💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
💥1 概述
📚2 运行结果
🎉3 参考文献
🌈4 Matlab代码实现
💥1 概述
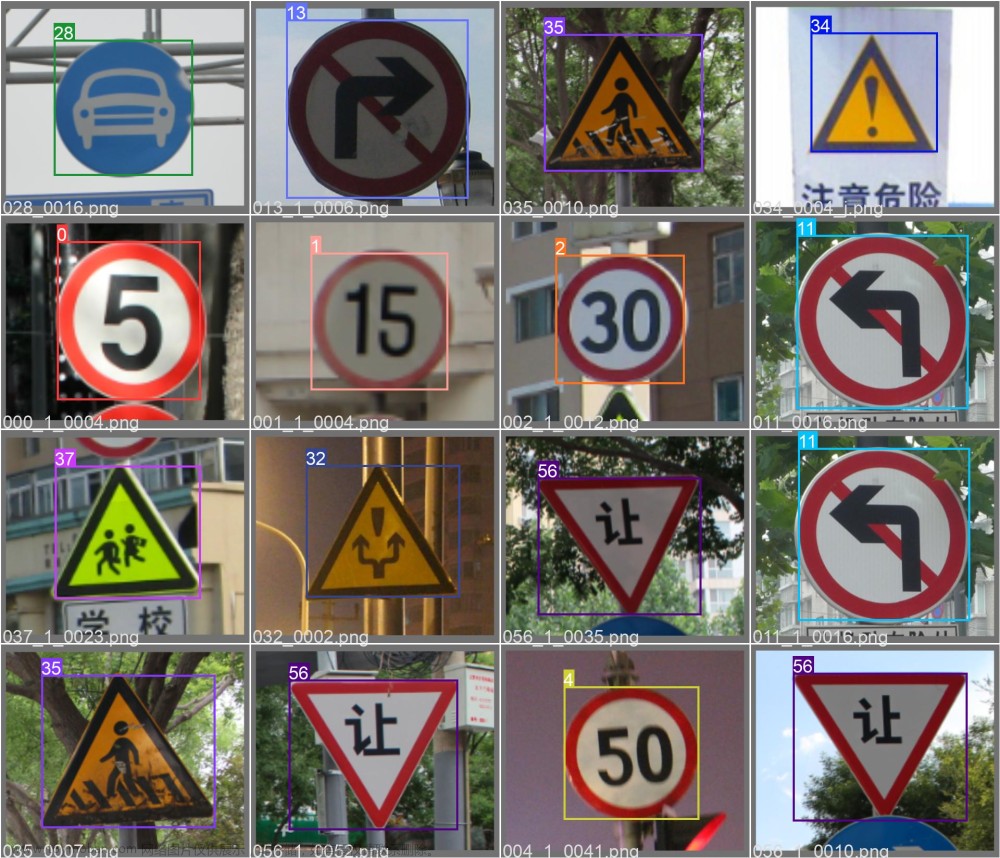
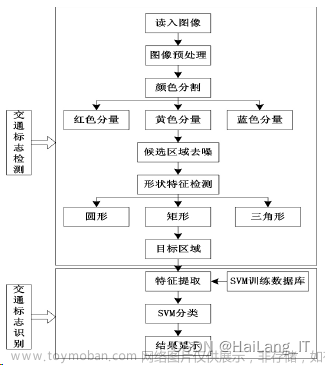
人工智能技术的快速发展使得无人驾驶技术在现实中得以实现,而对车身外界实时情况的感知则是无人驾驶核心环节之一。无人驾驶车辆获取外界信息的手段之一就是利用视觉传感器感知实时交通情况,如交通信号、交通标识、行人和车辆等。对交通标志的识别作为无人驾驶中一项重要任务,在实际检测过程中却极其复杂,如遇到交通标志被遮挡,雨天视线模糊等情况,所以对交通标志的识别在速度和精度上都是一项挑战。对交通标志的识别可以利用基于深度学习的卷积神经网络来实现,它通过在大量的图片数据中训练并学习到指定目标的特,实现对交通标志的检测和定位。同时考虑到模型要在无人驾驶移动端的使用,限速标志的基本特征(外边框为红色且为圆形)。本文利用颜色空间的方法,先提取出红色区域,在通过图像的开闭运算,膨胀腐蚀操作进行预处理,最后在利用不同区域是目标的可能性进行逐一筛选。这里要指出目标的可能性这一说法,是指该区域类圆的概率以及该区域的面积的加权和。最后,针对一些红的目标可能重叠的情况,进行最后的加工。 紧接着提取标志中的数字,通过对给定的图像进行统计,可以发现如果是限速标志,其直方图通常是双峰,一个峰为目标区域,另一个则为背景。这样就可以分别处理数字了。
📚2 运行结果




















部分代码:
clear all;
close all;
for name = 1 : 20% for name = 2 : 2
% name = 10;//16
% for name = 16 : 16
figure(name)
filename = ['test' num2str(name) '.jpg'];
% filename = [num2str(name) '.bmp'];
img_rgb = imread(filename);
% rgb 转 hsv 空间
img_hsv = rgb2hsv(img_rgb);
%****************** 提取红色 ******************%
[height,width,c]= size(img_hsv);
for i=1:height
for j=1:width
h=img_hsv(i,j,1);
s=img_hsv(i,j,2);
v=img_hsv(i,j,3);
%通过将h通道颜色值特定范围内饱和度设为0,保留范围外颜色值
if ( h > 156/180 || h < 10/180 ) && s > 43/255 && v > 46/255
% if ( h > 156/180 || h < 10/180 ) && s > 60/255 && v > 60/255
img_hsv(i,j,1) = 0;
img_hsv(i,j,2) = 0;
img_hsv(i,j,3) = 1;
else
img_hsv(i,j,1) = 0;
img_hsv(i,j,2) = 0;
img_hsv(i,j,3) = 0;
end
end
end
img_red = hsv2rgb(img_hsv);
%****************** 二值化 ******************%
level=graythresh(img_red);
% img_bw = img_red;
img_bw = im2bw(img_red,level);
% % subplot(221),imshow(img_rgb);
% % subplot(222),imshow(img_red)
% % subplot(223),imshow(img_bw);
%****************** 膨胀后填充 ******************%
se_dilate_fill = strel('disk',3);
img_dilate = imdilate(img_bw,se_dilate_fill);
img_dilate_closed = bwfill(img_dilate,'holes');
%****************** 腐蚀重建后在填充 ******************%
se_erode_restruct = strel('disk',5);
img_bw_eroded = imerode(img_dilate_closed,se_erode_restruct);
img_eroded_restruct = imreconstruct(img_bw_eroded,img_dilate_closed);
img_eroded_restruct_fill = bwfill(img_eroded_restruct,'holes');
%****************** 开运算 ******************%
se_open = strel('disk',10);
img_eroded_restruct_fill_open = imopen(img_eroded_restruct_fill,se_open);
% % subplot(221),imshow(img_rgb);
