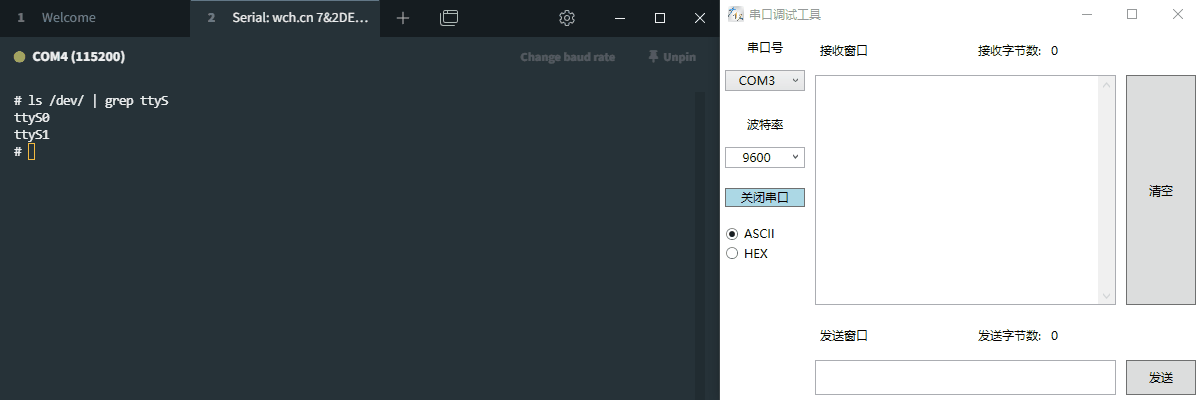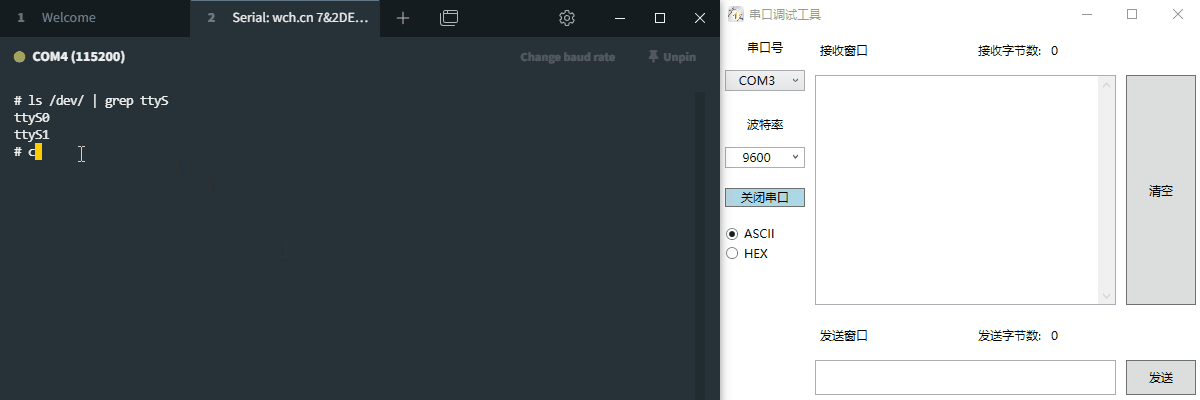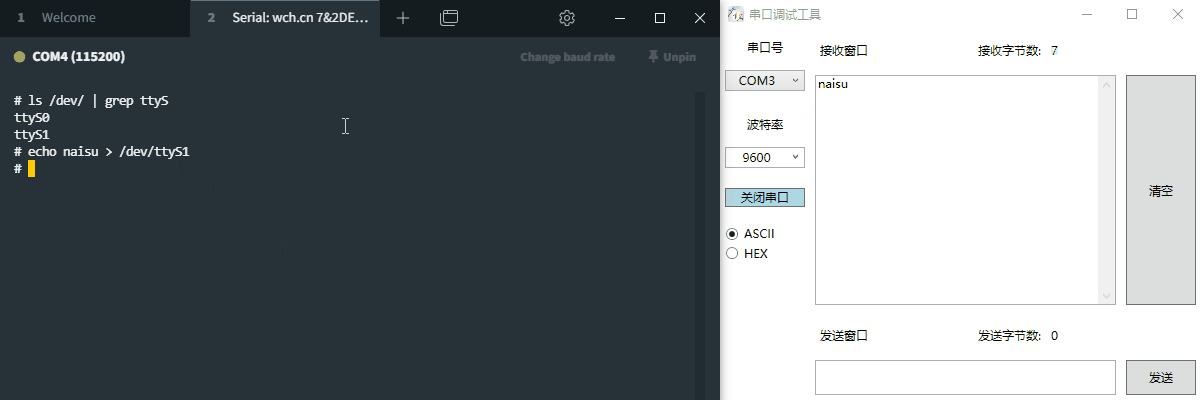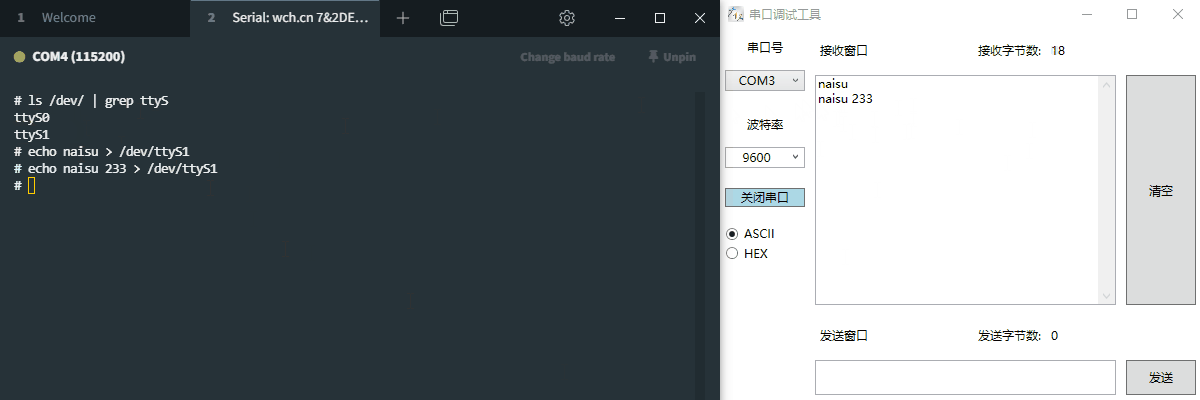
目录
1、为什么需要platform总线
2、设备端:platform_device
2.1 platform_device结构体
2.2 注册
2.3 注销
3、驱动端:platform_driver
3.1 platform_driver结构体
3.2 注册
3.3 注销
4、总线
4.1 bus_type
4.2 platform_bus_type
5、匹配
5.1 匹配规则,platform_match
5.2 platform_device匹配流程
5.3 platform_driver匹配流程
6、在没有设备树时,使用name进行匹配
6.1 设备端程序
6.2 驱动端程序
7、在没有设备树时,使用 idtable 进行匹配
7.1 设备端程序
7.2 驱动端程序
8、获取设备信息
8.1 获取设备信息的API
8.1.1 platform_get_resource
8.1.2 platform_get_irq
8.1.3 根据device_node获取设备信息
8.2 驱动程序
9、module_platform_driver:一键注册platform
10、MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE:实现热插拔
10.1 定义以及使用方法
10.2 如何实现热插拔的功能
11、 platform设备树匹配
11.1 修改设备树以及驱动程序的compatible属性
11.1.1 驱动端
11.1.2 设备树
11.2 驱动程序:获取设备树中的中断以及GPIO资源
11.2.1 修改设备树
11.2.2 驱动程序
11.3 应用程序
1、为什么需要platform总线
举一个例子,对于同一个主机来说,他可以支持很多I2C设备,对于同一个I2C设备来说,他也可以给很多主机来用,如果每个主机对应每个设备都需要一段驱动代码的话,会非常的冗余,根据高内聚低耦合的原则,这样是非常不好的。所以就需要这么一个统一的接口,将二者分离开来,设备端只负责设备,驱动端只负责驱动。于是提出platform这个虚拟总线,相应的就有 platform_driver 和 platform_device。当设备或者驱动加载时,就会去对面查看是否有匹配的内容。

2、设备端:platform_device
2.1 platform_device结构体
struct platform_device {
const char *name; //用于匹配的名字
int id; //总线号 PLATFORM_DEVID_AUTO
//bool id_auto; //TRUE
struct device dev; //父类
u32 num_resources; //资源的个数
struct resource *resource; //设备信息结构体
char *driver_override;
}
struct device{
void (*release)(struct device *dev); //释放资源的函数
};
struct resource { //设备信息结构体
resource_size_t start; //资源的起始值
resource_size_t end; //资源的结束值
unsigned long flags; //资源的类型
IORESOURCE_IO //GPIO类型的资源
IORESOURCE_MEM //内存类型的资源
IORESOURCE_IRQ //中断类型的资源
IORESOURCE_DMA //DMA类型的资源
};2.2 注册
int platform_device_register(struct platform_device *);2.3 注销
void platform_device_unregister(struct platform_device *);3、驱动端:platform_driver
3.1 platform_driver结构体
struct platform_driver {
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *); //匹配成功执行的函数
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *); //分离的时候执行的函数
struct device_driver driver; //父类
const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
};
struct device_driver {
const char *name;
const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
};
3.2 注册
int platform_driver_register (struct platform_driver *);3.3 注销
void platform_driver_unregister(struct platform_driver *);4、总线
4.1 bus_type
Linux 内核用 bus_type 结构体来表示总线,我们所用的 I2C、SPI、USB 都是用这个结构体来定义的。该结构体如下:
struct bus_type {
const char *name;
const char *dev_name;
struct device *dev_root;
struct device_attribute *dev_attrs; /* use dev_groups instead */
const struct attribute_group **bus_groups;
