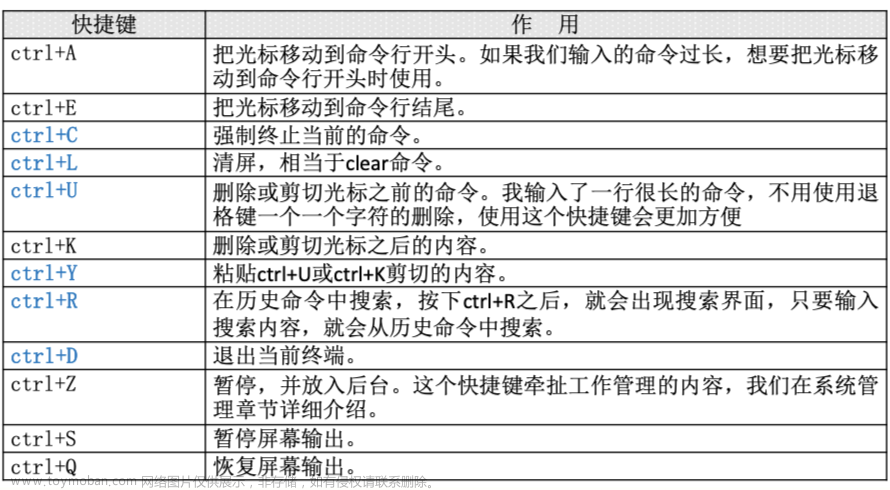
前言
本篇文章属于学习笔记,来源于B站教学视频,相关代码工程请从源地址自行下载。这位Up讲解得很好,适合同学们一起学习,在这里推荐给大家。本文为个人学习笔记,只能做参考,细节方面建议观看视频,肯定受益匪浅。
51单片机入门教程-2020版 程序全程纯手打 从零开始入门_哔哩哔哩_bilibilihttps://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Mb411e7re?p=1
一、环境搭建
1、开发软件Keil5C51

2、烧录软件stc-isp

3、普中51单片机开发板

二、单片机介绍
1、单片机(Micro Controller Unit ,即MCU)
2、本篇所使用的单片机为STC89C52单片机
所属系列为8051,即51单片机。8051最开始指在80年代生产的8051内核的单片机。后延伸为只要是8051内核的单片机,都统称为51单片机。
3、51单片机命名规则

4、51单片机结构

三、单片机实操一:点亮一个LED
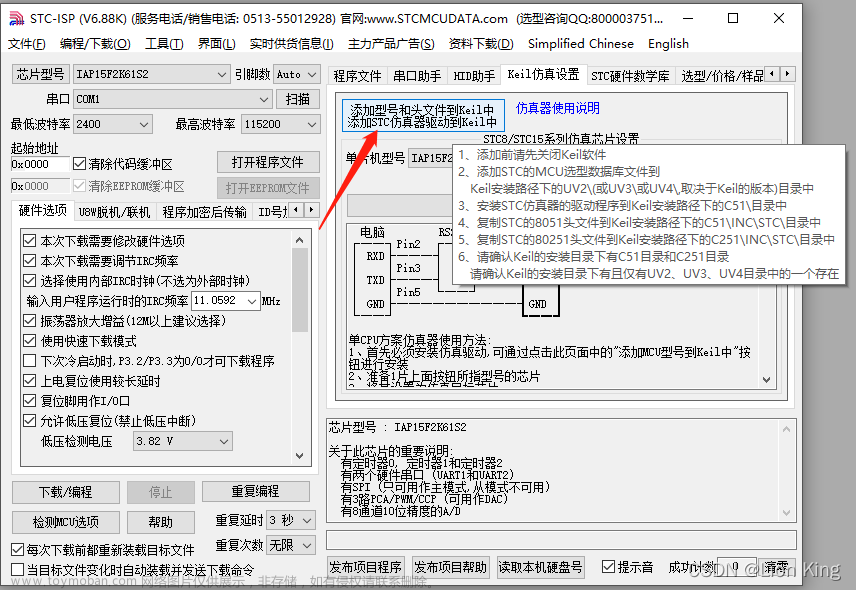
1、打开STC-ISP添加芯片包到开发环境
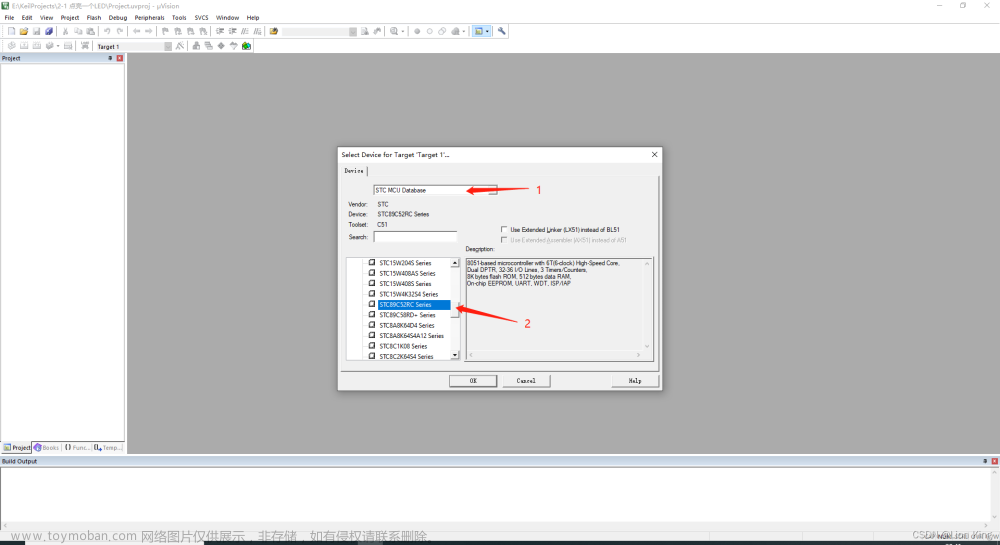
2、创建工程



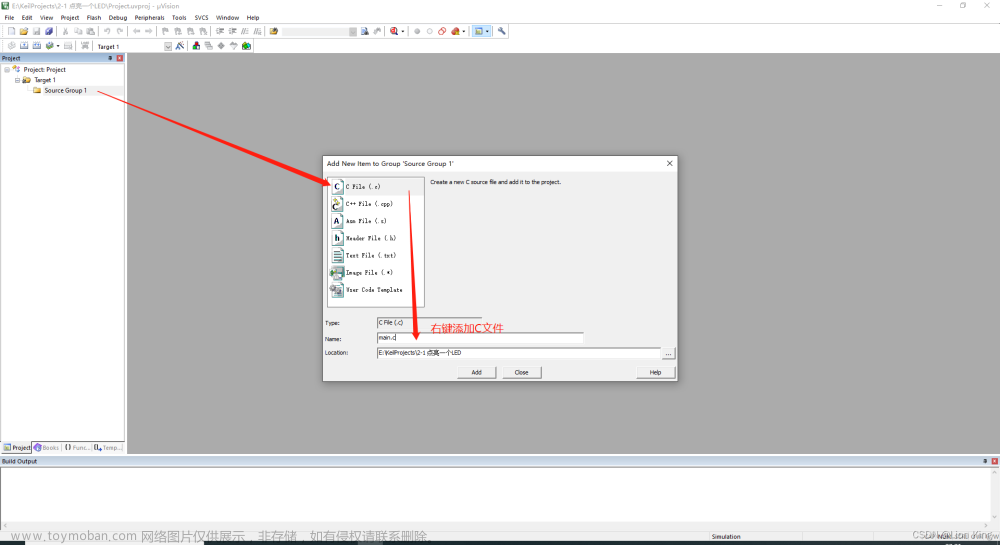
3、创建文件
4、LED的硬件原理图
在下面的图中,我们可以看到LED最终连上了单片机的管脚。而单片机需要通过CPU控制寄存器的值,进而通过驱动器加大控制力度,由控制电路输出高低电平(对应寄存器1/0)。因此,程序需要在对应的寄存器上写1或0,即可控制LED的亮灭。

5、编写程序
根据硬件原理图和寄存器定义,来对操作寄存器地址,实现灯的点亮
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
void main()
{
P2 = 0xFE; //1111 1110
}6、实验过程与代码解释
(1)点击F7编译单个文件,编译失败,给出P2不认识的提示

(2)添加H文件,继续编译,编译通过 ,说明头文件定义了P2

(3)为什么控制的是P2?因为硬件原理图以及头文件的定义,拉低电平即可点亮一盏灯!

7、生成文件,下载到板子上,重新上电之后可运行该程序




四、单片机实操二:LED闪烁
1、在指定路径下创建工程并添加新文件
2、通过STC-ISP拷贝延时代码

3、编写程序
加入延时,方便观察灯的闪烁
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include <INTRINS.H>
void Delay500ms() //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j, k;
_nop_(); //An empty function, from INTRINS.H
i = 4;
j = 205;
k = 187;
do
{
do
{
while (--k);
} while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
void main()
{
P2=0xFE;
Delay500ms();
P2=0xFF;
Delay500ms();
}4、实验过程


五、单片机实操三:LED流水灯
1、在指定路径下创建工程并添加新文件
2、编写程序
让LED循环点亮,像流水一样
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include <INTRINS.H>
void Delay500ms() //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j, k;
_nop_();
i = 4;
j = 205;
k = 187;
do
{
do
{
while (--k);
} while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
P2=0xFE; //1111 1110
Delay500ms();
P2=0xFD; //1111 1101
Delay500ms();
P2=0xFB; //1111 1011
Delay500ms();
P2=0xF7; //1111 0111
Delay500ms();
P2=0xEF; //1110 1111
Delay500ms();
P2=0xDF; //1101 1111
Delay500ms();
P2=0xBF; //1011 1111
Delay500ms();
P2=0x7F; //0111 1111
Delay500ms();
}
}六、单片机实操四:LED流水灯Plus
1、在指定路径下创建工程并添加新文件
2、编写程序
将延时函数参数化。
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include <INTRINS.H>
void Delayxms(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--; //xms=xms-1
}
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
P2=0xFE; //1111 1110
Delayxms(500);
P2=0xFD; //1111 1101
Delayxms(500);
P2=0xFB; //1111 1011
Delayxms(500);
P2=0xF7; //1111 0111
Delayxms(500);
P2=0xEF; //1110 1111
Delayxms(500);
P2=0xDF; //1101 1111
Delayxms(500);
P2=0xBF; //1011 1111
Delayxms(500);
P2=0x7F; //0111 1111
Delayxms(500);
}
}3、51单片机的数据类型
我们在上面的程序中使用到了数据类型unsigned int xms,即xms在单片机中能表示0~65535

七、单片机实操五:独立按键控制LED灯亮灭
1、在指定路径下创建工程并添加新文件
2、独立按键原理图

3、编写程序
按下按键亮灯,松开按键灭灯。
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
void main()
{
while(1)
{
if(P30==0)
{
P20=0;
}
else
{
P20=1;
}
}
}4、51单片机数据运算
上述代码中,我们使用到了==这个运算符,表示等于。

