————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「神韵499」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41055045/article/details/112002440
————————————————
目录
一、JDK源码源码导入IDEA前资源准备
1.在自己安装好的JDK1.8版本目录下,找到src.zip,这个就是源码(没有JDK1.8的自行去官网下载,我的版本是jdk1.8.0_271)
2.在自己电脑磁盘新建项目目录JDK1.8.0_271_source,将src解压到项目目录下,然后删掉src.zip
二、导入IDEA并配置
1.File-Open,找到自己项目导入
2.导进入后,你打开一个java文件会发现这个不可识别。此时需要将src标记为资源目录即可
3.设置编译内存,由原来的700改成1000或者更高,防止后面编译内存不足而失败
4.新建sun包,awt包和UNIXToolkit类,font包和FontConfigManager。类的具体内容文章最后面会给出
5.打开项目配置,将Jdk的lib目录下的tools.jar导入项目,编译所需要它
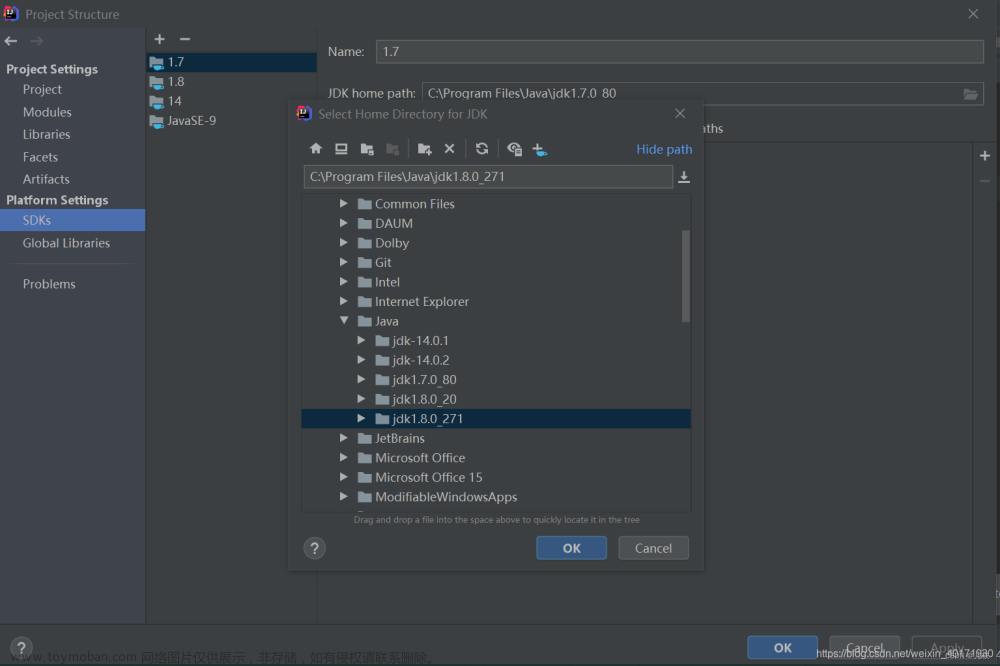
6.配置一个新的JDK,然后改名称,并配置源码为自己的代码 待会debug可以切换进来
三、编写测试类
1.在src目录下编写一个测试类MainTest.java并运行,便会自动编译(确保上面每一步做到位,编译才不会出错)
2.编译成功后,在自己源码HashMap构造函数加断点并加注释
3.debug运行MainTest.java进入源码
四、JDK缺少的类内容
1.sun.awt.UNIXToolkit
2.sun.font.FontConfigManager
一、JDK源码源码导入IDEA前资源准备
1.在自己安装好的JDK1.8版本目录下,找到src.zip,这个就是源码(没有JDK1.8的自行去官网下载,我的版本是jdk1.8.0_271)