% % subplot(222),imshow(img_red)
% % subplot(223),imshow(img_eroded_restruct_fill_open);
% %****************** 根据面积信息再腐蚀 ******************%
region = regionprops(bwlabel(img_eroded_restruct_fill_open),'Area','Perimeter','Centroid','Boundingbox');
%%% 自适应构造结构元素
%%% 取前三个最像圆的区域求平均面积
CIRCLESIMLIAR = 0.6;
WEIGHTMINCOMPUTERATE = 0.2;
RADIUSRATE = 2/3;
Circle_simliarity_result = zeros(1,size(region,1));
maxarea = 0;
for i = 1 : size(region,1)
circle_simliarity = 4*pi*region(i).Area/(region(i).Perimeter^2);
Circle_simliarity_result(1,i) = circle_simliarity;
if region(i).Area > maxarea
maxarea = region(i).Area;
end
end
[Circle_simliarity,Circle_simliarity_index] = sort(-Circle_simliarity_result);
area = 0;i = 0;
for i = 1 : size(region,1)
% if i > maxcount || -Circle_simliarity(i) < CIRCLESIMLIAR
% if -Circle_simliarity(i) < CIRCLESIMLIAR || region( Circle_simliarity_index(i) ).Area/maxarea < WEIGHTMINCOMPUTERATE
if -Circle_simliarity(i) < CIRCLESIMLIAR && region( Circle_simliarity_index(i) ).Area/maxarea > WEIGHTMINCOMPUTERATE
break;
end
area = area + region( Circle_simliarity_index(i) ).Area;
end
radius = floor(sqrt( area/i/pi ) * RADIUSRATE );
se_better_erode = strel('disk',radius);
img_better_eroded = imerode(img_eroded_restruct_fill_open,se_better_erode);
img_better_eroded_restruct = imreconstruct(img_better_eroded,img_eroded_restruct_fill_open);
% subplot(221),imshow(img_rgb);
% subplot(222),imshow(img_eroded_restruct_fill_open)
% subplot(223),imshow(img_better_eroded_restruct);
%
% % %****************** 提取目标区域 ******************%
CIRCLEWEIGHT = 0.7;
CIRCLESIMILARITYTHRESHOLD = 0.9;
AREAWEIGHTTHRESHOLD = 0.2;
WEIGHTTHRESHOLD = 0.7;
[region,result] = detectTarget(img_better_eroded_restruct,CIRCLEWEIGHT,CIRCLESIMILARITYTHRESHOLD,AREAWEIGHTTHRESHOLD);
[target_num,Target_index] = drawTarget(img_rgb,region,result,WEIGHTTHRESHOLD);
% subplot(221),imshow(img_rgb);
% subplot(222),imshow(img_eroded_restruct_fill_open)
% subplot(223),imshow(img_better_eroded_restruct);
% % % 标定数字
for i = 1 : target_num
tmpimg = img_rgb;
rectanglesize = region(Target_index(i)).BoundingBox;
[height,width,c]= size(img_hsv);
for m = 1 : height
for n = 1 : width
if ( ~( n > rectanglesize(1) && n < rectanglesize(1)+rectanglesize(3) && m > rectanglesize(2) && m < rectanglesize(2) + rectanglesize(4)) ...