5、51单片机基本语句
上述程序用到了if语句,通过判断按键的动作来实现灯的亮灭

6、注意事项
程序写的是P30独立按键,根据原理图,需要按下K2才能点亮第一盏灯。(原理图设计者并没有按照顺序一一对应按键,这是设计者埋下的小坑)
P30是H文件中定义的,如果是其他H文件可能没有或者用另一个变量表示,这个时候需要你自己去写或者更改变量
八、单片机实操六:独立按键控制LED灯状态
1、在指定路径下创建工程并添加新文件
2、编写程序
按键消抖,检测松手,才改变LED灯的状态,使其松开按键后长亮或长灭。
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
if(P31==0)
{
Delay(20); // Keys away shaking
while(P31==0);
Delay(20); // Detection of let go
P20=~P20;
}
}
}九、单片机实操七:独立按键控制LED显示二进制
1、在指定路径下创建工程并添加新文件
2、编写程序
通过不停的按下按键,使得灯以二进制的方式,不断往上加一,达到用灯来表示按键次数
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}
void main()
{
unsigned char LEDNum=0; // char max num is 255
while(1)
{
if(P31==0)
{
Delay(20);
while(P31==0);
Delay(20);
LEDNum++;
P2=~LEDNum;
}
}
}十、单片机实操八:独立按键控制LED移位
1、在指定路径下创建工程并添加新文件
2、编写程序
按下P31,往左边移一位;按下P30,往右边移一位,以LED灯来展示。
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
void Delay(unsigned int xms); // must statement
unsigned char LEDNum; // The global variable
void main()
{
P2=~0x01; //int P2
while(1)
{
if(P31==0)
{
Delay(20);
while(P31==0);
Delay(20);
LEDNum++;
if(LEDNum>=8)
LEDNum=0;
P2=~(0x01<<LEDNum); // 0x01 of P2 need shift to the left LEDNum, and get the not
}
if(P30==0)
{
Delay(20);
while(P30==0);
Delay(20);
if(LEDNum==0)
LEDNum=7;
else
LEDNum--;
P2=~(0x01<<LEDNum);
}
}
}
void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}
十一、单片机实操九:静态数码管显示
1、在指定路径下创建工程并添加新文件
2、单个数码管引脚定义
数码管的接法,有共阳和共阴之分。共阴时,拉高电压即可点亮。共阳时,拉低电平点亮。

3、开发板四位一体的数码管引脚定义

4、硬件原理图
138译码器控制数码管使能(使用3个单片机输入控制8个数码管显示),每个数字的一个笔画由双向数据缓存器245(单片机输出能力有限,需要该芯片提高输入能力)控制亮灭。
因此,首先控制P22~P24来选中数码管,然后选中数码管的笔画,最终呈现数据。


5、C51单片机数组

6、C51单片机子函数

7、数码管段码表(共阴极电路,共阳极则不一样)

8、编写程序
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
unsigned char NixieTable[]={
0x3f,0x06,0x5b,0x4f,
0x66,0x6d,0x7d,0x07,
0x7f,0x6f,0x77,0x7c,
0x39,0x5e,0x79,0x71, 0x00};
void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number)
{
switch(Location)
{
case 1:
P24=1;P23=1;P22=1;break;
case 2:
P24=1;P23=1;P22=0;break;
case 3:
P24=1;P23=0;P22=1;break;
case 4:
P24=1;P23=0;P22=0;break;
case 5:
P24=0;P23=1;P22=1;break;
case 6:
P24=0;P23=1;P22=0;break;
case 7:
P24=0;P23=0;P22=1;break;
case 8:
P24=0;P23=0;P22=0;break;
}
P0=NixieTable[Number];
}
void main()
{
// P24=1; //Controls a nixie tube
// P23=0;
// P22=1;
// P0=0x7D; //value is 6
Nixie(2,3);
while(1)
{
}
}十二、单片机实操十:动态数码管显示
1、在指定路径下创建工程并添加新文件
2、编写程序
动态清零,数字消影,来实现动态数码管显示,这是单片机不断扫描来成像的,将耗费大量CPU资源。因此,硬件电路一般会加1640的芯片来驱动,将大量减少扫描带来的CPU损耗。
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
unsigned char NixieTable[]={
0x3f,0x06,0x5b,0x4f,
0x66,0x6d,0x7d,0x07,
0x7f,0x6f,0x77,0x7c,
0x39,0x5e,0x79,0x71, 0x00};
void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}
void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number)
{
switch(Location)
{
case 1:
P24=1;P23=1;P22=1;break;
case 2:
P24=1;P23=1;P22=0;break;
case 3:
P24=1;P23=0;P22=1;break;
case 4:
P24=1;P23=0;P22=0;break;
case 5:
P24=0;P23=1;P22=1;break;
case 6:
P24=0;P23=1;P22=0;break;
case 7:
P24=0;P23=0;P22=1;break;
case 8:
P24=0;P23=0;P22=0;break;
}
P0=NixieTable[Number];
Delay(1); // Shadow elimination
P0=0x00; // reset
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
Nixie(1,1);
Nixie(2,2);
Nixie(3,3);
}
}十三、单片机实操十一:模块化编程
1、在指定路径下创建工程并添加新文件
2、模块化编程

3、模块化编程框图

4、模块化编程注意事项

5、C预编译

6、增加中文注释

7、编写代码
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h" // 使用双引号,优先查询工程目录
#include "Nixie.h"
void main()
{
while(1)
{
Nixie(1,1);
Nixie(2,2);
Nixie(3,3);
}
}Delay.c
void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}Delay.h
#ifndef __DELAY_H__
#define __DELAY_H__
void Delay(unsigned int xms);
#endifNixie.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
unsigned char NixieTable[]={
0x3f,0x06,0x5b,0x4f,
0x66,0x6d,0x7d,0x07,
0x7f,0x6f,0x77,0x7c,
0x39,0x5e,0x79,0x71, 0x00};
void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number)
{
switch(Location)
{
case 1:
P24=1;P23=1;P22=1;break;
case 2:
P24=1;P23=1;P22=0;break;
case 3:
P24=1;P23=0;P22=1;break;
case 4:
P24=1;P23=0;P22=0;break;
case 5:
P24=0;P23=1;P22=1;break;
case 6:
P24=0;P23=1;P22=0;break;
case 7:
P24=0;P23=0;P22=1;break;
case 8:
P24=0;P23=0;P22=0;break;
}
P0=NixieTable[Number];
Delay(1); // Shadow elimination
P0=0x00; // reset
}Nixie.h
#ifndef __NIXIE_H__
#define __NIXIE_H__
void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number);
#endif十四、单片机实操十二:LCD1602调试工具
1、在指定路径下创建工程并添加新文件
2、LCD1602调试工具

3、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "LCD1602.h"
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowChar(1,1,'B');
LCD_ShowString(1,3,"Hello");
LCD_ShowNum(1,9,123,3);
LCD_ShowSignedNum(1,13,-66,2);
LCD_ShowHexNum(2,1,0xA8,2);
LCD_ShowBinNum(2,4,0xAA,8);
LCD_ShowChar(2,13,'A');
while(1)
{
}
}LCD1602.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
//引脚配置:
sbit LCD_RS=P2^6;
sbit LCD_RW=P2^5;
sbit LCD_EN=P2^7;
#define LCD_DataPort P0
//函数定义:
/**
* @brief LCD1602延时函数,12MHz调用可延时1ms
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_Delay()
{
unsigned char i, j;
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
/**
* @brief LCD1602写命令
* @param Command 要写入的命令
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_WriteCommand(unsigned char Command)
{
LCD_RS=0;
LCD_RW=0;
LCD_DataPort=Command;
LCD_EN=1;
LCD_Delay();
LCD_EN=0;
LCD_Delay();
}
/**
* @brief LCD1602写数据
* @param Data 要写入的数据
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_WriteData(unsigned char Data)
{
LCD_RS=1;
LCD_RW=0;
LCD_DataPort=Data;
LCD_EN=1;
LCD_Delay();
LCD_EN=0;
LCD_Delay();
}
/**
* @brief LCD1602设置光标位置
* @param Line 行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 列位置,范围:1~16
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_SetCursor(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column)
{
if(Line==1)
{
LCD_WriteCommand(0x80|(Column-1));
}
else if(Line==2)
{
LCD_WriteCommand(0x80|(Column-1+0x40));
}
}
/**
* @brief LCD1602初始化函数
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_Init()
{
LCD_WriteCommand(0x38);//八位数据接口,两行显示,5*7点阵
LCD_WriteCommand(0x0c);//显示开,光标关,闪烁关
LCD_WriteCommand(0x06);//数据读写操作后,光标自动加一,画面不动
LCD_WriteCommand(0x01);//光标复位,清屏
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置上显示一个字符
* @param Line 行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Char 要显示的字符
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowChar(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,char Char)
{
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
LCD_WriteData(Char);
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始显示所给字符串
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param String 要显示的字符串
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowString(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,char *String)
{
unsigned char i;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
for(i=0;String[i]!='\0';i++)
{
LCD_WriteData(String[i]);
}
}
/**
* @brief 返回值=X的Y次方
*/
int LCD_Pow(int X,int Y)
{
unsigned char i;
int Result=1;
for(i=0;i<Y;i++)
{
Result*=X;
}
return Result;
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始显示所给数字
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Number 要显示的数字,范围:0~65535
* @param Length 要显示数字的长度,范围:1~5
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length)
{
unsigned char i;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
for(i=Length;i>0;i--)
{
LCD_WriteData(Number/LCD_Pow(10,i-1)%10+'0');
}
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始以有符号十进制显示所给数字
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Number 要显示的数字,范围:-32768~32767
* @param Length 要显示数字的长度,范围:1~5
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowSignedNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,int Number,unsigned char Length)
{
unsigned char i;
unsigned int Number1;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
if(Number>=0)
{
LCD_WriteData('+');
Number1=Number;
}
else
{
LCD_WriteData('-');
Number1=-Number;
}
for(i=Length;i>0;i--)
{
LCD_WriteData(Number1/LCD_Pow(10,i-1)%10+'0');
}
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始以十六进制显示所给数字
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Number 要显示的数字,范围:0~0xFFFF
* @param Length 要显示数字的长度,范围:1~4
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowHexNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length)
{
unsigned char i,SingleNumber;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
for(i=Length;i>0;i--)
{
SingleNumber=Number/LCD_Pow(16,i-1)%16;
if(SingleNumber<10)
{
LCD_WriteData(SingleNumber+'0');
}
else
{
LCD_WriteData(SingleNumber-10+'A');
}
}
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始以二进制显示所给数字
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Number 要显示的数字,范围:0~1111 1111 1111 1111
* @param Length 要显示数字的长度,范围:1~16
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowBinNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length)
{
unsigned char i;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
for(i=Length;i>0;i--)
{
LCD_WriteData(Number/LCD_Pow(2,i-1)%2+'0');
}
}
LCD1602.h
#ifndef __LCD1602_H__
#define __LCD1602_H__
//用户调用函数:
void LCD_Init();
void LCD_ShowChar(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,char Char);
void LCD_ShowString(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,char *String);
void LCD_ShowNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length);
void LCD_ShowSignedNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,int Number,unsigned char Length);
void LCD_ShowHexNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length);
void LCD_ShowBinNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length);
#endif
4、注意事项
单引号和双引号都有全角和半角之分,全角的又叫中文字符,半角的又称英文字符。在c语言中,全角字符没有任何意义,它就是一个普通字符,没有含义;半角字符才有不同的意义:
双引号用来括起一个字符串,如"China";
单引号原来括起一个字符,如'f'。
二者含义不同,不能混用。

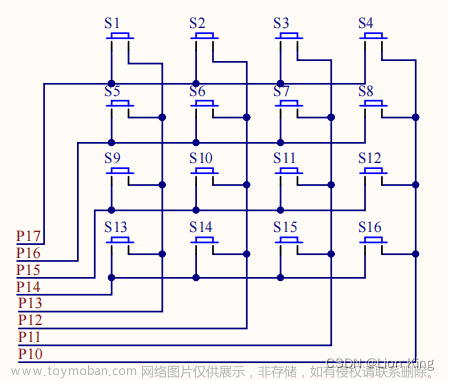
十五、单片机实操十三:矩阵键盘
1、在指定路径下创建工程并添加新文件
2、矩阵键盘介绍