2.在自己电脑磁盘新建项目目录JDK1.8.0_271_source,将src解压到项目目录下,然后删掉src.zip

二、导入IDEA并配置
1.File-Open,找到自己项目导入


最终项目目录效果
2.导进入后,你打开一个java文件会发现这个不可识别。此时需要将src标记为资源目录即可


3.设置编译内存,由原来的700改成1000或者更高,防止后面编译内存不足而失败

4.新建sun包,awt包和UNIXToolkit类,font包和FontConfigManager。类的具体内容文章最后面会给出
添加缺少内容

5.打开项目配置,将Jdk的lib目录下的tools.jar导入项目,编译所需要它
引入tools.jar



tools.jar

最终效果
6.配置一个新的JDK,然后改名称,并配置源码为自己的代码 待会debug可以切换进来
配置一个新的JDK



改名称
这一步是关键,设置了后,待会debug就可以切换成自己源码目录了

替换源码目录
Apply 保存以上所有配置,IDEA配置结束!
三、编写测试类
1.在src目录下编写一个测试类MainTest.java并运行,便会自动编译(确保上面每一步做到位,编译才不会出错)

提示设置输出class目录

点击OK,跳出目录,先在源码路径下建立文件夹out,然后设置在项目路径下out目录下即可

运行编译中

编译成功,用了差不多2分钟
2.编译成功后,在自己源码HashMap构造函数加断点并加注释
双击shift搜索HashMap,确保是进入本项目源码构造函数,而不是jdk自带的源码那

本项目下搜索
加断点和注释

给自己项目源码加断点加注释
3.debug运行MainTest.java进入源码

进自己源码还需要自行去切换,有些如果没有disable这个弹出,需要自己搜索去配置(https://blog.csdn.net/qq_28455613/article/details/81382484)

切换,进来了

最终完成编译与测试。
事后补充(重重重!!!)
这里有三个注意点
第一个是尽量不要将debug断点打在构造函数上,上面打在构造函数上是我的过失(上面会初始化很多HashMap容器,你应该打在已经初始化完成后的地方)

第二个是如果debug不能一步一步点进去,则需要将IDEA默认不支持JDK调试的开关打开,如下图

第三个是尽量不要新起注释行,否则导致和源码行号对不上,debug错位(其实我也不喜欢行尾注释,难...,还有解决方法,参考:写Java这么久,JDK源码编译过没?编译JDK源码踩坑纪实)

