了解DHCP
DHCP全称为Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol,中文含义为“动态主机配置协议”,通常被应用在大型的局域网络环境中,主要作用是集中的管理、分配IP地址,使网络环境中的主机动态的获得IP地址、Gateway地址、DNS服务器地址等信息,并能够提升地址的使用率。
DHCP协议采用客户端/服务器模型,主机地址的动态分配任务由网络主机驱动。当DHCP服务器接收到来自网络主机申请地址的信息时,才会向网络主机发送相关的地址配置等信息,以实现网络主机地址信息的动态配置。
DHCP好处
1.避免IP地址冲突
2.降低了发生配置错误的可能性
3.减少工作量,自动分配IP地址
4.提高IP地址利用率
5.方便客户端配置
6.可以集中化管理设备的IP地址分配
DHCP工作原理
DHCP的交互过程总共有六个步骤组成,前四步是完成交互的主要过程
重点:
第一步:客户端在网络中搜索服务端(通过发送一个dicover报文寻找DHCP的服务器),是通过广播的方式进行大量搜寻,并且等待响应
第二步:服务器向客户端响应服务(其中是通过发送offer报文,以广播的方式进行响应,另外:华为的路由为单播方式)
第三步:客户端向服务端发送服务请求(其中是通过发送request报文以广播的形式,只给第一个响应自己的服务端发送服务请求)
第四步:服务端向客户端提供确认可用的IP和租期信息(以广播形式,回复ACK报文)
了解:
第五步:客户端进行重新登录,发送一个以包含之前DHCP服务端分配的IP地址信息的renew Request报文,当服务端收到该请求后,会尝试让DHCP客户端继续使用该IP地址。并回答一个ACK报文
第六步:DHCP获取到的IP地址都有一个租约,租约过期后,服务端将回收该IP地址,所以如果客户端如果想继续使用该IP地址,则必须更新器租约。更新的方式就是,当当前租约期限过了一半后,客户端都会发送renew报文来续约租期
DHCP八种报文
| 报文 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| DHCP DISCOVER | 客户端到服务器 |
| DHCP OFFER | 服务器到客户端 |
| DHCP REQUEST | 客户端到服务器 |
| DHCPACK | 服务器到客户端 |
| DHCPNAK | 服务器到客户端通知用户无法分配合适的IP地址 |
| DHCP DECLINE | 客户端到服务器,指示地址已被使用 |
| DHCP RELEASE | 客户端到服务器,放弃网络地地口取消剩余的租约时间 |
| DHCP INFORM | 客户端到服务器,客户端如果需要从DHCP服务器端获取更为单ffl的配置信息,则 发送Inform报文向服务器进行请求,极少用到 |
DHCP安装dhcp
检查并且安装dhcp有关软件包
[root@localhost ~]#rpm -qc dhcp
[root@localhost ~]#yum install -y dhcp
[root@localhost ~]#cp /usr/share/doc/dhcp-4.2.5/dhcpd.conf.example /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
[root@localhost ~]#vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
DHCP服务的配置文件在 /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
设置DHCP全局配置参数
option domain-name "benet.com"; #指定默认域名
option domain-name-servers ip1,ip2; #指定 DNS 服务器地址
default-lease-time n ; #默认租约为 n,单位为秒
max-lease-time x; #最大租约为 n ,单位为秒
另外可添加: ddns-update-style none; #禁用 DNS 动态更新
subnet网段声明(作用于整个子网段,部分配置参数优先级高于全局配置参数)
subnet 192.168.233.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { #声明要分配的网段地址
range 192.168.233.30 192.168.233.50; #设置地址池
option routers 192.168.233.2; #指定默认网关地址
}
#host主机声明(给单机分配固定的 IP 地址)
host hostname { #指定需要分配固定 IP地址的客户机名称
hardware ethernet 00:c0:c3:22:46:81; #指定该主机的 MAC地址
fixed-address 192.168.4.100; #指定保留给该主机的 IP地址
}
DHCP场景应用实验
实验目的:在单位时,运用DHCP协议设置地址池,让公司员工的主机都能自动识别,并且分发范围内的IP地址
实验思路:
第一步: 在Linux虚拟机中安装好dhcpd软件应用
第二步:将相对应的example复制到dhcpd.conf中
第三步:关掉防火墙和selinux保护
第四步:修改虚拟机网络模式为仅主机模式,修改网卡配置文件,重启网络服务
第五步:编辑/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf,设置网段、地址池、网关,并且重启服务
第六步:测试客户端虚拟机是否能获取到服务器虚拟机DHCP配置的IP地址池网段
第一步: 在Linux虚拟机中安装好dhcpd软件应用
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qc dhcp //检测是否安装DHCP
未安装软件包 dhcp
[root@localhost ~]# yum install dhcp -y //安装DHCP
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
/var/run/yum.pid 已被锁定,PID 为 3809 的另一个程序正在运行。
Another app is currently holding the yum lock; waiting for it to exit...
