本是青灯不归客,却因浊酒恋红尘
一,基本使用
关于Room数据库的基本使用,请参考文章Android--Jetpack--数据库Room详解一-CSDN博客
二,Room与ViewModle,LiveData的结合使用
LiveData与ViewModle的使用,请参考文章Android--Jetpack--LiveData-CSDN博客
我们通过结合Room与LiveData和ViewModle的使用,可以使当我们的数据库发生变化的时候,自动的去更新UI。
下面来看一个简单的使用案例:
1,还是 Android--Jetpack--数据库Room详解一-CSDN博客
中创建的数据库,表还是YuanZhen这张表, 我们把YuanZhenDao这个Dao类添加一个新的方法,使得可以查询到LiveData包装的集合:
@Dao
public interface YuanZhenDao {
@Insert
void insert(YuanZhen... yuanzhens);
@Delete
void delete(YuanZhen yuanZhen);
@Update
void update(YuanZhen yuanZhen);
@Query("select * from YuanZhen")
List<YuanZhen> getAll();
@Query("select * from YuanZhen where name like :name")
YuanZhen getByName(String name);
@Query("select * from YuanZhen where age in(:ages)")
List<YuanZhen> getByAges(int[] ages);
@Query("select name,address from YuanZhen ")
public List<YuanZhenNew> getNew();
@Query("select * from YuanZhen")
LiveData<List<YuanZhen>> getAllLiveDataYZ();
}2,将数据库MyDatabase修改为单例模式:
@Database(entities = {YuanZhen.class},version = 1)
public abstract class MyDatabase extends RoomDatabase {
private static MyDatabase instance;
public static synchronized MyDatabase getInstance(Context context){
if(instance==null){
instance= Room.databaseBuilder(context.getApplicationContext(),MyDatabase.class
,"YuanZhenDb")
.build();
}
return instance;
}
public abstract YuanZhenDao yuanZhenDao();
}3,创建一个包装类,包装LiveData给ViewModel使用:
public class YuanZhenDecorate {
private LiveData<List<YuanZhen>> liveDataAllYZ;
private YuanZhenDao yuanZhenDao;
public YuanZhenDecorate(Context context) {
yuanZhenDao =MyDatabase.getInstance(context).yuanZhenDao();
if(liveDataAllYZ==null){
liveDataAllYZ=yuanZhenDao.getAllLiveDataYZ();
}
}
void insert(YuanZhen... yuanZhens){
yuanZhenDao.insert(yuanZhens);
}
void delete(YuanZhen yuanZhen){
yuanZhenDao.delete(yuanZhen);
}
void update(YuanZhen yuanZhen){
yuanZhenDao.update(yuanZhen);
}
List<YuanZhen> getAll(){
return yuanZhenDao.getAll();
}
LiveData<List<YuanZhen>> getAllLiveDataYZ(){
return yuanZhenDao.getAllLiveDataYZ();
}
}4,创建一个viewmodle:
public class YZViewModdel extends AndroidViewModel {
private YuanZhenDecorate yuanZhenDecorate;
public YZViewModdel(@NonNull Application application) {
super(application);
yuanZhenDecorate =new YuanZhenDecorate(application);
}
void insert(YuanZhen... yuanZhens){
yuanZhenDecorate.insert(yuanZhens);
}
void delete(YuanZhen yuanZhen){
yuanZhenDecorate.delete(yuanZhen);
}
void update(YuanZhen yuanZhen){
yuanZhenDecorate.update(yuanZhen);
}
List<YuanZhen> getAll(){
return yuanZhenDecorate.getAll();
}
LiveData<List<YuanZhen>> getAllLiveDataYZ(){
return yuanZhenDecorate.getAllLiveDataYZ();
}
}5,创建一个recyclerview的adapter:
public class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter {
private LayoutInflater mLayoutInflater;
private List<YuanZhen> mList;
public MyAdapter(Context context,List<YuanZhen> mList) {
mLayoutInflater =LayoutInflater.from(context);
this.mList =mList;
}
public void setData(List<YuanZhen> mList) {
this.mList = mList;
}
@NonNull
@Override
public RecyclerView.ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
return new ViewHolder(mLayoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.item, parent, false));
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull RecyclerView.ViewHolder holder, int position) {
((ViewHolder)holder).mTxt.setText(mList.get(position).getName());
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
if(mList!=null){