四、JDK缺少的类内容文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-762358.html
1.sun.awt.UNIXToolkit
package sun.awt;
/**
* @author :HUANG ZHI XUE
* @date :Create in 2020-12-31
*/
import com.sun.java.swing.plaf.gtk.GTKConstants.TextDirection;
import sun.java2d.opengl.OGLRenderQueue;
import sun.security.action.GetIntegerAction;
import sun.security.action.GetPropertyAction;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.color.ColorSpace;
import java.awt.image.*;
import java.security.AccessController;
import java.security.PrivilegedAction;
import static java.awt.RenderingHints.*;
public abstract class UNIXToolkit extends SunToolkit
{
/** All calls into GTK should be synchronized on this lock */
public static final Object GTK_LOCK = new Object();
private static final int[] BAND_OFFSETS = { 0, 1, 2 };
private static final int[] BAND_OFFSETS_ALPHA = { 0, 1, 2, 3 };
private static final int DEFAULT_DATATRANSFER_TIMEOUT = 10000;
// Allowed GTK versions
public enum GtkVersions {
ANY(0),
GTK2(Constants.GTK2_MAJOR_NUMBER),
GTK3(Constants.GTK3_MAJOR_NUMBER);
static class Constants {
static final int GTK2_MAJOR_NUMBER = 2;
static final int GTK3_MAJOR_NUMBER = 3;
}
final int number;
GtkVersions(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
public static GtkVersions getVersion(int number) {
switch (number) {
case Constants.GTK2_MAJOR_NUMBER:
return GTK2;
case Constants.GTK3_MAJOR_NUMBER:
return GTK3;
default:
return ANY;
}
}
// major GTK version number
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
};
private Boolean nativeGTKAvailable;
private Boolean nativeGTKLoaded;
private BufferedImage tmpImage = null;
public static int getDatatransferTimeout() {
Integer dt = (Integer)AccessController.doPrivileged(
new GetIntegerAction("sun.awt.datatransfer.timeout"));
if (dt == null || dt <= 0) {
return DEFAULT_DATATRANSFER_TIMEOUT;
} else {
return dt;
}
}
/**
* Returns true if the native GTK libraries are capable of being
* loaded and are expected to work properly, false otherwise. Note
* that this method will not leave the native GTK libraries loaded if
* they haven't already been loaded. This allows, for example, Swing's
* GTK L&F to test for the presence of native GTK support without
* leaving the native libraries loaded. To attempt long-term loading
* of the native GTK libraries, use the loadGTK() method instead.
*/
@Override
public boolean isNativeGTKAvailable() {
synchronized (GTK_LOCK) {
if (nativeGTKLoaded != null) {
// We've already attempted to load GTK, so just return the
// status of that attempt.
return nativeGTKLoaded;
} else if (nativeGTKAvailable != null) {
// We've already checked the availability of the native GTK
// libraries, so just return the status of that attempt.
return nativeGTKAvailable;
} else {
boolean success = check_gtk(getEnabledGtkVersion().getNumber());
nativeGTKAvailable = success;
return success;
}
}
}
/**
* Loads the GTK libraries, if necessary. The first time this method
* is called, it will attempt to load the native GTK library. If
* successful, it leaves the library open and returns true; otherwise,
* the library is left closed and returns false. On future calls to
* this method, the status of the first attempt is returned (a simple
* lightweight boolean check, no native calls required).
*/
public boolean loadGTK() {
synchronized (GTK_LOCK) {
if (nativeGTKLoaded == null) {
nativeGTKLoaded = load_gtk(getEnabledGtkVersion().getNumber(),
isGtkVerbose());
}
}
return nativeGTKLoaded;
}
/**
* Overridden to handle GTK icon loading
*/
protected Object lazilyLoadDesktopProperty(String name) {
if (name.startsWith("gtk.icon.")) {
return lazilyLoadGTKIcon(name);
}
return super.lazilyLoadDesktopProperty(name);
}
/**
* Load a native Gtk stock icon.
*
* @param longname a desktop property name. This contains icon name, size
* and orientation, e.g. <code>"gtk.icon.gtk-add.4.rtl"</code>
* @return an <code>Image</code> for the icon, or <code>null</code> if the
* icon could not be loaded
*/
protected Object lazilyLoadGTKIcon(String longname) {