另一个应用程序是:PackageKit
内存:158 M RSS (1.5 GB VSZ)
已启动: Mon Jan 2 08:54:10 2023 - 00:34之前
状态 :睡眠中,进程ID:3809
^Z
[1]+ 已停止 yum install dhcp -y
[root@localhost ~]# kill -9 3809 //杀掉进程
[root@localhost ~]# yum install dhcp -y //安装DHCP成功
BDB2053 Freeing read locks for locker 0xe38: 3809/140644507739968
BDB2053 Freeing read locks for locker 0xe3a: 3809/140644507739968
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.huaweicloud.com
* extras: mirrors.huaweicloud.com
* updates: mirrors.huaweicloud.com
正在解决依赖关系
--> 正在检查事务
---> 软件包 dhcp.x86_64.12.4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1 将被 安装
--> 正在处理依赖关系 dhcp-libs(x86-64) = 12:4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1,它被软件包 12:dhcp-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 dhcp-common = 12:4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1,它被软件包 12:dhcp-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libisc-export.so.169()(64bit),它被软件包 12:dhcp-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64 需要
--> 正在处理依赖关系 libdns-export.so.1102()(64bit),它被软件包 12:dhcp-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64 需要
--> 正在检查事务
---> 软件包 bind-export-libs.x86_64.32.9.11.4-26.P2.el7_9.10 将被 安装
---> 软件包 dhcp-common.x86_64.12.4.2.5-58.el7.centos 将被 升级
--> 正在处理依赖关系 dhcp-common = 12:4.2.5-58.el7.centos,它被软件包 12:dhclient-4.2.5-58.el7.centos.x86_64 需要
---> 软件包 dhcp-common.x86_64.12.4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1 将被 更新
---> 软件包 dhcp-libs.x86_64.12.4.2.5-58.el7.centos 将被 升级
---> 软件包 dhcp-libs.x86_64.12.4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1 将被 更新
--> 正在检查事务
---> 软件包 dhclient.x86_64.12.4.2.5-58.el7.centos 将被 升级
---> 软件包 dhclient.x86_64.12.4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1 将被 更新
--> 解决依赖关系完成
依赖关系解决
================================================================================
Package 架构 版本 源 大小
================================================================================
正在安装:
dhcp x86_64 12:4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1 updates 515 k
为依赖而安装:
bind-export-libs x86_64 32:9.11.4-26.P2.el7_9.10 updates 1.1 M
为依赖而更新:
dhclient x86_64 12:4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1 updates 286 k
dhcp-common x86_64 12:4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1 updates 177 k
dhcp-libs x86_64 12:4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1 updates 133 k
事务概要
================================================================================
安装 1 软件包 (+1 依赖软件包)
升级 ( 3 依赖软件包)
总下载量:2.2 M
Downloading packages:
No Presto metadata available for updates
警告:/var/cache/yum/x86_64/7/updates/packages/dhcp-libs-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64.rpm: 头V3 RSA/SHA256 Signature, 密钥 ID f4a80eb5: NOKEY
dhcp-libs-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64.rpm 的公钥尚未安装
(1/5): dhcp-libs-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64.rpm | 133 kB 00:00
(2/5): dhclient-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64.rpm | 286 kB 00:00