const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;
const struct attribute_group **drv_groups;
int (*match)(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv);
int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
int (*probe)(struct device *dev);
int (*remove)(struct device *dev);
void (*shutdown)(struct device *dev);
int (*online)(struct device *dev);
int (*offline)(struct device *dev);
int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct device *dev);
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
const struct iommu_ops *iommu_ops;
struct subsys_private *p;
struct lock_class_key lock_key;
};4.2 platform_bus_type
platform总线是 bus_type的一个具体实例,定义如下:
struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {
.name = "platform",
.dev_groups = platform_dev_groups,
.match = platform_match,
.uevent = platform_uevent,
.pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops,
};5、匹配
5.1 匹配规则,platform_match
在platform_bus_type中,match函数就是用来匹配的,platform_match函数实现如下:
static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);
/* When driver_override is set, only bind to the matching driver */
if (pdev->driver_override)
return !strcmp(pdev->driver_override, drv->name);
/* Attempt an OF style match first */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try ACPI style match */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try to match against the id table */
if (pdrv->id_table)
return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;
/* fall-back to driver name match */
return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);
}
static inline int of_driver_match_device(struct device *dev,
const struct device_driver *drv)
{
return of_match_device(drv->of_match_table, dev) != NULL;
}1、platform_device.driver_override 和 platform_driver.driver.name
2、设备树中的compatible 和 platform_driver.driver.of_match_table 的 compatible
3、platform_device.name 和 platform_driver.id_table[i].name
4、platform_device.name 和 platform_driver.driver.name
5.2 platform_device匹配流程
platform_device_register(&pdev){
return platform_device_add(pdev)
}
->
pdev->dev.bus = &platform_bus_type
device_add(&pdev->dev)
->
bus_add_device(dev) //放入链表
bus_probe_device(dev)
->
device_initial_probe(dev)
->
__device_attach(dev, true)
->
bus_for_each_drv(dev->bus, NULL, &data, __device_attach_driver)
->
__device_attach_driver
->
driver_match_device(drv, dev) //是否匹配
return driver_probe_device(drv, dev) //调用 probe 函数5.3 platform_driver匹配流程
#define platform_driver_register(drv)
->
__platform_driver_register(drv, THIS_MODULE)
->
drv->driver.bus = &platform_bus_type; //指定为platform bus
