第3章:App UI设计
3.1:UI设计的相关概念
3.3:布局管理器
3.4:常用APP UI界面设计
3.1:UI设计的相关概念
View
View类在Android中可以理解为视图。它占据屏幕上的一个矩形区域,负责提供控件绘制和事件处理的方法。如果把Android界面比喻成窗户,那么每块玻璃都是一个view,View类是所有UI控件。

View类位于android.view包中;文本框控件TextView是View类的子类,位于android.widget包中。
在Android中,View类及其子类的相关属性,既可以在XML布局文件中进行设置,也可以通过成员方法在Java代码中动态设置。
View类支持的常用XML属性及对应的方法
| XMA属性 |
方法 |
描述 |
| android:background |
setBackgroundResource(int) |
设置背景,其属性值为Drawable资源或者颜色值 |
| android:clickable |
setClickable(boolean) |
设置是否响应单击事件,其属性值为boolean型的 true或者false |
| android:clevation |
setElevation(float) |
Android API21新添加的,用于设置z轴深度,其 属性值为带单位的有效浮点数 |
| androidid |
setId(int) |
设置控件的唯一标识符ID,可以通过 findViewByld()方法获取 |
| android:longChckable |
setLongClickable(boolean) |
设置是否响应长单击事件,其属性值为boolean型 的true或者false |
| androidminHeight |
setMinimumHeight(int) |
设置最小高度,其属性值为带单位的整数 |
| android:minWidth |
setMinimumWidth(int) |
设置最小宽度,其属性值为带单位的整数 |
| android:onClick |
设置单击事件触发的方法 |
|
| android:padding |
setPaddingRelative(int,int,int,int) |
设置4个边的内边距 |
| android:paddingBottom |
setPaddingRelative(int,int,int,int) |
设置底边的内边距 |
| android:paddingEnd |
setPaddingRelative(int,int,int,int) |
设置右边的内边距 |
| android:paddingLeft |
setPadding(int,int,int,int) |
设置左边的内边距 |
| android:paddingRight |
setPadding(int,int,int,int) |
设置右边的内边距 |
| android:paddingStart |
setPaddingRelative(int,int,int,int) |
设置左边的内边距 |
| android:paddingTop |
setPaddingRelative(int,int,int) |
设置顶边的内边距 |
| android:visibility |
setVisibility(int) |
设置View的可见性 |
ViewGroup
ViewGroup在Android中代表容器。如果还用窗户来比喻的话,ViewGroup就相当于窗户框,用于控制玻璃的安放。ViewGroup类继承自View类,它是View类的扩展,是用来容纳其他控件的容器,但是由于ViewGroup是一个抽象类,所以在实际应用中通常是使用ViewGroup的子类来作为容器。

ViewGroup控制其子控件的分布时(例如,设置子控件的内边距、宽度和高度等),还经常依赖于ViewGroup.LayoutParams和ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams两个内部类,下面分别进行介绍。
◆【ViewGroup.LayoutParams】
ViewGroup.LayoutParams类封装了布局的位置、高和宽等信息。它支持 android:layout_height 和 android:layout_width 两个XML属性,它们的属性值可以使用精确的数值,也可以使用FILL PARENT(表示与父容器相同)、MATCH PARENT(表示与父容器相同,需要API8或以上版本才支持)或者WRAP CONTENT(表示包裹其自身的内容)指定。
◆【ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams】
ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams类用于控制其子控件的外边距。
支持的常用XML属性
| XML属性 |
描述 |
| android:layout_marginBottom |
设置底外边距 |
| android:layout_marginEnd |
该属性为Android 4.2新增加的属性,设置右外边距 |
| android:layout_marginLeft |
设置左外边距 |
| android:layout_marginRight |
设置右外边距 |
| android:layout_marginStart |
该属性为Android 4.2新增加的属性,用于设置左外边距 |
| android:layout_marginTop |
设置顶外边距 |
在Android中,所有UI界面都是由View类和ViewGroup类及其子类组合而成的。在ViewGroup 类中,除了可以包含普通的View类外,还可以再次包含ViewGroup类。实际上,这使用了Composite (组合)设计模式。
View类和ViewGroup类的层次结构

3.2:设计UI界面

使用XML布局文件设计UI界面
Android提供了一种非常简单、方便的方法用于设计UI界面。该方法采用XML文件来进行界面布局,从而将布局界面的代码和逻辑控制的Java代码分离开来,使程序的结构更加清晰、明了。
使用XML布局文件设计UI界面可以分为以下两个关键步骤:
(1) 在Android应用的res/layout目录下创建XML布局文件,该布局文件的名称可以采用任何符合Java命名规则的文件名。
(2) 在Activity中使用以下Java代码显示XML文件中布局的内容:
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);在上面的代码中, activity_main 是XML布局文件的文件名。
通过上面的步骤就可以轻松实现布局并显示UI界面的功能。下面通过一个例子来演示如何使用XML布局文件设计UI界面。
例:游戏的进入界面
(1) 在Android Studio中打开一个已经存在的项目,然后在主菜单中选择【File→New→New Project】菜单项,将打开新建模块对话框:


(2) 单击Next按钮,将进入到配置新模块对话框,在该对话框中指定应用名称、模块名称、包名和最小SDK版本等信息:

(3) 单击Next按钮,将进入到选择创建Activity类型对话框,在该对话框中,将列出一些用于创建Activity的模板,这里我们选择创建一个空白的Activity,即Empty Activity。然后单击Next按钮,在进入的自定义Activity对话框中,设置自动创建的Activity的类名和布局文件名称,这里采用默认设置,单击Finish按钮完成Project的创建。
(4) 在源码中,把名称为bg.png的背景图片复制到mipmap-xhdpi目录中:

(5) 修改res/values节点下的strings.xml文件,并且在该文件中添加一个用于定义开始按钮内容的常量,名称为start,内容为“开始游戏”。修改后的代码如下:
<resources>
<string name="app_name">开始游戏</string>
</resources>
说明:strings.xml文件用于定义程序中应用的字符串常量。其中,每一个<string>子元素都可以定义一个字符串常量,常量名称由name属性指定,常量内容写在起始标<string>和结束标记</string>记之间。
(6) 修改新建 Project 的 res/ layout 节点下的布局文件 activity main.xml,将默认创建的布局管理器修改为帧布局管理器FrameLayout,并且为其设置背景,然后修改默认添加的TextView控件,用于实现在窗体的正中间位置显示“开始游戏”按钮。修改后的代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@mipmap/bg"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:text="@string/string"
android:textColor="#115572"
android:textSize="18sp" />
</FrameLayout>
说明:在布局文件 activity main 中,通过设置布局管理器的 android:background 属性,可以为窗体设置背景图片;使用 android:layout_gravity=“center”可以让该控件在帧布局管理器中居中显示;android:textSize 属性用于设置字体大小:androidtextColor属性用于设置文字的颜色。
(7) 在主活动中,也就是MainActivity中,应用setContentView()方法指定活动应用的布局文件。在应用Android Studio 创建Android应用时,Android Studio会自动在主活动的onCreate()方法中添加以下代码指定使用的布局文件,不需要我们手动添加。
setContentView(R.layout, activity_main);说明:由于目前还没有学习Android中的UI控件,所以这里的“开始游戏”按钮先使用文本框控件代替。在实际应用开发时,通常采用按钮控件实现。
(8) 运行本实例,将显示如图所示的运行结果。

在Java代码中设计UI界面
在Android中,支持像Java Swing那样完全通过代码设计UI界面。也就是所有的UI控件都通过new关键字创建出来,然后将这些UI控件添加到布局管理器中,从而实现用户UI界面。
在代码中设计UI界面可以分为以下3个关键步骤:
(1) 创建布局管理器,例如,帧布局管理器、表格布局管理器、线性布局管理器、相对布局管理器和网格布局管理器等,并且设置布局管理器的属性。例如,为布局管理器设置背景图片等。
(2) 创建具体的控件,例如,TextView、ImageView、EditText和Button等任何Android提供的控件,并且设置控件的布局和属性。
(3) 将创建的控件添加到布局管理器中。
下面我们将通过一个具体的例子来演示如何使用Java代码设计UI界面。
例:游戏的进入界面
在Android Studio中创建Module【File→New→New Module】




实现本实例的具体步骤如下:
(1) 在新创建的Module中,打开jMainActivity.java文件,然后将默认生成的下面这行代码删除。
//setContentView(R.layout, activity_main);
(2) 在MainActivity的onCreate()方法的上方声明一个TextView控件text1
public TextView text1;
说明:如果提示报错,在输入代码public TextView后,按下快捷键【Ctrl+Enter】单击【Import class】导入TextView类。
(3) 在MainActivity的onCreate()方法中,创建一个帧布局管理器,并为该布局管理器设置背景,关键代码如下:
FrameLayout frameLayout = new FrameLayout(this);//初始化一个帧布局管理器对象
frameLayout.setBackgroundResource(R.mipmap.bg);//设置背景图片
setContentView(frameLayout);//设置在Activity中显示frameLayout
(4) 实例化textl控件,设置其显示文字、文字大小、颜色和布局,具体代码如下:
text1 = new TextView(this);//初始化本控件对象
text1.setText("开始游戏");//设置显示文字
text1.setTextSize(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_SP, 18);//设置文字大小,单位为SP(缩放像素)
text1.setTextColor(Color.rgb(17, 85, 114));//设置文字颜色
FrameLayout.LayoutParams params = new FrameLayout.LayoutParams( //初始化布局参数对象
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT
);
params.gravity = Gravity.CENTER;//设置居中显示
text1.setLayoutParams(params);//设置布局参数
说明:在通过setfextSize()方法设置TextView的文字大小时,可以指定使用的单位,在上面的代码中, int型的常量【TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_SP】表示单位是可细放像素,如果要设置单位是像素,可以使用常量【TypedValve.COMPLEX_UNIT_PX】,这些常量可以在 Android 官方提供的API中找到。
(5) 实现单击“开始游戏”按钮时,显示询问对话框。具体方法是:为textl控件添加单击事件监听器,并在重写的onClick()方法中,显示询问对话框,关键代码如下:
text1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {//为text1按钮添加单击事件监听器
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {//重写单击方法
new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this)//初始化对话提示框对象
.setTitle("系统提示")
.setMessage("游戏有风险,进入需谨慎,真的要进入吗?")
.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {//确定按钮事件
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Log.i("桌面台球", "进入游戏");//输出日志
}
})
.setNegativeButton("退出", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {//取消按钮事件
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Log.i("桌面台球", "退出游戏");//输出日志
finish();//结束游戏关闭对话框
}
})
.show();//显示对话框
}
});

(6) 将文本框控件textl添加到布局管理器中,具体代码如下:
frameLayout.addView(text1);//将text1添加到布局管理器中
(7) 运行本实例,将显示如图所示的运行结果:

使用XML和Java代码混合设计UI界面
完全通过XML布局文件设计UI界面,实现比较方便快捷,但是有失灵活;而完全通过Java 代码设计UI界面,虽然比较灵活,但是开发过程比较烦琐。鉴于这两种方法的优缺点,下面来看另一种设计UI界面的方法,即使用XML和Java代码混合设计UI界面。
使用XML和Java代码混合设计UI界面,习惯上把变化较小、行为比较固定的控件放在XML 布局文件中,把变化较多、行为控制比较复杂的控件交给Java代码来管理。下面通过一个具体的实例来演示如何使用XML和Java代码混合设计UI界面。
例:QQ相册照片列表
在Android Studio中创建Module,名称为“QQ Album Photo List”。实现本实例的具体步骤如下:
(1) 修改新建 Module 的 res/layout 节点下的布局文件 activity_main.xml,将默认添加的相对布局管理器修改为网格布局管理器,并将默认创建的器设置androidid属性以及按水平方向排列,再设置该网格布局管理器包括3行4列。修改后的代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:columnCount="4"
android:rowCount="3"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
</GridLayout>(2) 在MainActivity中,声明img和imagePath两个成员变量,其中,imgs是一个ImageView 类型的一维数组,用于保存ImageView控件;imagePaths是一个it型的一维数组,用于保存要访问的图片资源。关键代码如下:
private ImageView[] imgs = new ImageView[12];//声明并初始化图像控件数组
private int[] imagePaths = new int[]{//声明并初始化图像数组
R.mipmap.img1, R.mipmap.img2, R.mipmap.img3, R.mipmap.img4,
R.mipmap.img5, R.mipmap.img6, R.mipmap.img7, R.mipmap.img8,
R.mipmap.img9, R.mipmap.img10, R.mipmap.img11, R.mipmap.img12
};
说明:请自行在res/mipmap-xhdpi中存入相关图片

(3) 在MainActivity的onCreate()方法中,首先获取在XML布局文件中创建的网格布局管理器,然后通过一个for循环创建12个显示图片的ImageView控件,并将其添加到布局管理器中。关键代码如下:
GridLayout layout = (GridLayout) findViewById(R.id.layout);//根据ID名称获取网格布局管理器对象
for (int i = 0; i < imagePaths.length; i++) {
imgs[i] = new ImageView(MainActivity.this);//初始化赋值图片控件并
imgs[i].setImageResource(imagePaths[i]);//为控件指定要显示的图片
imgs[i].setPadding(2, 2, 2, 2);//设置图片控件内边距
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(116, 68);//初始化控件参数对象,设置宽高
imgs[i].setLayoutParams(params);//为图片控件设置布局参数
layout.addView(imgs[i]);//将图片控件添加到布局管理器中
}
(4) 运行本实例,将显示如图所示的运行结果

开发自定义的View类
一般情况下,开发Android应用程序的UI界面,都不直接使用View类和ViewGroup类,而是使用这两个类的子类。例如,要显示一个图片,就可以使用View类的子类ImageView。虽然Android提供了很多继承了View类的UI控件,但是在实际开发时,还会出现不足以满足程序需要的情况。这时,我们就可以通过继承View类来开发自己的控件。开发自定义的View控件大致分为以下3个步骤。
(1) 创建一个继承android.view.View类的Java类,并且重写构造方法。注意,在自定义的View类中,至少需要重写一个构造方法。
(2) 根据需要重写其他的方法,被重写的方法可以通过下面的方法找到。
在代码中单击鼠标右键,在弹出的快捷菜单中选择“Generate”菜单项,将打开快捷菜单,在该菜单中选择“Override Methods”菜单项,将打开选择覆盖或实现的方法对话框,在该对话框的列表中显示出了可以被重写的方法。我们只需要选中要重写方法前面的复选框,并单击“确定”按钮,Android Studio将自动重写指定的方法。通常情况下,不需要重写全部的方法。



(3) 在项目的活动中,创建并实例化自定义View类,然后将其添加到布局管理器中。下面通过一个实例演示如何开发自定义的View类。
例:跟随手指的小兔子
在Android Studio中创建Module,名称为“Follow Finger Bunny”。实现本实例的具体步骤如下:
(1) 修改新建 Module 的 res/ layout 节点下的布局文件 activity_main.xml,将默认创建的布局管理器修改为帧布局管理器FrameLayout,并且设置其背景和ID属性,然后将TextView控件删除。修改后的代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/mylayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@mipmap/bg"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
</FrameLayout>(2) 在com.mingrisoft包上单击右键,选择“View”→“Java Class”选项,新建一个名称为RabbitView的Java类,该类继承自android.view.View类,重写带一个参数Context的构造方法和onDraw()方法。其中,在构造方法中设置兔子的默认显示位置,在onDraw()方法中根据图片绘制小兔子。


RabbitView类的关键代码如下:
package com.so.followfingerbunny;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.view.View;
public class RabbitView extends View {//继承View类
public float bitmapX;//声明对象,兔子显示的X坐标
public float bitmapY;//声明对象,兔子显示的Y坐标
public RabbitView(Context context) {//重写父类带context的构造方法
super(context);
bitmapX = 210;//初始化兔子X坐标
bitmapY = 130;//初始化兔子Y坐标
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {//重写父类onDraw方法
super.onDraw(canvas);
Paint point = new Paint();//初始化画笔对象
//根据提供的图片初始化位图对象
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(this.getResources(), R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, bitmapX, bitmapY, point);
if (!bitmap.isRecycled()) {//如果图片没有被回收
bitmap.recycle();//手动回收释放图片占用
}
}
}