// Check if we have already loaded it.
Object result = desktopProperties.get(longname);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
// We need to have at least gtk.icon.<stock_id>.<size>.<orientation>
String str[] = longname.split("\\.");
if (str.length != 5) {
return null;
}
// Parse out the stock icon size we are looking for.
int size = 0;
try {
size = Integer.parseInt(str[3]);
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
return null;
}
// Direction.
TextDirection dir = ("ltr".equals(str[4]) ? TextDirection.LTR :
TextDirection.RTL);
// Load the stock icon.
BufferedImage img = getStockIcon(-1, str[2], size, dir.ordinal(), null);
if (img != null) {
// Create the desktop property for the icon.
setDesktopProperty(longname, img);
}
return img;
}
/**
* Returns a BufferedImage which contains the Gtk icon requested. If no
* such icon exists or an error occurs loading the icon the result will
* be null.
*
* @param filename
* @return The icon or null if it was not found or loaded.
*/
public BufferedImage getGTKIcon(final String filename) {
if (!loadGTK()) {
return null;
} else {
// Call the native method to load the icon.
synchronized (GTK_LOCK) {
if (!load_gtk_icon(filename)) {
tmpImage = null;
}
}
}
// Return local image the callback loaded the icon into.
return tmpImage;
}
/**
* Returns a BufferedImage which contains the Gtk stock icon requested.
* If no such stock icon exists the result will be null.
*
* @param widgetType one of WidgetType values defined in GTKNativeEngine or
* -1 for system default stock icon.
* @param stockId String which defines the stock id of the gtk item.
* For a complete list reference the API at www.gtk.org for StockItems.
* @param iconSize One of the GtkIconSize values defined in GTKConstants
* @param textDirection One of the TextDirection values defined in
* GTKConstants
* @param detail Render detail that is passed to the native engine (feel
* free to pass null)
* @return The stock icon or null if it was not found or loaded.
*/
public BufferedImage getStockIcon(final int widgetType, final String stockId,
final int iconSize, final int direction,
final String detail) {
if (!loadGTK()) {
return null;
} else {
// Call the native method to load the icon.
synchronized (GTK_LOCK) {
if (!load_stock_icon(widgetType, stockId, iconSize, direction, detail)) {
tmpImage = null;
}
}
}
// Return local image the callback loaded the icon into.
return tmpImage; // set by loadIconCallback
}
/**
* This method is used by JNI as a callback from load_stock_icon.
* Image data is passed back to us via this method and loaded into the
* local BufferedImage and then returned via getStockIcon.
*
* Do NOT call this method directly.
*/
public void loadIconCallback(byte[] data, int width, int height,
int rowStride, int bps, int channels, boolean alpha) {
// Reset the stock image to null.
tmpImage = null;
// Create a new BufferedImage based on the data returned from the
// JNI call.
DataBuffer dataBuf = new DataBufferByte(data, (rowStride * height));
// Maybe test # channels to determine band offsets?
WritableRaster raster = Raster.createInterleavedRaster(dataBuf,
width, height, rowStride, channels,
(alpha ? BAND_OFFSETS_ALPHA : BAND_OFFSETS), null);
ColorModel colorModel = new ComponentColorModel(
ColorSpace.getInstance(ColorSpace.CS_sRGB), alpha, false,
ColorModel.TRANSLUCENT, DataBuffer.TYPE_BYTE);
// Set the local image so we can return it later from
// getStockIcon().
tmpImage = new BufferedImage(colorModel, raster, false, null);
}
private static native boolean check_gtk(int version);
private static native boolean load_gtk(int version, boolean verbose);
private static native boolean unload_gtk();
private native boolean load_gtk_icon(String filename);
private native boolean load_stock_icon(int widget_type, String stock_id,
int iconSize, int textDirection, String detail);
private native void nativeSync();
private static native int get_gtk_version();
@Override
public void sync() {
// flush the X11 buffer
nativeSync();
