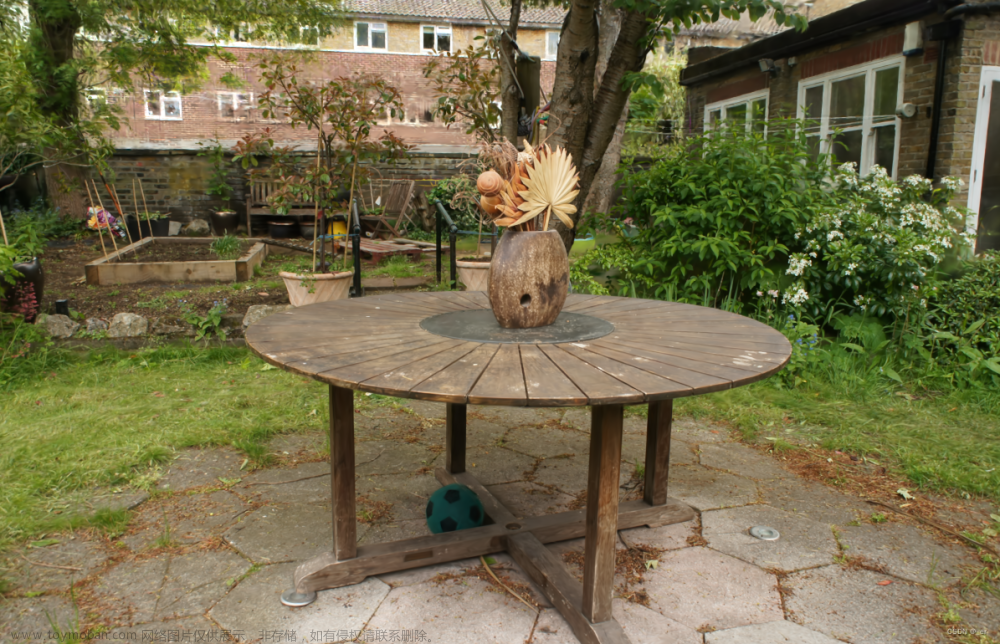
训练结果可视化的尝试
- cmd输入以下命令,开始训练
python train.py -s ./dataset/db/drjohnson -m ./dataset/db/drjohnson/output- 整个训练(30,000步)大约需要20分钟,但7000步后会保存一个中间模型,效果已经很不错了。训练结束后得到output文件
- 在Ubuntu 22.04上,运行以下命令来构建可视化工具:
# Dependencies
sudo apt install -y libglew-dev libassimp-dev libboost-all-dev libgtk-3-dev libopencv-dev libglfw3-dev libavdevice-dev libavcodec-dev libeigen3-dev libxxf86vm-dev libembree-dev
# Project setup
cd SIBR_viewers
cmake -Bbuild . -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release # add -G Ninja to build faster
cmake --build build -j24 --target install- 安装后,找到SIBR_gaussianViewer_app二进制文件,并以模型的路径作为参数运行它:
SIBR_gaussianViewer_app -m ./dataset/db/drjohnson/output代码细节
参考AI葵的代码讲解
cuda_rasterizer文件夹中,forward.cu文件的preprocessCUDA函数
(1)计算投影出来的半径圆心等,把椭圆近似成圆;
- line200,将3D点的矩阵投影;
// Transform point by projecting
float3 p_orig = { orig_points[3 * idx], orig_points[3 * idx + 1], orig_points[3 * idx + 2] };
float4 p_hom = transformPoint4x4(p_orig, projmatrix);
float p_w = 1.0f / (p_hom.w + 0.0000001f);
float3 p_proj = { p_hom.x * p_w, p_hom.y * p_w, p_hom.z * p_w };- line215,计算椭球投影成椭圆的样子,用对称2D矩阵记录abbc;
// Compute 2D screen-space covariance matrix
float3 cov = computeCov2D(p_orig, focal_x, focal_y, tan_fovx, tan_fovy, cov3D, viewmatrix);- line229,求矩阵特征值,解出椭圆的半径,取长轴的半径;
float mid = 0.5f * (cov.x + cov.z);
float lambda1 = mid + sqrt(max(0.1f, mid * mid - det));
float lambda2 = mid - sqrt(max(0.1f, mid * mid - det));
float my_radius = ceil(3.f * sqrt(max(lambda1, lambda2)));- line243,计算每个高斯的颜色
// If colors have been precomputed, use them, otherwise convert
// spherical harmonics coefficients to RGB color.
