:

然后继续处理,直到calculated[j]的元素都为1:

我们来看现在的pathVal[j]和pre[j]:

可以知道以下内容:
(1) 顶点5,即E,对应的pathVal[5]是43,pre[4]是4,因此顶点0->5,即C->E的最短路径是43,且中间肯定会经过顶点4即顶点F,即肯定有C->F->E;
(2) 顶点4,即F,对应的pathVal[4]是26,pre[4]是3,因此顶点0->4,即C->F的最短路径是26,且中间肯定会经过顶点3即顶点B,即肯定有C->B->F,结点(1),那么肯定有C->B->F->E;
(3) 顶点3,即B,对应的pathVal[3]是12,pre[3]是0,因此顶点0->3,即C->B的最短路径是12,且无中间顶点,那么,结点(1)和(2),得到结论;
1) C到B的最短路径是12,路径是C->B;
2) C到F的最短路径是26,路径是C->B->F;
3) C到E的最短路径是43,路径是C->B->F->E;
(4) 同样的规则,能分析到:
1) C到A的最短路径是15,路径是C->A;
2) C到D的最短路径是15,路径是C->A->D;
以上即为迪杰斯特拉算法。
由上也可知,邻接矩阵的迪杰斯特拉算法实现代码如下所示:
/**
* 迪杰斯特拉算法获取最短路径
*
* @param fromVertexIndex 起始顶点下标
* @return 起始顶点到各顶点的最短路径及前驱顶点列表
* @author Korbin
* @date 2023-02-20 14:54:35
**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object[][] shortestPathDijkstra(int fromVertexIndex) {
// 最短路径权值,初始化为fromVertexIndex的权
W[] pathVal = (W[]) Array.newInstance(infinity.getClass(), vertexNum);
// 是否已计算,初始值为false
boolean[] calculated = new boolean[vertexNum];
// 要到达此顶点应先从哪个顶点过来,初始值为fromVertexIndex
Integer[] pre = new Integer[vertexNum];
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
pathVal[i] = arc[fromVertexIndex][i];
pre[i] = fromVertexIndex;
}
// 最小权值
W minWeight = null;
// 最小权值对应的索引下标
int minWeightIndex = fromVertexIndex;
// 已计算的顶点数量,初始值为0
int calculatedNum;
// 从fromVertexIndex到fromVertexIndex,令pathVal[fromVertexIndex]为0,令pre[fromVertexIndex]为fromVertexIndex
// ,令calculated[fromVertexIndex]为true
pathVal[fromVertexIndex] = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);
pre[fromVertexIndex] = fromVertexIndex;
calculated[fromVertexIndex] = true;
calculatedNum = 1;
while (calculatedNum < vertexNum) {
// 循环到所有顶点都计算完毕
// 处理arc[minWeightIndex][j]
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
// 跳过calculated[j]为true的顶点
if (!calculated[i]) {
// 与现有pathVal[j]比较
if (infinity instanceof Integer) {
// 对于arc[minWeightIndex][i]为无穷大的也不处理
if (!arc[minWeightIndex][i].equals(infinity)) {
// 只处理权值是Integer的情况,其他类型的类似处理
if (null == minWeight) {
minWeight = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);
}
W arcI = (W) (Integer.valueOf((Integer) arc[minWeightIndex][i] + (Integer) minWeight));
if (arcI.compareTo(pathVal[i]) < 0) {
// 令pathVal[j]=arc[minWeightIndex][j] + minWeight
pathVal[i] = arcI;
// 令pre[j]=minWeightIndex
pre[i] = minWeightIndex;
}
}
}
}
}
// 从pathVal和pre中取出新的minWeight和minWeightIndex
minWeight = null;
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
// 跳过已计算最短路径的顶点
if (!calculated[i] && (null == minWeight || minWeight.compareTo(pathVal[i]) > 0)) {
minWeight = pathVal[i];
minWeightIndex = i;
}
}
// 设置minWeightIndex对应的顶点为已访问
calculated[minWeightIndex] = true;
calculatedNum++;
// 用于测试
System.out.println("min weight is " + minWeight + ", min weight index is " + minWeightIndex);
StringBuilder builder1 = new StringBuilder("path val is [");
StringBuilder builder2 = new StringBuilder("pre vertex is [");
StringBuilder builder3 = new StringBuilder("calculated is [");