3、扫描的概念

4、硬件连线
我们想选取1、5、9、13,即第一列,可以先把P1全部置为高,即全部拉高;接着让P13拉低,则选中了第一列。其他也这样操作。
5、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "Delay.h"
#include "MatrixKey.h"
unsigned char KeyNum;
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
// LCD_ShowChar(1,1,'B');
LCD_ShowString(1,3,"MatrixKey:");
// LCD_ShowNum(1,9,123,3);
// LCD_ShowSignedNum(1,13,-66,2);
// LCD_ShowHexNum(2,1,0xA8,2);
// LCD_ShowBinNum(2,4,0xAA,8);
// LCD_ShowChar(2,13,'A');
while(1)
{
KeyNum=MatrixKey();
if(KeyNum)
{
LCD_ShowNum(2,3,KeyNum,2);
}
}
}MatrixKey.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
unsigned char MatrixKey()
{
unsigned char KeyNumber=0;
P1=0xFF;
P13=0;
if(P17==0){Delay(20);while(P17==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=1;}
if(P16==0){Delay(20);while(P16==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=5;}
if(P15==0){Delay(20);while(P15==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=9;}
if(P14==0){Delay(20);while(P14==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=13;}
P1=0xFF;
P12=0;
if(P17==0){Delay(20);while(P17==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=2;}
if(P16==0){Delay(20);while(P16==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=6;}
if(P15==0){Delay(20);while(P15==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=10;}
if(P14==0){Delay(20);while(P14==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=14;}
P1=0xFF;
P11=0;
if(P17==0){Delay(20);while(P17==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=3;}
if(P16==0){Delay(20);while(P16==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=7;}
if(P15==0){Delay(20);while(P15==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=11;}
if(P14==0){Delay(20);while(P14==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=15;}
P1=0xFF;
P10=0;
if(P17==0){Delay(20);while(P17==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=4;}
if(P16==0){Delay(20);while(P16==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=8;}
if(P15==0){Delay(20);while(P15==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=12;}
if(P14==0){Delay(20);while(P14==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=16;}
return KeyNumber;
}MatrixKey.h
#ifndef __MATRIXKEY_H__
#define __MATRIXKEY_H__
unsigned char MatrixKey();
#endif其它文件:复制之前写的模块即可。
6、软件使用技巧:配置模板


十六、单片机实操十四:矩阵键盘密码锁
1、复制工程后打开
2、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "Delay.h"
#include "MatrixKey.h"
unsigned char KeyNum;
unsigned int Password, Count;
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
// LCD_ShowChar(1,1,'B');
LCD_ShowString(1,1,"Password:");
// LCD_ShowNum(1,9,123,3);
// LCD_ShowSignedNum(1,13,-66,2);
// LCD_ShowHexNum(2,1,0xA8,2);
// LCD_ShowBinNum(2,4,0xAA,8);
// LCD_ShowChar(2,13,'A');
while(1)
{
KeyNum=MatrixKey();
if(KeyNum)
{
if(KeyNum<=10) // 如果S1~S10按键按下,输入密码
{
if(Count<4) // 密码四位数
{
Password*=10; // 密码左移一位,这样就可以依次输入密码
Password+=KeyNum%10; // 获取一位密码,加入到原密码,此时10为0
Count++;
}
}
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Password,4);
if(KeyNum==11) // 确认
{
if(Password==1234)
{
LCD_ShowString(1,14,"OK ");
Password=0;
Count=0;
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Password,4);
}
else
{
LCD_ShowString(1,14,"ERR");
Password=0;
Count=0;
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Password,4);
}
}
if(KeyNum==12) //取消
{
Password=0;
Count=0;
LCD_ShowString(1,14," ");
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Password,4);
}
}
}
}其它文件:复制之前写的模块即可。
十七、单片机实操十五:定时器与按键控制LED流水灯模式
1、定时器介绍

2、STC89C52定时器资源

3、定时器狂框图
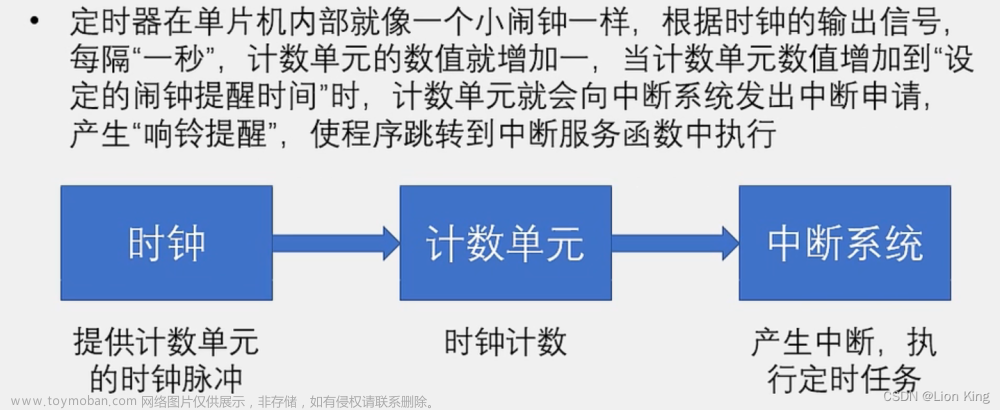
4、定时器工作模式

5、中断系统

6、中断程序流程
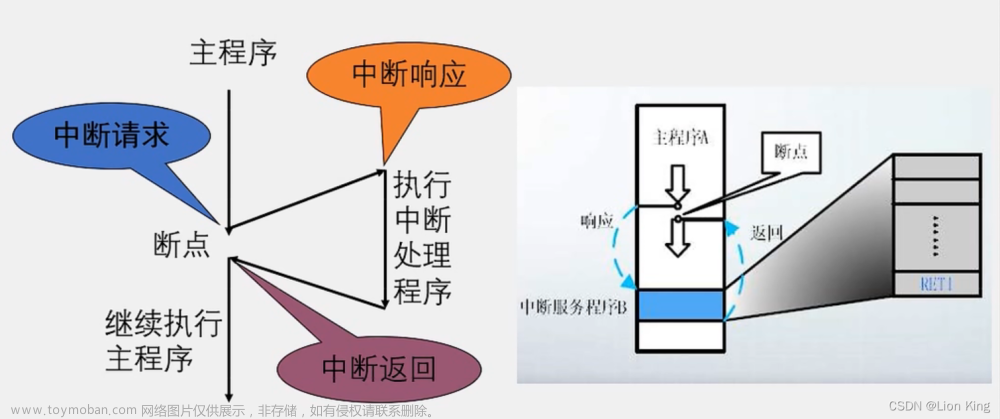
7、STC89C52中断资源

8、定时器和中断系统
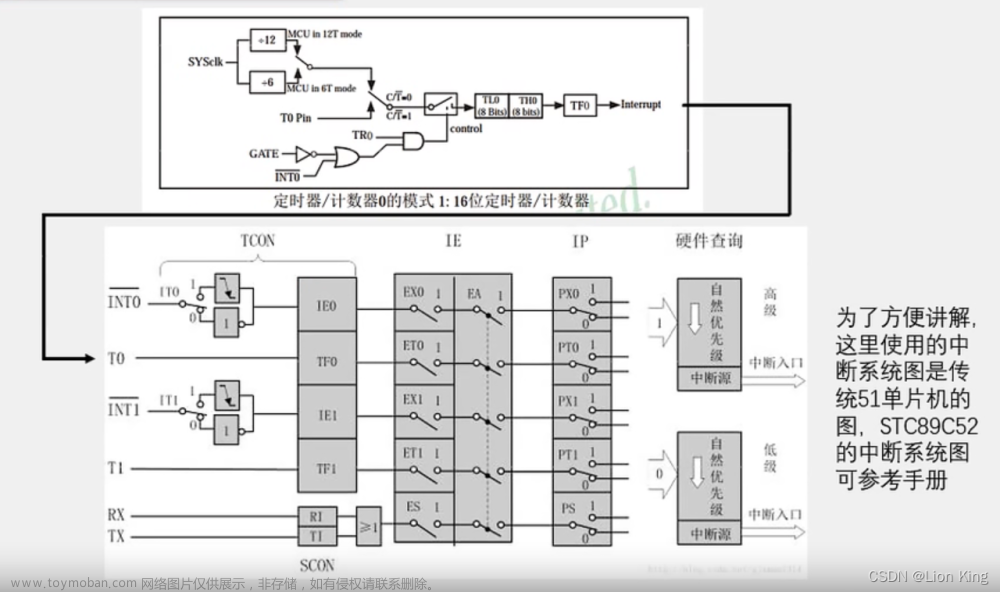
9、定时器相关寄存器

10、编写程序
通过独立按键控制流水灯模式,并由定时器执行流水灯。
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Timer0.h"
#include "Key.h"
#include <INTRINS.H>
unsigned char KeyNum,LEDMode;
void main()
{
P2=0xFE;
Timer0Init();
while(1)
{
KeyNum=Key(); //获取独立按键键码
if(KeyNum) //如果按键按下
{
if(KeyNum==1) //如果K1按键按下
{
LEDMode++; //模式切换,按1下按键是模式1,按2下是模式0,默认模式0
if(LEDMode>=2)LEDMode=0;
}
}
}
}
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1 //中断函数标识,含优先级
{
static unsigned int T0Count; //静态变量,拥有局部作用域,全局生命周期
TL0 = 0x18; //设置定时初值
TH0 = 0xFC; //设置定时初值
T0Count++; //T0Count计次,对中断频率进行分频
if(T0Count>=500)//分频500次,500ms
{
T0Count=0;
if(LEDMode==0) //模式判断
P2=_crol_(P2,1); //LED输出(循环左移函数,即使流水灯循环左移)
if(LEDMode==1)
P2=_cror_(P2,1);
}
}
Timer0.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
/**
* @brief 定时器0初始化,1毫秒@12.000MHz
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void Timer0Init(void)
{
TMOD &= 0xF0; //设置定时器模式,只改变T0,避免T1改变
TMOD |= 0x01; //设置定时器模式
TL0 = 0x18; //高位设置定时初值 65535/256
TH0 = 0xFC; //低位设置定时初值 65535%256
TF0 = 0; //清除TF0标志
TR0 = 1; //定时器0开始计时
ET0=1;
EA=1;
PT0=0;
}
/*定时器中断函数模板
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1
{
static unsigned int T0Count; //静态变量,拥有局部作用域,全局生命周期
TL0 = 0x18; //设置定时初值,像沙漏,重置沙漏时间
TH0 = 0xFC; //设置定时初值
T0Count++;
if(T0Count>=1000)
{
T0Count=0;
}
}
*/
Timer0.h
#ifndef __TIMER0_H__
#define __TIMER0_H__
void Timer0Init(void);
#endif
Key.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
/**
* @brief 获取独立按键键码
* @param 无
* @retval 按下按键的键码,范围:0~4,无按键按下时返回值为0
*/
unsigned char Key()
{
unsigned char KeyNumber=0;
if(P31==0){Delay(20);while(P31==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=1;}
if(P30==0){Delay(20);while(P30==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=2;}
if(P32==0){Delay(20);while(P32==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=3;}
if(P33==0){Delay(20);while(P33==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=4;}
return KeyNumber;
}
Key.h
#ifndef __KEY_H__
#define __KEY_H__
unsigned char Key();
#endif
其它文件:复制之前写的模块即可。
11、定时器代码获取