|| img_better_eroded_restruct(m,n) == 0 || img_bw(m,n) )
tmpimg(m,n,:) = [255 255 255];
end
end
end
tmpimg = tmpimg(rectanglesize(2) : rectanglesize(2) + rectanglesize(4) ,rectanglesize(1):rectanglesize(1)+rectanglesize(3) );
len = rectanglesize(3)+rectanglesize(4);
%%% 双峰阈值分割
h = imhist(tmpimg);
% 求极大值 粗略的算了一下
[cnt,x] = findpeaks(h,'minpeakdistance',40,'minpeakheight',20);
if cnt > 2
n = length(x);
yu = x(1)+x(n)-2;
img_num_bw = ~im2bw(tmpimg,yu/510);
else
% level = graythresh(tmpimg);
% img_num_bw = ~im2bw(tmpimg,level);
% subplot(221),imhist(tmpimg);
% subplot(222),imshow(img_num_bw)
% subplot(223),imshow(sep_2)
continue
end
se_sep = strel('rectangle',[1,min(15,floor(len/20))] );
sep_1 = imerode(img_num_bw,se_sep);
sep_2 = imreconstruct(sep_1,img_num_bw);
sep_region = regionprops(bwlabel(sep_2),'Area','Perimeter','Centroid','Boundingbox');
for k = 1 : size(sep_region)
subplot(224)
rectangle('Position',sep_region(k).BoundingBox + [rectanglesize(1) rectanglesize(2) 0 0],'Curvature',[0,0],'LineWidth',2 ,'LineStyle','-','EdgeColor','r');
hold on
subplot(221),imhist(tmpimg);
subplot(222),imshow(img_num_bw)
subplot(223),imshow(sep_2)
end
% % sep_2 = bwfill(sep_2,'holes');
end
if target_num > 0 || maxarea == 0
continue;
end
% 没发现目标,但存在可能目标块,认为目标可能位于最大块中
%
% %****************** 提取最大色块 ******************%
[Area,Area_index]=sort(-[region.Area]);
maxarea = 0;
if size(region,1) > 1
maxarea = -Area(1);
end
rectanglesize = region(Area_index(1)).BoundingBox;
[height,width,c]= size(img_hsv);
for i=1:height
for j=1:width
if ~( j > rectanglesize(1) && j < rectanglesize(1)+rectanglesize(3) && i > rectanglesize(2) && i < rectanglesize(2) + rectanglesize(4))
img_bw(i,j) = 0;
end
end
end
img_bigest_eroded = imerode(img_bw,se_better_erode);
img_bigest_eroded_restruct = imreconstruct(img_bigest_eroded,img_bw);
img_dilate = imdilate(img_bw,se_better_erode);
img_bigest_eroded_restruct_fill = bwfill(img_bigest_eroded_restruct,'holes');
% subplot(224),imshow(img_red);
% subplot(224),imshow(img_bigest_eroded_restruct_fill);
% subplot(221),imshow(img_bw);
% %****************** 提取目标区域 ******************%
CIRCLEWEIGHT = 0.7;
CIRCLESIMILARITYTHRESHOLD = 0.1;
AREAWEIGHTTHRESHOLD = 0.2;
WEIGHTTHRESHOLD = 0.5;
[region,result] = detectTarget(img_bigest_eroded_restruct_fill,CIRCLEWEIGHT,CIRCLESIMILARITYTHRESHOLD,AREAWEIGHTTHRESHOLD);
[target_num,index] = drawTarget(img_rgb,region,result,WEIGHTTHRESHOLD);
end
🎉3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
[1]陈哲. 自然场景下的小目标交通标志检测技术研究[D].南京邮电大学,2022.DOI:10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2022.001500.文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-775760.html
[2]王强(Eric Wang). 基于深度学习的交通标志检测和识别[D].南京邮电大学,2021.DOI:10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2021.001659.文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-775760.html
🌈4 Matlab代码实现
到了这里,关于【图像处理】交通标志检测(Matlab代码实现)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!