driver_register(&drv->driver)
->
bus_add_driver(drv) //放入链表
->
driver_attach(drv)
->
bus_for_each_dev(drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach)
->
__driver_attach
->
driver_match_device(drv, dev)
->
drv->bus->match(dev, drv) //是否匹配6、在没有设备树时,使用name进行匹配
6.1 设备端程序
struct resource res[] = {
[0] = {
.start = 0x12345678,
.end = 0x12345678+49,
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[1] = {
.start = 71,
.end = 71,
.flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ,
}
};
void pdev_release(struct device *dev)
{
}
struct platform_device pdev = {
.name = "aabbccdd",
.id = PLATFORM_DEVID_AUTO, //自动分配
.dev = {
.release = pdev_release,
},
.resource = res,
.num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(res),
};
static int __init pdev_init(void)
{
return platform_device_register(&pdev);
}
static void __exit pdev_exit(void)
{
platform_device_unregister(&pdev);
}
6.2 驱动端程序
int pdrv_probe(struct platform_device*pdev)
{
return 0;
}
int pdrv_remove(struct platform_device*pdev)
{
return 0;
}
struct platform_driver pdrv = {
.probe = pdrv_probe,
.remove = pdrv_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "aabbccdd",
},
};
static int __init pdrv_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&pdrv);
}
static void __exit pdrv_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&pdrv);
}7、在没有设备树时,使用 idtable 进行匹配
7.1 设备端程序
与 6.1 设备端不一样的地方
struct platform_device pdev = {
.name = "hello1",
.id = PLATFORM_DEVID_AUTO, //自动分配
.dev = {
.release = pdev_release,
},
.resource = res,
.num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(res),
};7.2 驱动端程序
与 6.2 驱动端不一样的地方
struct platform_device_id idtable[] = {
{"hello1",0},
{"hello2",1},
{"hello3",2},
{/*end*/}
};
struct platform_driver pdrv = {
.probe = pdrv_probe,
.remove = pdrv_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "aabbccdd", //这个name一定要填,因为要以这个名字创建文件夹
},
.id_table = idtable,
};8、获取设备信息
8.1 获取设备信息的API
8.1.1 platform_get_resource
struct resource *platform_get_resource(struct platform_device *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int index)
/*
功能:在驱动中获取设备信息
参数:
@dev :platform_device的结构体指针
@type:资源的类型
@index:同类型资源的索引号
返回值:成功返回resource的结构体指针,失败返回NULL
*/8.1.2 platform_get_irq
int platform_get_irq(struct platform_device *dev, unsigned int index)
/*
功能:获取中断类型的资源
参数:
@dev :platform_device的结构体指针
@index:中断类型资源的索引号
返回值:成功返回中断号,失败返回错误码
*/8.1.3 根据device_node获取设备信息
Linux驱动开发:设备树节点与属性_凛冬将至__的博客-CSDN博客的7与8两节
8.2 驱动程序
完整的驱动程序就不再重写了,在 6.2 驱动程序中 probe 函数中得到设备信息
struct resource *res;
int pdrv_probe(struct platform_device*pdev)
{
res = platform_get_resource(pdev,IORESOURCE_MEM,0);
