有向无环图的拓扑排序理解和算法
- 有向无环图(DAG)定义
引用子维基百科的DAG定义, 在数学中,尤其是图论和计算机科学中,DAG是一类不含环的有向图(In mathematics, particularly graph theory, and computer science, a directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a directed graph with no directed cycles). 对比之前的有向图的强连通分量,凡是在图中能能够找到强连通分量的有向图(单个顶点除外),都排除在DAG之外。对于有向无环图,拓扑排序是其关键的操作,通过拓扑排序,便能把有向无环图的先后遍历顺序”线性化“。
- DAG的应用
现实世界中,很多场合都涉及到DAG的应用,最常见的应用包括,项目管理中各个事件先后顺序排列的可行性,学校选课系统设计, 程序设计的互相依附以及事件的模拟等等。
我们以某高校的选课系统为例进行说明,如果要选择Class H, 那么选修之前需要完成Class D 和 Class E课程,如果要选择Class D课程,就需要提前学习Class A和 Class B.

选择Class H的前置条件

- 拓扑排序目标
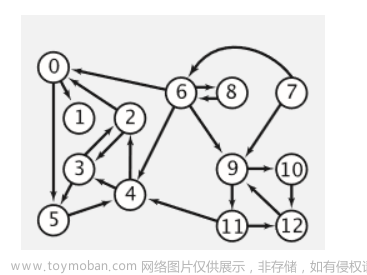
在拓扑排序中,我们需要对有向无环图每个顶点进行检查,经过拓扑排序后,我们会形成一个类似数组的线性结构来表示各个顶点的先后顺序,Dynamic Programming就需要利用DAG形成某些节点,对这些节点进行共用,减少计算事件。值得一提的是,拓扑排序的结果不一定唯一,同一个DAG图形可能会有几个不同的拓扑排序。我们以下图为例,

