RT-Thread STM32 GoKit V2.1 开发板BSP说明

简介
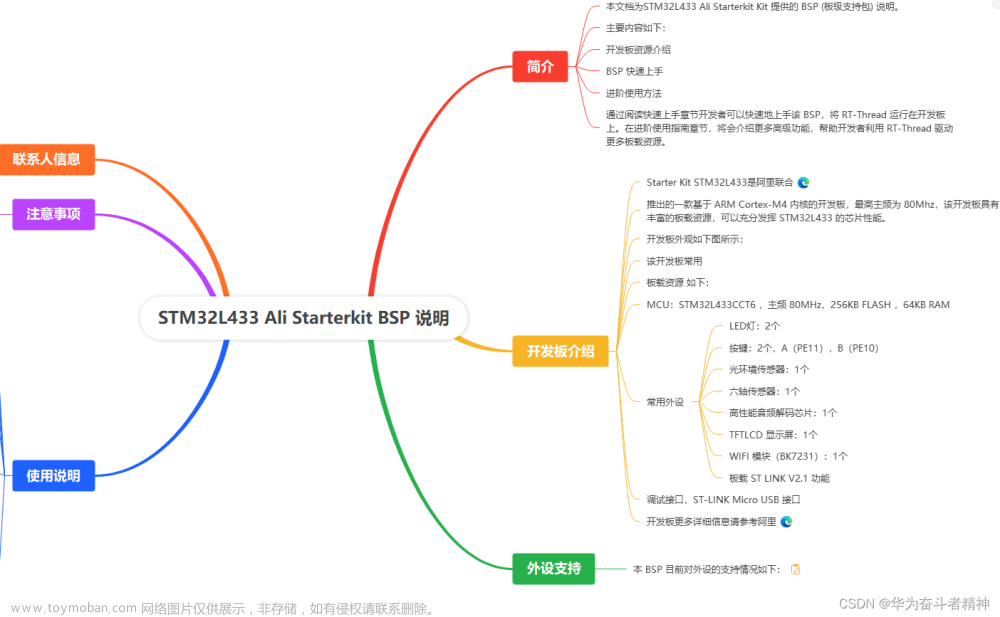
本文档为刘恒为 GoKit V2.1 开发板提供的 BSP (板级支持包) 说明。
主要内容如下:
- 开发板资源介绍
- BSP 快速上手
- 进阶使用方法
通过阅读快速上手章节开发者可以快速地上手该 BSP,将 RT-Thread 运行在开发板上。在进阶使用指南章节,将会介绍更多高级功能,帮助开发者利用 RT-Thread 驱动更多板载资源。
开发板介绍
GoKit V2.1 是机智云 (GizWits) 推出的一款基于 ARM Cortex-M3 内核的开发板,最高主频为 72Mhz,该开发板专为物联网打造的硬件开发平台原型,具有丰富的板载资源,可以充分发挥 STM32F103 的芯片性能。采用底板加扩展板结构,方便扩展模块。
开发板外观如下图所示:
该开发板常用 板载资源 如下:
- MCU:STM32F103C8T6,主频 72MHz,64KB FLASH ,20KB RAM
- 常用外设
- LED:4个,LED1 - LED4,红色
- 按键:1个,RESET 复位
- 常用接口:USB 转串口等
- 调试接口,标准 SWD
开发板更多详细信息请参考【机智云】 GoKit V2.1 开发板介绍。
外设支持
本 BSP 目前对外设的支持情况如下:
| 板载外设 | 支持情况 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| USB 转串口 | 支持 | |
| LED | 支持 | |
| RGB LED | 暂不支持 | |
| 片上外设 | 支持情况 | 备注 |
| GPIO | 支持 | PA0-PA15,PB0-PB15,PC13 |
| UART | 支持 | UART1 |
| SPI | 暂不支持 | |
| I2C | 暂不支持 | |
| SDIO | 暂不支持 | |
| RTC | 暂不支持 | |
| PWM | 暂不支持 | |
| USB Device | 暂不支持 | |
| USB Host | 暂不支持 | |
| IWG | 暂不支持 | |
| 扩展模块 | 支持情况 | 备注 |
| gokit v2.3 | 暂不支持 |
使用说明
使用说明分为如下两个章节:
-
快速上手
本章节是为刚接触 RT-Thread 的新手准备的使用说明,遵循简单的步骤即可将 RT-Thread 操作系统运行在该开发板上,看到实验效果 。
-
进阶使用
本章节是为需要在 RT-Thread 操作系统上使用更多开发板资源的开发者准备的。通过使用 ENV 工具对 BSP 进行配置,可以开启更多板载资源,实现更多高级功能。
快速上手
本 BSP 为开发者提供 MDK4、MDK5 和 IAR 工程,并且支持 GCC 开发环境。下面以 MDK5 开发环境为例,介绍如何将系统运行起来。
硬件连接
使用数据线连接开发板到 PC,打开电源开关。
编译下载
双击 project.uvprojx 文件,打开 MDK5 工程,编译并下载程序到开发板。
工程默认配置使用 Jlink 仿真器下载程序,在通过 Jlink 连接开发板的基础上,点击下载按钮即可下载程序到开发板
运行结果
下载程序成功之后,系统会自动运行,LED4 闪烁。
连接开发板对应串口到 PC , 在终端工具里打开相应的串口(115200-8-1-N),复位设备后,可以看到 RT-Thread 的输出信息:
\ | /
- RT - Thread Operating System
/ | \ 4.0.2 build Jun 7 2019
2006 - 2019 Copyright by rt-thread team
msh >
进阶使用
此 BSP 默认只开启了 GPIO 和 串口1 的功能,如果需使用扩展模块等更多高级功能,需要利用 ENV 工具对BSP 进行配置,步骤如下:
-
在 bsp 下打开 env 工具。
-
输入
menuconfig命令配置工程,配置好之后保存退出。 -
输入
pkgs --update命令更新软件包。 -
输入
scons --target=mdk4/mdk5/iar命令重新生成工程。
本章节更多详细的介绍请参考 STM32 系列 BSP 外设驱动使用教程。
注意事项
示例代码
…\components\libc\compilers\armlibc\syscalls.c
/*
* Copyright (c) 2006-2022, RT-Thread Development Team
*
* SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
*
* Change Logs:
* Date Author Notes
* 2012-11-23 Yihui The first version
* 2013-11-24 aozima fixed _sys_read()/_sys_write() issues.