irqno = platform_get_irq(pdev,0);
printk("addr = %#llx,irqno = %d\n",res->start,irqno);
return 0;
}9、module_platform_driver:一键注册platform
//在linux/platform_device.h中
#define module_platform_driver(__platform_driver)
module_driver(__platform_driver, platform_driver_register,
platform_driver_unregister)
//##代表字符串的拼接
#define module_driver(__driver, __register, __unregister, ...)
static int __init __driver##_init(void)
{
return __register(&(__driver) , ##__VA_ARGS__);
}
module_init(__driver##_init);
static void __exit __driver##_exit(void)
{
__unregister(&(__driver) , ##__VA_ARGS__);
}
module_exit(__driver##_exit);
使用该宏: module_platform_driver(pdrv),即被转化为:
#define module_platform_driver(pdrv)
module_driver(pdrv, platform_driver_register, platform_driver_unregister)
#define module_driver(pdrv, platform_driver_register, platform_driver_unregister)
static int __init pdrv_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&pdrv);
}
static void __exit pdrv_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&pdrv);
}
module_init(pdrv_init);
module_exit(pdrv_exit);
10、MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE:实现热插拔
10.1 定义以及使用方法
//定义在linux/module.h中
#define MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(type, name)
extern const typeof(name) __mod_##type##__##name##_device_table
__attribute__ ((unused, alias(__stringify(name))))使用时,参数如下:
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of,match_table)
of:总线类型
match_table:idtable数组首地址
10.2 如何实现热插拔的功能
1.先将 pdev.ko 和 pdrv.ko 放到下面的目录中
/lib/modules/5.4.0-148-generic/kernel/drivers/platform
2.执行depmod -a命令,让内核重新检索文件的位置
3.安装 pdev.ko , pdrv.ko 会被自动安装
11、 platform设备树匹配
11.1 修改设备树以及驱动程序的compatible属性
11.1.1 驱动端
在 5.1 中我们已经看过了匹配的流程,其中第二种方式就是用设备树匹配:设备树中的compatible 和 platform_driver.driver.of_match_table 的 compatible进行匹配
struct of_device_id oftable[] = {
{.compatible = "aaa,aaa",},
{.compatible = "bbb,bbb",},
{.compatible = "ccc,ccc",},
{/*end*/} //一定要有一个空的在
};
struct platform_driver {
.driver = {
.of_match_table = oftable,
},
};
struct device_driver driver {
struct device_driver driver;
}
struct device_driver {
const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
}
struct of_device_id {
char name[32];
char type[32];
char compatible[128]; //通过本选项和设备树完成匹配
const void *data;
};11.1.2 设备树
节点下需要有个 compatible 属性,并且该属性需要与 oftable 中的 compatible 名字相同,例如:
myplatform{
compatible = "aaa,aaa";
}; 11.2 驱动程序:获取设备树中的中断以及GPIO资源
有关GPIO部分请看:
Linux驱动开发:gpio子系统_凛冬将至__的博客-CSDN博客
有关中断部分请看:
Linux驱动开发:中断子系统_凛冬将至__的博客-CSDN博客
有关阻塞部分请看:
Linux驱动开发 IO模型:阻塞IO_linux阻塞io_凛冬将至__的博客-CSDN博客文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-772826.html