// now flush the OGL pipeline (this is a no-op if OGL is not enabled)
OGLRenderQueue.sync();
}
/*
* This returns the value for the desktop property "awt.font.desktophints"
* It builds this by querying the Gnome desktop properties to return
* them as platform independent hints.
* This requires that the Gnome properties have already been gathered.
*/
public static final String FONTCONFIGAAHINT = "fontconfig/Antialias";
@Override
protected RenderingHints getDesktopAAHints() {
Object aaValue = getDesktopProperty("gnome.Xft/Antialias");
if (aaValue == null) {
/* On a KDE desktop running KWin the rendering hint will
* have been set as property "fontconfig/Antialias".
* No need to parse further in this case.
*/
aaValue = getDesktopProperty(FONTCONFIGAAHINT);
if (aaValue != null) {
return new RenderingHints(KEY_TEXT_ANTIALIASING, aaValue);
} else {
return null; // no Gnome or KDE Desktop properties available.
}
}
/* 0 means off, 1 means some ON. What would any other value mean?
* If we require "1" to enable AA then some new value would cause
* us to default to "OFF". I don't think that's the best guess.
* So if its !=0 then lets assume AA.
*/
boolean aa = ((aaValue instanceof Number)
&& ((Number) aaValue).intValue() != 0);
Object aaHint;
if (aa) {
String subpixOrder =
(String)getDesktopProperty("gnome.Xft/RGBA");
if (subpixOrder == null || subpixOrder.equals("none")) {
aaHint = VALUE_TEXT_ANTIALIAS_ON;
} else if (subpixOrder.equals("rgb")) {
aaHint = VALUE_TEXT_ANTIALIAS_LCD_HRGB;
} else if (subpixOrder.equals("bgr")) {
aaHint = VALUE_TEXT_ANTIALIAS_LCD_HBGR;
} else if (subpixOrder.equals("vrgb")) {
aaHint = VALUE_TEXT_ANTIALIAS_LCD_VRGB;
} else if (subpixOrder.equals("vbgr")) {
aaHint = VALUE_TEXT_ANTIALIAS_LCD_VBGR;
} else {
/* didn't recognise the string, but AA is requested */
aaHint = VALUE_TEXT_ANTIALIAS_ON;
}
} else {
aaHint = VALUE_TEXT_ANTIALIAS_DEFAULT;
}
return new RenderingHints(KEY_TEXT_ANTIALIASING, aaHint);
}
private native boolean gtkCheckVersionImpl(int major, int minor,
int micro);
/**
* Returns {@code true} if the GTK+ library is compatible with the given
* version.
*
* @param major
* The required major version.
* @param minor
* The required minor version.
* @param micro
* The required micro version.
* @return {@code true} if the GTK+ library is compatible with the given
* version.
*/
public boolean checkGtkVersion(int major, int minor, int micro) {
if (loadGTK()) {
return gtkCheckVersionImpl(major, minor, micro);
}
return false;
}
public static GtkVersions getEnabledGtkVersion() {
String version = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new GetPropertyAction("jdk.gtk.version"));
if (version == null) {
return GtkVersions.ANY;
} else if (version.startsWith("2")) {
return GtkVersions.GTK2;
} else if("3".equals(version) ){
return GtkVersions.GTK3;
}
return GtkVersions.ANY;
}
public static GtkVersions getGtkVersion() {
return GtkVersions.getVersion(get_gtk_version());
}
public static boolean isGtkVerbose() {
return AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)()
-> Boolean.getBoolean("jdk.gtk.verbose"));
}
}2.sun.font.FontConfigManager
package sun.font;
/**
* @author :HUANG ZHI XUE
* @date :Create in 2020-12-31
*/
import sun.awt.SunHints;
import sun.awt.SunToolkit;
import sun.util.logging.PlatformLogger;
import java.util.Locale;
/**
* Small utility class to manage FontConfig.
*/
public class FontConfigManager {
static boolean fontConfigFailed = false;
/* This is populated by native */
private static final FontConfigInfo fcInfo = new FontConfigInfo();
/* Begin support for GTK Look and Feel - query libfontconfig and
* return a composite Font to Swing that uses the desktop font(s).
*/
/* These next three classes are just data structures.
*/
public static class FontConfigFont {
public String familyName; // eg Bitstream Vera Sans
public String styleStr; // eg Bold
public String fullName; // eg Bitstream Vera Sans Bold
public String fontFile; // eg /usr/X11/lib/fonts/foo.ttf
}
public static class FcCompFont {
public String fcName; // eg sans