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
builder1.append(pathVal[i]).append(",");
builder2.append(pre[i]).append(",");
builder3.append(calculated[i]).append(",");
}
builder1.append("]");
builder2.append("]\n\r");
builder3.append("]");
System.out.println(builder3);
System.out.println(builder1);
System.out.println(builder2);
}
Object[][] result = new Object[2][];
result[0] = pathVal;
result[1] = pre;
return result;
}
邻接表代码如下:
/**
* 迪杰斯特拉算法获取最短路径
*
* @param fromVertexIndex 起始顶点下标
* @return 起始顶点到各顶点的最短路径及前驱顶点列表
* @author Korbin
* @date 2023-02-20 14:54:35
**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object[][] shortestPathDijkstra(int fromVertexIndex) {
// 最短路径权值,初始化为fromVertexIndex的权
W[] pathVal = (W[]) Array.newInstance(infinity.getClass(), vertexNum);
// 是否已计算,初始值为false
boolean[] calculated = new boolean[vertexNum];
// 要到达此顶点应先从哪个顶点过来,初始值为fromVertexIndex
Integer[] pre = new Integer[vertexNum];
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
pre[i] = fromVertexIndex;
pathVal[i] = infinity;
}
// 处理第一个顶点
VertexNode<T, W> vertexNode = vertexes[fromVertexIndex];
EdgeNode<W> edgeNode = vertexNode.getFirstEdge();
while (null != edgeNode) {
int refIndex = edgeNode.getIndex();
W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();
pathVal[refIndex] = weight;
edgeNode = edgeNode.getNext();
}
// 最小权值
W minWeight = null;
// 最小权值对应的索引下标
int minWeightIndex = fromVertexIndex;
// 已计算的顶点数量,初始值为0
int calculatedNum;
// 从fromVertexIndex到fromVertexIndex,令pathVal[fromVertexIndex]为0,令pre[fromVertexIndex]为fromVertexIndex
// ,令calculated[fromVertexIndex]为true
pathVal[fromVertexIndex] = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);
pre[fromVertexIndex] = fromVertexIndex;
calculated[fromVertexIndex] = true;
calculatedNum = 1;
while (calculatedNum < vertexNum) {
// 循环到所有顶点都计算完毕
// 处理本顶点指向的顶点
vertexNode = vertexes[minWeightIndex];
edgeNode = vertexNode.getFirstEdge();
while (null != edgeNode) {
int refIndex = edgeNode.getIndex();
W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();
// 跳过calculated[j]为true的顶点
if (!calculated[refIndex]) {
// 与现有pathVal[j]比较
if (infinity instanceof Integer) {
// 对于weight为无穷大的也不处理
if (!weight.equals(infinity)) {
// 只处理权值是Integer的情况,其他类型的类似处理
if (null == minWeight) {
minWeight = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);
}
W arcI = (W) (Integer.valueOf((Integer) weight + (Integer) minWeight));
if (arcI.compareTo(pathVal[refIndex]) < 0) {
// 令pathVal[j]=arc[minWeightIndex][j] + minWeight
pathVal[refIndex] = arcI;
// 令pre[j]=minWeightIndex
pre[refIndex] = minWeightIndex;
}
}
}
}
edgeNode = edgeNode.getNext();
}
// 从pathVal和pre中取出新的minWeight和minWeightIndex
minWeight = null;
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
// 跳过已计算最短路径的顶点
if (!calculated[i] && (null == minWeight || minWeight.compareTo(pathVal[i]) > 0)) {
minWeight = pathVal[i];
minWeightIndex = i;
}
}
// 设置minWeightIndex对应的顶点为已访问
