实践要求
1. 问题描述
文学研究人员需要统计某篇英文小说中某些形容词的出现次数和位置。试写一个实现这一目标的文字统计系统,称为"文学研究助手"。
2. 基本要求
英文小说存于文本文件中。待统计的词汇集合要一次输入完毕,即统计工作必需在程序的一次运行后就全部完成。程序的输出结果是每个词出现次数和出现位置所在行的行号,格式自行设计。
3. 测试数据
以你的C源程序模拟英文小说,C语言的保留字集作为待统计的词汇集。
4. 实现提示
设小说中的词汇一律不跨行。这样每读入一行就统计每个词在这行中的出现次数。出现位置所在行的行号可以用链表存储。若某行中出现不止一次,不必存多个相同的行号。如果希望达到选作部分(1)和(2)所提出的要求,则首先应把KMP(见教科书P86)算法改写成如下的等价形式,再将它推广到多个模式的情形。
do{
do {
j=next[j];
} while (j!=0 && s.ch[i]!=t.ch[j]);
j++;
i++; //每次进入循环体i只增加一次
} while (i!=(s.curlen+1)&&j!=(t.curlen+1));
5. 选作内容
(1) 模式匹配要基于KMP算法。
(2) 整个统计过程中只对小说文字扫描一遍以提高效率。
(3) 假设小说中的每个单词或者从行首开始,或者前置以一个空格符。利用单词匹配特点另写一个高效的统计程序,与KMP算法统计程序进行效率比较。
(4) 推广到更一般的模式集匹配问题,并设待查模式串可以跨行。
(提示: 定义操作getachar)。
实践报告
1. 题目分析
说明程序设计的任务,强调的是程序要做什么,此外列出各成员分工
程序设计任务:
设计一个文字统计系统“文学研究助手”,统计文本文件中输入的词汇出现次数和位置
2. 数据结构设计
说明程序用到的数据结构的定义,主程序的流程及各模块之间的层次关系
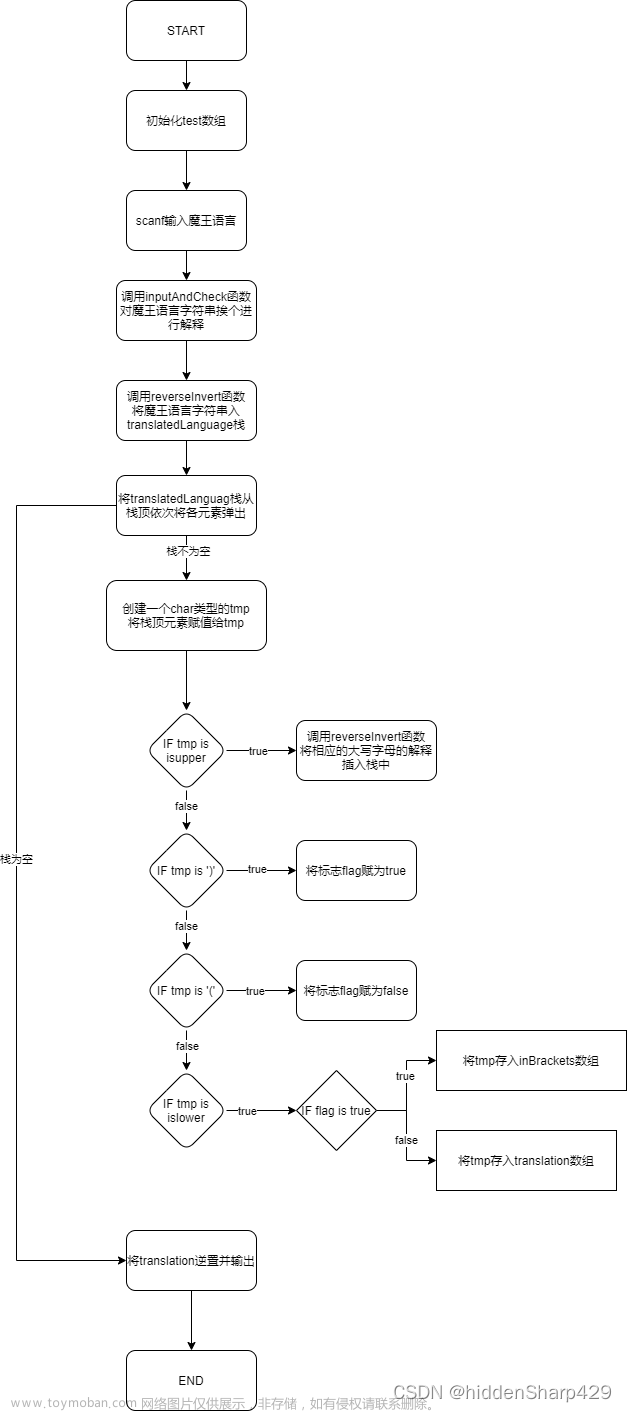
该程序主要用到的数据结构是动态数组
主程序流程图

