1. JSON介绍
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,易于阅读和写入,同时也易于机器解析和生成。它基于JavaScript的子集,采用完全独立于语言的文本格式来存储和表示数据。JSON是纯文本,并且完全是语言无关的。
JSON使用JavaScript语法来描述数据结构,但实际上JSON所用的数据结构都是诸如对象、数组、键/值对等的常见数据结构。
* 对象是由键/值对组成的集合,使用大括号 `{}` 表示。
* 数组是由一组值组成的集合,使用方括号 `[]` 表示。
例如:
```json
{
"name": "张三",
"age": 30,
"isStudent": false,
"subjects": ["数学", "英语", "历史"]
}
```
在这个例子中,我们有一个对象,包含四个键/值对。其中,"name" 的值为 "张三","age" 的值为 30,"isStudent" 的值为 false。最后一个键是 "subjects",其值是一个数组,包含三个字符串元素。
JSON的主要优点是它的简洁性和可读性。在JSON中,对象由花括号 `{}` 包围,而数组由方括号 `[]` 包围。此外,JSON支持多种数据类型,包括字符串、数字、布尔值、null、数组和对象。这使得JSON成为一种非常灵活的数据格式,可以用来表示各种复杂的数据结构。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-759148.html
2. 简单使用
1 .导框架 Gson
Maven 存储库:com.google.code.gson » gson (mvnrepository.com)文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-759148.html
dependencies {
// https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.google.code.gson/gson
implementation("com.google.code.gson:gson:2.10.1")
}2 .Student.java
package com.example.json;
public class Student {
// 不要某个属性序列化 transient
// private transient String name;
//序列化时自定义名字 把 name 改成 user_name
// @SerializedName("user_name")
// private String name;
private String name;
private int age;
private Score score;
public Student(String name, int age, Score score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Score getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(Score score) {
this.score = score;
}
}
3. Score.java
package com.example.json;
public class Score {
private float math;
private float english;
private float chinese;
private String grade;
public Score(float math, float english, float chinese) {
this.math = math;
this.english = english;
this.chinese = chinese;
if (math >= 90 && english >= 90 && chinese >= 90) {
this.grade = "A";
} else if (math >= 80 && english >= 80 && chinese >= 80) {
this.grade = "B";
} else {
this.grade = "C";
}
}
public float getMath() {
return math;
}
public void setMath(float math) {
this.math = math;
}
public float getEnglish() {
return english;
}
public void setEnglish(float english) {
this.english = english;
}
public float getChinese() {
return chinese;
}
public void setChinese(float chinese) {
this.chinese = chinese;
}
public String getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(String grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
}
4.MainActivity.java
package com.example.json;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
try {
//JSONObject 生成Json 数据
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("name", "jack");
jsonObject.put("age", 19);
String json = jsonObject.toString(); //{"name":"jack","age":19}
Log.e("JSON", "Json 数据:" + json.toString());
//JSONObject 解析 Json 数据
String data = "{ name:\"jack\", age: 19 }";
