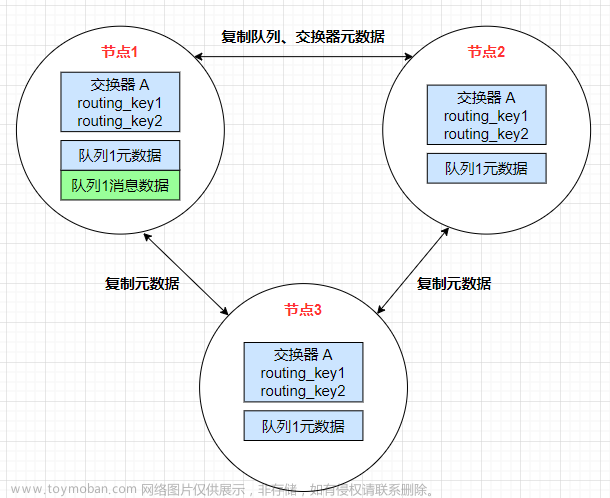
RabbitMQ是一种常用的消息队列系统,可以快速搭建一个高可用的集群环境,以提高系统的弹性和可靠性。下面是搭建RabbitMQ集群的步骤:
基于centos9 stream系统
1. 安装Erlang和RabbitMQ
首先需要在所有节点上安装Erlang和RabbitMQ。建议使用官方提供的安装包进行安装。
##直接从yum,repo源安装,建议一起装上librabbitmq*
yum install rabbitmq-server
#安装时会默认安装erlang相关依赖包。
#加入系统自动启动并立即运行rabbit
systemctl enable rabbitmq-server.service --now
2. 配置hosts文件
在所有节点上编辑hosts文件,将各节点的IP地址和主机名映射到一起。这样可以通过主机名进行通信,而不是依赖IP地址。
这个就不在讲了,直接编辑 /etc/hosts这个文件即可
个人主机内容参考如下:
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
110.110.10.5 host1
110.110.10.6 host2
110.110.10.7 host3 3. 配置rabbit集群
一般情况下一个节点的rabbit也差不多够用了,但为了稳定性使用高可用集群还是有必要的,配置集群可以直接编辑每个节点上的RabbitMQ配置文件,可以在/etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf中修改。常见的配置项:
# 节点名称
node_name = rabbit@node1
# 集群节点列表
cluster_nodes = {['rabbit@node1', 'rabbit@node2', 'rabbit@node3'], disc}
# Cookie值,用于节点间通信
erlang_cookie = abcde12345fghij
还有自定义rabbit的ip,各类服务端口,还有ssl等高级配置在这里不说了。
注意,这些配置项必须在所有节点上保持一致。
命令方式配置集群
默认情况下rabbit会直接获取hostname作为节点名,所以不用去配置文件中修改,这里主要讲使用命令直接配置和启动rabbit集群。
### 先配置管理节点,再将管理节点cookie复制到其他节点
for i in {host1,host2,host3};do ssh $i systemctl stop rabbitmq-server;done
for i in {host1,host2,host3};do scp /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie $i:/var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie;done
for i in {host1,host2,host3};do ssh $i chown rabbitmq:rabbitmq /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie;done
for i in {host1,host2,host3};do ssh $i chmod 400 /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie;done
for i in {host1,host2,host3};do ssh $i systemctl start rabbitmq-server;done
###节点加入集群,从拟定的主节点以外的其他节点操作,新加入节点操作也一样。;
rabbitmqctl stop_app
rabbitmqctl join_cluster --ram rabbit@host1
rabbitmqctl start_app
# 查看rabbitmq集群服务状态,每加入一个节点都可以查看一下是否加入成功
rabbitmqctl cluster_status
# 单个新节点加入集群操作,在新节点上操作,与上面多节点操作基本一致。
systemctl stop rabbitmq-server
scp host1:/var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie
chown rabbitmq:rabbitmq /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie
chmod 400 /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie
systemctl start rabbitmq-server
rabbitmqctl stop_app
rabbitmqctl join_cluster --ram rabbit@host1
rabbitmqctl start_app
读写测试
写入和读取测试:
python
import pika
# 连接到 rabbitmq 服务器
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters('localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
# 定义队列名称
queue_name = 'test_queue'
# 向队列写入消息
channel.queue_declare(queue=queue_name)
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key=queue_name,
body='Hello World!')
print(" [x] Sent 'Hello World!'")
