一、目的
本篇主要介绍ESP32的ADC功能,ESP32有两个ADC模块,分别为ADC1/ADC2,每个ESP32系列具有的通道数不一样,详情请看下表。
在WiFi在使用时,ADC2的使用受到一些限制,实际应用场景中一般只使用ADC1即可。
二、介绍
ADC的IO引脚分配
ESP32系列 (下表来自ESP-IDF开发文档)
| GPIO |
Analog Function |
RTC GPIO |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPIO0 |
ADC2_CH1 |
RTC_GPIO11 |
Strapping pin |
| GPIO1 |
TXD |
||
| GPIO2 |
ADC2_CH2 |
RTC_GPIO12 |
Strapping pin |
| GPIO3 |
RXD |
||
| GPIO4 |
ADC2_CH0 |
RTC_GPIO10 |
|
| GPIO5 |
Strapping pin |
||
| GPIO6 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO7 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO8 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO9 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO10 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO11 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO12 |
ADC2_CH5 |
RTC_GPIO15 |
Strapping pin; JTAG |
| GPIO13 |
ADC2_CH4 |
RTC_GPIO14 |
JTAG |
| GPIO14 |
ADC2_CH6 |
RTC_GPIO16 |
JTAG |
| GPIO15 |
ADC2_CH3 |
RTC_GPIO13 |
Strapping pin; JTAG |
| GPIO16 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO17 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO18 |
|||
| GPIO19 |
|||
| GPIO21 |
|||
| GPIO22 |
|||
| GPIO23 |
|||
| GPIO25 |
ADC2_CH8 |
RTC_GPIO6 |
|
| GPIO26 |
ADC2_CH9 |
RTC_GPIO7 |
|
| GPIO27 |
ADC2_CH7 |
RTC_GPIO17 |
|
| GPIO32 |
ADC1_CH4 |
RTC_GPIO9 |
|
| GPIO33 |
ADC1_CH5 |
RTC_GPIO8 |
|
| GPIO34 |
ADC1_CH6 |
RTC_GPIO4 |
GPI |
| GPIO35 |
ADC1_CH7 |
RTC_GPIO5 |
GPI |
| GPIO36 |
ADC1_CH0 |
RTC_GPIO0 |
GPI |
| GPIO37 |
ADC1_CH1 |
RTC_GPIO1 |
GPI |
| GPIO38 |
ADC1_CH2 |
RTC_GPIO2 |
GPI |
| GPIO39 |
ADC1_CH3 |
RTC_GPIO3 |
GPI |
从上表我们可以看到ADC1可以使用的IO引脚为GPIO32-GPIO39总共8个通道。
ESP32S2系列 (下表来自ESP-IDF开发文档)
| GPIO |
Analog Function |
RTC GPIO |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPIO0 |
RTC_GPIO0 |
Strapping pin |
|
| GPIO1 |
ADC1_CH0 |
RTC_GPIO1 |
|
| GPIO2 |
ADC1_CH1 |
RTC_GPIO2 |
|
| GPIO3 |
ADC1_CH2 |
RTC_GPIO3 |
|
| GPIO4 |
ADC1_CH3 |
RTC_GPIO4 |
|
| GPIO5 |
ADC1_CH4 |
RTC_GPIO5 |
|
| GPIO6 |
ADC1_CH5 |
RTC_GPIO6 |
|
| GPIO7 |
ADC1_CH6 |
RTC_GPIO7 |
|
| GPIO8 |
ADC1_CH7 |
RTC_GPIO8 |
|
| GPIO9 |
ADC1_CH8 |
RTC_GPIO9 |
|
| GPIO10 |
ADC1_CH9 |
RTC_GPIO10 |
|
| GPIO11 |
ADC2_CH0 |
RTC_GPIO11 |
|
| GPIO12 |
ADC2_CH1 |
RTC_GPIO12 |
|
| GPIO13 |
ADC2_CH2 |
RTC_GPIO13 |
|
| GPIO14 |
ADC2_CH3 |
RTC_GPIO14 |
|
| GPIO15 |
ADC2_CH4 |
RTC_GPIO15 |
|
| GPIO16 |
ADC2_CH5 |
RTC_GPIO16 |
|
| GPIO17 |
ADC2_CH6 |
RTC_GPIO17 |
|
| GPIO18 |
ADC2_CH7 |
RTC_GPIO18 |
|
| GPIO19 |
ADC2_CH8 |
RTC_GPIO19 |
|
| GPIO20 |
ADC2_CH9 |
RTC_GPIO20 |
|
| GPIO21 |
RTC_GPIO21 |
||