(3) 在MainActivity的onCreate()方法中,首先获取帧布局管理器,并实例化小兔子对象rabbit,然后为rabbit添加触摸事件监听器,在重写的触摸事件中设置rabbit的显示位置,并重绘rabbit控件,最后将rabbit添加到布局管理器中,关键代码如下:
FrameLayout frameLayout = findViewById(R.id.mylayout);//根据ID获取帧布局管理器对象
RabbitView rabbit = new RabbitView(this);//初始化一个兔子控件对象
rabbit.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() { //为小兔子添加触摸事件
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
rabbit.bitmapX = event.getX();//将鼠标触摸的X位置设置为小兔子的X位置
rabbit.bitmapY = event.getY();//将鼠标触摸的Y位置设置为小兔子的Y位置
rabbit.invalidate();//重新绘制兔子控件
return true;
}
});
frameLayout.addView(rabbit);//将小兔子控件添加到布局管理器中
(4) 运行本实例,将显示如图所示的运行结果。当用手指在屏幕上拖动时,小兔子将跟随手指的拖动轨迹移动。

3.3:布局管理器
在Android中,每个控件在窗体中都有具体的位置和大小,在窗体中摆放各种控件时,很难进行判断。不过,使用Android布局管理器可以很方便地控制各控件的位置和大小。Android提供了以下5种布局管理器:
- ◆ 相对布局管理器(RelativeLayout):通过相对定位的方式来控制控件的摆放位置。
- ◆ 线性布局管理器(LinearLayout):是指在垂直或水平方向上依次摆放控件。
- ◆ 帧布局管理器(FrameLayout):没有任何定位方式,默认情况下,所有的控件都会摆放在容器的左上角,逐个覆盖。
- ◆ 表格布局管理器(TableLayout):使用表格的方式按行、列来摆放控件。
- ◆ 绝对布局管理器(AbsoluteLayout):通过绝对定位(x、y坐标)的方式来控制控件的摆放位置。
其中,绝对布局在Android 2.0中被标记为已过期,不过可以使用帧布局或相对布局替代。另外,在Android 4.0版本以后,又提供了一个新的布局管理器,网格布局管理器(GridLayout)。通过它可以实现跨行或跨列摆放控件。
Android提供的布局管理器均直接或间接继承自ViewGroup类,如图所示。因此,所有的布局管理器都可以作为容器使用,我们可以向布局管理器中添加多个UI控件。当然,也可以将一个或多个布局管理器嵌套到其他的布局管理器中。

相对布局管理器
相对布局管理器是通过相对定位的方式让控件出现在布局的任何位置的。例如,如图所示的界面就是采用相对布局管理器来进行布局的,其中先放置控件A,然后放置控件B,让其位于控件A的下方,再放置控件C,让其位于控件A的下方,并且位于控件B的右侧。

在Android中,可以在XML布局文件中定义相对布局管理器,也可以使用Java代码来创建。推荐使用在XML布局文件中定义相对布局管理器。在XML布局文件中,定义相对布局管理器可以使用:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</RelativeLayout>在上面的语法中,<RelativeLayout>为起始标记,</RelativeLayout>为结束标记。在起始标记中的 xmlns:android 为设置XML命名空间的属性,其属性值为固定写法。
下面哪里在Android中,无论是创建哪一种布局管理器都有两种方法:一种是在XML布局文件中定义,另一种是使用Java代码来创建。推荐使用的是在XML布局文件中定义,所以在本书中将只介绍在XML布局文件中创建这一种方法。
RelativeLayout支持的常用XML属性
| XML属性 |
描述 |
| android:gravity |
用于设置布局管理器中各子控件的对齐方式 |
| android:ignoreGravity |
用于指定哪个控件不受Gravity属性的影响 |
在相对布局管理器中,只有上面介绍的两个属性是不够的,为了更好地控制该布局管理器中各子控件的布局分布,RelativeLayout提供了一个内部类 RelativeLayout.LayoutParams,通过该类提供的大量XML属性,可以很好地控制相对布局管理器中各控件的分布方式。
RelativelLayout. LayoutParams 支持的常用XML属性
| XML属性 |
描述 |
| android:layout_above |
其属性值为其他UI控件的ID属性,用于指定该控件位于哪个控件的上方 |
| android:layout_alignBottom |
其属性值为其他UI控件的ID属性,用于指定该控件与哪个控件的下边界对齐 |
| android:layout_alignLeft |
其属性值为其他UI控件的ID属性,用于指定该控件与哪个控件的左边界对齐 |
| android:layout_alignParentBottom |
其属性值为boolean值,用于指定该控件是否与布局管理器底端对齐 |
| android:layout_alignParentLeft |
其属性值为boolean值,用于指定该控件是否与布局管理器左边对齐 |
| android:layout_alignParentRight |
其属性值为boolean值,用于指定该控件是否与布局管理器右边对齐 |
| android:layout_alignParentTop |
其属性值为boolean值,用于指定该控件是否与布局管理器顶端对齐 |
| android:layout_alignRight |
其属性值为其他UI控件的ID属性,用于指定该控件与哪个控件的右边界对齐 |
| android:layout_alignTop |
其属性值为其他UI控件的ID属性,用于指定该控件与哪个控件的上边界对齐 |
| android layout_below |
其属性值为其他UI控件的ID属性,用于指定该控件位于哪个控件的下方 |
| android:layout_centerHorizontal |
其属性值为boolean值,用于指定该控件是否位于布局管理器水平居中的位置 |
| android:layout_centerInParent |
其属性值为boolean值,用于指定该控件是否位于布局管理器的中央位置 |
| android:layout_centerVertical |
其属性值为boolean值,用于指定该控件是否位于布局管理器垂直居中的位置 |
| android:layout_toLeftOf |
其属性值为其他UI控件的ID属性,用于指定该控件位于哪个控件的左侧 |
| android:layout_toRightOf |
其属性值为其他UI控件的ID属性,用于指定该控件位于哪个控件的右侧 |
例:软件更新提示界面
在Android Studio中创建Module,名称为“Software Update Tips”。实现本实例的具体步骤如下:
(1) 修改新建 Module 的 res/layout 目录下的布局文件 activity main.xml,把背景图片复制到mipmap-xhdpi 目录中,将默认添加的布局管理器修改为相对布局管理器(RelativeLayout),然后为其设置背景,再设置默认添加的文本框(TextView)居中显示,并且为其设置ID和要显示的文字,最后在该布局管理器中,添加两个Button,并设置它们的显示位置及对齐方式。修改后的代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@mipmap/bg"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<!--添加一个居中显示的文本视图textView1-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="发现有Widget的新版本,您想现在就安装吗?" />
<!--添加一个按钮button2,让按钮与textView1的右边界对齐-->
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textView1"
android:text="以后再说" />
<!--添加一个按钮button1,让按钮与button2的右边界对齐-->
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/button2"
android:text="现在更新" />
</RelativeLayout>说明:在上面的代码中,将提示文本控件textViewl设置为在屏幕中央显示,然后设置“以后再说”按钮 button1 在 textView1 的下方居右边界对齐,最后设置“现在更新”按钮button2在“以后再说”按钮的左侧显示。
(2) 运行本实例,将显示如图所示的运行结果。