# 从队列中读取消息
method_frame, header_frame, body = channel.basic_get(queue=queue_name, auto_ack=True)
if method_frame:
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
else:
print('No message returned')
# 关闭连接
connection.close()
# 在上述代码中,我们首先连接到了本地的 rabbitmq 服务器。然后定义了一个名为 test_queue 的队列,并向队列中写入了一条消息:Hello World!。接着,我们又从队列中读取了一条消息,并将其打印出来。在Node.js中使用RabbitMQ
在Node.js中使用RabbitMQ需要先安装amqplib库,可以通过npm进行安装:
npm install amqplib
##以下是使用RabbitMQ的基本步骤:
##建立与RabbitMQ服务器的连接
const amqp = require('amqplib');
amqp.connect('amqp://localhost').then(function(conn) {
//执行后续操作
});
###创建通道(channel)
conn.createChannel().then(function(ch) {
//执行后续操作
});
#发送消息
const queueName = "hello";
ch.assertQueue(queueName, { durable: false });
ch.sendToQueue(queueName, new Buffer('Hello World!'));
# 接收消息
const queueName = "hello";
ch.assertQueue(queueName, { durable: false });
ch.consume(queueName, function(msg) {
console.log("Received message: %s", msg.content.toString());
}, { noAck: true });
#######完整示例代码:
const amqp = require('amqplib');
amqp.connect('amqp://localhost').then(function(conn) {
conn.createChannel().then(function(ch) {
const queueName = "hello";
ch.assertQueue(queueName, { durable: false });
ch.sendToQueue(queueName, new Buffer('Hello World!'));
ch.assertQueue(queueName, { durable: false });
ch.consume(queueName, function(msg) {
console.log("Received message: %s", msg.content.toString());
}, { noAck: true });
});
}).catch(function(err) {
console.log('Error:', err);
});
4. 常用管理命令
#添加新用户
sudo rabbitmqctl add_user username password
#删除用户
sudo rabbitmqctl delete_user username
#分配用户权限
sudo rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / virtual-hostname 'username' '.*' '.*' '.*'
#查看用户列表
sudo rabbitmqctl list_users
#查看队列列表
sudo rabbitmqctl list_queues
#查看交换机列表
sudo rabbitmqctl list_exchanges
#查看绑定列表
sudo rabbitmqctl list_bindings
#查看 vhost 列表
sudo rabbitmqctl list_vhosts
#查看某个 vhost 的权限控制列表
sudo rabbitmqctl list_permissions -p virtual-hostname
#查看 RabbitMQ 服务器信息
sudo rabbitmqctl status5. 设置集群policy设置
##语句格式
rabbitmqctl set_policy [-p <vhost>] <name> <pattern> <definition>
rabbitmqctl clear_policy [-p <vhost>] <name>
rabbitmqctl list_policies [-p <vhost>]
## [ host1 ] 设置 ha-mode 高可用模式
rabbitmqctl set_policy ha-all '^(?!amq\.).*' '{"ha-mode": "all"}';
## 置一个队列的最大长度为1000条消息:
rabbitmqctl set_policy max-length-1000 "^my-queue$" '{"max-length":1000}' --apply-to queues
6. 启用web面板插件
# 启用web插件
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
##在本服务器或者同网段其他主机打开浏览器即可访问rabbitmq集群状态和管理页面

使用前面命令添加用户并设置为管理员即可登陆web界面。 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-742457.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-742457.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-742457.html
7. rabbitmq配置文件参考
###一般情况下不用在这里修改配置文件,但自定义参数的时候还是很有用的。
cat /etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf
## This example configuration file demonstrates various settings
## available via rabbitmq.conf. It primarily focuses core broker settings
## but some tier 1 plugin settings are also covered.
##
## This file is AN EXAMPLE. It is NOT MEANT TO BE USED IN PRODUCTION. Instead of
## copying the entire (large!) file, create or generate a new rabbitmq.conf for the target system
## and populate it with the necessary settings.
##
## See https://rabbitmq.com/configure.html to learn about how to configure RabbitMQ,
## the ini-style format used by rabbitmq.conf, how it is different from `advanced.config`,
## how to verify effective configuration, and so on.
##
## See https://rabbitmq.com/documentation.html for the rest of RabbitMQ documentation.
##
## In case you have questions, please use RabbitMQ community Slack and the rabbitmq-users Google group
## instead of GitHub issues.
# ======================================
# Core broker section
# ======================================
####这下面的5672,5671如果已经被占用时或者为了安全考虑可修改为其他端口,在服务应用时也需要调整成新的端口
## Networking
## ====================
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/networking.html.