(3/5): bind-export-libs-9.11.4-26.P2.el7_9.10.x86_64.rpm | 1.1 MB 00:00
(4/5): dhcp-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64.rpm | 515 kB 00:00
(5/5): dhcp-common-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64.rpm | 177 kB 00:01
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
总计 1.6 MB/s | 2.2 MB 00:01
从 file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 检索密钥
导入 GPG key 0xF4A80EB5:
用户ID : "CentOS-7 Key (CentOS 7 Official Signing Key) <security@centos.org>"
指纹 : 6341 ab27 53d7 8a78 a7c2 7bb1 24c6 a8a7 f4a8 0eb5
软件包 : centos-release-7-4.1708.el7.centos.x86_64 (@anaconda)
来自 : /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
正在更新 : 12:dhcp-libs-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64 1/8
正在更新 : 12:dhcp-common-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64 2/8
正在安装 : 32:bind-export-libs-9.11.4-26.P2.el7_9.10.x86_64 3/8
正在安装 : 12:dhcp-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64 4/8
正在更新 : 12:dhclient-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64 5/8
清理 : 12:dhclient-4.2.5-58.el7.centos.x86_64 6/8
清理 : 12:dhcp-common-4.2.5-58.el7.centos.x86_64 7/8
清理 : 12:dhcp-libs-4.2.5-58.el7.centos.x86_64 8/8
验证中 : 32:bind-export-libs-9.11.4-26.P2.el7_9.10.x86_64 1/8
验证中 : 12:dhcp-common-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64 2/8
验证中 : 12:dhcp-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64 3/8
验证中 : 12:dhcp-libs-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64 4/8
验证中 : 12:dhclient-4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1.x86_64 5/8
验证中 : 12:dhcp-common-4.2.5-58.el7.centos.x86_64 6/8
验证中 : 12:dhcp-libs-4.2.5-58.el7.centos.x86_64 7/8
验证中 : 12:dhclient-4.2.5-58.el7.centos.x86_64 8/8
已安装:
dhcp.x86_64 12:4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1
作为依赖被安装:
bind-export-libs.x86_64 32:9.11.4-26.P2.el7_9.10
作为依赖被升级:
dhclient.x86_64 12:4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1
dhcp-common.x86_64 12:4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1
dhcp-libs.x86_64 12:4.2.5-83.el7.centos.1
完毕!
[root@localhost ~]# less dhcpd.conf
dhcpd.conf: 没有那个文件或目录
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/share/doc/dhcp-4.2.5/
第二步:将相对应的example复制到dhcpd.conf中
[root@localhost dhcp-4.2.5]# cp /usr/share/doc/dhcp-4.2.5/dhcpd.conf.example /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf //拷贝文件
cp:是否覆盖"/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf"? y
[root@localhost dhcp-4.2.5]# ls
dhcpd6.conf.example dhcpd.conf.example ldap
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf 配置文件信息
# dhcpd.conf
#
# Sample configuration file for ISC dhcpd
#
# option definitions common to all supported networks...
option domain-name "example.org";
option domain-name-servers ns1.example.org, ns2.example.org;
default-lease-time 600;
max-lease-time 7200;
# Use this to enble / disable dynamic dns updates globally.
#ddns-update-style none;