calculated[minWeightIndex] = true;
calculatedNum++;
// 用于测试
System.out.println("min weight is " + minWeight + ", min weight index is " + minWeightIndex);
StringBuilder builder1 = new StringBuilder("path val is [");
StringBuilder builder2 = new StringBuilder("pre vertex is [");
StringBuilder builder3 = new StringBuilder("calculated is [");
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
builder1.append(pathVal[i]).append(",");
builder2.append(pre[i]).append(",");
builder3.append(calculated[i]).append(",");
}
builder1.append("]");
builder2.append("]\n\r");
builder3.append("]");
System.out.println(builder3);
System.out.println(builder1);
System.out.println(builder2);
}
Object[][] result = new Object[2][];
result[0] = pathVal;
result[1] = pre;
return result;
}
十字链表的迪杰斯特拉算法实现:
/**
* 迪杰斯特拉算法获取最短路径
*
* @param fromVertexIndex 起始顶点下标
* @return 起始顶点到各顶点的最短路径及前驱顶点列表
* @author Korbin
* @date 2023-02-20 14:54:35
**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object[][] shortestPathDijkstra(int fromVertexIndex) {
// 最短路径权值,初始化为fromVertexIndex的权
W[] pathVal = (W[]) Array.newInstance(infinity.getClass(), vertexNum);
// 是否已计算,初始值为false
boolean[] calculated = new boolean[vertexNum];
// 要到达此顶点应先从哪个顶点过来,初始值为fromVertexIndex
Integer[] pre = new Integer[vertexNum];
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
pre[i] = fromVertexIndex;
pathVal[i] = infinity;
}
// 处理第一个顶点
AcrossLinkVertexNode<T, W> vertexNode = vertexes[fromVertexIndex];
AcrossLinkEdgeNode<W> edgeNode = vertexNode.getFirstOut();
while (null != edgeNode) {
int refIndex = edgeNode.getHeadIndex();
W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();
pathVal[refIndex] = weight;
edgeNode = edgeNode.getNextHead();
}
// 最小权值
W minWeight = null;
// 最小权值对应的索引下标
int minWeightIndex = fromVertexIndex;
// 已计算的顶点数量,初始值为0
int calculatedNum;
// 从fromVertexIndex到fromVertexIndex,令pathVal[fromVertexIndex]为0,令pre[fromVertexIndex]为fromVertexIndex
// ,令calculated[fromVertexIndex]为true
pathVal[fromVertexIndex] = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);
pre[fromVertexIndex] = fromVertexIndex;
calculated[fromVertexIndex] = true;
calculatedNum = 1;
while (calculatedNum < vertexNum) {
// 循环到所有顶点都计算完毕
// 处理本顶点指向的顶点
vertexNode = vertexes[minWeightIndex];
edgeNode = vertexNode.getFirstOut();
while (null != edgeNode) {
int refIndex = edgeNode.getHeadIndex();
W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();
// 跳过calculated[j]为true的顶点
if (!calculated[refIndex]) {
// 与现有pathVal[j]比较
if (infinity instanceof Integer) {
// 对于weight为无穷大的也不处理
if (!weight.equals(infinity)) {
// 只处理权值是Integer的情况,其他类型的类似处理
if (null == minWeight) {
minWeight = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);
}
W arcI = (W) (Integer.valueOf((Integer) weight + (Integer) minWeight));
if (arcI.compareTo(pathVal[refIndex]) < 0) {
// 令pathVal[j]=arc[minWeightIndex][j] + minWeight
pathVal[refIndex] = arcI;
// 令pre[j]=minWeightIndex