if (colors_precomp == nullptr)
{
glm::vec3 result = computeColorFromSH(idx, D, M, (glm::vec3*)orig_points, *cam_pos, shs, clamped);
rgb[idx * C + 0] = result.x;
rgb[idx * C + 1] = result.y;
rgb[idx * C + 2] = result.z;
}(2)计算圆所覆盖的像素,即高斯对颜色的贡献。一种加速的方式是,将整张图片分割成很多16*16的小格子,将与圆有交集的格子近似;
- line235,getRect函数计算圆覆盖了哪些tile
getRect(point_image, my_radius, rect_min, rect_max, grid);- line249,保存各个值,其中tilesTouch存储了所覆盖的tile
// Store some useful helper data for the next steps.
depths[idx] = p_view.z;
radii[idx] = my_radius;
points_xy_image[idx] = point_image;
// Inverse 2D covariance and opacity neatly pack into one float4
conic_opacity[idx] = { conic.x, conic.y, conic.z, opacities[idx] };
tiles_touched[idx] = (rect_max.y - rect_min.y) * (rect_max.x - rect_min.x);(3)计算每个Gaussian的前后顺序(深度),还有alpha blending;
- 排顺序,tile(32位的编号)+gaussian(32位)
cuda_rasterizer文件夹中,forward.cu文件的renderCUDA函数文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-761956.html
(4)计算每个像素的颜色文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-761956.html
- line263,把每个tile当做一个block,每一个block里的thread就是tile的pixel
// Main rasterization method. Collaboratively works on one tile per
// block, each thread treats one pixel. Alternates between fetching
// and rasterizing data.
template <uint32_t CHANNELS>
__global__ void __launch_bounds__(BLOCK_X * BLOCK_Y)
renderCUDA(
const uint2* __restrict__ ranges,
const uint32_t* __restrict__ point_list,
int W, int H,
const float2* __restrict__ points_xy_image,
const float* __restrict__ features,
const float4* __restrict__ conic_opacity,
float* __restrict__ final_T,
uint32_t* __restrict__ n_contrib,
const float* __restrict__ bg_color,
float* __restrict__ out_color)- line295,存在共享内存里,读取一次就好
// Allocate storage for batches of collectively fetched data.
__shared__ int collected_id[BLOCK_SIZE];
__shared__ float2 collected_xy[BLOCK_SIZE];
__shared__ float4 collected_conic_opacity[BLOCK_SIZE];- line300,T是透过率,穿过越多gaussian就越小,小到一定程度就提前终止,contributor记录经过了多少gaussian
// Initialize helper variables
float T = 1.0f;
uint32_t contributor = 0;
uint32_t last_contributor = 0;
float C[CHANNELS] = { 0 };- line333,d是gaussian到中心的距离,power计算点在gaussian分布的概率
// Resample using conic matrix (cf. "Surface
// Splatting" by Zwicker et al., 2001)
float2 xy = collected_xy[j];
float2 d = { xy.x - pixf.x, xy.y - pixf.y };
float4 con_o = collected_conic_opacity[j];
float power = -0.5f * (con_o.x * d.x * d.x + con_o.z * d.y * d.y) - con_o.y * d.x * d.y;
if (power > 0.0f)
continue;- line343,透明度随着概率的减小而减小
// Eq. (2) from 3D Gaussian splatting paper.
// Obtain alpha by multiplying with Gaussian opacity
// and its exponential falloff from mean.
// Avoid numerical instabilities (see paper appendix).
float alpha = min(0.99f, con_o.w * exp(power));
if (alpha < 1.0f / 255.0f)
continue;
float test_T = T * (1 - alpha);
if (test_T < 0.0001f)
{
done = true;
continue;
}到了这里,关于3D Gaussian Splatting学习记录11.2的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!