3. 程序设计
实现概要设计中的数据类型,对主程序、模块及主要操作写出伪代码,画出函数的调用关系
各函数层次关系图

各模块伪代码
获取单词数量

存储要查询的单词

读取文本文件

KMP算法

Main函数

4. 调试分析
问题1:内存管理,如何选择初始空间大小,扩容时机
解决:选取较小初始空间,当空间使用率过高时扩容,每次增加一倍空间
问题2:如何让KMP算法在匹配成功后继续匹配而不重复记录行号
解决:记录最后匹配行号,仅当匹配行号改变时更新并打印
时间复杂度O(文本长度 * 查询单词数量),空间复杂度O(文本长度 + 查询单词数量)
5. 测试结果
列出测试结果,包括输入和输出
输入还包括novel.txt,文本较长,可见附件
6. 用户使用说明
给出主界面及主要功能界面
首先输入你想查询的单词的数量,然后一次输入你想要查询的单词,然后程序会打印查询的单词所在的行号
7. 选作内容
实现了(1) (2)和(4)
(1) 模式匹配要基于KMP算法。
(2) 整个统计过程中只对小说文字扫描一遍以提高效率。
(3) 假设小说中的每个单词或者从行首开始,或者前置以一个空格符。利用单词匹配特点另写一个高效的统计程序,与KMP算法统计程序进行效率比较。
(4) 推广到更一般的模式集匹配问题,并设待查模式串可以跨行。
8. 附件
源程序文件清单:
literary_research_assistance.c //主程序
novel.txt //文本文件文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-775422.html
literary_research_assistance.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 获取需要查找的单词数
int get_word_count() {
int word_count;
scanf("%d", &word_count);
return word_count;
}
// 为word_count个单词分配空间,并检查内存分配是否成功
char **allocate_words(int count) {
char **words = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * count);
if (words == NULL) {
printf("Memory allocation failed!\n");
exit(1); // 内存分配失败则退出程序
}
return words;
}
// 读取word_count个单词到words中,并检查每个单词的内存分配是否成功
void get_words(char **words, int count) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
char *word = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 50);
if (word == NULL) {
printf("Memory allocation failed!\n");
exit(1); // 内存分配失败则退出程序
}
scanf("%s", word);
words[i] = word;
}
}
// 动态读取文本内容到*text中,记录每行开始位置到*line_numbers
// 使用扩容机制,每次内存不足时多分配一倍的空间,直到文件末尾
void read_text(FILE *fp, char **text, int **line_numbers, int *char_count, int *line_count) {
int size = 100;
*text = (char *)malloc(size * sizeof(char));
*line_numbers = (int *)malloc(size * sizeof(int));
if (*text == NULL || *line_numbers == NULL) {
printf("Memory allocation failed!\n");
exit(1);
}
// 读取文本内容
while (!feof(fp)) {
// 扩容
if (*char_count + 1 >= size) {
size *= 2;
char *tmp = (char *)malloc(size * sizeof(char));
int *line_numbers_tmp = (int *)malloc(size * sizeof(int));
if (tmp == NULL || line_numbers_tmp == NULL) {
printf("Memory allocation failed!\n");
exit(1);
}
strcpy(tmp, *text);
free(*text);
*text = tmp;
memcpy(line_numbers_tmp, *line_numbers, (*char_count) * sizeof(int));
free(*line_numbers);
*line_numbers = line_numbers_tmp;
}
char next_char = fgetc(fp);
if (next_char == '\n')
(*line_count)++; // 记录行数
else {
(*line_numbers)[*char_count] = *line_count; // 记录当前行号
(*text)[*char_count] = next_char; // 添加字符
(*char_count)++; // 统计字符数
}
}
}
// KMP算法在text中查找pattern,打印所在行号
void kmp(char *text, char *pattern, int *line_numbers, int char_count, int line_count) {
int text_len = strlen(text);
int pat_len = strlen(pattern);
if (text_len < pat_len) {
return;
}
int last_line = -1;
int *next = (int *)malloc(pat_len * sizeof(int));
next[0] = 0;
// 构建next数组
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i < pat_len;) {
if (pattern[i] == pattern[j]) { // 如果当前字符匹配前缀
j++;
next[i] = j;
