题目
Qestion: 分别以邻接矩阵和邻接表作为存储结构,实现以下图的基本操作
- 增加一个新顶点v,
InsertVex(G, v); - 删除顶点v及其相关的边,
DeleteVex(G, v); - 增加一条边<v,w>,
InsertArc(G, v, w); - 删除一条边<v,w>,
DeleteArc(G, v, w)。
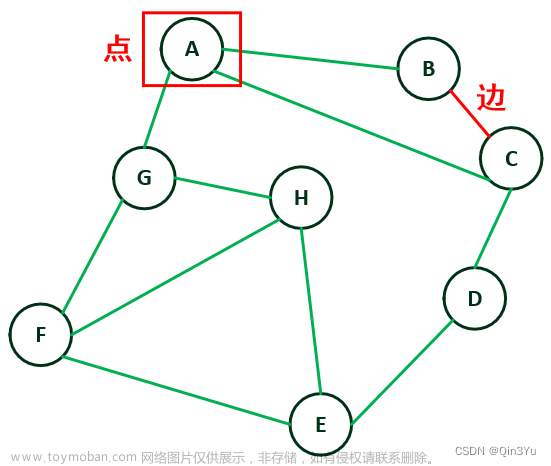
该题所用的图结构

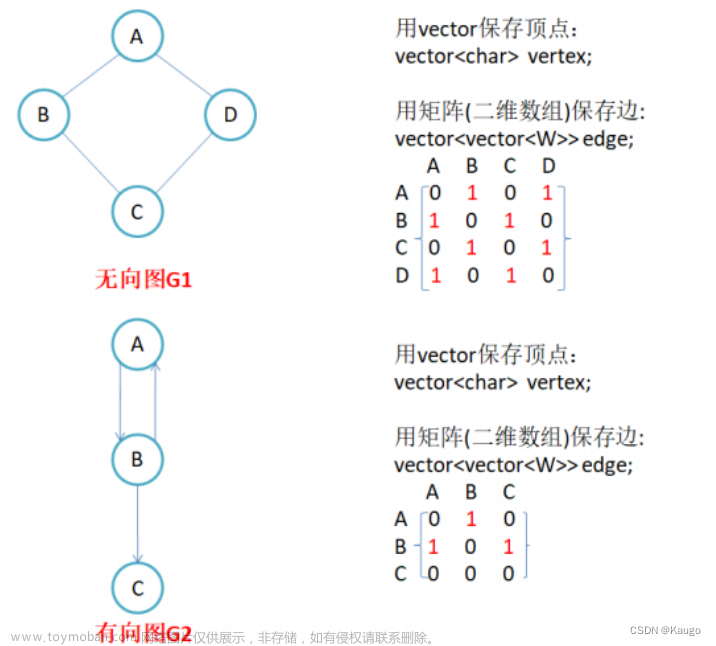
该题所用到的邻接表和邻接矩阵的图形表示
邻接表

邻接矩阵表示

数据结构与定义
因为要分别用邻接表和邻接矩阵来完成上述四个算法,故有两个数据结构的定义文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-753765.html
邻接表数据结构定义
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxSize 20 // 最大顶点的个数
struct Node
{
int weight;
int index;
struct Node *next;
};
struct HNode
{
char nodeData;
struct Node *next;
};
struct Graph
{
int vertexNum;
int arcNum;
bool isDireted;
HNode verList[MaxSize];
};
邻接矩阵数据结构定义
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define Max 20
// 顶点信息
struct VertexItem
{
char Vertex; // 顶点信息
int index; // 顶点在邻接矩阵中的下标
};
// 图的邻接矩阵存储
struct Graph
{
int vertexNum;
int arcNum;
bool isDireted;
int Matrix[Max][Max];
VertexItem vertexList[Max]; // 顶点信息表
};
邻接表
增加一个新顶点v
void InsertVex(Graph &G, char v)
{
G.verList[G.vertexNum].nodeData = v;
G.verList[G.vertexNum].next = nullptr;
G.vertexNum++;
}
删除顶点v及其相关的边
void DeleteVex(Graph &G, char v)
{
int index = Locate(v, G); // 该顶点的下标
// 释放与该顶点有关的所有边
Node *p = G.verList[index].next; // 临时指针p指向该顶点邻接表的第一个结点
while (p != nullptr)
{
if (!G.isDireted) // G为无向图
{
Node *q = G.verList[p->index].next; // 临时指针q指向待删除结点所在邻接表中的第一个结点
while (q->next->index != index) // 一直找,直到找到q的next结点的index值为删除顶点的index
{
q = q->next;
}
Node *needDel = q->next; // 创建一个临时指针,指向待删除的结点
q->next = needDel->next; // 保证邻接表不断
free(needDel); // 释放空间
}
G.verList[index].next = p->next;
G.arcNum--;
free(p);
}
// 释放顶点
G.verList[index].nodeData = NULL;
G.verList[index].next = nullptr;
G.vertexNum--;
return;
}
增加一条边<v,w>
void InsertArc(Graph &G, char tail, char head)
{
int TailIndex, HeadIndex;
TailIndex = Locate(tail, G);
HeadIndex = Locate(head, G);
if (HeadIndex == -1 || TailIndex == -1) // 输入的弧头或者弧尾不存在
{
return;
}
// 无论G为有向图还是无向图
Node *newNode = new Node;
newNode->next = G.verList[TailIndex].next; // 头插法插入到邻接表中
newNode->index = HeadIndex;
G.verList[TailIndex].next = newNode;
if (!G.isDireted) // G为无向图
{
Node *newNode = new Node;
newNode->next = G.verList[HeadIndex].next; // 头插法插入到邻接表中
newNode->index = TailIndex;
G.verList[HeadIndex].next = newNode;
}
}
删除一条边<v,w>
void DeleteArc(Graph &G, char tail, char head)
{
int TailIndex = Locate(tail, G);
int HeadIndex = Locate(head, G);
Node *p = G.verList[TailIndex].next; // 临时指针p指向弧尾顶点邻接表的第一个结点
while (p->next->index != HeadIndex)
{
p = p->next;