# If this DHCP server is the official DHCP server for the local
# network, the authoritative directive should be uncommented.
#authoritative;
# Use this to send dhcp log messages to a different log file (you also
# have to hack syslog.conf to complete the redirection).
log-facility local7;
# No service will be given on this subnet, but declaring it helps the
# DHCP server to understand the network topology.
subnet 10.152.187.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
}
# This is a very basic subnet declaration.
subnet 10.254.239.0 netmask 255.255.255.224 {
range 10.254.239.10 10.254.239.20;
option routers rtr-239-0-1.example.org, rtr-239-0-2.example.org;
}
# This declaration allows BOOTP clients to get dynamic addresses,
# which we don't really recommend.
subnet 10.254.239.32 netmask 255.255.255.224 {
range dynamic-bootp 10.254.239.40 10.254.239.60;
option broadcast-address 10.254.239.31;
option routers rtr-239-32-1.example.org;
}
# A slightly different configuration for an internal subnet.
subnet 10.5.5.0 netmask 255.255.255.224 {
range 10.5.5.26 10.5.5.30;
option domain-name-servers ns1.internal.example.org;
option domain-name "internal.example.org";
option routers 10.5.5.1;
option broadcast-address 10.5.5.31;
default-lease-time 600;
max-lease-time 7200;
}
# Hosts which require special configuration options can be listed in
# host statements. If no address is specified, the address will be
# allocated dynamically (if possible), but the host-specific information
# will still come from the host declaration.
host passacaglia {
hardware ethernet 0:0:c0:5d:bd:95;
filename "vmunix.passacaglia";
server-name "toccata.fugue.com";
}
# Fixed IP addresses can also be specified for hosts. These addresses
# should not also be listed as being available for dynamic assignment.
# Hosts for which fixed IP addresses have been specified can boot using
# BOOTP or DHCP. Hosts for which no fixed address is specified can only
# be booted with DHCP, unless there is an address range on the subnet
# to which a BOOTP client is connected which has the dynamic-bootp flag
# set.
host fantasia {
hardware ethernet 08:00:07:26:c0:a5;
fixed-address fantasia.fugue.com;
}
# You can declare a class of clients and then do address allocation
# based on that. The example below shows a case where all clients
# in a certain class get addresses on the 10.17.224/24 subnet, and all
# other clients get addresses on the 10.0.29/24 subnet.
class "foo" {
match if substring (option vendor-class-identifier, 0, 4) = "SUNW";
}
shared-network 224-29 {
subnet 10.17.224.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers rtr-224.example.org;
}
subnet 10.0.29.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers rtr-29.example.org;
}
pool {
allow members of "foo";
range 10.17.224.10 10.17.224.250;
}
pool {
deny members of "foo";
range 10.0.29.10 10.0.29.230;
}
}
第三步:关掉防火墙和selinux保护
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
第四步:修改虚拟机网络模式为仅主机模式,修改网卡配置文件,重启网络服务

[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 //修改网卡配置文件
ifcfg-ens33配置文件信息
TYPE=Ethernet
PROXY_METHOD=none
BROWSER_ONLY=no
BOOTPROTO=static
DEFROUTE=yes
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6INIT=yes
IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes
IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy
NAME=ens33
UUID=12a880c9-318e-4aa5-b143-e730606be7f1
DEVICE=ens33
ONBOOT=yes
IPADDR=20.0.0.200
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=20.0.0.2
//清除或注释DNS
#DNS1=8.8.8.8
#DNS2=114.114.114.114
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart network //重启网络服务
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 20.0.0.200 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 20.0.0.255
inet6 fe80::1e19:a8d4:a94a:6a4e prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:a4:34:b5 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 118 bytes 18656 (18.2 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
第五步:编辑/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf,设置网段、地址池、网关,并且重启服务
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
27 subnet 20.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { //设置网段
28 range 20.0.0.200 20.0.0.220; //设置地址池
29 option routers 20.0.0.2; //设置网关
30 }
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart dhcpd //重启dhcp服务
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl status dhcpd //查看dhcp状态,是否已启动
● dhcpd.service - DHCPv4 Server Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/dhcpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since 一 2023-01-02 10:39:27 CST; 5s ago
Docs: man:dhcpd(8)
man:dhcpd.conf(5)
Main PID: 4201 (dhcpd)
Status: "Dispatching packets..."
CGroup: /system.slice/dhcpd.service
└─4201 /usr/sbin/dhcpd -f -cf /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf -user dhcpd -group dhcpd --no-pid
1月 02 10:39:27 localhost.localdomain dhcpd[4201]: No subnet declaration for virbr0 (192.168.122.1).