线性布局管理器
线性布局管理器是将放入其中的控件按照垂直或水平方向来布局,也就是控制放入其中的控件横向排列或纵向排列。其中,纵向排列的称为垂直线性布局管理器;横向排列的称为水平线性布局管理器。在垂直线性布局管理器中,每一行中只能放一个控件,面在水平线性布局管理器中,每一列中只能放一个控件。另外Android的线性布局管理器中的控件不会换行,当控件一个挨着一个排列到窗体的边缘后,剩下的控件将不会被显示出来。


说明:在线性布局管理器中,排列方式由 android:orientation 属性来控制,对齐方式由 android:gravity 属性来控制。
在XML布局文件中定义线性布局管理器,需要使用如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</RelativeLayout>LinearLayout支持的常用XML属性
| XML属性 |
描 述 |
| android:orientation |
用于设置布局管理器内控件的排列方式,其可选值为 horizontal 和 vertical,默认值为 vertical。其中,horizontal 表示水平排列,vertical 表示垂直排列 |
| android:gravity |
android:gravity 属性用于设置布局管理器内控件的显示位置,其可选值包括 top、bottom、left、right、center_vertical、fill_vertical、center_horizontal、fill_horizontal、center、fill、clip_vertical 和 clip_horizontal。这些属性值也可以同时指定,各属性值之间用竖线隔开(竖线前后不能有空格)。例如,要指定控件靠右下角对齐,可以使用属性值 right|bottom |
| android:layout_width |
用于设置该控件的基本宽度,其可选值有 fill_parent、match_parent 和 wrap_content,其中 fill_parent 表示该控件的宽度与父容器的宽度相同;match_parent 与 fill_parent 的作用完全相同,从Android 2.2开始推荐使用;wrap_content 表示该控件的宽度恰好能包裹它的内容 |
| android:layout_height |
用于设置该控件的基本高度,其可选值有 fill_parent、match_parent 和 wrap_content,其中 fill_parent 表示该控件的高度与父容器的高度相同;match_parent 与 fill_parent 的作用完全相同,从Android 2.2开始推荐使用;wrap_content 表示该控件的高度恰好能包裹它的内容 |
| android:id |
用于为当前布局管理器指定一个ID属性,在Java代码中可以应用该属性单独引用这个布局管理器。为布局管理器指定ID属性后,在R.java文件中,会自动派生一个对应的属性,在Java代码中,可以通过 findViewById() 方法来获取它 |
| android:background |
用于为该控件设置背景。可以是背景图片,也可以是背景颜色。为控件指定背景 图片时可以将准备好的背景图片复制到 :drawable 目录下,然后使用下面的代码 进行设置:android:background="@drawable/background"。如果想指定背景颜色,可以使用颜色值,例如,要想指定背景颜色为白色,可以使用下面的代码:android:background="#FFFFFFFF" |
说明:android:layout_width 和 android:layout_height 属性是 ViewGroup.LayoutParams 所支持的XML属性,对于其他的布局管理器同样适用。
注意:
在水平线性布局管理器中,子控件的 android:layout_width 属性值通常不设置为 match_parent 或 fill_parent 。如果这样设置,在该布局管理器中一行将只能显示一个控件;
在垂直线性布局管理器中,android:layout_height 属性值通常不设置为 match_parent 或 fill_parent。如果这样设置,在该布局管理器中一列将只能显示一个控件。
在LinearLayout中放置的子控件,还经常用到两个属性。
LinearLayout子控件的常用XML属性及描述
| XM.属性 |
描 述 |
| android:layout_gravity |
用于设置控件在其父容器中的位置。它的属性值与 android:gravity 属性相同,也是 top、bottom、left、right、center_vertical、fill_vertical、center_horizontal、fill_horizontal、center、fill、clip_vertical 和 clip_horizontal。这些属性值也可以同时指定,各属性值之间用竖线隔开,但竖线前后一定不能有空格 |
| android:layout_weight |
用于设置控件所占的权重,即用于设置控件占父容器剩余空间的比例。该属性的默认值为0,表示需要显示多大的视图就占据多大的屏幕空间。当设置一个高于零的值时,则将父容器的剩余空间分割,分割的大小取决于每个控件的 layout_weight 属性值。例如,在一个 320*480 的屏幕中,放置一个水平的线性布局管理器,并且在该布局管理器中放置两个控件,并且这两个控件的android:layout_weight 属性值都设置为1,那么,每个控件将分配到父容器的1/2的剩余空间,如图所示 |