pre[refIndex] = minWeightIndex;
}
}
}
}
edgeNode = edgeNode.getNextHead();
}
// 从pathVal和pre中取出新的minWeight和minWeightIndex
minWeight = null;
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
// 跳过已计算最短路径的顶点
if (!calculated[i] && (null == minWeight || minWeight.compareTo(pathVal[i]) > 0)) {
minWeight = pathVal[i];
minWeightIndex = i;
}
}
// 设置minWeightIndex对应的顶点为已访问
calculated[minWeightIndex] = true;
calculatedNum++;
// 用于测试
System.out.println("min weight is " + minWeight + ", min weight index is " + minWeightIndex);
StringBuilder builder1 = new StringBuilder("path val is [");
StringBuilder builder2 = new StringBuilder("pre vertex is [");
StringBuilder builder3 = new StringBuilder("calculated is [");
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
builder1.append(pathVal[i]).append(",");
builder2.append(pre[i]).append(",");
builder3.append(calculated[i]).append(",");
}
builder1.append("]");
builder2.append("]\n\r");
builder3.append("]");
System.out.println(builder3);
System.out.println(builder1);
System.out.println(builder2);
}
Object[][] result = new Object[2][];
result[0] = pathVal;
result[1] = pre;
return result;
}
邻接多重表的迪杰斯特拉算法实现如下:
/**
* 迪杰斯特拉算法获取最短路径
*
* @param fromVertexIndex 起始顶点下标
* @return 起始顶点到各顶点的最短路径及前驱顶点列表
* @author Korbin
* @date 2023-02-20 14:54:35
**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object[][] shortestPathDijkstra(int fromVertexIndex) {
// 最短路径权值,初始化为fromVertexIndex的权
W[] pathVal = (W[]) Array.newInstance(infinity.getClass(), vertexNum);
// 是否已计算,初始值为false
boolean[] calculated = new boolean[vertexNum];
// 要到达此顶点应先从哪个顶点过来,初始值为fromVertexIndex
Integer[] pre = new Integer[vertexNum];
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
pre[i] = fromVertexIndex;
pathVal[i] = infinity;
}
// 处理第一个顶点
AdjacencyMultiVertexNode<T, W> vertexNode = vertexes[fromVertexIndex];
AdjacencyMultiEdgeNode<W> edgeNode = vertexNode.getFirstEdge();
boolean firstEdge = true;
while (null != edgeNode) {
int refIndex = 0;
W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();
if (firstEdge) {
refIndex = edgeNode.getJVex();
edgeNode = edgeNode.getILink();
firstEdge = false;
} else {
int iVex = edgeNode.getIVex();
int jVex = edgeNode.getJVex();
if (iVex == fromVertexIndex) {
refIndex = jVex;
edgeNode = edgeNode.getJLink();
} else if (jVex == fromVertexIndex) {
refIndex = iVex;
edgeNode = edgeNode.getILink();
}
}
pathVal[refIndex] = weight;
}
// 最小权值
W minWeight = null;
// 最小权值对应的索引下标
int minWeightIndex = fromVertexIndex;
// 已计算的顶点数量,初始值为0
int calculatedNum;
// 从fromVertexIndex到fromVertexIndex,令pathVal[fromVertexIndex]为0,令pre[fromVertexIndex]为fromVertexIndex
// ,令calculated[fromVertexIndex]为true
pathVal[fromVertexIndex] = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);
pre[fromVertexIndex] = fromVertexIndex;
calculated[fromVertexIndex] = true;
calculatedNum = 1;
while (calculatedNum < vertexNum) {
// 循环到所有顶点都计算完毕
// 处理本顶点指向的顶点