十八、单片机实操十六:定时器时钟
1、编写程序
制作一个一天时间的计时器。
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Timer0.h"
#include "Delay.h"
#include "LCD1602.h"
unsigned char Sec, Min=59, Hour=23;
void main()
{
Timer0Init();
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowString(1,1,"Clock:");
while(1)
{
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Hour,2);
LCD_ShowString(2,3,":");
LCD_ShowNum(2,4,Min,2);
LCD_ShowString(2,6,":");
LCD_ShowNum(2,7,Sec,2);
}
}
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1 //中断函数标识,含优先级
{
static unsigned int T0Count; //静态变量,拥有局部作用域,全局生命周期
TL0 = 0x18; //设置定时初值
TH0 = 0xFC; //设置定时初值
T0Count++; //T0Count计次,对中断频率进行分频
if(T0Count>=1000)//1000ms
{
T0Count=0;
Sec++;
if(Sec>=60)
{
Sec=0;
Min++;
if(Min>=60)
{
Min=0;
Hour++;
if(Hour>=24)
{
Hour=0;
}
}
}
}
}
其它文件:复制之前写的模块即可。
十九、单片机实操十七:串口通信与串口向电脑发送数据
1、串口介绍

2、接口及引脚定义
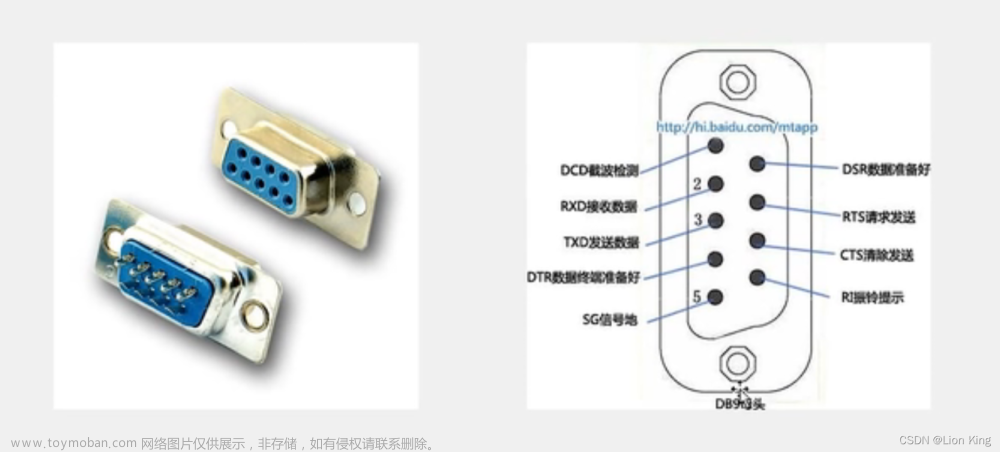
3、硬件电路

4、电平标准

5、常见通信接口比较

6、相关术语

7、51单片机的UART

8、串口参数与时序图

9、串口模式图
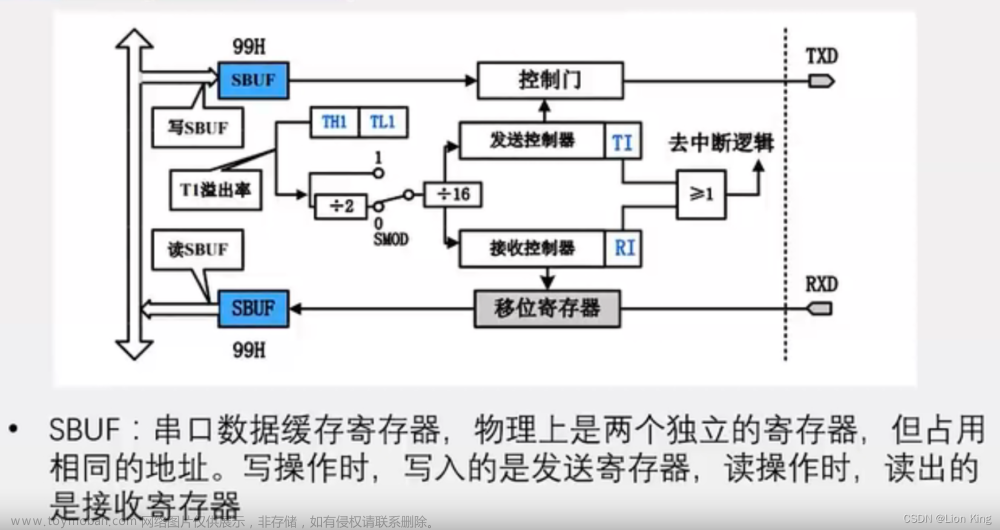
10、串口相关寄存器

11、串口和中断系统
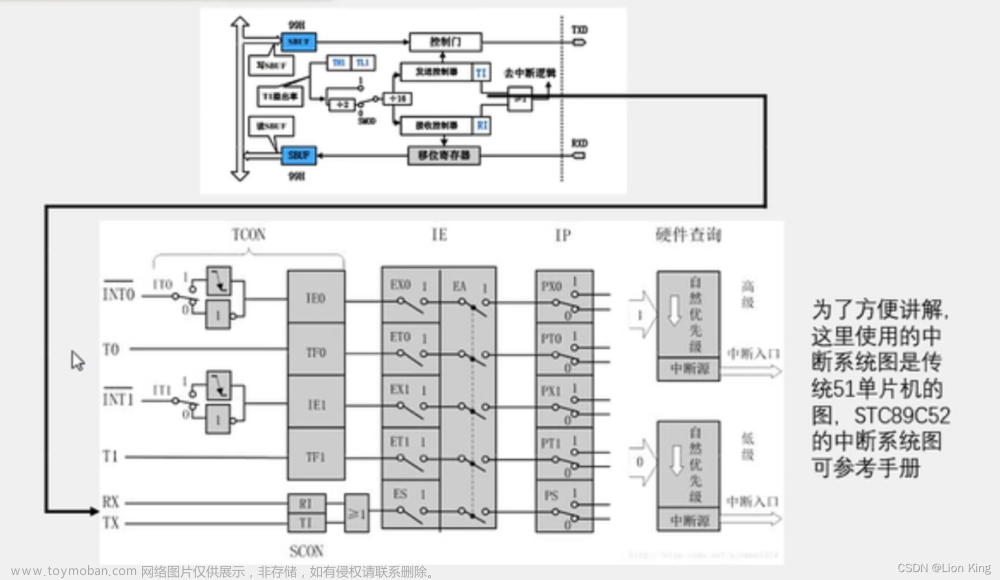
11、使用工具生成串口配置

12、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
#include "UART.h"
unsigned char Sec;
void main()
{
UartInit();
while(1)
{
UART_SendByte(Sec);
Sec++;
Delay(1); // 必要的延时,避免误差导致乱码,没误差的时候可以不需要
}
}UART.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
void UartInit(void) //4800bps@11.0592MHz
{
PCON &= 0x80; //波特率不倍速
SCON = 0x40; //8位数据,可变波特率
TMOD &= 0x0F; //设置定时器模式
TMOD |= 0x20; //设置定时器模式
TL1 = 0xFA; //设置定时初始值
TH1 = 0xFA; //设置定时重载值
ET1 = 0; //禁止定时器%d中断
TR1 = 1; //定时器1开始计时
}
void UART_SendByte(unsigned char Byte)
{
SBUF=Byte; // 根据硬件原理,操作寄存器
while(TI==0); // 操作寄存器,检测是否完成
TI=0; // 按要求重新赋值为0
}UART.h
#ifndef __UART_H__
#define __UART_H__
void UartInit(void);
void UART_SendByte(unsigned char Byte);
#endif
其他文件:复制之前写的模块即可。
13、调试程序
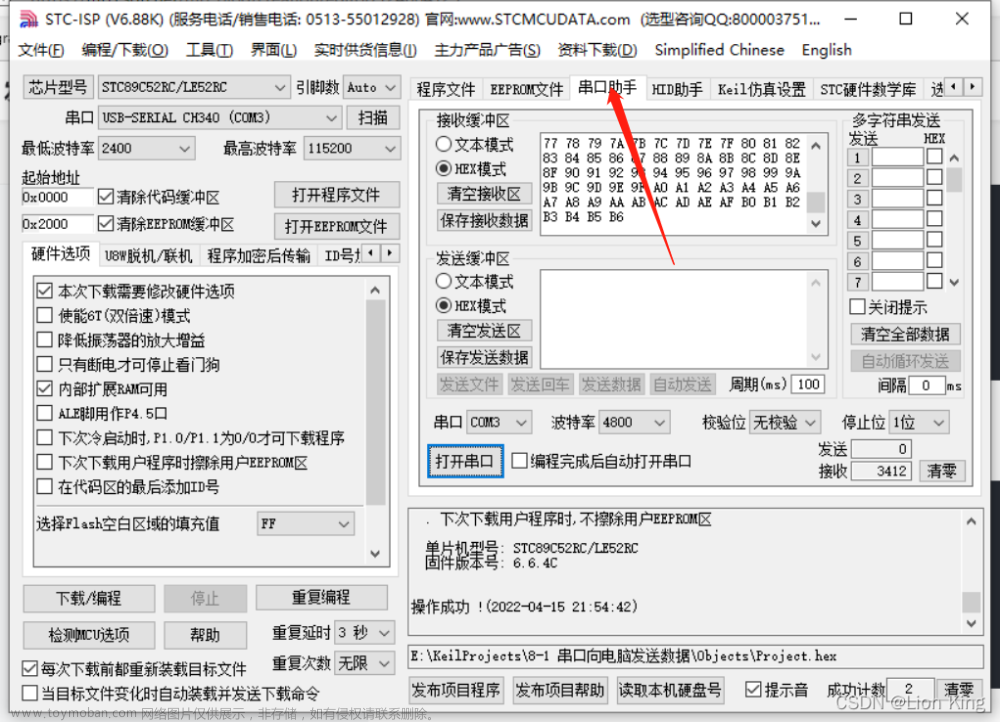
二十、单片机实操十八:电脑通过串口控制LED
1、编写程序
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
#include "UART.h"
unsigned char Sec;
void main()
{
UartInit();
while(1)
{
}
}
void UART_Routine() interrupt 4
{
if(RI==1)
{
P2=~SBUF; // 读寄存器的数据
UART_SendByte(SBUF);
RI=0; // 说明书要求手动复位
}
}其他文件:复制之前写的模块即可。
2、波特率计算
(1)内部逻辑图

(2)配置的定时初值
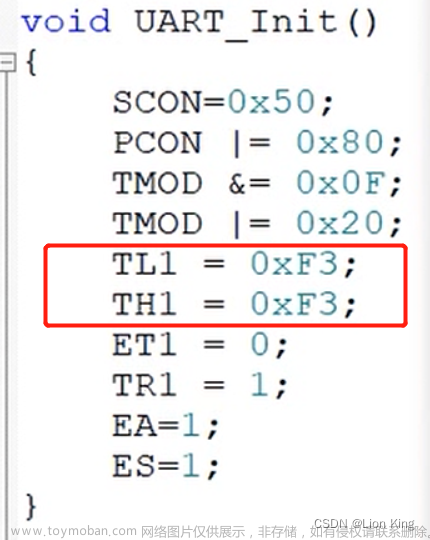
(3)计算方式
F3=243;
256-243=13us;
每记13次数,溢出1次;
1/13=0.0769230769230769MHz;
0.0769230769230769/16=0.0048076923076923MHz=4,807.692307692308HZ
3、ASCII码编码表
文本模式与Hex模式对应情况。