说明:在线性布局管理器的定义中,使用 android:layout_gravity 属性设置放入其中的控件的摆放位置不起作用,要想实现这一功能,需要使用 android:gravity 属性。
下面编写一个在程序中使用线性布局的实例。
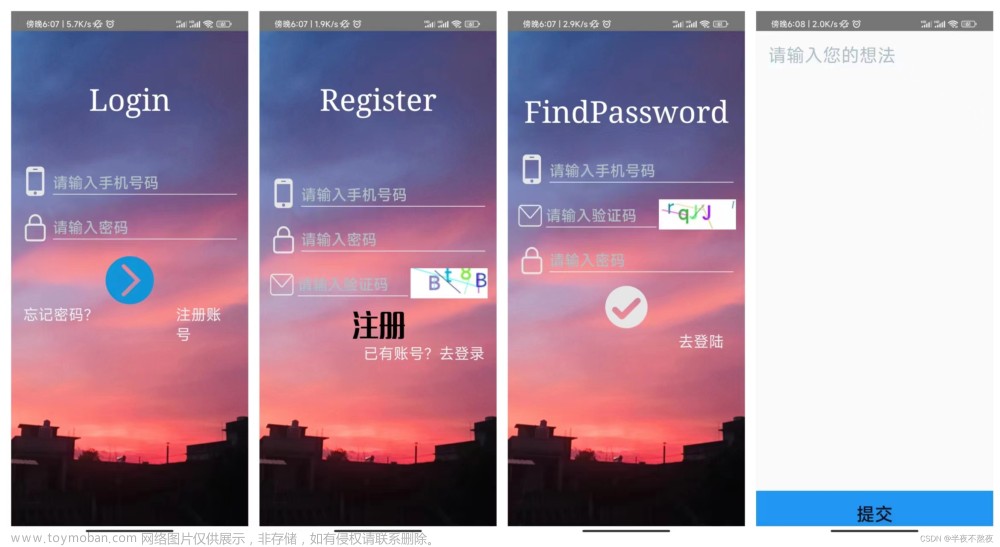
例:登录微信界面
在Android Studio中创建Module,名称为 WeChat Login。实现本实例的具体步骤如下:
(1) 修改新建 Module 的 res/layout 目录下的布局文件 activity_main.xml,将默认添加的布局管理器修改为线性布局管理器 LinearLayout,然后将其设置为垂直线性布局管理器。
(2) 将名称为 zhanghao.png 和 mima.png 的图片复制到 mipmap-xxhdpi 目录中,并且在线性布局管理器中添加两个 EditText 控件,用于输入账号和密码,然后添加一个“登录”按钮,并且在“登录”按钮下面再添加一个TextView,用来填写登录遇到的问题,关键代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawableLeft="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:hint="QQ号/微信号/Email"
android:paddingBottom="20dp" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawableLeft="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:hint="密码"
android:paddingBottom="20dp" />
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FF009688"
android:text="登录"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:paddingTop="20dp"
android:text="登录遇到问题?" />
</LinearLayout>(3) 改变默认的主题颜色为深色 ActionBar 主题,打开 AndroidMainfest.xml 文件,将其中的<application> 标记的 android:theme 属性值 @style/AppTheme 修改为 @style/Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar,修改后的 android:theme 属性代码如下:
android:theme="@style/Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar"
(4) 运行本实例,将显示的运行结果:

帧布局管理器
在帧布局管理器中,每加入一个控件都将创建一个空白的区域,通常称为一帧,默认情况下,这些帧都会被放置在屏幕的左上角,即帧布局是从屏幕的左上角(0,0)坐标点开始布局。多个控件层叠排序,后面的控件覆盖前面的控件,如图所示。