| GPIO26 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO27 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO28 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO29 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO30 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO31 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO32 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO33 |
|||
| GPIO34 |
|||
| GPIO35 |
|||
| GPIO36 |
|||
| GPIO37 |
|||
| GPIO38 |
|||
| GPIO39 |
JTAG |
||
| GPIO40 |
JTAG |
||
| GPIO41 |
JTAG |
||
| GPIO42 |
JTAG |
||
| GPIO43 |
|||
| GPIO44 |
|||
| GPIO45 |
Strapping pin |
||
| GPIO46 |
GPI;Strapping pin |
从上表我们可以看到ADC1可以使用的IO引脚为GPIO1-GPIO10总共10个通道。
ESP32S3系列 (下表来自ESP-IDF开发文档)
| GPIO |
Analog Function |
RTC GPIO |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPIO0 |
RTC_GPIO0 |
Strapping pin |
|
| GPIO1 |
ADC1_CH0 |
RTC_GPIO1 |
|
| GPIO2 |
ADC1_CH1 |
RTC_GPIO2 |
|
| GPIO3 |
ADC1_CH2 |
RTC_GPIO3 |
Strapping pin |
| GPIO4 |
ADC1_CH3 |
RTC_GPIO4 |
|
| GPIO5 |
ADC1_CH4 |
RTC_GPIO5 |
|
| GPIO6 |
ADC1_CH5 |
RTC_GPIO6 |
|
| GPIO7 |
ADC1_CH6 |
RTC_GPIO7 |
|
| GPIO8 |
ADC1_CH7 |
RTC_GPIO8 |
|
| GPIO9 |
ADC1_CH8 |
RTC_GPIO9 |
|
| GPIO10 |
ADC1_CH9 |
RTC_GPIO10 |
|
| GPIO11 |
ADC2_CH0 |
RTC_GPIO11 |
|
| GPIO12 |
ADC2_CH1 |
RTC_GPIO12 |
|
| GPIO13 |
ADC2_CH2 |
RTC_GPIO13 |
|
| GPIO14 |
ADC2_CH3 |
RTC_GPIO14 |
|
| GPIO15 |
ADC2_CH4 |
RTC_GPIO15 |
|
| GPIO16 |
ADC2_CH5 |
RTC_GPIO16 |
|
| GPIO17 |
ADC2_CH6 |
RTC_GPIO17 |
|
| GPIO18 |
ADC2_CH7 |
RTC_GPIO18 |
|
| GPIO19 |
ADC2_CH8 |
RTC_GPIO19 |
USB-JTAG |
| GPIO20 |
ADC2_CH9 |
RTC_GPIO20 |
USB-JTAG |
| GPIO21 |
RTC_GPIO21 |
||
| GPIO26 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO27 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO28 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO29 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO30 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO31 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO32 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO33 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO34 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO35 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO36 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO37 |
SPI0/1 |
||
| GPIO38 |
|||
| GPIO39 |
|||
| GPIO40 |
|||
| GPIO41 |
|||
| GPIO42 |
|||
| GPIO43 |
|||
| GPIO44 |
|||
| GPIO45 |
Strapping pin |
||
| GPIO46 |
Strapping pin |
||
| GPIO47 |
|||
| GPIO48 |
从上表我们可以看到ADC1可以使用的IO引脚为GPIO1-GPIO10总共10个通道。
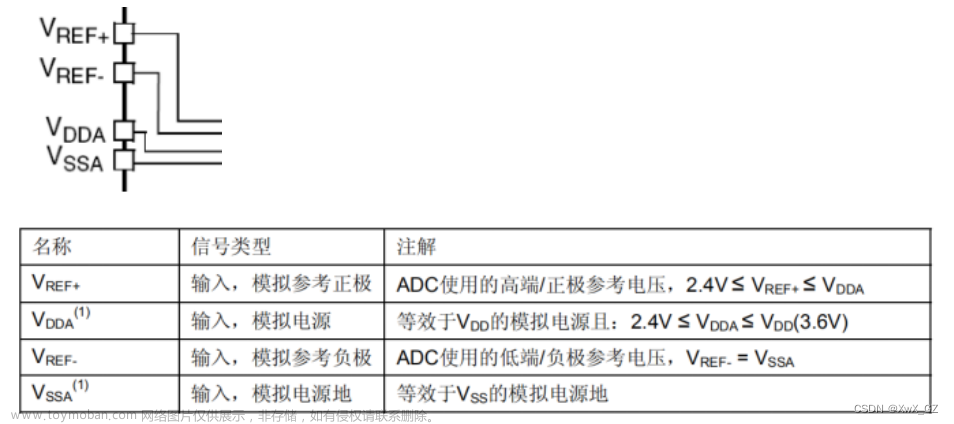
ADC的参考电压
ESP32默认的参考电压是1.1V(每个芯片间有差异,非精准),所以只能测量0-1.1V的电压;
ADC的量程设置
为了能够测量更大量程的电压,需要使用其衰减配置;每个通道都可以单独配置
/**
* @brief ADC attenuation parameter. Different parameters determine the range of the ADC. See ``adc1_config_channel_atten``.