二十一、单片机实操十九:LED点阵屏与显示图形
1、LED点阵屏介绍

2、显示原理

3、74HC595模块原理图

4、74HC595介绍

5、接线
OE要通过跳线帽与GND相连,而开发板默认OE与VCC相连,因此需要操作。
6、开发板引脚对应关系

7、C51的sfr、sbit

8、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.H"
sbit RCK=P3^5; //RCLK
sbit SCK=P3^6; //SRCLK
sbit SER=P3^4; //SER
#define MATRIX_LED_PORT P0
void _74HC595_WriteByte(unsigned char Byte)
{
// SER=Byte&0x80; //一般是0、1赋值,不过,如果非0,都会当作1
// SCK=1;
// SCK=0;
// SER=Byte&0x60;
// SCK=1;
// SCK=0;
unsigned char i;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
SER=Byte&(0x80>>i);
SCK=1;
SCK=0;
}
RCK=1;
RCK=0;
}
void MatrixLED_ShowColumn(unsigned char Column, Data)
{
_74HC595_WriteByte(Data);
// if(Column==0){P0=~0x80;}
// if(Column==1){P0=~0x40;}
MATRIX_LED_PORT=~(0x80>>Column);
Delay(1);
MATRIX_LED_PORT=0xFF;
}
void main()
{
SCK=0;
RCK=0;
while(1)
{
// _74HC595_WriteByte(0xAA);
MatrixLED_ShowColumn(0,0x80);
MatrixLED_ShowColumn(1,0x40);
MatrixLED_ShowColumn(2,0x20);
MatrixLED_ShowColumn(3,0x10);
}
}二十二、单片机实操二十:LED点阵屏显示动画
1、字模提取软件





取出数据如下,将作为程序数组使用:
0xFF,0x10,0x10,0x10,0xFF,0x00,0x1E,0x29,0x29,0x29,0x18,0x00,0xFE,0x01,0x02,0x00,
0xFE,0x01,0x02,0x00,0x0E,0x11,0x11,0x0E,0x00,0x7D,0x7D,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,
2、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.H"
#include "MatrixLED.H"
unsigned char Animation[]={
0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00, // 为了显示更好看,避免第一列直接显示字符本身
0xFF,0x10,0x10,0x10,0xFF,0x00,0x1E,0x29,0x29,0x29,0x18,0x00,0xFE,0x01,0x02,0x00,
0xFE,0x01,0x02,0x00,0x0E,0x11,0x11,0x0E,0x00,0x7D,0x7D,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,
0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00, // 为了显示更好看
};
void main()
{
unsigned char i, Offset=1, Count=0;
while(1)
{
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
MatrixLED_ShowColumn(i,Animation[i+Offset]);
}
Count++;
if(Count>10)
{
Count=0;
Offset++;
if(Offset>40)
{
Offset=0; //防止数组溢出
}
}
}
}MatrixLED.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.H"
sbit RCK=P3^5; //RCLK
sbit SCK=P3^6; //SRCLK
sbit SER=P3^4; //SER
#define MATRIX_LED_PORT P0
void _74HC595_WriteByte(unsigned char Byte)
{
// SER=Byte&0x80; //一般是0、1赋值,不过,如果非0,都会当作1
// SCK=1;
// SCK=0;
// SER=Byte&0x60;
// SCK=1;
// SCK=0;
unsigned char i;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
SER=Byte&(0x80>>i);
SCK=1;
SCK=0;
}
RCK=1;
RCK=0;
}
void MatrixLED_Init()
{
SCK=0;
RCK=0;
}
void MatrixLED_ShowColumn(unsigned char Column, Data)
{
_74HC595_WriteByte(Data);
// if(Column==0){P0=~0x80;}
// if(Column==1){P0=~0x40;}
MATRIX_LED_PORT=~(0x80>>Column);
Delay(1);
MATRIX_LED_PORT=0xFF;
}
MatrixLED.h
#ifndef __MATRIXLED_H__
#define __MATRIXLED_H__
void MatrixLED_ShowColumn(unsigned char Column, Data);
void MatrixLED_Init();
#endif
3、注意事项
将数据放在flash里面,用来避免内存被消耗过多,但这种数据是不能更改的,方法如下:
将
unsigned char Animation[]
改为
unsigned char code Animation[]
二十三、单片机实操二十一:DS1302实时时钟
1、DS1302介绍

2、引脚定义和应用电路
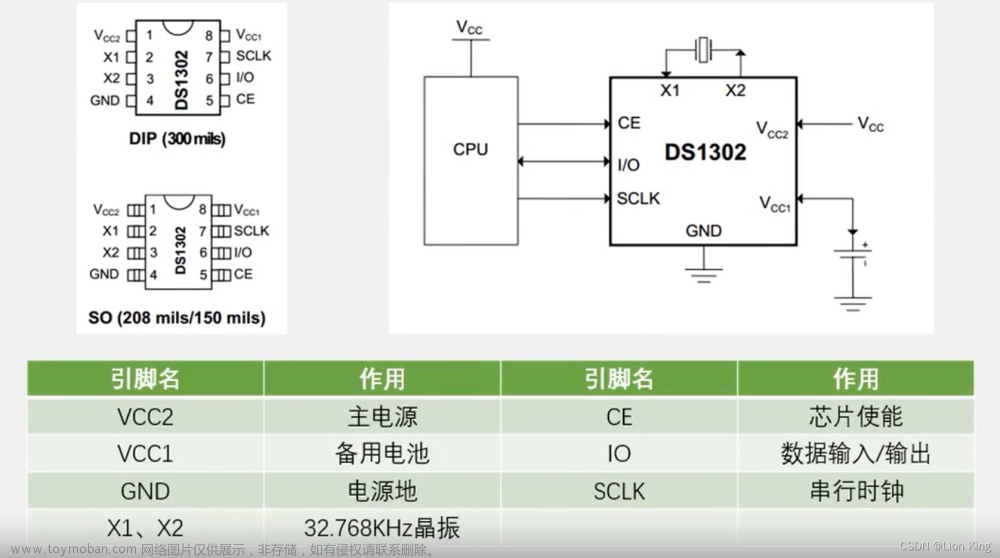
3、内部结构图

4、寄存器定义
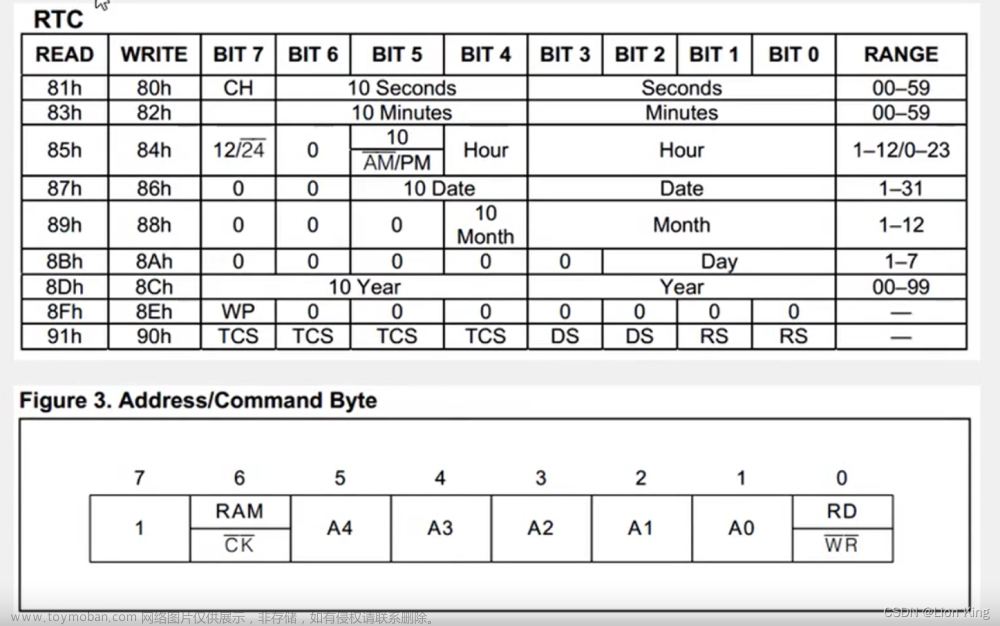
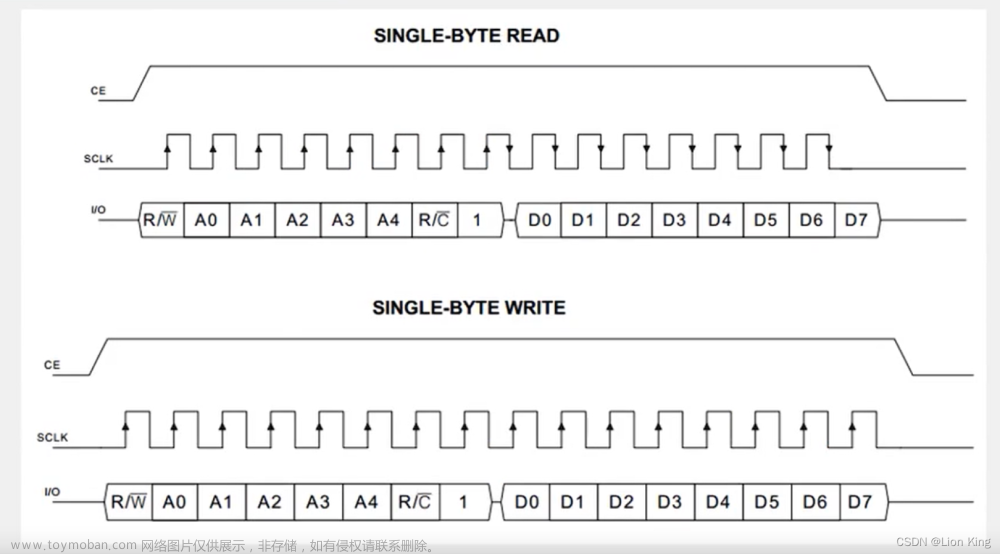
5、时序定义
6、BCD码