}
Node *needDel = p->next;
p->next = needDel->next;
free(needDel);
G.arcNum--;
if (!G.isDireted) // G为无向图
{
Node *q = G.verList[HeadIndex].next;
while (q->next->index != TailIndex)
{
q = q->next;
}
needDel = q->next;
q->next = needDel->next;
free(needDel);
}
}
邻接矩阵
增加一个新顶点v
// 添加顶点
void InsertVex(Graph &G, char c)
{
G.vertexList[G.vertexNum].Vertex = c; // 顶点信息存入顶点表中
G.vertexList[G.vertexNum].index = G.vertexNum; // 顶点的在邻接矩阵的索引存入顶点表中 // 顶点数量加一
// 对新插入的顶点对应的矩阵初始化
for (int i = 0; i <= G.vertexNum; i++)
{
G.Matrix[G.vertexNum][i] = 0;
G.Matrix[i][G.vertexNum] = 0;
}
G.vertexNum++;
}
删除顶点v及其相关的边
// 删除顶点以及相关的边
void DeletVex(Graph &G, char c)
{
int vexIndex = Locate(G, c);
G.vertexNum--;
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; i++)
{
if (G.Matrix[vexIndex][i] == 1) // 有边
{
G.Matrix[vexIndex][i] = 0;
G.arcNum--;
}
if (G.Matrix[i][vexIndex] == 1)
{
G.Matrix[i][vexIndex] = 0;
}
}
G.vertexList[vexIndex].index = -1;
}
增加一条边<v,w>
// 添加弧
void InsertArc(Graph &G, char tail, char head)
{
int tailIndex = Locate(G, tail);
int headIndex = Locate(G, head);
if (headIndex == -1 || tailIndex == -1) // 输入的弧头或者弧尾不存在
{
return;
}
G.Matrix[tailIndex][headIndex] = 1;
G.arcNum++;
if (!G.isDireted)
{
G.Matrix[headIndex][tailIndex] = 1; // 若不是有向图则再添加一条对称边
}
}
删除一条边<v,w>
// 删除弧
void DeleteArc(Graph &G, char tail, char head)
{
int tailIndex = Locate(G, tail);
int headIndex = Locate(G, head);
if (headIndex == -1 || tailIndex == -1)
{
return;
}
G.Matrix[tailIndex][headIndex] = 0;
G.arcNum--;
if (!G.isDireted)
{
G.Matrix[headIndex][tailIndex] = 0; // 若不是有向图则再删除一条对称边
G.arcNum--;
}
}
完整代码
//这个是邻接表的完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxSize 20 // 最大顶点的个数
struct Node
{
int weight;
int index;
struct Node *next;
};
struct HNode
{
char nodeData;
struct Node *next;
};
struct Graph
{
int vertexNum;
int arcNum;
bool isDireted;
HNode verList[MaxSize];
};
int Locate(char c, Graph G)
{
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; i++)
{
if (G.verList[i].nodeData == c)
{
index = i;
}
}
return index;
}
void InsertVex(Graph &G, char v)
{
G.verList[G.vertexNum].nodeData = v;
G.verList[G.vertexNum].next = nullptr;
G.vertexNum++;
}
void InsertArc(Graph &G, char tail, char head)
{
int TailIndex, HeadIndex;
TailIndex = Locate(tail, G);
HeadIndex = Locate(head, G);
if (HeadIndex == -1 || TailIndex == -1) // 输入的弧头或者弧尾不存在
{
return;
}
// 无论G为有向图还是无向图
Node *newNode = new Node;
newNode->next = G.verList[TailIndex].next; // 头插法插入到邻接表中
newNode->index = HeadIndex;
G.verList[TailIndex].next = newNode;