11.2.1 修改设备树
在根节点下添加自己的节点文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-772826.html
myplatform{
compatible = "aaa,aaa";
interrupt-parent = <&gpiof>;
interrupts = <9 0>;
reg = <0x12345678 0x40>;
led1 = <&gpioe 10 0>;
};11.2.2 驱动程序
#define IRQNAME "key_irq"
int irqno, major;
struct gpio_desc* desc;
struct class* cls;
struct device* dev;
wait_queue_head_t wq;
int condition=0;
int status=0;
irqreturn_t key_irq_handle(int irq, void* dev)
{
//1.设置status和led1
status = gpiod_get_value(desc);
status = !status;
gpiod_set_value(desc,status);
//2唤醒
condition=1;
wake_up_interruptible(&wq);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
int pdrv_open(struct inode* inode, struct file* file)
{
return 0;
}
ssize_t pdrv_read(struct file*file,
char __user*ubuf, size_t size, loff_t*offs)
{
int ret;
if(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK){
return -EINVAL;
}else{
ret = wait_event_interruptible(wq,condition);
}
ret = copy_to_user(ubuf,&status,size);
condition = 0;
return size;
}
int pdrv_close(struct inode* inode, struct file* file)
{
return 0;
}
struct file_operations fops = {
.open = pdrv_open,
.read = pdrv_read,
.release = pdrv_close,
};
int pdrv_probe(struct platform_device* pdev)
{
int ret;
// 1.获取设备树中的设备信息
irqno = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0);
desc = gpiod_get_from_of_node(pdev->dev.of_node, "led1", 0, GPIOD_OUT_LOW, NULL);
// 2.注册中断
ret = request_irq(irqno, key_irq_handle, IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, IRQNAME, NULL);
// 3.注册字符设备驱动
major = register_chrdev(0, IRQNAME, &fops);
cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, IRQNAME);
dev = device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, IRQNAME);
//4.初始化等待队列头
init_waitqueue_head(&wq);
return 0;
}
int pdrv_remove(struct platform_device* pdev)
{
device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(cls);
unregister_chrdev(major, IRQNAME);
free_irq(irqno, NULL);
gpiod_put(desc);
return 0;
}
const struct of_device_id oftable[] = {
{
.compatible = "aaa,aaa",
},
{ /*end*/ }
};
struct platform_driver pdrv = {
.probe = pdrv_probe,
.remove = pdrv_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "bbb", //虽然用不到,但是一定要写
.of_match_table = oftable,
},
};
//一键注册
module_platform_driver(pdrv);11.3 应用程序
int main(int argc,const char * argv[])
{
int fd,status;
if((fd = open("/dev/key_irq",O_RDWR))==-1)
PRINT_ERR("open error");
while(1){
read(fd,&status,sizeof(status));
printf("status = %d\n",status);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}到了这里,关于Linux驱动开发:platform总线驱动的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!