7、编写代码
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "DS1302.h"
// unsigned char Second, Minute;
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
DS1302_Init();
// DS1302_WriteByte(0x8E, 0x00); // 解除芯片写保护,避免数值不动
// DS1302_WriteByte(0x80, 0x54);
DS1302_SetTime();
while(1)
{
DS1302_ReadTime();
LCD_ShowNum(1,1,DS1302_TIME[0],2);
LCD_ShowNum(1,4,DS1302_TIME[1],2);
LCD_ShowNum(1,7,DS1302_TIME[2],2);
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,DS1302_TIME[3],2);
LCD_ShowNum(2,4,DS1302_TIME[4],2);
LCD_ShowNum(2,7,DS1302_TIME[5],2);
// Second=DS1302_ReadByte(0x81);
// Minute=DS1302_ReadByte(0x83);
// LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Second/16*10+Second%16,2);
// LCD_ShowNum(2,3,Minute/16*10+Minute%16,2);
}
}DS1302.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
sbit DS1302_SCLK=P3^6;
sbit DS1302_IO=P3^4;
sbit DS1302_CE=P3^5;
#define DS1302_SECOND 0x80
#define DS1302_MINUTE 0x82
#define DS1302_HOUR 0x84
#define DS1302_DATE 0x86
#define DS1302_MONTH 0x88
#define DS1302_DAY 0x8A
#define DS1302_YEAR 0x8C
#define DS1302_WP 0x8E
unsigned char DS1302_TIME[]={19,11,16,12,59,55,6};
void DS1302_Init(void)
{
DS1302_CE=0;
DS1302_SCLK=0;
}
void DS1302_WriteByte(unsigned char Command, Data)
{
unsigned char i;
DS1302_CE=1;
// DS1302_IO=Command&0x01;
// DS1302_SCLK=1; // 速度慢可以不加延时,有些速度快的芯片需要增加延时
// DS1302_SCLK=0;
//
// DS1302_IO=Command&0x02;
// DS1302_SCLK=1;
// DS1302_SCLK=0;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
DS1302_IO=Command&(0x01<<i);
DS1302_SCLK=1;
DS1302_SCLK=0;
}
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
DS1302_IO=Data&(0x01<<i);
DS1302_SCLK=1;
DS1302_SCLK=0;
}
DS1302_CE=0; //完成一次操作,释放IO
}
unsigned char DS1302_ReadByte(unsigned char Command)
{
unsigned char i,Data=0x00;
Command|=0x01; //
DS1302_CE=1;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
DS1302_IO=Command&(0x01<<i);
DS1302_SCLK=0; //根据时序操作
DS1302_SCLK=1;
}
// DS1302_SCLK=0;
// DS1302_SCLK=1;
// if(DS1302_IO)
// {
// Data=Data|0x01;
// }
// DS1302_SCLK=0;
// DS1302_SCLK=1;
// if(DS1302_IO)
// {
// Data=Data|0x02;
// }
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
DS1302_SCLK=1; //重复置1是去掉一个周期,为的是满足时序
DS1302_SCLK=0;
if(DS1302_IO){Data|=(0x01<<i);}
}
DS1302_CE=0;
DS1302_IO=0; // 如果不加这一行,将显示全0
return Data;
}
void DS1302_SetTime(void)
{
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_WP,0x00);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_YEAR,DS1302_TIME[0]/10*16+DS1302_TIME[0]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_MONTH,DS1302_TIME[1]/10*16+DS1302_TIME[1]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_DATE,DS1302_TIME[2]/10*16+DS1302_TIME[2]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_HOUR,DS1302_TIME[3]/10*16+DS1302_TIME[3]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_MINUTE,DS1302_TIME[4]/10*16+DS1302_TIME[4]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_SECOND,DS1302_TIME[5]/10*16+DS1302_TIME[5]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_DAY,DS1302_TIME[6]/10*16+DS1302_TIME[6]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_WP,0x00);
}
void DS1302_ReadTime(void)
{
unsigned char Temp;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_YEAR);
DS1302_TIME[0]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_MONTH);
DS1302_TIME[1]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_DATE);
DS1302_TIME[2]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_HOUR);
DS1302_TIME[3]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_MINUTE);
DS1302_TIME[4]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_SECOND);
DS1302_TIME[5]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_DAY);
DS1302_TIME[6]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
}DS1302.h
#ifndef __DS1302_H__
#define __DS1302_H__
extern unsigned char DS1302_TIME[]; // 声明数组
void DS1302_Init(void);
void DS1302_WriteByte(unsigned char Command, Data);
unsigned char DS1302_ReadByte(unsigned char Command);
void DS1302_SetTime(void);
void DS1302_ReadTime(void);
#endif
二十四、单片机实操二十二:DS1302可调时钟
1、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "DS1302.h"
#include "Key.h"
#include "Timer0.h"
unsigned char KeyNum,MODE,TimeSetSelect,TimeSetFlashFlag;
void TimeShow(void)//时间显示功能
{
DS1302_ReadTime();//读取时间
LCD_ShowNum(1,1,DS1302_Time[0],2);//显示年
LCD_ShowNum(1,4,DS1302_Time[1],2);//显示月
LCD_ShowNum(1,7,DS1302_Time[2],2);//显示日
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,DS1302_Time[3],2);//显示时
LCD_ShowNum(2,4,DS1302_Time[4],2);//显示分
LCD_ShowNum(2,7,DS1302_Time[5],2);//显示秒
}
void TimeSet(void)//时间设置功能
{
if(KeyNum==2)//按键2按下
{
TimeSetSelect++;//设置选择位加1
TimeSetSelect%=6;//越界清零
}
if(KeyNum==3)//按键3按下
{
DS1302_Time[TimeSetSelect]++;//时间设置位数值加1
if(DS1302_Time[0]>99){DS1302_Time[0]=0;}//年越界判断
if(DS1302_Time[1]>12){DS1302_Time[1]=1;}//月越界判断
if( DS1302_Time[1]==1 || DS1302_Time[1]==3 || DS1302_Time[1]==5 || DS1302_Time[1]==7 ||
DS1302_Time[1]==8 || DS1302_Time[1]==10 || DS1302_Time[1]==12)//日越界判断
{
if(DS1302_Time[2]>31){DS1302_Time[2]=1;}//大月
}
else if(DS1302_Time[1]==4 || DS1302_Time[1]==6 || DS1302_Time[1]==9 || DS1302_Time[1]==11)
{
if(DS1302_Time[2]>30){DS1302_Time[2]=1;}//小月
}
else if(DS1302_Time[1]==2)
{
if(DS1302_Time[0]%4==0)
{
if(DS1302_Time[2]>29){DS1302_Time[2]=1;}//闰年2月
}
else
{
if(DS1302_Time[2]>28){DS1302_Time[2]=1;}//平年2月
}
}
if(DS1302_Time[3]>23){DS1302_Time[3]=0;}//时越界判断
if(DS1302_Time[4]>59){DS1302_Time[4]=0;}//分越界判断
if(DS1302_Time[5]>59){DS1302_Time[5]=0;}//秒越界判断
}
if(KeyNum==4)//按键3按下
{
DS1302_Time[TimeSetSelect]--;//时间设置位数值减1
if(DS1302_Time[0]<0){DS1302_Time[0]=99;}//年越界判断
if(DS1302_Time[1]<1){DS1302_Time[1]=12;}//月越界判断
if( DS1302_Time[1]==1 || DS1302_Time[1]==3 || DS1302_Time[1]==5 || DS1302_Time[1]==7 ||
DS1302_Time[1]==8 || DS1302_Time[1]==10 || DS1302_Time[1]==12)//日越界判断
{
if(DS1302_Time[2]<1){DS1302_Time[2]=31;}//大月
if(DS1302_Time[2]>31){DS1302_Time[2]=1;}
}
else if(DS1302_Time[1]==4 || DS1302_Time[1]==6 || DS1302_Time[1]==9 || DS1302_Time[1]==11)
{
if(DS1302_Time[2]<1){DS1302_Time[2]=30;}//小月
if(DS1302_Time[2]>30){DS1302_Time[2]=1;}
}
else if(DS1302_Time[1]==2)
{
if(DS1302_Time[0]%4==0)
{
if(DS1302_Time[2]<1){DS1302_Time[2]=29;}//闰年2月
if(DS1302_Time[2]>29){DS1302_Time[2]=1;}
}
else
{
if(DS1302_Time[2]<1){DS1302_Time[2]=28;}//平年2月
if(DS1302_Time[2]>28){DS1302_Time[2]=1;}
}
}
if(DS1302_Time[3]<0){DS1302_Time[3]=23;}//时越界判断
if(DS1302_Time[4]<0){DS1302_Time[4]=59;}//分越界判断
if(DS1302_Time[5]<0){DS1302_Time[5]=59;}//秒越界判断
}
//更新显示,根据TimeSetSelect和TimeSetFlashFlag判断可完成闪烁功能
if(TimeSetSelect==0 && TimeSetFlashFlag==1){LCD_ShowString(1,1," ");}
else {LCD_ShowNum(1,1,DS1302_Time[0],2);}
if(TimeSetSelect==1 && TimeSetFlashFlag==1){LCD_ShowString(1,4," ");}
else {LCD_ShowNum(1,4,DS1302_Time[1],2);}
if(TimeSetSelect==2 && TimeSetFlashFlag==1){LCD_ShowString(1,7," ");}
else {LCD_ShowNum(1,7,DS1302_Time[2],2);}
if(TimeSetSelect==3 && TimeSetFlashFlag==1){LCD_ShowString(2,1," ");}
else {LCD_ShowNum(2,1,DS1302_Time[3],2);}
if(TimeSetSelect==4 && TimeSetFlashFlag==1){LCD_ShowString(2,4," ");}
else {LCD_ShowNum(2,4,DS1302_Time[4],2);}
if(TimeSetSelect==5 && TimeSetFlashFlag==1){LCD_ShowString(2,7," ");}
else {LCD_ShowNum(2,7,DS1302_Time[5],2);}
}
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
DS1302_Init();
Timer0Init();
LCD_ShowString(1,1," - - ");//静态字符初始化显示
LCD_ShowString(2,1," : : ");
DS1302_SetTime();//设置时间
while(1)
{
KeyNum=Key();//读取键码
if(KeyNum==1)//按键1按下
{
if(MODE==0){MODE=1;TimeSetSelect=0;}//功能切换
else if(MODE==1){MODE=0;DS1302_SetTime();}
}
switch(MODE)//根据不同的功能执行不同的函数
{
case 0:TimeShow();break;
case 1:TimeSet();break;
}
}
}
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1
{
static unsigned int T0Count;
TL0 = 0x18; //设置定时初值
TH0 = 0xFC; //设置定时初值
T0Count++;
if(T0Count>=500)//每500ms进入一次
{
T0Count=0;
TimeSetFlashFlag=!TimeSetFlashFlag;//闪烁标志位取反
}
}
DS1302.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
//引脚定义
sbit DS1302_SCLK=P3^6;
sbit DS1302_IO=P3^4;
sbit DS1302_CE=P3^5;
//寄存器写入地址/指令定义
#define DS1302_SECOND 0x80
#define DS1302_MINUTE 0x82
#define DS1302_HOUR 0x84
#define DS1302_DATE 0x86
#define DS1302_MONTH 0x88
#define DS1302_DAY 0x8A
#define DS1302_YEAR 0x8C
#define DS1302_WP 0x8E
//时间数组,索引0~6分别为年、月、日、时、分、秒、星期,设置为有符号的便于<0的判断
char DS1302_Time[]={19,11,16,12,59,55,6};
/**
* @brief DS1302初始化
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void DS1302_Init(void)
{
DS1302_CE=0;
DS1302_SCLK=0;
}
/**
* @brief DS1302写一个字节
* @param Command 命令字/地址
* @param Data 要写入的数据
* @retval 无
*/
void DS1302_WriteByte(unsigned char Command,Data)
{
unsigned char i;
DS1302_CE=1;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
DS1302_IO=Command&(0x01<<i);
DS1302_SCLK=1;
DS1302_SCLK=0;
}
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
DS1302_IO=Data&(0x01<<i);
DS1302_SCLK=1;
DS1302_SCLK=0;
}
DS1302_CE=0;
}
/**
* @brief DS1302读一个字节
* @param Command 命令字/地址
* @retval 读出的数据
*/
unsigned char DS1302_ReadByte(unsigned char Command)
{
unsigned char i,Data=0x00;
Command|=0x01; //将指令转换为读指令
DS1302_CE=1;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
DS1302_IO=Command&(0x01<<i);
DS1302_SCLK=0;
DS1302_SCLK=1;
}
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
DS1302_SCLK=1;
DS1302_SCLK=0;
if(DS1302_IO){Data|=(0x01<<i);}
}
DS1302_CE=0;
DS1302_IO=0; //读取后将IO设置为0,否则读出的数据会出错
return Data;
}
/**
* @brief DS1302设置时间,调用之后,DS1302_Time数组的数字会被设置到DS1302中
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void DS1302_SetTime(void)
{
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_WP,0x00);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_YEAR,DS1302_Time[0]/10*16+DS1302_Time[0]%10);//十进制转BCD码后写入
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_MONTH,DS1302_Time[1]/10*16+DS1302_Time[1]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_DATE,DS1302_Time[2]/10*16+DS1302_Time[2]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_HOUR,DS1302_Time[3]/10*16+DS1302_Time[3]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_MINUTE,DS1302_Time[4]/10*16+DS1302_Time[4]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_SECOND,DS1302_Time[5]/10*16+DS1302_Time[5]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_DAY,DS1302_Time[6]/10*16+DS1302_Time[6]%10);
DS1302_WriteByte(DS1302_WP,0x80);
}
/**
* @brief DS1302读取时间,调用之后,DS1302中的数据会被读取到DS1302_Time数组中
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void DS1302_ReadTime(void)
{
unsigned char Temp;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_YEAR);
DS1302_Time[0]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;//BCD码转十进制后读取
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_MONTH);
DS1302_Time[1]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_DATE);
DS1302_Time[2]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_HOUR);
DS1302_Time[3]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_MINUTE);
DS1302_Time[4]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_SECOND);
DS1302_Time[5]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
Temp=DS1302_ReadByte(DS1302_DAY);
DS1302_Time[6]=Temp/16*10+Temp%16;
}
DS1302.h
#ifndef __DS1302_H__
#define __DS1302_H__
//外部可调用时间数组,索引0~6分别为年、月、日、时、分、秒、星期,设置为有符号的便于<0的判断
extern char DS1302_Time[];
void DS1302_Init(void);
void DS1302_WriteByte(unsigned char Command,Data);
unsigned char DS1302_ReadByte(unsigned char Command);
void DS1302_SetTime(void);
void DS1302_ReadTime(void);
#endif
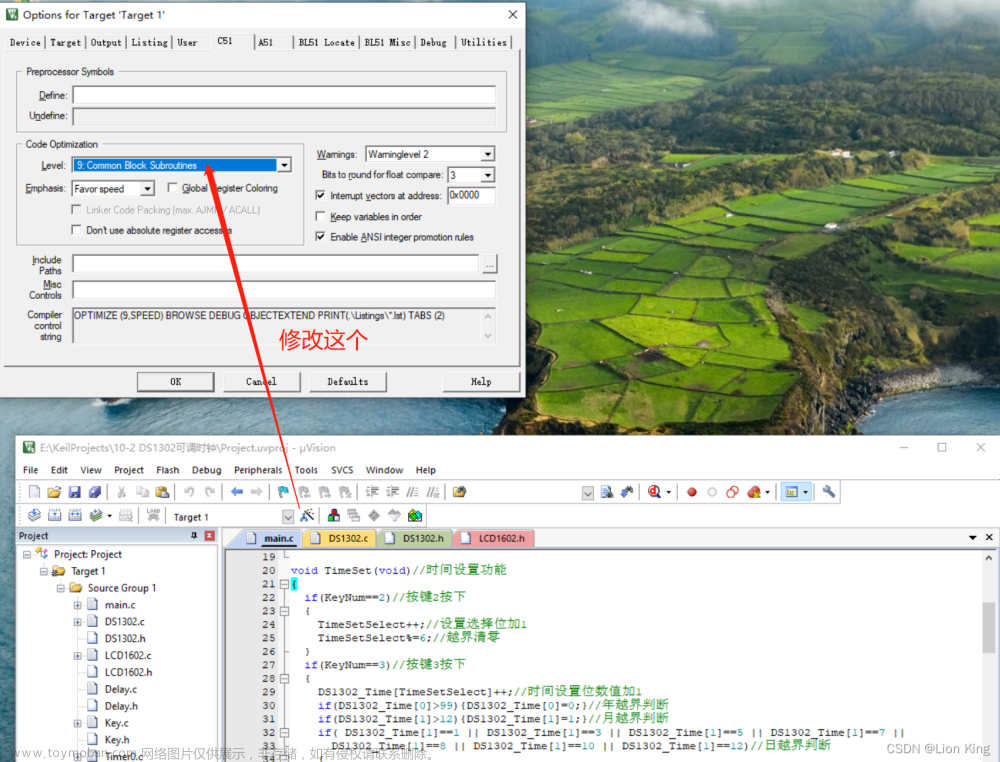
2、遇到问题
*** FATAL ERROR L250: CODE SIZE LIMIT IN RESTRICTED VERSION EXCEEDED
MODULE: D:\KEIL5\C51\LIB\C51S.LIB (-----)
LIMIT: 0800H BYTES
Target not created.
Build Time Elapsed: 00:00:01