public String fcFamily; // eg sans
public String jdkName; // eg sansserif
public int style; // eg 0=PLAIN
public FontConfigFont firstFont;
public FontConfigFont[] allFonts;
//boolean preferBitmaps; // if embedded bitmaps preferred over AA
public CompositeFont compFont; // null if not yet created/known.
}
public static class FontConfigInfo {
public int fcVersion;
public String[] cacheDirs = new String[4];
}
/* fontconfig recognises slants roman, italic, as well as oblique,
* and a slew of weights, where the ones that matter here are
* regular and bold.
* To fully qualify what we want, we can for example ask for (eg)
* Font.PLAIN : "serif:regular:roman"
* Font.BOLD : "serif:bold:roman"
* Font.ITALIC : "serif:regular:italic"
* Font.BOLD|Font.ITALIC : "serif:bold:italic"
*/
private static String[] fontConfigNames = {
"sans:regular:roman",
"sans:bold:roman",
"sans:regular:italic",
"sans:bold:italic",
"serif:regular:roman",
"serif:bold:roman",
"serif:regular:italic",
"serif:bold:italic",
"monospace:regular:roman",
"monospace:bold:roman",
"monospace:regular:italic",
"monospace:bold:italic",
};
/* This array has the array elements created in Java code and is
* passed down to native to be filled in.
*/
private FcCompFont[] fontConfigFonts;
/**
* Instantiates a new FontConfigManager getting the default instance
* of FontManager from the FontManagerFactory.
*/
public FontConfigManager() {
}
/* Called from code that needs to know what are the AA settings
* that apps using FC would pick up for the default desktop font.
* Note apps can change the default desktop font. etc, so this
* isn't certain to be right but its going to correct for most cases.
* Native return values map to the text aa values in sun.awt.SunHints.
* which is used to look up the renderinghint value object.
*/
public static Object getFontConfigAAHint() {
return getFontConfigAAHint("sans");
}
/* This is public solely so that for debugging purposes it can be called
* with other names, which might (eg) include a size, eg "sans-24"
* The return value is a text aa rendering hint value.
* Normally we should call the no-args version.
*/
public static Object getFontConfigAAHint(String fcFamily) {
if (FontUtilities.isWindows) {
return null;
} else {
int hint = getFontConfigAASettings(getFCLocaleStr(), fcFamily);
if (hint < 0) {
return null;
} else {
return SunHints.Value.get(SunHints.INTKEY_TEXT_ANTIALIASING,
hint);
}
}
}
private static String getFCLocaleStr() {
Locale l = SunToolkit.getStartupLocale();
String localeStr = l.getLanguage();
String country = l.getCountry();
if (!country.equals("")) {
localeStr = localeStr + "-" + country;
}
return localeStr;
}
/* This does cause the native libfontconfig to be loaded and unloaded,
* but it does not incur the overhead of initialisation of its
* data structures, so shouldn't have a measurable impact.
*/
public static native int getFontConfigVersion();
/* This can be made public if it's needed to force a re-read
* rather than using the cached values. The re-read would be needed
* only if some event signalled that the fontconfig has changed.
* In that event this method would need to return directly the array
* to be used by the caller in case it subsequently changed.
*/
public synchronized void initFontConfigFonts(boolean includeFallbacks) {
if (fontConfigFonts != null) {
if (!includeFallbacks || (fontConfigFonts[0].allFonts != null)) {
return;
}
}
if (FontUtilities.isWindows || fontConfigFailed) {
return;
}
long t0 = 0;
if (FontUtilities.isLogging()) {
t0 = System.nanoTime();
}
FcCompFont[] fontArr = new FcCompFont[fontConfigNames.length];
for (int i = 0; i< fontArr.length; i++) {
fontArr[i] = new FcCompFont();
fontArr[i].fcName = fontConfigNames[i];
int colonPos = fontArr[i].fcName.indexOf(':');
fontArr[i].fcFamily = fontArr[i].fcName.substring(0, colonPos);
fontArr[i].jdkName = FontUtilities.mapFcName(fontArr[i].fcFamily);
fontArr[i].style = i % 4; // depends on array order.
}
getFontConfig(getFCLocaleStr(), fcInfo, fontArr, includeFallbacks);