##
## By default, RabbitMQ will listen on all interfaces, using
## the standard (reserved) AMQP 0-9-1 and 1.0 port.
##
# listeners.tcp.default = 5672
## To listen on a specific interface, provide an IP address with port.
## For example, to listen only on localhost for both IPv4 and IPv6:
##
# IPv4
# listeners.tcp.local = 127.0.0.1:5672
# IPv6
# listeners.tcp.local_v6 = ::1:5672
## You can define multiple listeners using listener names
# listeners.tcp.other_port = 5673
# listeners.tcp.other_ip = 10.10.10.10:5672
## TLS listeners are configured in the same fashion as TCP listeners,
## including the option to control the choice of interface.
##
# listeners.ssl.default = 5671
## It is possible to disable regular TCP (non-TLS) listeners. Clients
## not configured to use TLS and the correct TLS-enabled port won't be able
## to connect to this node.
# listeners.tcp = none
## Number of Erlang processes that will accept connections for the TCP
## and TLS listeners.
##
# num_acceptors.tcp = 10
# num_acceptors.ssl = 10
## Socket writer will force GC every so many bytes transferred.
## Default is 1 GiB (`1000000000`). Set to 'off' to disable.
##
# socket_writer.gc_threshold = 1000000000
#
## To disable:
# socket_writer.gc_threshold = off
## Maximum amount of time allowed for the AMQP 0-9-1 and AMQP 1.0 handshake
## (performed after socket connection and TLS handshake) to complete, in milliseconds.
##
# handshake_timeout = 10000
## Set to 'true' to perform reverse DNS lookups when accepting a
## connection. rabbitmqctl and management UI will then display hostnames
## instead of IP addresses. Default value is `false`.
##
# reverse_dns_lookups = false
##
## Security, Access Control
## ==============
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html.
## The default "guest" user is only permitted to access the server
## via a loopback interface (e.g. localhost).
## {loopback_users, [<<"guest">>]},
##
# loopback_users.guest = true
## Uncomment the following line if you want to allow access to the
## guest user from anywhere on the network.
# loopback_users.guest = false
## TLS configuration.
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/ssl.html.
##
# listeners.ssl.1 = 5671
#
# ssl_options.verify = verify_peer
# ssl_options.fail_if_no_peer_cert = false
# ssl_options.cacertfile = /path/to/cacert.pem
# ssl_options.certfile = /path/to/cert.pem
# ssl_options.keyfile = /path/to/key.pem
#
# ssl_options.honor_cipher_order = true
# ssl_options.honor_ecc_order = true
#
## These are highly recommended for TLSv1.2 but cannot be used
## with TLSv1.3. If TLSv1.3 is enabled, these lines MUST be removed.
# ssl_options.client_renegotiation = false
# ssl_options.secure_renegotiate = true
#
## Limits what TLS versions the server enables for client TLS
## connections. See https://www.rabbitmq.com/ssl.html#tls-versions for details.
##
## Cutting edge TLS version which requires recent client runtime
## versions and has no cipher suite in common with earlier TLS versions.
# ssl_options.versions.1 = tlsv1.3
## Enables TLSv1.2 for best compatibility
# ssl_options.versions.2 = tlsv1.2
## Older TLS versions have known vulnerabilities and are being phased out
## from wide use.
## Limits what cipher suites the server will use for client TLS
## connections. Narrowing this down can prevent some clients
## from connecting.
## If TLSv1.3 is enabled and cipher suites are overridden, TLSv1.3-specific
## cipher suites must also be explicitly enabled.
## See https://www.rabbitmq.com/ssl.html#cipher-suites and https://wiki.openssl.org/index.php/TLS1.3#Ciphersuites
## for details.
#
## The example below uses TLSv1.3 cipher suites only
#
# ssl_options.ciphers.1 = TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.2 = TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.3 = TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.4 = TLS_AES_128_CCM_SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.5 = TLS_AES_128_CCM_8_SHA256
#
## The example below uses TLSv1.2 cipher suites only
#
# ssl_options.ciphers.1 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.2 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.3 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.4 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.5 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.6 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.7 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.8 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.9 = DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.10 = DHE-DSS-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.11 = DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.12 = DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.13 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.14 = ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.15 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.16 = ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.17 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.18 = ECDH-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.19 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.20 = ECDH-RSA-AES128-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.21 = DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.22 = DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.23 = DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.24 = DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.25 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.26 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.27 = DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.28 = DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.29 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.30 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.31 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.32 = ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.33 = DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.34 = DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.35 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES128-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.36 = ECDH-RSA-AES128-SHA
# ssl_options.bypass_pem_cache = true
## Select an authentication/authorisation backend to use.
##
## Alternative backends are provided by plugins, such as rabbitmq-auth-backend-ldap.
##
## NB: These settings require certain plugins to be enabled.
##
## Related doc guides:
##
## * https://rabbitmq.com/plugins.html
## * https://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html
##
# auth_backends.1 = rabbit_auth_backend_internal
## uses separate backends for authentication and authorisation,
## see below.
# auth_backends.1.authn = rabbit_auth_backend_ldap
# auth_backends.1.authz = rabbit_auth_backend_internal
## The rabbitmq_auth_backend_ldap plugin allows the broker to
## perform authentication and authorisation by deferring to an
## external LDAP server.
##
## Relevant doc guides:
##
## * https://rabbitmq.com/ldap.html
## * https://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html
##
## uses LDAP for both authentication and authorisation
# auth_backends.1 = rabbit_auth_backend_ldap
## uses HTTP service for both authentication and
## authorisation
# auth_backends.1 = rabbit_auth_backend_http
## uses two backends in a chain: HTTP first, then internal
# auth_backends.1 = rabbit_auth_backend_http
# auth_backends.2 = rabbit_auth_backend_internal
## Authentication
## The built-in mechanisms are 'PLAIN',
## 'AMQPLAIN', and 'EXTERNAL' Additional mechanisms can be added via
## plugins.
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/authentication.html.