if (!G.isDireted) // G为无向图
{
Node *newNode = new Node;
newNode->next = G.verList[HeadIndex].next; // 头插法插入到邻接表中
newNode->index = TailIndex;
G.verList[HeadIndex].next = newNode;
}
}
void DeleteVex(Graph &G, char v)
{
int index = Locate(v, G); // 该顶点的下标
// 释放与该顶点有关的所有边
Node *p = G.verList[index].next; // 临时指针p指向该顶点邻接表的第一个结点
while (p != nullptr)
{
if (!G.isDireted) // G为无向图
{
Node *q = G.verList[p->index].next; // 临时指针q指向待删除结点所在邻接表中的第一个结点
while (q->next->index != index) // 一直找,直到找到q的next结点的index值为删除顶点的index
{
q = q->next;
}
Node *needDel = q->next; // 创建一个临时指针,指向待删除的结点
q->next = needDel->next; // 保证邻接表不断
free(needDel); // 释放空间
}
G.verList[index].next = p->next;
G.arcNum--;
free(p);
}
// 释放顶点
G.verList[index].nodeData = NULL;
G.verList[index].next = nullptr;
G.vertexNum--;
return;
}
void DeleteArc(Graph &G, char tail, char head)
{
int TailIndex = Locate(tail, G);
int HeadIndex = Locate(head, G);
Node *p = G.verList[TailIndex].next; // 临时指针p指向弧尾顶点邻接表的第一个结点
while (p->next->index != HeadIndex)
{
p = p->next;
}
Node *needDel = p->next;
p->next = needDel->next;
free(needDel);
G.arcNum--;
if (!G.isDireted) // G为无向图
{
Node *q = G.verList[HeadIndex].next;
while (q->next->index != TailIndex)
{
q = q->next;
}
needDel = q->next;
q->next = needDel->next;
free(needDel);
}
}
void CreateGraph(Graph &G)
{
cin >> G.vertexNum >> G.arcNum; // 输入顶点数和边数
cin >> G.isDireted; // 输入是否为有向图
if (G.vertexNum > MaxSize)
{
return;
}
// 初始化顶点列表
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; i++)
{
cin >> G.verList[i].nodeData;
G.verList[i].next = nullptr;
}
// 依次输入各边的信息
for (int j = 0; j < G.arcNum; j++)
{
char ArcHead, ArcTail;
cin >> ArcTail >> ArcHead;
InsertArc(G, ArcTail, ArcHead);
}
}
void HNodeIndegree(Graph G)
{
int IndegreeCnt[G.vertexNum] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; i++)
{
Node *tmp = G.verList[i].next;
while (tmp != nullptr)
{
IndegreeCnt[tmp->index]++;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
cout << "all node's indegree" << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < G.vertexNum; j++)
{
cout << G.verList[j].nodeData << ':' << IndegreeCnt[j] << endl;
}
}
void HNodeOutdegree(Graph G)
{
int OutdegreeCnt[G.vertexNum] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; i++)
{
Node *tmp = G.verList[i].next;
while (tmp != nullptr)
{
OutdegreeCnt[i]++;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
cout << "all node's outdegree" << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < G.vertexNum; j++)
{
cout << G.verList[j].nodeData << ':' << OutdegreeCnt[j] << endl;