JSONObject js = new JSONObject(data);
String name = (String) js.get("name");
Integer age = (Integer) js.get("age");
Log.e("JSON", "解析 Json 数据---name:" + name + "---age:" + age);
//Gson 对象 生成json数据
Student student = new Student("jack", 25, new Score(60, 60, 60));
String json2 = new Gson().toJson(student);
//{"age":25,"name":"jack","score":{"chinese":60.0,"english":60.0,"grade":"C","math":60.0}}
Log.e("JSON", "Json 数据:" + json2);
//Gson 解析json数据 生成对象
String data2 = "{\"age\":25,\"name\":\"jack\",\"score\":{\"chinese\":60.0,\"english\":60.0,\"grade\":\"C\",\"math\":60.0}}";
Student student2 = new Gson().fromJson(data2, Student.class);
Log.e("JSON", "Json student2 数据:" + student2);
//Gson 数组对象 生成json数据
Student student3 = new Student("jack", 25, new Score(90, 90, 90));
Student student4 = new Student("Tom", 24, new Score(80, 80, 80));
Student[] students = new Student[]{student3, student4};
String json3 = new Gson().toJson(students);
//[{"age":25,"name":"jack","score":{"chinese":90.0,"english":90.0,"grade":"A","math":90.0}},
// {"age":24,"name":"Tom","score":{"chinese":80.0,"english":80.0,"grade":"B","math":80.0}}]
Log.e("JSON", "Json 数据:" + json3);
// Gson 解析json数据 数组对象
String data3 = "[{\"age\":25,\"name\":\"jack\",\"score\":{\"chinese\":90.0,\"english\":90.0,\"grade\":\"A\",\"math\":90.0}}," +
"{\"age\":24,\"name\":\"Tom\",\"score\":{\"chinese\":80.0,\"english\":80.0,\"grade\":\"B\",\"math\":80.0}}]";
Student[] students2 = new Gson().fromJson(data3, Student[].class);
Log.e("JSON", "Json 数据:" + students2);
//Gson List 对象 生成json数据
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<>();
studentList.add(new Student("jack", 25, new Score(90, 90, 90)));
studentList.add(new Student("Tom", 24, new Score(80, 80, 80)));
String json4 = new Gson().toJson(studentList);
//[{"age":25,"name":"jack","score":{"chinese":90.0,"english":90.0,"grade":"A","math":90.0}},
// {"age":24,"name":"Tom","score":{"chinese":80.0,"english":80.0,"grade":"B","math":80.0}}]
Log.e("JSON", "Json 数据:" + json4);
//Gson 解析json数据 生成 List 对象
String data4 = "[{\"age\":25,\"name\":\"jack\",\"score\":{\"chinese\":90.0,\"english\":90.0,\"grade\":\"A\",\"math\":90.0}}," +
"{\"age\":24,\"name\":\"Tom\",\"score\":{\"chinese\":80.0,\"english\":80.0,\"grade\":\"B\",\"math\":80.0}}]";
List<Student> students3 = new Gson().fromJson(data4, new TypeToken<List<Student>>() {
}.getType());
Log.e("JSON", "Json 数据:" + students3);
} catch (JSONException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}到了这里,关于Android : 序列化 JSON简单应用的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!


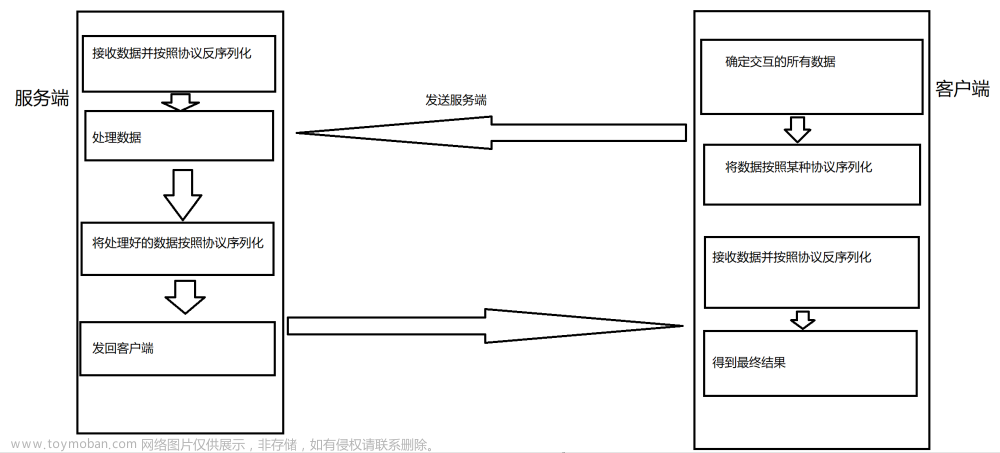
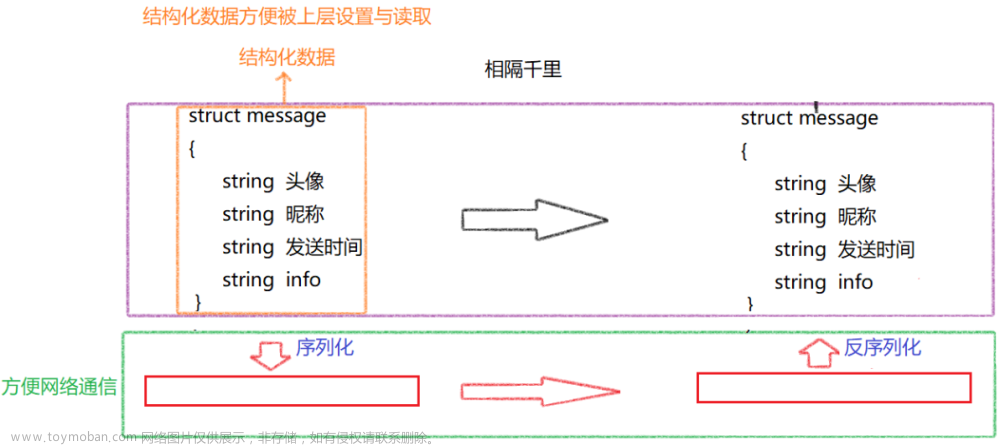
![【探索Linux】P.30(序列化和反序列化 | JSON序列化库 [ C++ ] )](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/04/844473-1.png)