*/
typedef enum {
ADC_ATTEN_DB_0 = 0, ///<No input attenumation, ADC can measure up to approx. 800 mV
ADC_ATTEN_DB_2_5 = 1, ///<The input voltage of ADC will be attenuated extending the range of measurement by about 2.5 dB (1.33 x)
ADC_ATTEN_DB_6 = 2, ///<The input voltage of ADC will be attenuated extending the range of measurement by about 6 dB (2 x)
ADC_ATTEN_DB_11 = 3, ///<The input voltage of ADC will be attenuated extending the range of measurement by about 11 dB (3.55 x)
} adc_atten_t;每个配置推荐的输入范围

ADC最小化噪声
1.在输入引脚接一个100nF的陶瓷电容
2.多次采样取平均
ADC的校准方式
不同芯片的参考电压不一样(1000mV - 1200mV),所以建议进行硬件校准
/**
* @brief Type of calibration value used in characterization
*/
typedef enum {
ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_VREF = 0, /**< Characterization based on reference voltage stored in eFuse*/
ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP = 1, /**< Characterization based on Two Point values stored in eFuse*/
ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_DEFAULT_VREF = 2, /**< Characterization based on default reference voltage*/
ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP_FIT = 3, /**< Characterization based on Two Point values and fitting curve coefficients stored in eFuse */
ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_MAX,
ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_NOT_SUPPORTED = ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_MAX,
} esp_adc_cal_value_t;ESP32支持ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP/ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_VREF
ESP32S2支持ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP
ESP32S3支持ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP_FIT
ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP根据EFUSE里面两个采样值进行校准(150mV/850mV)
ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_VREF根据EFUSE里面的参考电压校准
ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP_FIT根据EFUSE里面两个采样点和特性曲线校准
有些ESP32模组出厂时已经做了校准,我们可以通过工具查看
ADC相关的efuse设置
$espefuse.py -p /dev/cu.SLAB_USBtoUART adc_info
Connecting......
Detecting chip type... Unsupported detection protocol, switching and trying again...
Connecting......
Detecting chip type... ESP32
espefuse.py v4.1
=== Run "adc_info" command ===
ADC VRef calibration: 1128mV通过espefuse.py adc_info命令我们可以看到我的ESP32模组默认支持VRef校验。
如果不支持VRef校准输出如下
ADC VRef calibration: None (1100 mV nominal)如果支持两点校准,输出如下
ADC VRef calibration: 1149 mV
ADC readings stored in efuse BLK3:
ADC1 Low reading (150 mV): 306
ADC1 High reading (850 mV): 3153
ADC2 Low reading (150 mV): 389
ADC2 High reading (850 mV): 3206三、实战
接口说明
1.检查是否支持指定的校准方式
esp_err_t esp_adc_cal_check_efuse(esp_adc_cal_value_t value_type);
2.设置采样量化位数
esp_err_t adc1_config_width(adc_bits_width_t width_bit);
3.设置指定通道的衰减
esp_err_t adc1_config_channel_atten(adc1_channel_t channel, adc_atten_t atten);
4.获取指定通道校准特征值
esp_adc_cal_value_t esp_adc_cal_characterize(adc_unit_t adc_num,
adc_atten_t atten,
adc_bits_width_t bit_width,
uint32_t default_vref,
esp_adc_cal_characteristics_t *chars);
5.获取指定通道的采样值
int adc1_get_raw(adc1_channel_t channel);
6.根据校准特征值获取实际电压值
uint32_t esp_adc_cal_raw_to_voltage(uint32_t adc_reading, const esp_adc_cal_characteristics_t *chars);文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-744229.html
参考代码
/* ADC1 Example
This example code is in the Public Domain (or CC0 licensed, at your option.)