}
}
void MaxOutDegreeNode(Graph G)
{
int index = -1; // 出度最大的数组下标
int res = 0; // 出度
// 与HNodeOutdegree同
// same code
int OutdegreeCnt[G.vertexNum] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; i++)
{
Node *tmp = G.verList[i].next;
while (tmp != nullptr)
{
OutdegreeCnt[i]++;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
// same code
for (int j = 0; j < G.vertexNum; j++)
{
if (OutdegreeCnt[j] > res)
{
res = OutdegreeCnt[j];
index = j;
}
}
cout << "the max out degree is" << ':' << G.verList[index].nodeData << endl;
}
void ZeroOutdegree(Graph G)
{
int cnt = 0;
// same code
int OutdegreeCnt[G.vertexNum] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; i++)
{
Node *tmp = G.verList[i].next;
while (tmp != nullptr)
{
OutdegreeCnt[i]++;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
// same code
for (int j = 0; j < G.vertexNum; j++)
{
if (OutdegreeCnt[j] == 0)
{
cnt++;
}
}
cout << "the number of zero outdegree is" << ' ' << cnt;
}
bool IsArcExist(char a, char b, Graph G)
{
int AIndex, BIndex; // 找到弧头和弧尾的数组下标
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; i++)
{
if (G.verList[i].nodeData == a)
{
AIndex = i;
continue;
}
if (G.verList[i].nodeData == b)
{
BIndex = i;
continue;
}
}
Node *tmp = G.verList[AIndex].next;
while (tmp != nullptr)
{
if (tmp->index == BIndex)
{
return true;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
Graph G;
CreateGraph(G);
// HNodeIndegree(G);
// HNodeOutdegree(G);
// MaxOutDegreeNode(G);
// ZeroOutdegree(G);
// char head, tail;
// cin >> head >> tail;
// bool isit = IsArcExist(head, tail, G);
// cout << isit << endl;
return 0;
}
//这个是邻接矩阵的完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define Max 20
// 顶点信息
struct VertexItem
{
char Vertex; // 顶点信息
int index; // 顶点在邻接矩阵中的下标
};
// 图的邻接矩阵存储
struct Graph
{
int vertexNum;
int arcNum;
bool isDireted;
int Matrix[Max][Max];
VertexItem vertexList[Max]; // 顶点信息表
};
// 初始化图
void InitGraph(Graph &G)
{
G.arcNum = 0;
G.vertexNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Max; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Max; j++)
{
G.Matrix[i][j] = -1;
}
}
}
// 获取顶点下标
int Locate(Graph G, char c)
{
int res = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; i++)
{
if (G.vertexList[i].Vertex == c)
{
res = G.vertexList[i].index;
}
}
return res;
}
// 创造图
void CreateGraph(Graph &G)
{
if (G.vertexNum > Max) // 输入的顶点数量超过最大值
{
return;
}
//
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < G.vertexNum; j++)
{
G.Matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; i++)