##
# auth_mechanisms.1 = PLAIN
# auth_mechanisms.2 = AMQPLAIN
## The rabbitmq-auth-mechanism-ssl plugin makes it possible to
## authenticate a user based on the client's x509 (TLS) certificate.
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/authentication.html.
##
## To use auth-mechanism-ssl, the EXTERNAL mechanism should
## be enabled:
##
# auth_mechanisms.1 = PLAIN
# auth_mechanisms.2 = AMQPLAIN
# auth_mechanisms.3 = EXTERNAL
## To force x509 certificate-based authentication on all clients,
## exclude all other mechanisms (note: this will disable password-based
## authentication even for the management UI!):
##
# auth_mechanisms.1 = EXTERNAL
## This pertains to both the rabbitmq-auth-mechanism-ssl plugin and
## STOMP ssl_cert_login configurations. See the RabbitMQ STOMP plugin
## configuration section later in this file and the README in
## https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-auth-mechanism-ssl for further
## details.
##
## To use the TLS cert's CN instead of its DN as the username
##
# ssl_cert_login_from = common_name
## TLS handshake timeout, in milliseconds.
##
# ssl_handshake_timeout = 5000
## Cluster name
##
# cluster_name = dev3.eng.megacorp.local
## Password hashing implementation. Will only affect newly
## created users. To recalculate hash for an existing user
## it's necessary to update her password.
##
## To use SHA-512, set to rabbit_password_hashing_sha512.
##
# password_hashing_module = rabbit_password_hashing_sha256
## When importing definitions exported from versions earlier
## than 3.6.0, it is possible to go back to MD5 (only do this
## as a temporary measure!) by setting this to rabbit_password_hashing_md5.
##
# password_hashing_module = rabbit_password_hashing_md5
##
## Default User / VHost
## ====================
##
## On first start RabbitMQ will create a vhost and a user. These
## config items control what gets created.
## Relevant doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html
##
# default_vhost = /
# default_user = guest
# default_pass = guest
# default_permissions.configure = .*
# default_permissions.read = .*
# default_permissions.write = .*
## Tags for default user
##
## For more details about tags, see the documentation for the
## Management Plugin at https://rabbitmq.com/management.html.
##
# default_user_tags.administrator = true
## Define other tags like this:
# default_user_tags.management = true
# default_user_tags.custom_tag = true
##
## Additional network and protocol related configuration
## =====================================================
##
## Set the server AMQP 0-9-1 heartbeat timeout in seconds.
## RabbitMQ nodes will send heartbeat frames at roughly
## the (timeout / 2) interval. Two missed heartbeats from
## a client will close its connection.
##
## Values lower than 6 seconds are very likely to produce
## false positives and are not recommended.
##
## Related doc guides:
##
## * https://rabbitmq.com/heartbeats.html
## * https://rabbitmq.com/networking.html
##
# heartbeat = 60
## Set the max permissible size of an AMQP frame (in bytes).
##
# frame_max = 131072
## Set the max frame size the server will accept before connection
## tuning occurs
##
# initial_frame_max = 4096
## Set the max permissible number of channels per connection.
## 0 means "no limit".
##
# channel_max = 128
## Customising TCP Listener (Socket) Configuration.
##
## Related doc guides:
##
## * https://rabbitmq.com/networking.html
## * https://www.erlang.org/doc/man/inet.html#setopts-2
##
# tcp_listen_options.backlog = 128
# tcp_listen_options.nodelay = true
# tcp_listen_options.exit_on_close = false
#
# tcp_listen_options.keepalive = true
# tcp_listen_options.send_timeout = 15000
#
# tcp_listen_options.buffer = 196608
# tcp_listen_options.sndbuf = 196608
# tcp_listen_options.recbuf = 196608
##
## Resource Limits & Flow Control
## ==============================
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/memory.html.