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, this
software is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR
CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "driver/gpio.h"
#include "driver/adc.h"
#include "esp_adc_cal.h"
#define DEFAULT_VREF 1100 //Use adc2_vref_to_gpio() to obtain a better estimate
#define NO_OF_SAMPLES 64 //Multisampling
static esp_adc_cal_characteristics_t *adc_chars;
#if CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32
static const adc_channel_t channel = ADC_CHANNEL_6; //GPIO34 if ADC1, GPIO14 if ADC2
static const adc_bits_width_t width = ADC_WIDTH_BIT_12;
#elif CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32S2
static const adc_channel_t channel = ADC_CHANNEL_6; // GPIO7 if ADC1, GPIO17 if ADC2
static const adc_bits_width_t width = ADC_WIDTH_BIT_13;
#endif
static const adc_atten_t atten = ADC_ATTEN_DB_0;
static const adc_unit_t unit = ADC_UNIT_1;
static void check_efuse(void)
{
#if CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32
//Check if TP is burned into eFuse
if (esp_adc_cal_check_efuse(ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP) == ESP_OK) {
printf("eFuse Two Point: Supported\n");
} else {
printf("eFuse Two Point: NOT supported\n");
}
//Check Vref is burned into eFuse
if (esp_adc_cal_check_efuse(ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_VREF) == ESP_OK) {
printf("eFuse Vref: Supported\n");
} else {
printf("eFuse Vref: NOT supported\n");
}
#elif CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32S2
if (esp_adc_cal_check_efuse(ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP) == ESP_OK) {
printf("eFuse Two Point: Supported\n");
} else {
printf("Cannot retrieve eFuse Two Point calibration values. Default calibration values will be used.\n");
}
#else
#error "This example is configured for ESP32/ESP32S2."
#endif
}
static void print_char_val_type(esp_adc_cal_value_t val_type)
{
if (val_type == ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP) {
printf("Characterized using Two Point Value\n");
} else if (val_type == ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_VREF) {
printf("Characterized using eFuse Vref\n");
} else {
printf("Characterized using Default Vref\n");
}
}
void app_main(void)
{
//Check if Two Point or Vref are burned into eFuse
check_efuse();
//Configure ADC
if (unit == ADC_UNIT_1) {
adc1_config_width(width);
adc1_config_channel_atten(channel, atten);
} else {
adc2_config_channel_atten((adc2_channel_t)channel, atten);
}
//Characterize ADC
adc_chars = calloc(1, sizeof(esp_adc_cal_characteristics_t));
esp_adc_cal_value_t val_type = esp_adc_cal_characterize(unit, atten, width, DEFAULT_VREF, adc_chars);
print_char_val_type(val_type);
//Continuously sample ADC1
while (1) {
uint32_t adc_reading = 0;
//Multisampling
for (int i = 0; i < NO_OF_SAMPLES; i++) {
if (unit == ADC_UNIT_1) {
adc_reading += adc1_get_raw((adc1_channel_t)channel);
} else {
int raw;
adc2_get_raw((adc2_channel_t)channel, width, &raw);
adc_reading += raw;
}
}
adc_reading /= NO_OF_SAMPLES;
//Convert adc_reading to voltage in mV
uint32_t voltage = esp_adc_cal_raw_to_voltage(adc_reading, adc_chars);
printf("Raw: %d\tVoltage: %dmV\n", adc_reading, voltage);
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
}
}以上,基本就讲完了ADC1的使用,点赞收藏不可少文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-744229.html
到了这里,关于ESP32系列--第九篇 ADC的使用的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!







![[嵌入式软件][启蒙篇][仿真平台] STM32F103实现串口输出输入、ADC采集](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/01/814721-1.gif)