{
char vertex;
cin >> vertex;
G.vertexList[i].Vertex = vertex;
G.vertexList[i].index = i;
}
char tail, head; // 弧尾和弧头
for (int i = 0; i < G.arcNum; i++)
{
cin >> tail >> head;
int tailIndex, headIndex;
tailIndex = Locate(G, tail);
headIndex = Locate(G, head);
// G为有向图
if (G.isDireted)
{
G.Matrix[tailIndex][headIndex] = 1;
}
// G为无向图
else
{
G.Matrix[tailIndex][headIndex] = 1;
G.Matrix[headIndex][tailIndex] = 1;
}
}
}
// 添加顶点
void InsertVex(Graph &G, char c)
{
G.vertexList[G.vertexNum].Vertex = c; // 顶点信息存入顶点表中
G.vertexList[G.vertexNum].index = G.vertexNum; // 顶点的在邻接矩阵的索引存入顶点表中 // 顶点数量加一
// 对新插入的顶点对应的矩阵初始化
for (int i = 0; i <= G.vertexNum; i++)
{
G.Matrix[G.vertexNum][i] = 0;
G.Matrix[i][G.vertexNum] = 0;
}
G.vertexNum++;
}
// 删除顶点以及相关的边
void DeletVex(Graph &G, char c)
{
int vexIndex = Locate(G, c);
G.vertexNum--;
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; i++)
{
if (G.Matrix[vexIndex][i] == 1) // 有边
{
G.Matrix[vexIndex][i] = 0;
G.arcNum--;
}
if (G.Matrix[i][vexIndex] == 1)
{
G.Matrix[i][vexIndex] = 0;
}
}
G.vertexList[vexIndex].index = -1;
}
// 添加弧
void InsertArc(Graph &G, char tail, char head)
{
int tailIndex = Locate(G, tail);
int headIndex = Locate(G, head);
if (headIndex == -1 || tailIndex == -1) // 输入的弧头或者弧尾不存在
{
return;
}
G.Matrix[tailIndex][headIndex] = 1;
G.arcNum++;
if (!G.isDireted)
{
G.Matrix[headIndex][tailIndex] = 1; // 若不是有向图则再添加一条对称边
}
}
// 删除弧
void DeleteArc(Graph &G, char tail, char head)
{
int tailIndex = Locate(G, tail);
int headIndex = Locate(G, head);
if (headIndex == -1 || tailIndex == -1)
{
return;
}
G.Matrix[tailIndex][headIndex] = 0;
G.arcNum--;
if (!G.isDireted)
{
G.Matrix[headIndex][tailIndex] = 0; // 若不是有向图则再删除一条对称边
G.arcNum--;
}
}
int main()
{
Graph G;
InitGraph(G);
cin >> G.vertexNum >> G.arcNum;
cin >> G.isDireted;
CreateGraph(G);
InsertVex(G, '6'); // 插入新顶点6
InsertVex(G, '7'); // 插入新顶点7
InsertArc(G, '1', '6'); // 添加一条边,从1 -> 6
InsertArc(G, '3', '6'); // 添加一条边,从3 -> 6
InsertArc(G, '1', '7'); // 添加一条边,从1 -> 7
InsertArc(G, '3', '7'); // 添加一条边,从3 -> 7
DeletVex(G, '6'); // 删除顶点6以及其关联的所有边
DeleteArc(G, '1', '6'); // 删除1->6的边
return 0;
}
结束语
因为是算法小菜,所以提供的方法和思路可能不是很好,请多多包涵~如果有疑问欢迎大家留言讨论,你如果觉得这篇文章对你有帮助可以给我一个免费的赞吗?我们之间的交流是我最大的动力!文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-753765.html
到了这里,关于【数据结构与算法】分别以邻接矩阵和邻接表作为存储结构实现以下操作:1.增加一个新顶点v、2.删除顶点v及其相关的边、3.增加一条边<v,w>、4.删除一条边<v,w>的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!





![[数据结构]:25-图深度优先遍历(邻接矩阵)(C语言实现)](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/01/409363-1.png)