return mList.size();
}
return 0;
}
class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
TextView mTxt;
public ViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) {
super(itemView);
mTxt = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.txt);
}
}
}6,activity的xml布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/rv_room"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>7,item的xml布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="30dp"
android:textSize="16sp"/>
</RelativeLayout>8,使用:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
StudentViewModel studentViewModel;
ListView listView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
listView = findViewById(R.id.listView);
studentViewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(this).get(StudentViewModel.class);
studentViewModel.getAllLiveDataStudent().observe(this, new Observer<List<Student>>() {
@Override
public void onChanged(List<Student> students) {
listView.setAdapter(new GoodsAdapter(MainActivity.this, students));
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
studentViewModel.insert(new Student("jett", "123", 1));
}
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
studentViewModel.update(new Student(6, "jett" + i, "123", 1));
}
}
}.start();
}
}9,运行:

三,数据库的升级
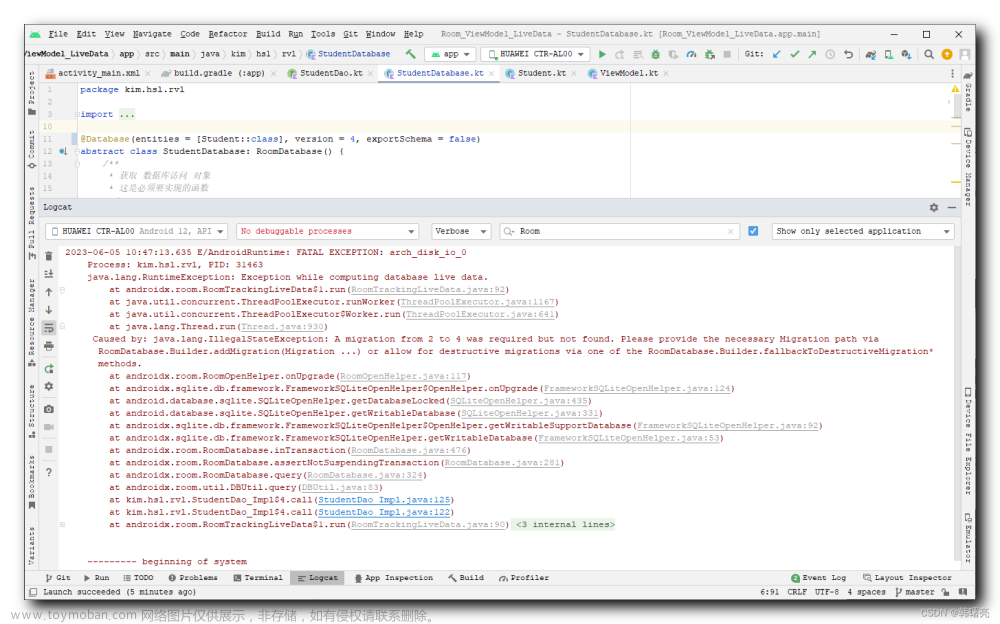
1,强制升级,执行之后数据库的结构会发生变化,但是数据库的数据会丢失。
这种情况比较适合toB开发,数据库版本高降到低的情况,紧急发一版新的程序给现场升级。
使用 :fallbackToDestructiveMigration()
@Database(entities = {YuanZhen.class},version = 2)
public abstract class MyDatabase extends RoomDatabase {
private static MyDatabase instance;
public static synchronized MyDatabase getInstance(Context context){
if(instance==null){
instance= Room.databaseBuilder(context.getApplicationContext(),MyDatabase.class
,"YuanZhenDb")
//强制升级
.fallbackToDestructiveMigration()
.build();
}
return instance;
}
public abstract YuanZhenDao yuanZhenDao();
}2,一般的升级方式
假如我们要增加一个字段price:
@Entity
public class YuanZhen {
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)
private int id;
@ColumnInfo(name ="name")
private String name;
@ColumnInfo(name ="age")
private int age;
@ColumnInfo(name ="address")
private String address;
@ColumnInfo(name = "price")
private int price;
@Ignore
private String sex;
public YuanZhen(String name, int age, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "YuanZhen{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
'}';
}
}在MyDatabase中增加升级功能:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-759147.html
@Database(entities = {YuanZhen.class},version = 2,exportSchema = false)
public abstract class MyDatabase extends RoomDatabase {
private static MyDatabase instance;
public static synchronized MyDatabase getInstance(Context context){
if(instance==null){
instance= Room.databaseBuilder(context.getApplicationContext(),MyDatabase.class
,"YuanZhenDb")
//强制升级
// .fallbackToDestructiveMigration()
.addMigrations(MIGRATION_1_2)
.build();
}
return instance;
}
public abstract YuanZhenDao yuanZhenDao();
static final Migration MIGRATION_1_2=new Migration(1,2) {
@Override
public void migrate(@NonNull SupportSQLiteDatabase database) {
//在这里用sql脚本完成数据变化
database.execSQL("alter table yuanzhen add column price integer not null default 1");
}
};
}这里和greendao最大的不同就是,这里需要自己去写升级脚本,虽然增加了工作量,但是也更加灵活了。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-759147.html
到了这里,关于Android--Jetpack--数据库Room详解二的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!