## Memory-based Flow Control threshold.
##
# vm_memory_high_watermark.relative = 0.4
## Alternatively, we can set a limit (in bytes) of RAM used by the node.
##
# vm_memory_high_watermark.absolute = 1073741824
## Or you can set absolute value using memory units (with RabbitMQ 3.6.0+).
## Absolute watermark will be ignored if relative is defined!
##
# vm_memory_high_watermark.absolute = 2GB
##
## Supported unit symbols:
##
## k, kiB: kibibytes (2^10 - 1,024 bytes)
## M, MiB: mebibytes (2^20 - 1,048,576 bytes)
## G, GiB: gibibytes (2^30 - 1,073,741,824 bytes)
## kB: kilobytes (10^3 - 1,000 bytes)
## MB: megabytes (10^6 - 1,000,000 bytes)
## GB: gigabytes (10^9 - 1,000,000,000 bytes)
## Fraction of the high watermark limit at which queues start to
## page message out to disc in order to free up memory.
## For example, when vm_memory_high_watermark is set to 0.4 and this value is set to 0.5,
## paging can begin as early as when 20% of total available RAM is used by the node.
##
## Values greater than 1.0 can be dangerous and should be used carefully.
##
## One alternative to this is to use durable queues and publish messages
## as persistent (delivery mode = 2). With this combination queues will
## move messages to disk much more rapidly.
##
## Another alternative is to configure queues to page all messages (both
## persistent and transient) to disk as quickly
## as possible, see https://rabbitmq.com/lazy-queues.html.
##
# vm_memory_high_watermark_paging_ratio = 0.5
## Selects Erlang VM memory consumption calculation strategy. Can be `allocated`, `rss` or `legacy` (aliased as `erlang`),
## Introduced in 3.6.11. `rss` is the default as of 3.6.12.
## See https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/issues/1223 and rabbitmq/rabbitmq-common#224 for background.