vertexNode = vertexes[minWeightIndex];
edgeNode = vertexNode.getFirstEdge();
firstEdge = true;
while (null != edgeNode) {
int refIndex = 0;
W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();
if (firstEdge) {
refIndex = edgeNode.getJVex();
edgeNode = edgeNode.getILink();
firstEdge = false;
} else {
int iVex = edgeNode.getIVex();
int jVex = edgeNode.getJVex();
if (iVex == fromVertexIndex) {
refIndex = jVex;
edgeNode = edgeNode.getJLink();
} else if (jVex == fromVertexIndex) {
refIndex = iVex;
edgeNode = edgeNode.getILink();
}
}
// 跳过calculated[j]为true的顶点
if (!calculated[refIndex]) {
// 与现有pathVal[j]比较
if (infinity instanceof Integer) {
// 对于weight为无穷大的也不处理
if (!weight.equals(infinity)) {
// 只处理权值是Integer的情况,其他类型的类似处理
if (null == minWeight) {
minWeight = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);
}
W arcI = (W) (Integer.valueOf((Integer) weight + (Integer) minWeight));
if (arcI.compareTo(pathVal[refIndex]) < 0) {
// 令pathVal[j]=arc[minWeightIndex][j] + minWeight
pathVal[refIndex] = arcI;
// 令pre[j]=minWeightIndex
pre[refIndex] = minWeightIndex;
}
}
}
}
}
// 从pathVal和pre中取出新的minWeight和minWeightIndex
minWeight = null;
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
// 跳过已计算最短路径的顶点
if (!calculated[i] && (null == minWeight || minWeight.compareTo(pathVal[i]) > 0)) {
minWeight = pathVal[i];
minWeightIndex = i;
}
}
// 设置minWeightIndex对应的顶点为已访问
calculated[minWeightIndex] = true;
calculatedNum++;
// 用于测试
System.out.println("min weight is " + minWeight + ", min weight index is " + minWeightIndex);
StringBuilder builder1 = new StringBuilder("path val is [");
StringBuilder builder2 = new StringBuilder("pre vertex is [");
StringBuilder builder3 = new StringBuilder("calculated is [");
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
builder1.append(pathVal[i]).append(",");
builder2.append(pre[i]).append(",");
builder3.append(calculated[i]).append(",");
}
builder1.append("]");
builder2.append("]\n\r");
builder3.append("]");
System.out.println(builder3);
System.out.println(builder1);
System.out.println(builder2);
}
Object[][] result = new Object[2][];
result[0] = pathVal;
result[1] = pre;
return result;
}
边集数组的迪杰斯特拉算法实现如下:
/**
* 迪杰斯特拉算法获取最短路径
*
* @param fromVertexIndex 起始顶点下标
* @return 起始顶点到各顶点的最短路径及前驱顶点列表
* @author Korbin
* @date 2023-02-20 14:54:35
**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object[][] shortestPathDijkstra(int fromVertexIndex) {
// 最短路径权值,初始化为fromVertexIndex的权
W[] pathVal = (W[]) Array.newInstance(infinity.getClass(), vertexNum);
// 是否已计算,初始值为false
boolean[] calculated = new boolean[vertexNum];
// 要到达此顶点应先从哪个顶点过来,初始值为fromVertexIndex
Integer[] pre = new Integer[vertexNum];
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
pre[i] = fromVertexIndex;
pathVal[i] = infinity;
}
for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; i++) {
EdgeListEdgeNode<W> edgeNode = arc[i];
int begin = edgeNode.getBegin();
int end = edgeNode.getEnd();