在XML布局文件中定义帧布局管理器可以使用:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</FrameLayout>FrameLayout支持的常用XML属性
| XML属性 |
描述 |
| android:foreground |
设置该帧布局管理器的前景图像 |
| android:foregroundGravity |
定义绘制前景图像的Gravity属性,即前景图像显示的位置 |
例:居中显示层叠的正方形
在Android Studio中创建Module,名称为Frame Layout ,实现本实例的具体步骤如下:
(1) 修改新建 Module 的 res/layout 目录下的布局文件 activity_main.xml,将默认添加的布局代码删除,然后添加一个 FrameLayout 帧布局管理器,并且为其设置背景和前景图像,以及前景图像显示的位置,之后再将前景图像文件 mr.png 复制到 mipmap-hdpi 目录下,最后在该布局管理器中,添加3个居中显示的 TextView 控件,并且为其指定不同的颜色和大小,用于更好地体现层叠效果。修改后的代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:foreground="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:foregroundGravity="bottom|right"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<!--添加居中显示的【蓝色】背景的TextView,将显示在最下层-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="280dp"
android:layout_height="280dp"
android:background="#FF0000FF"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:text="蓝色背景的TextView"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF" />
<!--添加居中显示的【天蓝色】背景的TextView,将显示在最下层-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="230dp"
android:layout_height="230dp"
android:background="#FF0077FF"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:text="天蓝色背景的TextView"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF" />
<!--添加居中显示的【水蓝色】背景的TextView,将显示在最下层-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_width="180dp"
android:layout_height="180dp"
android:background="#FF00B4FF"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:text="水蓝色背景的TextView"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF" />
</FrameLayout>(2) 运行本实例,将显示如图所示的运行结果。

表格布局管理器
表格布局管理器与常见的表格类似,它以行、列的形式来管理放入其中的UI控件,如图所示。表格布局管理器使用每个在也可以被设置为伸展的状态,从而填充可利用的屏幕空间,还可以设置为强制收缩,直到表格匹配屏幕大小。

说明:如 果在表格布局中,直接向<TableLayout>中添加UI控件,那么这个控件将独占一行,在XML布局文件中定义表格布局管理器的基本语法格式如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</TableLayout>TableLayout继承了LinearLayout,因此它完全支持 LinearLayout 所支持的全部XML属性,此外,TableLayout 还支持如表所示的XML属性。
TableLayout支持的XML属性
| XML属性 |
描 述 |
| android:collapseColumns |
设置需要被隐藏的列的列序号(序号从0开始),多个列序号之间用逗号“,”分隔 |
| android:shrinkColumns |
设置允许被收缩的列的列序号(序号从0开始),多个列序号之间用逗号“,”分隔 |
| android:stretchColumns |
设置允许被拉伸的列的列序号(序号从0开始),多个列序号之间用逗号“,”分隔 |
下面编写一个在程序中使用表格布局的实例。
例:仿喜马拉雅的用户登录界面
在Android Studio中创建Module,名称为 Xmly Login 。实现本实例的具体步骤如下:
(1) 修改新建 Module 的 res/layout 目录下的布局文件 activity_main.xml,将默认添加的布局代码删除,然后添加一个 TableLayout 表格布局管理器,并且在该布局管理器中,添加一个背景图片,将需要的背景图片复制到 mipmap-mdpi 中,然后添加4个 TableRow 表格行,接下来在每个表格行中添加相关的图片控件,最后设置表格的第一列和第四列允许被拉伸。修改后的代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:stretchColumns="0,3"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<!--第一行-->
<TableRow
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingTop="200dp">
<TextView />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="账 号:"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="邮箱或者手机号" />
<TextView />
</TableRow>
<!--第二行-->
<TableRow
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingTop="20dp">
<TextView />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="密 码:"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="输入6~16位数字或字母" />
<TextView />
</TableRow>
<!--第三行-->
<TableRow
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="注 册" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="登 录" />
<TextView />
</TableRow>
<!--第四行-->
<TableRow
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingTop="20dp">
<TextView />
<TextView />
<TextView
android:gravity="right"
android:text="忘记密码?"
android:textColor="#FF4500" />
<TextView />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>说明:在本实例中,添加了6个<TextView>,并且设置对应列允许被拉伸,这是为了让登录相关控件在水平方向上居中显示而设置的。
(2) 运行本实例,将显示如图所示的运行结果。

网格布局管理器
网格布局管理器是在Android 4.0版本中提出的,使用 GridLayout 来表示。在网格布局管理器中,屏幕被虚拟的细线划分成行、列和单元格,每个单元格放置一个控件,并且这个控件也可以跨行或跨列摆放,如图所示。