# vm_memory_calculation_strategy = rss
## Interval (in milliseconds) at which we perform the check of the memory
## levels against the watermarks.
##
# memory_monitor_interval = 2500
## The total memory available can be calculated from the OS resources
## - default option - or provided as a configuration parameter.
# total_memory_available_override_value = 2GB
## Set disk free limit (in bytes). Once free disk space reaches this
## lower bound, a disk alarm will be set - see the documentation
## listed above for more details.
##
## Absolute watermark will be ignored if relative is defined!
# disk_free_limit.absolute = 50000
## Or you can set it using memory units (same as in vm_memory_high_watermark)
## with RabbitMQ 3.6.0+.
# disk_free_limit.absolute = 500KB
# disk_free_limit.absolute = 50mb
# disk_free_limit.absolute = 5GB
## Alternatively, we can set a limit relative to total available RAM.
##
## Values lower than 1.0 can be dangerous and should be used carefully.
# disk_free_limit.relative = 2.0
##
## Clustering
## =====================
##
# cluster_partition_handling = ignore
## Pauses all nodes on the minority side of a partition. The cluster
## MUST have an odd number of nodes (3, 5, etc)
# cluster_partition_handling = pause_minority
## pause_if_all_down strategy require additional configuration
# cluster_partition_handling = pause_if_all_down
## Recover strategy. Can be either 'autoheal' or 'ignore'
# cluster_partition_handling.pause_if_all_down.recover = ignore
## Node names to check
# cluster_partition_handling.pause_if_all_down.nodes.1 = rabbit@localhost
# cluster_partition_handling.pause_if_all_down.nodes.2 = hare@localhost
## Mirror sync batch size, in messages. Increasing this will speed
## up syncing but total batch size in bytes must not exceed 2 GiB.
## Available in RabbitMQ 3.6.0 or later.
##
# mirroring_sync_batch_size = 4096
## Make clustering happen *automatically* at startup. Only applied
## to nodes that have just been reset or started for the first time.
##
## Relevant doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com//cluster-formation.html
##
###这里设置集群,所有节点必须保持一致,当然也可以按照前面命令的方式进行设置
# cluster_formation.peer_discovery_backend = rabbit_peer_discovery_classic_config
#
# cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.1 = rabbit1@hostname
# cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.2 = rabbit2@hostname
# cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.3 = rabbit3@hostname
# cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.4 = rabbit4@hostname
## DNS-based peer discovery. This backend will list A records
## of the configured hostname and perform reverse lookups for
## the addresses returned.
# cluster_formation.peer_discovery_backend = rabbit_peer_discovery_dns
# cluster_formation.dns.hostname = discovery.eng.example.local
## This node's type can be configured. If you are not sure
## what node type to use, always use 'disc'.
# cluster_formation.node_type = disc
## Interval (in milliseconds) at which we send keepalive messages
## to other cluster members. Note that this is not the same thing
## as net_ticktime; missed keepalive messages will not cause nodes
## to be considered down.
##
# cluster_keepalive_interval = 10000
##
## Statistics Collection
## =====================
##
## Statistics collection interval (in milliseconds). Increasing
## this will reduce the load on management database.
##
# collect_statistics_interval = 5000
## Fine vs. coarse statistics
#
# This value is no longer meant to be configured directly.
#
# See https://www.rabbitmq.com/management.html#fine-stats.
##
## Ra Settings
## =====================
##
# raft.segment_max_entries = 65536
# raft.wal_max_size_bytes = 1048576
# raft.wal_max_batch_size = 4096
# raft.snapshot_chunk_size = 1000000
##
## Misc/Advanced Options
## =====================
##
## NB: Change these only if you understand what you are doing!
##
## Timeout used when waiting for Mnesia tables in a cluster to
## become available.
##
# mnesia_table_loading_retry_timeout = 30000
## Retries when waiting for Mnesia tables in the cluster startup. Note that
## this setting is not applied to Mnesia upgrades or node deletions.
##
# mnesia_table_loading_retry_limit = 10
## Size in bytes below which to embed messages in the queue index.
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/persistence-conf.html
##
# queue_index_embed_msgs_below = 4096
## You can also set this size in memory units
##
# queue_index_embed_msgs_below = 4kb
## Whether or not to enable background periodic forced GC runs for all
## Erlang processes on the node in "waiting" state.
##
## Disabling background GC may reduce latency for client operations,
## keeping it enabled may reduce median RAM usage by the binary heap
## (see https://www.erlang-solutions.com/blog/erlang-garbage-collector.html).
##
## Before trying this option, please take a look at the memory
## breakdown (https://www.rabbitmq.com/memory-use.html).
##
# background_gc_enabled = false
## Target (desired) interval (in milliseconds) at which we run background GC.
## The actual interval will vary depending on how long it takes to execute
## the operation (can be higher than this interval). Values less than
## 30000 milliseconds are not recommended.
##
# background_gc_target_interval = 60000
## Whether or not to enable proxy protocol support.
## Once enabled, clients cannot directly connect to the broker
## anymore. They must connect through a load balancer that sends the
## proxy protocol header to the broker at connection time.
## This setting applies only to AMQP clients, other protocols
## like MQTT or STOMP have their own setting to enable proxy protocol.
## See the plugins documentation for more information.
##
# proxy_protocol = false
## Overriden product name and version.
## They are set to "RabbitMQ" and the release version by default.
# product.name = RabbitMQ
# product.version = 1.2.3
## "Message of the day" file.
## Its content is used to expand the logged and printed banners.
## Default to /etc/rabbitmq/motd on Unix, %APPDATA%\RabbitMQ\motd.txt
## on Windows.
# motd_file = /etc/rabbitmq/motd
## Consumer timeout
## If a message delivered to a consumer has not been acknowledge before this timer
## triggers the channel will be force closed by the broker. This ensure that
## faultly consumers that never ack will not hold on to messages indefinitely.
##
# consumer_timeout = 900000
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Advanced Erlang Networking/Clustering Options.
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/clustering.html
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# ======================================
# Kernel section
# ======================================
## Timeout used to detect peer unavailability, including CLI tools.
## Related doc guide: https://www.rabbitmq.com/nettick.html.
##
# net_ticktime = 60
## Inter-node communication port range.
## The parameters inet_dist_listen_min and inet_dist_listen_max
## can be configured in the classic config format only.
## Related doc guide: https://www.rabbitmq.com/networking.html#epmd-inet-dist-port-range.
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## RabbitMQ Management Plugin
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/management.html.
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# =======================================
# Management section
# =======================================
## Preload schema definitions from the following JSON file.
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/management.html#load-definitions.
##
# management.load_definitions = /path/to/exported/definitions.json
## Log all requests to the management HTTP API to a file.
##
# management.http_log_dir = /path/to/access.log
##这里就是web插件的访问地址和端口设置了,变更后访问地址也要跟着变更才能访问到
## HTTP listener and embedded Web server settings.
# ## See https://rabbitmq.com/management.html for details.
#
# management.tcp.port = 15672
# management.tcp.ip = 0.0.0.0
#
# management.tcp.shutdown_timeout = 7000
# management.tcp.max_keepalive = 120
# management.tcp.idle_timeout = 120
# management.tcp.inactivity_timeout = 120
# management.tcp.request_timeout = 120
# management.tcp.compress = true
##https配置,一般内网我们就不配置了,外网可以做url重写
## HTTPS listener settings.
## See https://rabbitmq.com/management.html and https://rabbitmq.com/ssl.html for details.
##
# management.ssl.port = 15671
# management.ssl.cacertfile = /path/to/ca_certificate.pem
# management.ssl.certfile = /path/to/server_certificate.pem
# management.ssl.keyfile = /path/to/server_key.pem
## More TLS options
# management.ssl.honor_cipher_order = true
# management.ssl.honor_ecc_order = true
## These are highly recommended for TLSv1.2 but cannot be used
## with TLSv1.3. If TLSv1.3 is enabled, these lines MUST be removed.
# management.ssl.client_renegotiation = false
# management.ssl.secure_renegotiate = true
## Supported TLS versions
# management.ssl.versions.1 = tlsv1.2
## Cipher suites the server is allowed to use
# management.ssl.ciphers.1 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.2 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.3 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.4 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.5 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.6 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.7 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.8 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.9 = DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