W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();
if (begin == fromVertexIndex) {
pathVal[end] = weight;
}
}
// 最小权值
W minWeight = null;
// 最小权值对应的索引下标
int minWeightIndex = fromVertexIndex;
// 已计算的顶点数量,初始值为0
int calculatedNum;
// 从fromVertexIndex到fromVertexIndex,令pathVal[fromVertexIndex]为0,令pre[fromVertexIndex]为fromVertexIndex
// ,令calculated[fromVertexIndex]为true
pathVal[fromVertexIndex] = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);
pre[fromVertexIndex] = fromVertexIndex;
calculated[fromVertexIndex] = true;
calculatedNum = 1;
while (calculatedNum < vertexNum) {
// 循环到所有顶点都计算完毕
// 处理本顶点指向的顶点
for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; i++) {
EdgeListEdgeNode<W> edgeNode = arc[i];
int begin = edgeNode.getBegin();
int end = edgeNode.getEnd();
W weight = edgeNode.getWeight();
int refIndex = -1;
if (type.equals(BusinessConstants.GRAPH_TYPE.DIRECTED_NETWORK)) {
if (begin == minWeightIndex) {
refIndex = end;
}
} else {
if (begin == minWeightIndex) {
refIndex = end;
} else if (end == minWeightIndex) {
refIndex = begin;
}
}
// 跳过calculated[j]为true的顶点
if (refIndex >= 0 && !calculated[refIndex]) {
// 与现有pathVal[j]比较
if (infinity instanceof Integer) {
// 对于weight为无穷大的也不处理
if (!weight.equals(infinity)) {
// 只处理权值是Integer的情况,其他类型的类似处理
if (null == minWeight) {
minWeight = (W) Integer.valueOf(0);
}
W arcI = (W) (Integer.valueOf((Integer) weight + (Integer) minWeight));
if (arcI.compareTo(pathVal[refIndex]) < 0) {
// 令pathVal[j]=arc[minWeightIndex][j] + minWeight
pathVal[refIndex] = arcI;
// 令pre[j]=minWeightIndex
pre[refIndex] = minWeightIndex;
}
}
}
}
}
// 从pathVal和pre中取出新的minWeight和minWeightIndex
minWeight = null;
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
// 跳过已计算最短路径的顶点
if (!calculated[i] && (null == minWeight || minWeight.compareTo(pathVal[i]) > 0)) {
minWeight = pathVal[i];
minWeightIndex = i;
}
}
// 设置minWeightIndex对应的顶点为已访问
calculated[minWeightIndex] = true;
calculatedNum++;
// 用于测试
System.out.println("min weight is " + minWeight + ", min weight index is " + minWeightIndex);
StringBuilder builder1 = new StringBuilder("path val is [");
StringBuilder builder2 = new StringBuilder("pre vertex is [");
StringBuilder builder3 = new StringBuilder("calculated is [");
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
builder1.append(pathVal[i]).append(",");
builder2.append(pre[i]).append(",");
builder3.append(calculated[i]).append(",");
}
builder1.append("]");
builder2.append("]\n\r");
builder3.append("]");
System.out.println(builder3);
System.out.println(builder1);
System.out.println(builder2);
}
Object[][] result = new Object[2][];
result[0] = pathVal;
result[1] = pre;
return result;
}
6.2 弗洛伊德(Floyd)算法
我们仍然以以下无向网举例:

首先,我们定义两个矩阵,一为shortestPath,表示最短路径矩阵,一为pre,表示前驱矩阵,初始化shortestPath=arc即无向网的邻接矩阵,令pre[i][j]=j。
然后我们开始处理,我们把这个过程放到Excel里面进行展示,为了方便计算,我们将“ ∞ \infty ∞”设置为一个大于所有权值的值,例如10000,那么,有如下表格:

我们先令所有顶点都通过顶点0中转一下后,再连接到其他顶点,来比较直接连接的权和中转连接的权值,假设起始顶点是i,终止顶点是j,那么直接连接的权是n=shortestPath[i][j],通过顶点0中转的权是m=shortestPath[i][0]+shortestPath[0][j],而如果m<n,则表示顶点i通过顶点0中转后,再连到顶点j的代价更小,这种情况,我们将pre[i][j]设置为pre[i][0],将shortestPath[i][j]设置为shortestPath[i][0]+shortestPath[0][j]。
注意到,在这个计算过程中,如果shortestPath[i][0]或者shortestPath[0][j]为无穷大,那么它们加起来的权值和肯定为无穷大,无论shortestPath[i][j]权值是多少,肯定大于shortestPath[i][j],因此当shortestPath[i][0]或者shortestPath[0][j]为无穷大时,不需要进行计算。
先来看i=1的情况,计算后,我们发现shortestPath[1][0]+shortestPath[0][3]小于shortestPath[1][3],因此令shortestPath[1][3]=shortestPath[1][0]+shortestPath[0][3],令pre[1][3]=pre[1][0],如下:

再来看i=2的情况,所有的m都大于n,不进行任何处理:

i=3时,shortestPath[3][0]+shortestPath[0][1]<shortestPath[3][1],令shortestPath[3][1]=shortestPath[3][0]+shortestPath[0][1],令pre[3][1]=pre[3][0]:

当i=4和i=5时,shortestPath[4][0]和shortestPath[5][0]都为无穷大,无论shortestPath[0][j](j=4或5)为多少,权值和肯定大于shortestPath[i][j](i=4或5,j=4或5),因此不需要计算。
到这里,所有顶点通过顶点0与其他顶点连通的处理已完毕。
接下来看所有顶点通过顶点1与其他顶点连通的情况,注意,处理时是基于前面已处理的shortestPath二维数组进行处理的。
我们发现,所有的shortestPath[i][1]+shortestPath[1][j]都大于shortestPath[i][j],因此不进行任何处理:

然后再看所有顶点通过顶点2连通其他顶点的情况,处理逻辑一致,结果如下:

然后是所有顶点通过顶点3连通其他顶点的情况,然后是所有顶点通过顶点4连通其他顶点的情况,依此类推,得到以下最终结果:

我们再来总结一下规则:
(1) 设有图G(V,E),令shortestPath[][]=arc[][],新建二维数组pre[][],令pre[i][j]=j;
(2) 计算所有顶点通过顶点x(
0
≤
x
≤
v
e
r
t
e
x
N
u
m
0 \leq x \leq vertexNum
0≤x≤vertexNum)连通到其他顶点,计算shortestPath[i][j]与shortestPath[i][x]+shortestPath[x][j],如果shortestPath[i][x]+shortestPath[x][j]<shortestPath[i][j],则表示i->x->j的代价比i->j小,于是令shortestPath[i][j]=shortestPath[i][x]+shortestPath[x][j],令pre[i][j]=pre[i][x];
(3) 迭代以上变量,其中
0
≤
i
≤
v
e
r
t
e
x
N
u
m
0 \leq i \leq vertexNum
0≤i≤vertexNum、
0
≤
j
≤
v
e
r
t
e
x
N
u
m
0 \leq j \leq vertexNum
0≤j≤vertexNum、
0
≤
x
≤
v
e
r
t
e
x
N
u
m
0 \leq x \leq vertexNum
0≤x≤vertexNum;
(4) 迭代过程中,若shortestPath[i][x]或者shortestPath[x][j]为无穷大则跳过;当i=x或x=j或j=i时也跳过;
现在我们已经得到了以下结果:

如何计算出顶点i到顶点j的最短路径了,方法如下:
(1) 顶点i到顶点j的最小代价为shortestPath[i][j];
(2) 取出pre[i][j],若pre[i][j]=a,则表示顶点i到顶点j要先经过顶点a,再取出pre[a][j],若pre[a][j]=b,则表示顶点i到顶点a要先经过顶点b,依此类推,直到pre[x][j]=j,于是得到顶点i到顶点j的最短路径为i->a->b…->x->j;
我们来看顶点1到顶点5的最短路径,按照上述规则,我们知道顶点1到顶点5的最小代价为shortestPath[1][5]=2。然后因pre[2][5]=3,pre[3][5]=4,pre[4][5]=5,因此顶点1到顶点5的最短路径为1->2->3->4->5。
于是,在邻接矩阵中,弗洛伊德算法的最短路径代码实现如下所示:
/**
* 使用弗洛伊德算法生成的最短路径,只需要计算一次,因此保留计算结果
**/
private W[][] shortestPath;
/**
* 使用弗洛伊德算法生成的最短路径中,各顶点的前驱顶点信息,只需要计算一次,因此保留计算结果
**/
private int[][] pre;
/**
* 使用弗洛伊德算法计算最短路径
*
* @author Korbin
* @date 2023-02-23 12:23:31
* @param from 起始顶点
* @param to 终止顶点
* @return 最短路径及权值
**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String shortestPathFloyd(int from, int to) {
if (null == shortestPath) {
// 弗洛伊德算法只需要计算一次
System.out.println("进行了运算");
// 初始化
shortestPath = arc;
pre = new int[vertexNum][vertexNum];
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i ++) {
for (int j = 0;j < vertexNum; j++) {
pre[i][j] = j;
}
}
// 生成最短路径矩阵
for (int k = 0; k < vertexNum; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