* 2014-08-03 bernard If using msh, use system() implementation
* in msh.
* 2020-08-05 Meco Man fixed _sys_flen() compiling-warning when
* RT_USING_DFS is not defined
* 2020-02-13 Meco Man re-implement exit() and abort()
* 2020-02-14 Meco Man implement _sys_tmpnam()
*/
#include <rt_sys.h>
#include <rtthread.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <compiler_private.h>
#ifdef RT_USING_POSIX_STDIO
#include <posix/stdio.h>
#endif /* RT_USING_POSIX_STDIO */
#define DBG_TAG "armlibc.syscalls"
#define DBG_LVL DBG_INFO
#include <rtdbg.h>
#ifdef __clang__
__asm(".global __use_no_semihosting\n\t");
#else
#pragma import(__use_no_semihosting_swi)
#endif
/* Standard IO device handles. */
#define STDIN 0
#define STDOUT 1
#define STDERR 2
/* Standard IO device name defines. */
const char __stdin_name[] = "STDIN";
const char __stdout_name[] = "STDOUT";
const char __stderr_name[] = "STDERR";
/**
* required by fopen() and freopen().
*
* @param name - file name with path.
* @param openmode - a bitmap hose bits mostly correspond directly to
* the ISO mode specification.
* @return -1 if an error occurs.
*/
FILEHANDLE _sys_open(const char *name, int openmode)
{
#ifdef DFS_USING_POSIX
int fd;
int mode = O_RDONLY;
#endif /* DFS_USING_POSIX */
/* Register standard Input Output devices. */
if (strcmp(name, __stdin_name) == 0)
return (STDIN);
if (strcmp(name, __stdout_name) == 0)
return (STDOUT);
if (strcmp(name, __stderr_name) == 0)
return (STDERR);
#ifndef DFS_USING_POSIX
LOG_W("%s: %s", __func__, _WARNING_WITHOUT_FS);
return -1; /* error */
#else
/* Correct openmode from fopen to open */
if (openmode & OPEN_PLUS)
{
if (openmode & OPEN_W)
{
mode |= (O_RDWR | O_TRUNC | O_CREAT);
}
else if (openmode & OPEN_A)
{
mode |= (O_RDWR | O_APPEND | O_CREAT);
}
else
mode |= O_RDWR;
}
else
{
if (openmode & OPEN_W)
{
mode |= (O_WRONLY | O_TRUNC | O_CREAT);
}
else if (openmode & OPEN_A)
{
mode |= (O_WRONLY | O_APPEND | O_CREAT);
}
}
fd = open(name, mode, 0);
if (fd < 0)
return -1; /* error */
else
return fd;
#endif /* DFS_USING_POSIX */
}
int _sys_close(FILEHANDLE fh)
{
#ifdef DFS_USING_POSIX
if (fh <= STDERR)
return 0; /* error */
return close(fh);
#else
LOG_W("%s: %s", __func__, _WARNING_WITHOUT_FS);
return 0; /* error */
#endif /* DFS_USING_POSIX */
}
/*
* Read from a file. Can return:
* - zero if the read was completely successful
* - the number of bytes _not_ read, if the read was partially successful
* - the number of bytes not read, plus the top bit set (0x80000000), if
* the read was partially successful due to end of file
* - -1 if some error other than EOF occurred
*
* It is also legal to signal EOF by returning no data but
* signalling no error (i.e. the top-bit-set mechanism need never
* be used).