最后形成的线性次序关系如下:
- 算法原理
一般实现Topological 排序方法有 Kahn’s 算法和 DFS算法,
- Kahn’s 算法非常直观,两步循环即可
(1)在有向图中选一个没有前驱的顶点且输出之
(2)在图中删除该顶点和所有以它为尾的弧,换言之;对于图上以此点为弧头的顶点,其入度减1
重复上述两步,直至全部顶点均已输出,或者当前图中不存在无前驱的顶点为止(存在环)
在Kahn’s 算法中:
(a)可以直接线性搜索 入度为0的顶点(没有前驱)
(b) 利用栈或队列进行保留入度为0的顶点,后面直接出栈,更新相关顶点的入度值
两类算法的事件复杂度分别为O(|V|2)和O(|V|+|E|).
-
DFS 算法当有向图中无环时,也可用DFS进行拓扑排序,因为图中无环,则由图中某点出发进行深度优先搜索遍历时,最先退出DFS函数的顶点即出度为零的顶点,是拓扑有序序列中的最后一个顶点。可以利用数组进行拓扑有序序列中的序号存储。
© DFS算法实现
- 算法代码实现
(a)可以直接线性搜索 入度为0的顶点(没有前驱)
/**
Use Adajacent list to go through each vertex
Work out the indegree array based on the traversal
*/
void assign_indegree(ALGraph G, int *indegree)
{
int i;
int v;
int w;
for(v=0;v<G.vexnum;v++)
{
for(w=FirstAdjVex(G,v);w>=0;w=NextAdjVex(G,v,w))
{
indegree[w]++;
}
}
}
/**
Linear search the indegree array and return the first new zero indegree vertex node
*/
int find_new_zero_indegree_vertex(ALGraph G, int *indegree, int *top_num)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++)
{
if(top_num[i]==-1 && indegree[i]==0)
{
return i;
}
}
return NOT_A_VERTEX; //NOT_A_VERTEX=-1;
}
/**
Find the topological sort of directed graph
*/
Status topological_sort(ALGraph G,void (*visit)(VertexType e))
{
int counter;
int indegree[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int top_num[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; //top_num will store the top order vertex #No.
int v;
int w;
for(counter=0;counter<G.vexnum;counter++)
{
*(top_num+counter)=-1;
}
memset(indegree,0,sizeof(int)*MAX_VERTEX_NUM);
assign_indegree(G,indegree);
for(counter=0;counter<G.vexnum;counter++)
{
v=find_new_zero_indegree_vertex(G,indegree,top_num);
//If v equals to NOT Available VERTEX,
//it must contain the cycle in the graph
//terminate the program
if(v==NOT_A_VERTEX)
{
return ERROR;
}
*(top_num+v)=counter;
for(w=FirstAdjVex(G,v);w>=0;w=NextAdjVex(G,v,w))
{
indegree[w]--;
}
}
dispay_order(G,top_num,visit);
}
/**
Display the topological order based on top_num array list
*/
void dispay_order(ALGraph G, int *top_num, void (*visit)(VertexType e))
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++)
{
visit(G.vertices[top_num[i]].data);
}
}
(b) 利用栈或队列进行保留入度为0的顶点,后面直接出栈,更新相关顶点的入度值
void assign_indegree(ALGraph G, int *indegree)
{
int i;
int v;
int w;
for(v=0;v<G.vexnum;v++)
{
for(w=FirstAdjVex(G,v);w>=0;w=NextAdjVex(G,v,w))
{
indegree[w]++;
}
}
}
Status topological_sort(ALGraph G,void (*visit)(VertexType e))
{
SqStack S;
int indegree[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int i;
int v;
int w;
int count;
InitStack_Sq(&S);
memset(indegree,0,sizeof(int)*MAX_VERTEX_NUM);
assign_indegree(G,indegree);
count =0;
for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++)
{
if(!indegree[i])
{
Push_Sq(&S,i);
}
}
while(!StackEmpty_Sq(S))
{
Pop_Sq(&S,&v);
visit(G.vertices[v].data);
count++;
for(w=FirstAdjVex(G,v);w>=0;w=NextAdjVex(G,v,w))
{
if(!(--indegree[w]))
{
Push_Sq(&S,w);
}
}
}
if(count<G.vexnum)
{
return ERROR;
}
return OK;
}
© DFS算法实现
Status find_topological_sort(ALGraph G, int *ordering)
{
int v;
int w;
count =0;
int index;
memset(visited,0,sizeof(int)*MAX_VERTEX_NUM);
index=G.vexnum-1;
for(v=0;v<G.vexnum;v++)
{
if(!visited[v])
{
dfs_topological_sort(G,v,index-count,ordering);
}
}
if(count<G.vexnum)
{
return ERROR;
}
return OK;
}
//----
int dfs_topological_sort(ALGraph G, int v0, int index, int *ordering)
{
int v;
int w;
visited[v0]=1;
count++;
v=v0;
for(w=FirstAdjVex(G,v);w>=0;w=NextAdjVex(G,v,w))
{
if(!visited[w])
{
//index will be kept as the same as DFS deep dive into search
//when the first recursive call ended, it will be decremented by 1
//and in the next loop, index will be upated in the recursive call
index=dfs_topological_sort(G,w,index,ordering);
}
}
ordering[index]=v;
return index-1;
}
//------
void dispay_ordering(int *ordering, ALGraph G, void (*visit)(VertexType e))
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++)
{
visit(G.vertices[ordering[i]].data);
}
}
- 总结
DAG的拓扑排序(全序)建立顶点或元素之间的先后关系,利用DAG的拓扑排序结果,可以有效地管理项目中不不同节点的先后顺序,可以更合理地进行选课,抑或对大型程序之间的依附关系进行罗列,做到逻辑次序先后合理,更好完成具体的应用工作。
具体来说,如果对于某个事件或节点,其没有任何前置约束,那么此事件或节点就可以作为当前的拓扑有序点。拓扑排序算法一般分为Kahn’s 和经典的DFS深度优先搜索法,Kahn’s 比较直观,DFS搜索法代码简练,各有千秋。
Reference book and video:
a)《数据结构》 严蔚敏文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-766664.html
b) Video, Topological Sort Algorithm|Graph Theory, William Fiset文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-766664.html
到了这里,关于有向无环图的拓扑排序理解和算法的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!