if (i != k) {
// 所有顶点通过顶点k访问其他顶点
for (int j = 0;j < vertexNum; j++) {
if (j != k && j != i && !shortestPath[i][k].equals(infinity) && !shortestPath[k][j].equals(infinity)) {
if (infinity instanceof Integer) {
// 以Integer举例,其他类型类似
W directWeight = shortestPath[i][j];
W transferWeight = (W)Integer.valueOf((Integer)shortestPath[i][k] + (Integer)shortestPath[k][j]);
if (transferWeight.compareTo(directWeight) < 0) {
shortestPath[i][j] = transferWeight;
pre[i][j] = pre[i][k];
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
// 获取最短路径
W weight = shortestPath[from][to];
StringBuilder pathBuilder = new StringBuilder("path is ").append(vertex[from]).append("->");
int index = pre[from][to];
while (index != to) {
pathBuilder.append(vertex[index]).append("->");
index = pre[index][to];
}
pathBuilder.append(vertex[to]);
pathBuilder.append(", weight is ").append(weight);
return pathBuilder.toString();
}
其他存储结构也可以使用弗洛伊德算法去尝试实现生成最短路径,本处不再赘述。
6.3 总结
最短路径,对于图来说,是两顶点之间经过的边数最少的路径;对于网来说,是指两顶点之间经过的边上权值之和最小的路径。路径上第一个顶点为源点,最后一个顶点是终点。
迪杰斯特拉算法步骤:
(1) 假设要计算顶点k到其他顶点的最短路径;
(2) 首先定义三个数组,calculated[i]表示k->i的最短路径是否已计算出来,所有元素初始值均为false;pathVal[i]表示k->i的最短路径,所有元素初始值均为无穷大;pre[i]表示k->i中经历的顶点;
(3) 定义一个变量minWeight,表示“k->上一个顶点的最小权值”,k表示minWeight对应的顶点的下标,定义minWeightIndex表示minWeight对应的下标,初始值为minWeightIndex=k;
(4) 然后把arc[minWeightIndex][i]与现有的pathVal[i]比较,规则是:
1) calculated[i]=true表示已找到最短路径,不进行任何处理;
2) 如果arc[minWeightIndex][i]+minWeight<pathVal[i],则令pathVal[i]=arc[minWeightIndex][i]+minWeight,令pre[i]=minWeightIndex,表示k->i至少要经过顶点minWeightIndex;同时设置calculated[minWeightIndex]=true;
3) 如果arc[minWeightIndex][i]+minWeight>=pathVal[i],则pathVal[i]不变,pre[i]也不变,表示k->i不会经过顶点minWeightIndex;
(5) 然后令minWeight为当前pathVal[i]中的最小值,令minWeightIndex为最小值对应的下标,重复第(4)步,直到所有顶点都已计算出最短路径,即calculated数组的元素值全为true;
费洛伊德算法步骤:
(1) 设有图G(V,E),令shortestPath[][]=arc[][],新建二维数组pre[][],令pre[i][j]=j;
(2) 计算所有顶点通过顶点x(
0
≤
x
≤
v
e
r
t
e
x
N
u
m
0 \leq x \leq vertexNum
0≤x≤vertexNum)连通到其他顶点,计算shortestPath[i][j]与shortestPath[i][x]+shortestPath[x][j],如果shortestPath[i][x]+shortestPath[x][j]<shortestPath[i][j],则表示i->x->j的代价比i->j小,于是令shortestPath[i][j]=shortestPath[i][x]+shortestPath[x][j],令pre[i][j]=pre[i][x];
(3) 迭代以上变量,其中
0
≤
i
≤
v
e
r
t
e
x
N
u
m
0 \leq i \leq vertexNum
0≤i≤vertexNum、
0
≤
j
≤
v
e
r
t
e
x
N
u
m
0 \leq j \leq vertexNum
0≤j≤vertexNum、
0
≤
x
≤
v
e
r
t
e
x
N
u
m
0 \leq x \leq vertexNum
0≤x≤vertexNum;
(4) 迭代过程中,若shortestPath[i][x]或者shortestPath[x][j]为无穷大则跳过;当i=x或x=j或j=i时也跳过;
迪杰斯特拉算法的时间复杂度是O(n2),主要用于解决特定顶点到其他顶点的最短路径问题,如果需要计算所有顶点到其他顶点的最短路径,则在迪杰斯特拉算法的基础上把起始顶点全部迭代一遍即可,这时时间复杂度为O(3)。
弗洛伊德算法的时间复杂度也是O(3),通常用于解决需要计算所有顶点到其他顶点最短距离问题。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-739200.html
注:本文为程 杰老师《大话数据结构》的读书笔记,其中一些示例和代码是笔者阅读后自行编制的。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-739200.html
到了这里,关于大话数据结构-迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra)和弗洛伊德算法(Floyd)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!