i++; // 继续匹配下一个字符
} else if (j > 0) {
j = next[j - 1];
} else {
next[i] = 0;
i++; // 继续匹配下一个字符
}
}
// KMP匹配算法
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < text_len;) {
if (text[i] == pattern[j]) { // 如果当前字符匹配
i++; // 文本下标右移
j++; // 模式下标右移
} else if (j != 0) {
j = next[j - 1]; // 模式下标回退到next[j-1]
} else {
i++; // 文本下标右移
}
if (j == pat_len) { // 如果找到匹配
if (line_numbers[i - j] != last_line) {
last_line = line_numbers[i - j];
printf("%d ", last_line); // 打印行号
}
}
}
printf("\n");
free(next); // 释放next数组空间
}
int main() {
// 获取需要查找的单词数
printf("Please enter the number of words you want to query: ");
int word_count = get_word_count();
// 为word_count个单词分配空间,并检查内存分配是否成功
char **words = allocate_words(word_count);
// 读取word_count个单词到words中,并检查每个单词的内存分配是否成功
printf("Please enter the words you want to query in order: \n");
get_words(words, word_count);
// 打开文本文件,检查文件打开是否成功
FILE *fp = fopen("./novel.txt", "r");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("File open failed!\n");
exit(1); // 文件打开失败则退出程序
}
// 定义变量,记录文本内容、文本长度、行号数组、字符数、行数
char *text;
int *line_numbers;
int char_count = 0;
int line_count = 1;
// 读取文本
read_text(fp, &text, &line_numbers, &char_count, &line_count);
// 查找每个单词并精准打印行号
for (int i = 0; i < word_count; ++i) {
printf("%s exist in lines: ", words[i]);
kmp(text, words[i], line_numbers, char_count, line_count);
}
// 释放所有内存空间,避免内存泄露
for (int i = 0; i < word_count; ++i)
free(words[i]);
free(words);
free(text);
free(line_numbers);
}
novel.txt
The Adventures of C Program
It was a bright morning. C Program woke up and checked if (time == 9AM) then he would go to work. C worked as a coder at a tech company.
While C was walking to work, he thought about the tasks for today. His boss asked him to implement some new functions for their software. C needed to design the functions, define the arguments, return the values and make sure no errors occurred.
When C arrived at the office, he turned on his computer and began to code. He wrote:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
char name[50];
printf("Please enter your name: ");
scanf("%s", name);
print("Hello %s! Welcome.", name);
if (age > 0 && age < 120){
print("Your age is %d.", age);
}else{
print("Invalid age!");
}
float height;
printf("Please enter your height (cm): ");
scanf("%f", &height);
switch(gender){
case 'm':
printf("Male");
break;
case 'f':
printf("Female");
break;
default:
printf("Invalid");
}
}
While C was coding, he sipped some coffee and took a break when he was tired. By the end of the day, his functions were finished. C felt content and looked forward to more work the next day.
The end.
结束语
因为是算法小菜,所以提供的方法和思路可能不是很好,请多多包涵~如果有疑问欢迎大家留言讨论,你如果觉得这篇文章对你有帮助可以给我一个免费的赞吗?我们之间的交流是我最大的动力!文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-775422.html
到了这里,关于【数据结构与算法】文学语言助手(C\C++)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!



![[数据结构-C语言] 算法的时间复杂度](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/432826-1.png)