FontConfigFont anyFont = null;
/* If don't find anything (eg no libfontconfig), then just return */
for (int i = 0; i< fontArr.length; i++) {
FcCompFont fci = fontArr[i];
if (fci.firstFont == null) {
if (FontUtilities.isLogging()) {
PlatformLogger logger = FontUtilities.getLogger();
logger.info("Fontconfig returned no font for " +
fontArr[i].fcName);
}
fontConfigFailed = true;
} else if (anyFont == null) {
anyFont = fci.firstFont;
}
}
if (anyFont == null) {
if (FontUtilities.isLogging()) {
PlatformLogger logger = FontUtilities.getLogger();
logger.info("Fontconfig returned no fonts at all.");
}
fontConfigFailed = true;
return;
} else if (fontConfigFailed) {
for (int i = 0; i< fontArr.length; i++) {
if (fontArr[i].firstFont == null) {
fontArr[i].firstFont = anyFont;
}
}
}
fontConfigFonts = fontArr;
if (FontUtilities.isLogging()) {
PlatformLogger logger = FontUtilities.getLogger();
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
logger.info("Time spent accessing fontconfig="
+ ((t1 - t0) / 1000000) + "ms.");
for (int i = 0; i< fontConfigFonts.length; i++) {
FcCompFont fci = fontConfigFonts[i];
logger.info("FC font " + fci.fcName+" maps to family " +
fci.firstFont.familyName +
" in file " + fci.firstFont.fontFile);
if (fci.allFonts != null) {
for (int f=0;f<fci.allFonts.length;f++) {
FontConfigFont fcf = fci.allFonts[f];
logger.info("Family=" + fcf.familyName +
" Style="+ fcf.styleStr +
" Fullname="+fcf.fullName +
" File="+fcf.fontFile);
}
}
}
}
}
public PhysicalFont registerFromFcInfo(FcCompFont fcInfo) {
SunFontManager fm = SunFontManager.getInstance();
/* If it's a TTC file we need to know that as we will need to
* make sure we return the right font */
String fontFile = fcInfo.firstFont.fontFile;
int offset = fontFile.length()-4;
if (offset <= 0) {
return null;
}
String ext = fontFile.substring(offset).toLowerCase();
boolean isTTC = ext.equals(".ttc");
/* If this file is already registered, can just return its font.
* However we do need to check in case it's a TTC as we need
* a specific font, so rather than directly returning it, let
* findFont2D resolve that.
*/
PhysicalFont physFont = fm.getRegisteredFontFile(fontFile);
if (physFont != null) {
if (isTTC) {
Font2D f2d = fm.findFont2D(fcInfo.firstFont.familyName,
fcInfo.style,
FontManager.NO_FALLBACK);
if (f2d instanceof PhysicalFont) { /* paranoia */
return (PhysicalFont)f2d;
} else {
return null;
}
} else {
return physFont;
}
}
/* If the font may hide a JRE font (eg fontconfig says it is
* Lucida Sans), we want to use the JRE version, so make it
* point to the JRE font.
*/
physFont = fm.findJREDeferredFont(fcInfo.firstFont.familyName,
fcInfo.style);
/* It is also possible the font file is on the "deferred" list,
* in which case we can just initialise it now.
*/
if (physFont == null &&
fm.isDeferredFont(fontFile) == true) {
physFont = fm.initialiseDeferredFont(fcInfo.firstFont.fontFile);
/* use findFont2D to get the right font from TTC's */
if (physFont != null) {
if (isTTC) {
Font2D f2d = fm.findFont2D(fcInfo.firstFont.familyName,
fcInfo.style,
FontManager.NO_FALLBACK);
if (f2d instanceof PhysicalFont) { /* paranoia */
return (PhysicalFont)f2d;
} else {
return null;
}
} else {
return physFont;
}
}
}
/* In the majority of cases we reach here, and need to determine
* the type and rank to register the font.
*/
if (physFont == null) {
int fontFormat = SunFontManager.FONTFORMAT_NONE;
int fontRank = Font2D.UNKNOWN_RANK;
if (ext.equals(".ttf") || isTTC) {
fontFormat = SunFontManager.FONTFORMAT_TRUETYPE;
fontRank = Font2D.TTF_RANK;
} else if (ext.equals(".pfa") || ext.equals(".pfb")) {
fontFormat = SunFontManager.FONTFORMAT_TYPE1;
fontRank = Font2D.TYPE1_RANK;
}
physFont = fm.registerFontFile(fcInfo.firstFont.fontFile, null,
fontFormat, true, fontRank);
}
return physFont;
}
/*
* We need to return a Composite font which has as the font in
* its first slot one obtained from fontconfig.
*/
public CompositeFont getFontConfigFont(String name, int style) {
name = name.toLowerCase();
initFontConfigFonts(false);