3、解决方式

二十五、单片机实操二十三:蜂鸣器与播放提示音
1、蜂鸣器介绍

2、驱动电路
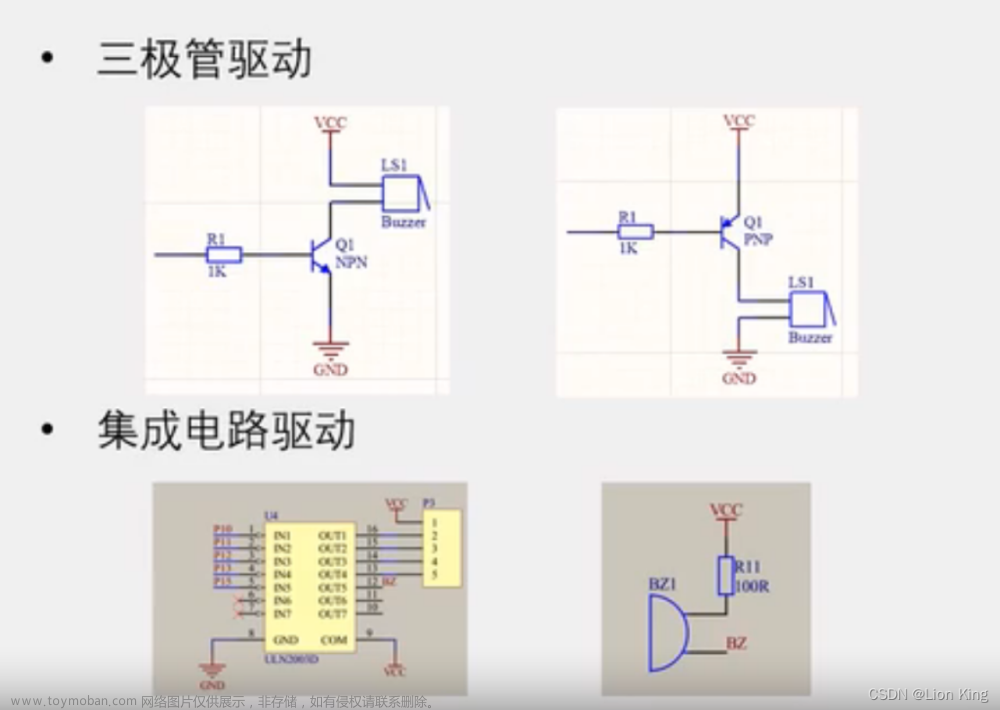
3、ULN2003

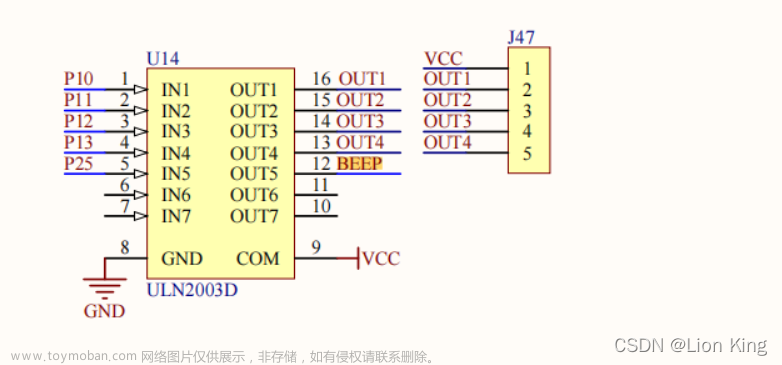
4、硬件原理图
无源蜂鸣器,使用的控制引脚是P25
5、钢琴键盘与音符对照

6、 简谱


7、C调音符与频率对照表

8、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
#include "Key.h"
#include "Nixie.h"
#include "Buzzer.h"
unsigned char KeyNum;
void main()
{
Nixie(1,0);
while(1)
{
KeyNum=Key();
if(KeyNum)
{
Buzzer_Time(1000);
Nixie(1,KeyNum);
}
}
}Buzzer.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include <INTRINS.H>
sbit Buzzer=P2^5;
void Buzzer_Delay500us() //@11.0592MHz
{
unsigned char i;
_nop_();
i = 227;
while (--i);
}
void Buzzer_Time(unsigned int ms)
{
unsigned int i;
for(i=0;i<ms*2;i++)
{
Buzzer=!Buzzer;
Buzzer_Delay500us();
}
}Buzzer.h
#ifndef __BUZZER_H__
#define __BUZZER_H__
void Buzzer_Time(unsigned int ms);
#endif二十六、单片机实操二十四:蜂鸣器与播放提示音
1、音符对应的重载值计算方式

2、编写天空之城音乐程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
#include "Timer0.h"
//蜂鸣器端口定义
sbit Buzzer=P2^5;
//播放速度,值为四分音符的时长(ms)
#define SPEED 500
//音符与索引对应表,P:休止符,L:低音,M:中音,H:高音,下划线:升半音符号#
#define P 0
#define L1 1
#define L1_ 2
#define L2 3
#define L2_ 4
#define L3 5
#define L4 6
#define L4_ 7
#define L5 8
#define L5_ 9
#define L6 10
#define L6_ 11
#define L7 12
#define M1 13
#define M1_ 14
#define M2 15
#define M2_ 16
#define M3 17
#define M4 18
#define M4_ 19
#define M5 20
#define M5_ 21
#define M6 22
#define M6_ 23
#define M7 24
#define H1 25
#define H1_ 26
#define H2 27
#define H2_ 28
#define H3 29
#define H4 30
#define H4_ 31
#define H5 32
#define H5_ 33
#define H6 34
#define H6_ 35
#define H7 36
//索引与频率对照表
unsigned int FreqTable[]={
0,
63628,63731,63835,63928,64021,64103,64185,64260,64331,64400,64463,64528,
64580,64633,64684,64732,64777,64820,64860,64898,64934,64968,65000,65030,
65058,65085,65110,65134,65157,65178,65198,65217,65235,65252,65268,65283,
};
//乐谱
unsigned char code Music[]={
//音符,时值,
//1
P, 4,
P, 4,
P, 4,
M6, 2,
M7, 2,
H1, 4+2,
M7, 2,
H1, 4,
H3, 4,
M7, 4+4+4,
M3, 2,
M3, 2,
//2
M6, 4+2,
M5, 2,
M6, 4,
H1, 4,
M5, 4+4+4,
M3, 4,
M4, 4+2,
M3, 2,
M4, 4,
H1, 4,
//3
M3, 4+4,
P, 2,
H1, 2,
H1, 2,
H1, 2,
M7, 4+2,
M4_,2,
M4_,4,
M7, 4,
M7, 8,
P, 4,
M6, 2,
M7, 2,
//4
H1, 4+2,
M7, 2,
H1, 4,
H3, 4,
M7, 4+4+4,
M3, 2,
M3, 2,
M6, 4+2,
M5, 2,
M6, 4,
H1, 4,
//5
M5, 4+4+4,
M2, 2,
M3, 2,
M4, 4,
H1, 2,
M7, 2+2,
H1, 2+4,
H2, 2,
H2, 2,
H3, 2,
H1, 2+4+4,
//6
H1, 2,
M7, 2,
M6, 2,
M6, 2,
M7, 4,
M5_,4,
M6, 4+4+4,
H1, 2,
H2, 2,
H3, 4+2,
H2, 2,
H3, 4,
H5, 4,
//7
H2, 4+4+4,
M5, 2,
M5, 2,
H1, 4+2,
M7, 2,
H1, 4,
H3, 4,
H3, 4+4+4+4,
//8
M6, 2,
M7, 2,
H1, 4,
M7, 4,
H2, 2,
H2, 2,
H1, 4+2,
M5, 2+4+4,
H4, 4,
H3, 4,
H3, 4,
H1, 4,
//9
H3, 4+4+4,
H3, 4,
H6, 4+4,
H5, 4,
H5, 4,
H3, 2,
H2, 2,
H1, 4+4,
P, 2,
H1, 2,
//10
H2, 4,
H1, 2,
H2, 2,
H2, 4,
H5, 4,
H3, 4+4+4,
H3, 4,
H6, 4+4,
H5, 4+4,
//11
H3, 2,
H2, 2,
H1, 4+4,
P, 2,
H1, 2,
H2, 4,
H1, 2,
H2, 2+4,
M7, 4,
M6, 4+4+4,
P, 4,
0xFF //终止标志
};
unsigned char FreqSelect,MusicSelect;
void main()
{
Timer0Init();
while(1)
{
if(Music[MusicSelect]!=0xFF) //如果不是停止标志位
{
FreqSelect=Music[MusicSelect]; //选择音符对应的频率
MusicSelect++;
Delay(SPEED/4*Music[MusicSelect]); //选择音符对应的时值
MusicSelect++;
TR0=0;
Delay(5); //音符间短暂停顿
TR0=1;
}
else //如果是停止标志位
{
TR0=0;
while(1);
}
}
}
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1
{
if(FreqTable[FreqSelect]) //如果不是休止符
{
/*取对应频率值的重装载值到定时器*/
TL0 = FreqTable[FreqSelect]%256; //设置定时初值
TH0 = FreqTable[FreqSelect]/256; //设置定时初值
Buzzer=!Buzzer; //翻转蜂鸣器IO口
}
}
二十七、单片机实操二十五:AT24C02(I2C总线)与数据存储
1、存储器介绍