*
* So if (for example) the user is trying to read 8 bytes at a time
* from a file in which only 5 remain, this routine can do three
* equally valid things:
*
* - it can return 0x80000003 (3 bytes not read due to EOF)
* - OR it can return 3 (3 bytes not read), and then return
* 0x80000008 (8 bytes not read due to EOF) on the next attempt
* - OR it can return 3 (3 bytes not read), and then return
* 8 (8 bytes not read, meaning 0 read, meaning EOF) on the next
* attempt
*
* `mode' exists for historical reasons and must be ignored.
*/
int _sys_read(FILEHANDLE fh, unsigned char *buf, unsigned len, int mode)
{
#ifdef DFS_USING_POSIX
int size;
if (fh == STDIN)
{
#ifdef RT_USING_POSIX_STDIO
if (rt_posix_stdio_get_console() < 0)
{
LOG_W("Do not invoke standard output before initializing Compiler");
return 0; /* error, but keep going */
}
size = read(STDIN_FILENO, buf, len);
return len - size; /* success */
#else
LOG_W("%s: %s", __func__, _WARNING_WITHOUT_STDIO);
return 0; /* error */
#endif /* RT_USING_POSIX_STDIO */
}
else if (fh == STDOUT || fh == STDERR)
{
return -1; /* 100% error */
}
else
{
size = read(fh, buf, len);
if (size >= 0)
{
return len - size; /* success */
}
else
{
return 0; /* error */
}
}
#else
LOG_W("%s: %s", __func__, _WARNING_WITHOUT_FS);
return 0; /* error */
#endif /* DFS_USING_POSIX */
}
/*
* Write to a file. Returns 0 on success, negative on error, and
* the number of characters _not_ written on partial success.
* `mode' exists for historical reasons and must be ignored.
* The return value is either:
* A positive number representing the number of characters not written
* (so any nonzero return value denotes a failure of some sort).
* A negative number indicating an error.
*/
int _sys_write(FILEHANDLE fh, const unsigned char *buf, unsigned len, int mode)
{
#ifdef DFS_USING_POSIX
int size;
#endif /* DFS_USING_POSIX */
if (fh == STDOUT || fh == STDERR)
{
#if defined(RT_USING_CONSOLE) && defined(RT_USING_DEVICE)
rt_device_t console;
console = rt_console_get_device();
if (console)
{
rt_device_write(console, -1, buf, len);
}
return 0; /* success */
#else
return 0; /* error */
#endif /* defined(RT_USING_CONSOLE) && defined(RT_USING_DEVICE) */
}
else if (fh == STDIN)
{
return -1; /* 100% error */
}
else
{
#ifdef DFS_USING_POSIX
size = write(fh, buf, len);
if (size >= 0)
{
/*
fflush doesn't have a good solution in Keil-MDK,
so it has to sync/flush when for each writen.
*/
fsync(fh);
return len - size; /* success */
}
else
{
return 0; /* error */
}
#else
LOG_W("%s: %s", __func__, _WARNING_WITHOUT_FS);
return 0; /* error */
#endif /* DFS_USING_POSIX */
}
}
/*
* Flush any OS buffers associated with fh, ensuring that the file
* is up to date on disk. Result is >=0 if OK, negative for an
* error.
* This function is deprecated. It is never called by any other library function,
* and you are not required to re-implement it if you are retargeting standard I/O (stdio).
*/
int _sys_ensure(FILEHANDLE fh)
{
#ifdef DFS_USING_POSIX
return fsync(fh);
#else
LOG_W("%s: %s", __func__, _WARNING_WITHOUT_FS);
return 0; /* error */
#endif /* DFS_USING_POSIX */
}
/*
* Move the file position to a given offset from the file start.
* Returns >=0 on success, <0 on failure.
*/
int _sys_seek(FILEHANDLE fh, long pos)
{
#ifdef DFS_USING_POSIX
if (fh < STDERR)
return 0; /* error */
/* position is relative to the start of file fh */
return lseek(fh, pos, 0);
#else
LOG_W("%s: %s", __func__, _WARNING_WITHOUT_FS);
return 0; /* error */
#endif /* DFS_USING_POSIX */
}
/**
* used by tmpnam() or tmpfile()
*/
#if __ARMCC_VERSION >= 6190000
void _sys_tmpnam(char *name, int fileno, unsigned maxlength)
{
rt_snprintf(name, maxlength, "tem%03d", fileno);
}
#else
int _sys_tmpnam(char *name, int fileno, unsigned maxlength)
{
rt_snprintf(name, maxlength, "tem%03d", fileno);
return 1;
}
#endif /* __ARMCC_VERSION >= 6190000 */
char *_sys_command_string(char *cmd, int len)
{
/* no support */
return RT_NULL;
}
源码下载
…\bsp\stm32\stm32f103-gizwits-gokitv21\project.uvproj
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-764619.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-764619.html
RT-Thread STM32 GoKit V2.1 开发板BSP说明 源码下载文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-764619.html
维护人:
- 华为奋斗者精神, 邮箱:1992152446@qq.com
到了这里,关于RT-Thread STM32 GoKit V2.1 开发板BSP说明的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!