## URL path prefix for HTTP API and management UI
# management.path_prefix = /a-prefix
## One of 'basic', 'detailed' or 'none'. See
## https://rabbitmq.com/management.html#fine-stats for more details.
# management.rates_mode = basic
## Configure how long aggregated data (such as message rates and queue
## lengths) is retained. Please read the plugin's documentation in
## https://rabbitmq.com/management.html#configuration for more
## details.
## Your can use 'minute', 'hour' and 'day' keys or integer key (in seconds)
# management.sample_retention_policies.global.minute = 5
# management.sample_retention_policies.global.hour = 60
# management.sample_retention_policies.global.day = 1200
# management.sample_retention_policies.basic.minute = 5
# management.sample_retention_policies.basic.hour = 60
# management.sample_retention_policies.detailed.10 = 5
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## RabbitMQ Shovel Plugin
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/shovel.html
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## See advanced.config.example for a Shovel plugin example
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## RabbitMQ STOMP Plugin
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/stomp.html
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# =======================================
# STOMP section
# =======================================
## See https://rabbitmq.com/stomp.html for details.
## TCP listeners.
##
# stomp.listeners.tcp.1 = 127.0.0.1:61613
# stomp.listeners.tcp.2 = ::1:61613
## TCP listener settings
##
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.backlog = 2048
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.recbuf = 131072
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.sndbuf = 131072
#
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.keepalive = true
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.nodelay = true
#
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.exit_on_close = true
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.send_timeout = 120
## Proxy protocol support
##
# stomp.proxy_protocol = false
## TLS listeners
## See https://rabbitmq.com/stomp.html and https://rabbitmq.com/ssl.html for details.
# stomp.listeners.ssl.default = 61614
#
# ssl_options.cacertfile = path/to/cacert.pem
# ssl_options.certfile = path/to/cert.pem
# ssl_options.keyfile = path/to/key.pem
# ssl_options.verify = verify_peer
# ssl_options.fail_if_no_peer_cert = true
## Number of Erlang processes that will accept connections for the TCP
## and TLS listeners.
##
# stomp.num_acceptors.tcp = 10
# stomp.num_acceptors.ssl = 1
## Additional TLS options
## Extract a name from the client's certificate when using TLS.
##
# stomp.ssl_cert_login = true
## Set a default user name and password. This is used as the default login
## whenever a CONNECT frame omits the login and passcode headers.
##
## Please note that setting this will allow clients to connect without
## authenticating!
##
# stomp.default_user = guest
# stomp.default_pass = guest
## If a default user is configured, or you have configured use TLS client
## certificate based authentication, you can choose to allow clients to
## omit the CONNECT frame entirely. If set to true, the client is
## automatically connected as the default user or user supplied in the
## TLS certificate whenever the first frame sent on a session is not a
## CONNECT frame.
##
# stomp.implicit_connect = true
## Whether or not to enable proxy protocol support.
## Once enabled, clients cannot directly connect to the broker
## anymore. They must connect through a load balancer that sends the
## proxy protocol header to the broker at connection time.
## This setting applies only to STOMP clients, other protocols
## like MQTT or AMQP have their own setting to enable proxy protocol.
## See the plugins or broker documentation for more information.
##
# stomp.proxy_protocol = false
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## RabbitMQ MQTT Adapter
##
## See https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-mqtt/blob/stable/README.md
## for details
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# =======================================