1月 02 10:39:27 localhost.localdomain dhcpd[4201]: ** Ignoring requests on virbr0. If this is not what
1月 02 10:39:27 localhost.localdomain dhcpd[4201]: you want, please write a subnet declaration
1月 02 10:39:27 localhost.localdomain dhcpd[4201]: in your dhcpd.conf file for the network segment
1月 02 10:39:27 localhost.localdomain dhcpd[4201]: to which interface virbr0 is attached. **
1月 02 10:39:27 localhost.localdomain dhcpd[4201]:
1月 02 10:39:27 localhost.localdomain dhcpd[4201]: Listening on LPF/ens33/00:0c:29:a4:34:b5/20.0.0.0/24
1月 02 10:39:27 localhost.localdomain dhcpd[4201]: Sending on LPF/ens33/00:0c:29:a4:34:b5/20.0.0.0/24
1月 02 10:39:27 localhost.localdomain dhcpd[4201]: Sending on Socket/fallback/fallback-net
1月 02 10:39:27 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Started DHCPv4 Server Daemon.
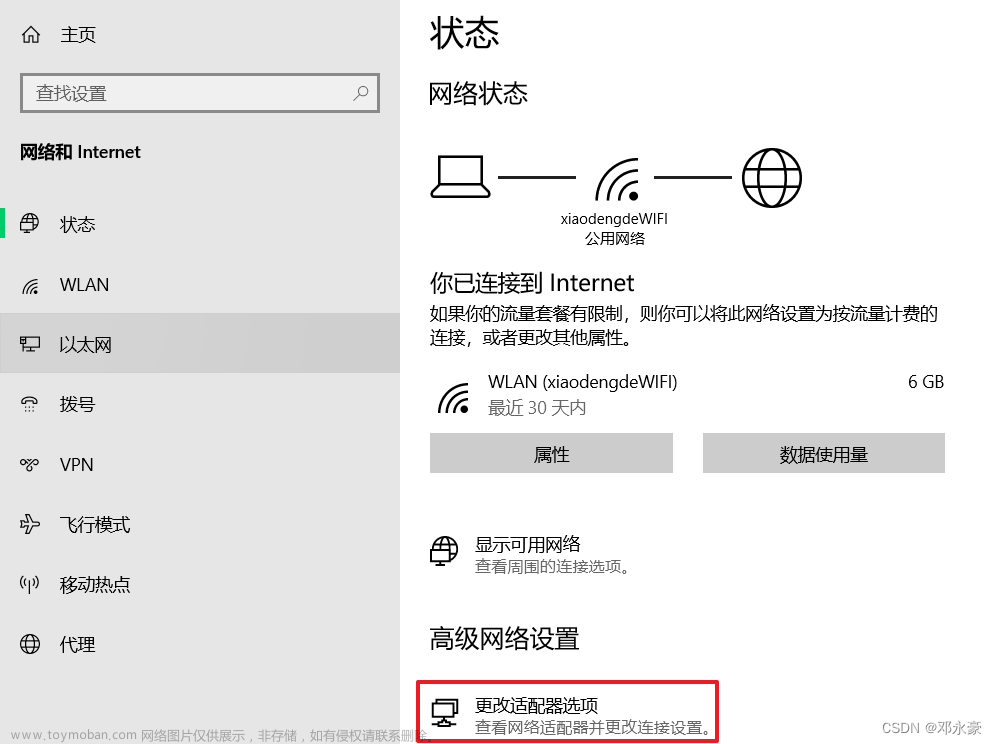
第六步:测试win10虚拟机是否能获取到服务器虚拟机DHCP配置的IP地址池网段
win10虚拟机设置仅主机模式
将win10设置为自动获取ip地址 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-770249.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-770249.html
ip地址获取为DHCP服务器配置地址池中的网段 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-770249.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-770249.html
到了这里,关于Linux网络服务-DHCP的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!