内容:二叉树的前、中,后序遍历,层序遍历,二叉树节点个数,叶子节点个数,二叉树高度,第k层节点的个数,查找某个节点,二叉树销毁,判断是否为完全二叉树
目录
前序遍历:
中序遍历:
后序遍历:
层次遍历:需要借助队列
二叉树节点个数:
二叉树叶子节点的个数:
二叉树的高度:
二叉树第k层的节点个数:
查找某个节点并返回其地址:
二叉树销毁:
判断是否为完全二叉树:借助队列
事前准备:
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode//二叉树节点
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode*right;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)//创建一个节点
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
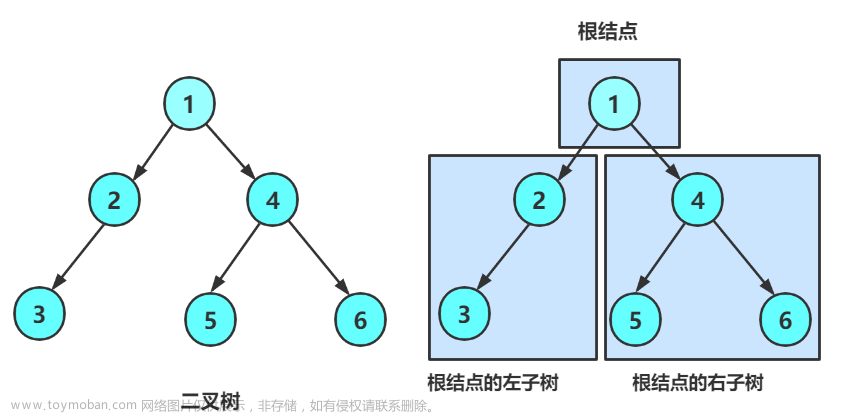
}手动构造一个二叉树,用以验证:图示如下
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node3;
node2->left = node4;
return node1;
}
前序遍历:
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)//进入一个空树
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);//访问根节点的值
PrevOrder(root->left);//访问左子树
PrevOrder(root->right);//访问右子树
}

中序遍历:
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);//访问左子树
printf("%d ", root->data);//访问根节点
InOrder(root->right);//访问右子树
}

后序遍历:
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);//访问左子树
PostOrder(root->right);//访问右子树
printf("%d ", root->data);//访问根节点
}
层次遍历:需要借助队列
借助队列先进先出的性质,一个节点出队,带入它不为空的左右孩子入队
相关队列功能的所需函数及队列结构的定义:
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode//队列中的节点
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue//队列
{
QNode* phead;//指向队头的指针
QNode* ptail;//指向队尾的指针
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);//初始化
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);//销毁
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);//插入
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);//删除
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);//获取队头元素
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//判空
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);//断言,pq一定不为空
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)//第一次插入,链表中没有节点
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else//尾插
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)//链表中仅有一个节点
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else//多个节点,头删
{
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}层序遍历:
void LeverOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)//将根节点入队
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))//一个节点出队,带入它的左右孩子
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", front->data);
if (front->left)//左孩子不为空,入队
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)//右孩子不为空,入队
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
二叉树节点个数:
空树返回0
非空树返回:左子树节点的个数+右子树节点的个数+1
int BTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : BTreeSize(root->left)
+ BTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
二叉树叶子节点的个数:
进入一个空树返回0
非空树:若本身是叶子,返回1,否则返回左子树叶子的个数+右子树叶子的个数
int BTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)//本身是叶子
{
return 1;
}
return BTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BTreeLeafSize(root->right);//非叶子
}
二叉树的高度:
进入一个空树,返回0
非空树:找出左右子树高度更高的一个,返回其+1
int BTreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = BTreeHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = BTreeHeight(root->right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
二叉树第k层的节点个数:
进入空树,返回0
非空树:若它的k==1,则求的就是它这一层,返回1
否则,返回它左子树第k-1层的节点个数+右子树第k-1层的节点个数
int BTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root,int k)
{
assert(k > 0);
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
return BTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1)
+ BTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}如求其第2层的节点个数:

查找某个节点并返回其地址:
BTNode* BTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (root->data == x)//根节点就是,直接返回
{
return root;
}
BTNode* ret1 = BTreeFind(root->left, x);//去左子树找
if (ret1)//找到了,返回
{
return ret1;
}
BTNode* ret2 = BTreeFind(root->right, x);//去右子树找
if (ret2)//找到了,返回
{
return ret2;
}
return NULL;//根,左子树,右子树全都找不到,返回NULL
}二叉树销毁:
void BTreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)//进入空树,返回
{
return;
}
BTreeDestroy(root->left);//销毁左子树
BTreeDestroy(root->right);//销毁右子树
free(root);//销毁根节点
}判断是否为完全二叉树:借助队列
一个节点出队,让它的左右孩子进队,不管左右孩子是否为空
若是完全·二叉树,则出到第一个NULL时,这个NULL后面的所有队列元素都是NULL
若不是完全二叉树,则出到第一个NULL时,这个NULL后面的所有队列元素中有元素不是NULL
bool BTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)//根节点入队
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))//出队列元素
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front == NULL)//出到第一个NULL,结束循环,进行判断它后面的所有处在队列中的元素是否都为NULL
{
break;
}
QueuePush(&q, front->left);//不管是否为空,左右孩子都进队
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))//判断第一个NULL出队后,队中所有元素的情况
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)//如果队中有非空节点,则不是完全二叉树
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;//第一个NULL出队后,队中所有元素均为NULL
} 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-771866.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-771866.html
完结撒花~ 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-771866.html
到了这里,关于数据结构-二叉树的代码实现(详解)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!