if (fontConfigFonts == null) {
// This avoids an immediate NPE if fontconfig look up failed
// but doesn't guarantee this is a recoverable situation.
return null;
}
FcCompFont fcInfo = null;
for (int i=0; i<fontConfigFonts.length; i++) {
if (name.equals(fontConfigFonts[i].fcFamily) &&
style == fontConfigFonts[i].style) {
fcInfo = fontConfigFonts[i];
break;
}
}
if (fcInfo == null) {
fcInfo = fontConfigFonts[0];
}
if (FontUtilities.isLogging()) {
FontUtilities.getLogger()
.info("FC name=" + name + " style=" + style +
" uses " + fcInfo.firstFont.familyName +
" in file: " + fcInfo.firstFont.fontFile);
}
if (fcInfo.compFont != null) {
return fcInfo.compFont;
}
/* jdkFont is going to be used for slots 1..N and as a fallback.
* Slot 0 will be the physical font from fontconfig.
*/
FontManager fm = FontManagerFactory.getInstance();
CompositeFont jdkFont = (CompositeFont)
fm.findFont2D(fcInfo.jdkName, style, FontManager.LOGICAL_FALLBACK);
if (fcInfo.firstFont.familyName == null ||
fcInfo.firstFont.fontFile == null) {
return (fcInfo.compFont = jdkFont);
}
/* First, see if the family and exact style is already registered.
* If it is, use it. If it's not, then try to register it.
* If that registration fails (signalled by null) just return the
* regular JDK composite.
* Algorithmically styled fonts won't match on exact style, so
* will fall through this code, but the regisration code will
* find that file already registered and return its font.
*/
FontFamily family = FontFamily.getFamily(fcInfo.firstFont.familyName);
PhysicalFont physFont = null;
if (family != null) {
Font2D f2D = family.getFontWithExactStyleMatch(fcInfo.style);
if (f2D instanceof PhysicalFont) {
physFont = (PhysicalFont)f2D;
}
}
if (physFont == null ||
!fcInfo.firstFont.fontFile.equals(physFont.platName)) {
physFont = registerFromFcInfo(fcInfo);
if (physFont == null) {
return (fcInfo.compFont = jdkFont);
}
family = FontFamily.getFamily(physFont.getFamilyName(null));
}
/* Now register the fonts in the family (the other styles) after
* checking that they aren't already registered and are actually in
* a different file. They may be the same file in CJK cases.
* For cases where they are different font files - eg as is common for
* Latin fonts, then we rely on fontconfig to report these correctly.
* Assume that all styles of this font are found by fontconfig,
* so we can find all the family members which must be registered
* together to prevent synthetic styling.
*/
for (int i=0; i<fontConfigFonts.length; i++) {
FcCompFont fc = fontConfigFonts[i];
if (fc != fcInfo &&
physFont.getFamilyName(null).equals(fc.firstFont.familyName) &&
!fc.firstFont.fontFile.equals(physFont.platName) &&
family.getFontWithExactStyleMatch(fc.style) == null) {
registerFromFcInfo(fontConfigFonts[i]);
}
}
/* Now we have a physical font. We will back this up with the JDK
* logical font (sansserif, serif, or monospaced) that corresponds
* to the Pango/GTK/FC logical font name.
*/
return (fcInfo.compFont = new CompositeFont(physFont, jdkFont));
}
/**
*
* @param locale
* @param fcFamily
* @return
*/
public FcCompFont[] getFontConfigFonts() {
return fontConfigFonts;
}
/* Return an array of FcCompFont structs describing the primary
* font located for each of fontconfig/GTK/Pango's logical font names.
*/
private static native void getFontConfig(String locale,
FontConfigInfo fcInfo,
FcCompFont[] fonts,
boolean includeFallbacks);
void populateFontConfig(FcCompFont[] fcInfo) {
fontConfigFonts = fcInfo;
}
FcCompFont[] loadFontConfig() {
initFontConfigFonts(true);
return fontConfigFonts;
}
FontConfigInfo getFontConfigInfo() {
initFontConfigFonts(true);
return fcInfo;
}
private static native int
getFontConfigAASettings(String locale, String fcFamily);
}
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「神韵499」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41055045/article/details/112002440文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-762358.html
到了这里,关于IDEA编译JDK1.8源码及运行测试的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!