# MQTT section
# =======================================
## TCP listener settings.
##
# mqtt.listeners.tcp.1 = 127.0.0.1:61613
# mqtt.listeners.tcp.2 = ::1:61613
## TCP listener options (as per the broker configuration).
##
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.backlog = 4096
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.recbuf = 131072
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.sndbuf = 131072
#
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.keepalive = true
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.nodelay = true
#
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.exit_on_close = true
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.send_timeout = 120
## TLS listener settings
## ## See https://rabbitmq.com/mqtt.html and https://rabbitmq.com/ssl.html for details.
#
# mqtt.listeners.ssl.default = 8883
#
# ssl_options.cacertfile = /path/to/tls/ca_certificate_bundle.pem
# ssl_options.certfile = /path/to/tls/server_certificate.pem
# ssl_options.keyfile = /path/to/tls/server_key.pem
# ssl_options.verify = verify_peer
# ssl_options.fail_if_no_peer_cert = true
#
## Number of Erlang processes that will accept connections for the TCP
## and TLS listeners.
##
# mqtt.num_acceptors.tcp = 10
# mqtt.num_acceptors.ssl = 10
## Whether or not to enable proxy protocol support.
## Once enabled, clients cannot directly connect to the broker
## anymore. They must connect through a load balancer that sends the
## proxy protocol header to the broker at connection time.
## This setting applies only to STOMP clients, other protocols
## like STOMP or AMQP have their own setting to enable proxy protocol.
## See the plugins or broker documentation for more information.
##
# mqtt.proxy_protocol = false
## Set the default user name and password used for anonymous connections (when client
## provides no credentials). Anonymous connections are highly discouraged!
##
# mqtt.default_user = guest
# mqtt.default_pass = guest
## Enable anonymous connections. If this is set to false, clients MUST provide
## credentials in order to connect. See also the mqtt.default_user/mqtt.default_pass
## keys. Anonymous connections are highly discouraged!
##
# mqtt.allow_anonymous = true
## If you have multiple vhosts, specify the one to which the
## adapter connects.
##
# mqtt.vhost = /
## Specify the exchange to which messages from MQTT clients are published.
##
# mqtt.exchange = amq.topic
## Specify TTL (time to live) to control the lifetime of non-clean sessions.
##
# mqtt.subscription_ttl = 1800000
## Set the prefetch count (governing the maximum number of unacknowledged
## messages that will be delivered).
##
# mqtt.prefetch = 10
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## RabbitMQ AMQP 1.0 Support
##
## See https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-amqp1.0/blob/stable/README.md.
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# =======================================
# AMQP 1.0 section
# =======================================
## Connections that are not authenticated with SASL will connect as this
## account. See the README for more information.
##
## Please note that setting this will allow clients to connect without
## authenticating!
##
# amqp1_0.default_user = guest
## Enable protocol strict mode. See the README for more information.
##
# amqp1_0.protocol_strict_mode = false
## Logging settings.
##
## See https://rabbitmq.com/logging.html for details.
##
## Log directory, taken from the RABBITMQ_LOG_BASE env variable by default.
##
# log.dir = /var/log/rabbitmq
## Logging to file. Can be false or a filename.
## Default:
# log.file = rabbit.log
## To disable logging to a file
# log.file = false
## Log level for file logging
##
# log.file.level = info
## File rotation config. No rotation by default.
## DO NOT SET rotation date to ''. Leave the value unset if "" is the desired value
# log.file.rotation.date = $D0
# log.file.rotation.size = 0
## Logging to console (can be true or false)
##
# log.console = false
## Log level for console logging
##
# log.console.level = info
## Logging to the amq.rabbitmq.log exchange (can be true or false)
##
# log.exchange = false
## Log level to use when logging to the amq.rabbitmq.log exchange
##
# log.exchange.level = info
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## RabbitMQ LDAP Plugin
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/ldap.html.
##
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# =======================================
# LDAP section
# =======================================
##
## Connecting to the LDAP server(s)
## ================================
##
## Specify servers to bind to. You *must* set this in order for the plugin
## to work properly.
##
# auth_ldap.servers.1 = your-server-name-goes-here
## You can define multiple servers
# auth_ldap.servers.2 = your-other-server
## Connect to the LDAP server using TLS
##
# auth_ldap.use_ssl = false
## Specify the LDAP port to connect to
##
# auth_ldap.port = 389
## LDAP connection timeout, in milliseconds or 'infinity'
##
# auth_ldap.timeout = infinity
## Or number
# auth_ldap.timeout = 500
## Enable logging of LDAP queries.
## One of
## - false (no logging is performed)
## - true (verbose logging of the logic used by the plugin)
## - network (as true, but additionally logs LDAP network traffic)
##
## Defaults to false.
##
# auth_ldap.log = false
## Also can be true or network
# auth_ldap.log = true
# auth_ldap.log = network
##
## Authentication
## ==============
##
## Pattern to convert the username given through AMQP to a DN before
## binding
##
# auth_ldap.user_dn_pattern = cn=${username},ou=People,dc=example,dc=com
## Alternatively, you can convert a username to a Distinguished
## Name via an LDAP lookup after binding. See the documentation for
## full details.
## When converting a username to a dn via a lookup, set these to
## the name of the attribute that represents the user name, and the
## base DN for the lookup query.
##
# auth_ldap.dn_lookup_attribute = userPrincipalName
# auth_ldap.dn_lookup_base = DC=gopivotal,DC=com
## Controls how to bind for authorisation queries and also to
## retrieve the details of users logging in without presenting a
## password (e.g., SASL EXTERNAL).
## One of
## - as_user (to bind as the authenticated user - requires a password)
## - anon (to bind anonymously)
## - {UserDN, Password} (to bind with a specified user name and password)
##
## Defaults to 'as_user'.
##
# auth_ldap.other_bind = as_user
## Or can be more complex:
# auth_ldap.other_bind.user_dn = User
# auth_ldap.other_bind.password = Password
## If user_dn and password defined - other options is ignored.
# -----------------------------
# Too complex section of LDAP
# -----------------------------
##
## Authorisation
## =============
##
## The LDAP plugin can perform a variety of queries against your
## LDAP server to determine questions of authorisation.
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/ldap.html#authorisation.
## Following configuration should be defined in advanced.config file
## DO NOT UNCOMMENT THESE LINES!
## Set the query to use when determining vhost access
##
## {vhost_access_query, {in_group,
## "ou=${vhost}-users,ou=vhosts,dc=example,dc=com"}},
## Set the query to use when determining resource (e.g., queue) access
##
## {resource_access_query, {constant, true}},
## Set queries to determine which tags a user has
##
## {tag_queries, []}
# ]},
# -----------------------------
到了这里,关于centos9 stream 下 rabbitmq高可用集群搭建及使用的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!