说明:网格布局管理器与表格布局管理器有些类似,都可以以行、列的形式管理放入其中的控件,但是它们之间最大的不同就是网格布局管理器可以跨行显示控件,表格布局管理器则不能。
在XML布局文件中,定义网格布局管理器可以使用
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</GridLayout>GridLayout支持的常用XML属性
| XML属性 |
描 述 |
| android:columnCount |
用于指定网格的最大列数 |
| android:orientation |
用于当没有为放入其中的控件分配行和列时,指定其排列方式。其属性值为 horizontal表示水平排列;属性值为vertical表示垂直排列 |
| android:rowCount |
用于指定网格的最大行数 |
| android:useDefaultMargins |
用于指定是否使用默认的边距,其属性值设置为true时,表示使用;属性值为 false时,表示不使用 |
| android:alignmentMode |
用于指定该布局管理器采用的对齐模式,其属性值为alignBounds时,表示对齐 边界;值为alignMargins时,表示对齐边距,默认值为alignMargins |
| android:rowOrderPreserved |
用于设置行边界显示的顺序和行索引的顺序是否相同,其属性值为true,表示 相同;属性值为false,表示不相同 |
| android:columnOrderPreserved |
用于设置列边界显示的顺序和列索引的顺序是否相同,其属性值为true,表示 相同:属性值为false,表示不相同 |
为了控制网格布局管理器中各子控件的布局分布,网格布局管理器提供了GridLayout. LayoutParams 内部类,在该类中提供了如表所示的XML属性,用于控制网格布局管理器中各子控件的布局分布。
GridLayout. LayoutParams支持的常用XML属性
| XML属性 |
描述 |
| android:layout_column |
用于指定该子控件位于网格的第几列 |
| android:layout_columnSpan |
用于指定该子控件横向跨几列(索引从0开始) |
| android:layout_columnWeight |
用于指定该子控件在水平方向上的权重,即该控件分配水平剩余空间的比例 |
| android:layout_gravity |
用于指定该子控件采用什么方式占据该网格的空间,其可选值有top(放置在 顶部)、bottom(放置在底部)、left(放置在左侧)、right(放置在右侧)、 center_vertical(垂直居中)、fill_vertical(垂直填满)、center_horizontal(水 平居中)、fill_horizontal(水平填满)、center(放置在中间)、fill(填满)、 clip_vertical(垂直剪切)、clip_horizontal(水平剪切)、start(放置在开始位置)、 end(放置在结束位置) |
| android:layout_row |
用于指定该子控件位于网格的第几行(索引从0开始) |
| android:layout_rowSpan |
用于指定该子控件纵向跨几行 |
| android:layout_row Weight |
用于指定该子控件在垂直方向上的权重,即该控件分配垂直剩余空间的比例 |
说明:在网格布局管理器中,如果想让某个控件跨行或跨列,那么需要先通过 android: layout_columnSpan或者 android: layout_rowSpan设置跨越的行或列数,然后再设置其 layout_gravity 属性为fill,表示该控件填满跨越的行或者列。
例:QQ聊天信息列表界面
在Android Studio中创建Module,名称为 QQ Chat Message。实现本实例的具体步骤如下:
(1) 修改新建 Module 的 res/layout 目录下的布局文件 activity_main.xml,将默认添加的布局管理器修改为网格布局管理器,并且将默认添加的文本框控件删除,将需要的图片复制到 mipmap-mdpi 目录下,图片资源详情:

然后为该网格布局设置背景和列数。修改后的代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@mipmap/bg"
android:columnCount="6"
android:paddingLeft="16dp"
android:paddingTop="16dp"
android:paddingRight="16dp"
android:paddingBottom="16dp"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<!--(2) 添加第一行要显示的信息和头像,这里需要两个图像视图控件(ImageView),
其中第一个ImageView用于显示聊天信息,占4个单元格,从第二列开始,居右放置;
第二个ImageView用于显示头像,占一个单元格,位于第六列。具体代码如下:-->
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView1"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="1"
android:layout_columnSpan="4"
android:layout_gravity="end"
android:layout_marginRight="5dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
android:src="@mipmap/a1" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView2"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="5"
android:src="@mipmap/ioc2" />
<!--(3) 在步骤(2)添加的相对布局管理器中,头像ImageView控件的右侧添加
3个文本框控件,分别用于显示发布人、内容和时间,具体代码如下:-->
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView3"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_column="0"
android:src="@mipmap/ioc1" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView4"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
android:src="@mipmap/b1" />
</GridLayout>(4) 运行本实例,将显示如图所示的运行结果。

布局管理器的嵌套
在进行用户界面设计时,很多时候只通过一种布局管理器很难实现想要的界面效果,这时就需要将多种布局管理器混合使用,即布局管理器的嵌套。在实现布局管理器的嵌套时,只需要记住以下几点原则就可以了。
- ◆ 根布局管理器必须包含xmlns属性。
- ◆ 在一个布局文件中,最多只能有一个根布局管理器。如果想要使用多个布局管理器,就需要使用一个根布局管理器将它们括起来。
- ◆ 不能嵌套太深。如果嵌套太深,则会影响性能,主要会降低界面的加载速度。
例:微信朋友圈界面
在Android Studio中创建Module,名称为 WeChat Circle Of Friends。实现本实例的具体步骤如下:
(1) 修改新建 Module 的 res/layout 节点下的布局文件 activity_main.xml,将默认添加的布局管理器修改为垂直线性布局管理器,然后将默认添加的文本框控件删除。修改后的代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<!--(2) 在步骤(1)中添加的垂直线性布局管理器中,添加一个用于显示第一条朋友圈信息的相对布局管理器,
然后在该布局管理器中添加一个显示头像的图像视图控件(ImageView),让它与父容器左对齐,具体代码如下:-->
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/ioc1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:src="@mipmap/ioc1" />
<!--(3) 在步骤(2)添加的相对布局管理器中,头像ImageView控件的右侧
添加3个文本框控件,分别用于显示发布人,内容和时间,具体代码如下:-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/name1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/ioc1"
android:text="雪绒花"
android:textColor="#576B95" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/content1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/name1"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="5dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/ioc1"
android:minLines="3"
android:text="祝我的亲人、朋友们新年快乐!" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/time1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/content1"
android:layout_marginTop="3dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/ioc1"
android:minLines="3"
android:text="昨天"
android:textColor="#9A9A9A" />
<!--(4) 在上段代码的下面继续添加一个ImageView控件,用于显示评论图标,具体代码如下:-->
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/comment1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/content1"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:src="@mipmap/comment" />
</RelativeLayout>
<!--(5) 在相对布局管理器的外面,线性布局管理器里面添加一个ImageView控件,用于显示一个分隔线,具体代码如下:-->
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@mipmap/line" />
</LinearLayout>(6) 按照步骤运行本实例,将显示如图所示的运行结果。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-766555.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-766555.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-766555.html
到了这里,关于Android开发详解:第3章《App UI 设计》的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!