2、存储器简化模型
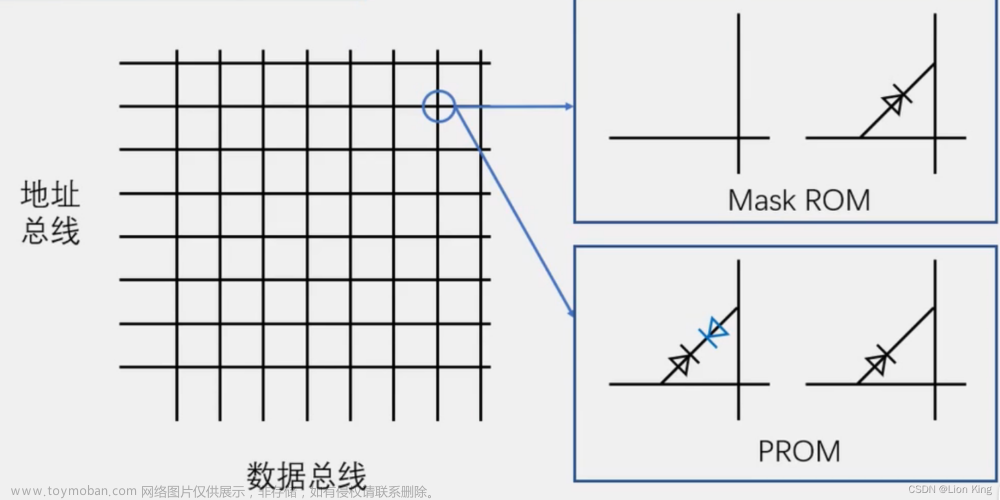
3、AT24C02介绍

4、引脚与芯片电路

5、内部结构框图

6、I2C总线介绍

7、I2C电路规范

8、I2C时序结构



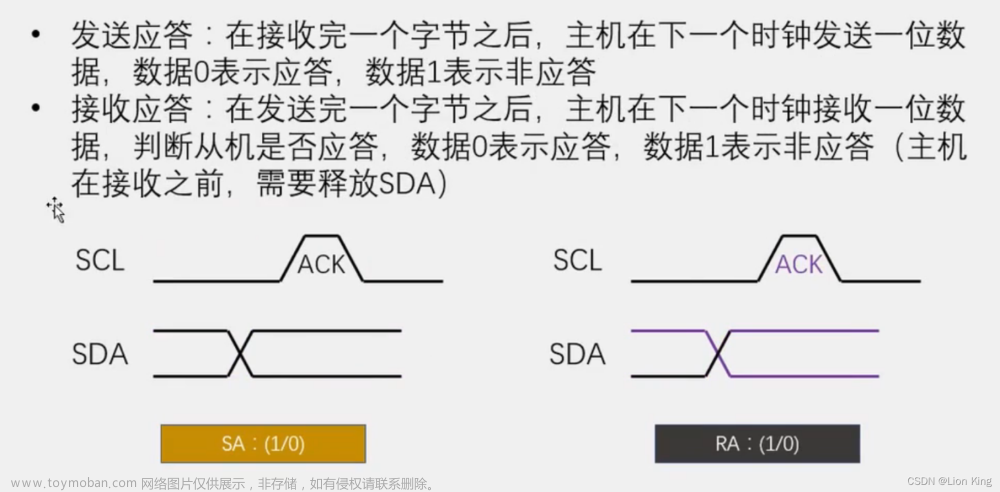
9、I2C数据帧

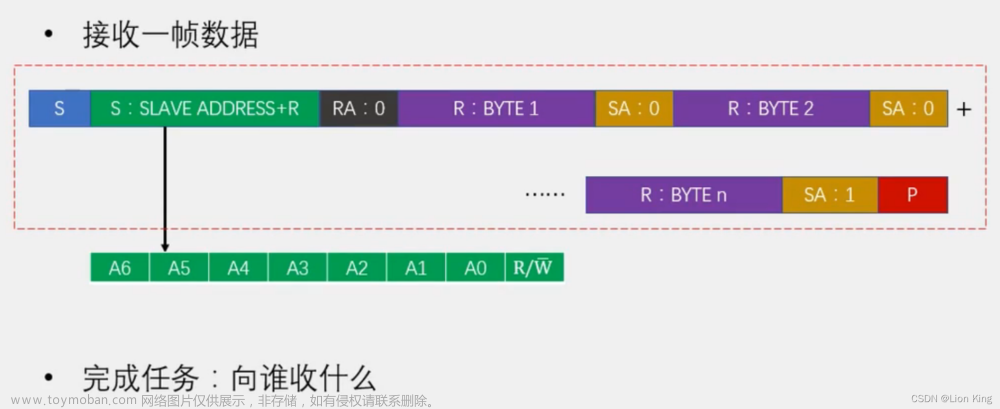
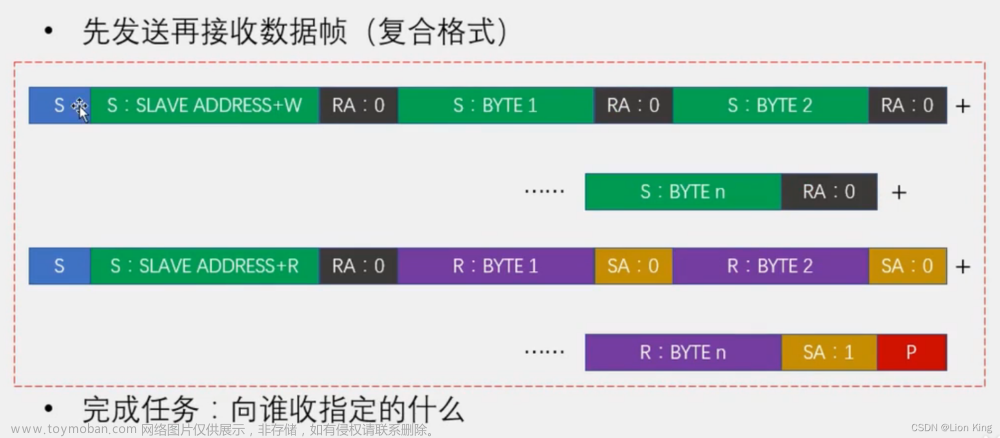
10、AT24C02数据帧


11、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "Key.h"
#include "AT24C02.h"
#include "Delay.h"
unsigned char KeyNum;
unsigned int Num;
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowNum(1,1,Num,5);
while(1)
{
KeyNum=Key();
if(KeyNum==1) //K1按键,Num自增
{
Num++;
LCD_ShowNum(1,1,Num,5);
}
if(KeyNum==2) //K2按键,Num自减
{
Num--;
LCD_ShowNum(1,1,Num,5);
}
if(KeyNum==3) //K3按键,向AT24C02写入数据
{
AT24C02_WriteByte(0,Num%256);
Delay(5);
AT24C02_WriteByte(1,Num/256);
Delay(5);
LCD_ShowString(2,1,"Write OK");
Delay(1000);
LCD_ShowString(2,1," ");
}
if(KeyNum==4) //K4按键,从AT24C02读取数据
{
Num=AT24C02_ReadByte(0);
Num|=AT24C02_ReadByte(1)<<8;
LCD_ShowNum(1,1,Num,5);
LCD_ShowString(2,1,"Read OK ");
Delay(1000);
LCD_ShowString(2,1," ");
}
}
}
I2C.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
sbit I2C_SCL=P2^1;
sbit I2C_SDA=P2^0;
/**
* @brief I2C开始
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void I2C_Start(void)
{
I2C_SDA=1;
I2C_SCL=1;
I2C_SDA=0;
I2C_SCL=0;
}
/**
* @brief I2C停止
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void I2C_Stop(void)
{
I2C_SDA=0;
I2C_SCL=1;
I2C_SDA=1;
}
/**
* @brief I2C发送一个字节
* @param Byte 要发送的字节
* @retval 无
*/
void I2C_SendByte(unsigned char Byte)
{
unsigned char i;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
I2C_SDA=Byte&(0x80>>i);
I2C_SCL=1;
I2C_SCL=0;
}
}
/**
* @brief I2C接收一个字节
* @param 无
* @retval 接收到的一个字节数据
*/
unsigned char I2C_ReceiveByte(void)
{
unsigned char i,Byte=0x00;
I2C_SDA=1;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
I2C_SCL=1;
if(I2C_SDA){Byte|=(0x80>>i);}
I2C_SCL=0;
}
return Byte;
}
/**
* @brief I2C发送应答
* @param AckBit 应答位,0为应答,1为非应答
* @retval 无
*/
void I2C_SendAck(unsigned char AckBit)
{
I2C_SDA=AckBit;
I2C_SCL=1;
I2C_SCL=0;
}
/**
* @brief I2C接收应答位
* @param 无
* @retval 接收到的应答位,0为应答,1为非应答
*/
unsigned char I2C_ReceiveAck(void)
{
unsigned char AckBit;
I2C_SDA=1;
I2C_SCL=1;
AckBit=I2C_SDA;
I2C_SCL=0;
return AckBit;
}
I2C.h
#ifndef __I2C_H__
#define __I2C_H__
void I2C_Start(void);
void I2C_Stop(void);
void I2C_SendByte(unsigned char Byte);
unsigned char I2C_ReceiveByte(void);
void I2C_SendAck(unsigned char AckBit);
unsigned char I2C_ReceiveAck(void);
#endif
AT21C02.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "I2C.h"
#define AT24C02_ADDRESS 0xA0
/**
* @brief AT24C02写入一个字节
* @param WordAddress 要写入字节的地址
* @param Data 要写入的数据
* @retval 无
*/
void AT24C02_WriteByte(unsigned char WordAddress,Data)
{
I2C_Start();
I2C_SendByte(AT24C02_ADDRESS);
I2C_ReceiveAck();
I2C_SendByte(WordAddress);
I2C_ReceiveAck();
I2C_SendByte(Data);
I2C_ReceiveAck();
I2C_Stop();
}
/**
* @brief AT24C02读取一个字节
* @param WordAddress 要读出字节的地址
* @retval 读出的数据
*/
unsigned char AT24C02_ReadByte(unsigned char WordAddress)
{
unsigned char Data;
I2C_Start();
I2C_SendByte(AT24C02_ADDRESS);
I2C_ReceiveAck();
I2C_SendByte(WordAddress);
I2C_ReceiveAck();
I2C_Start();
I2C_SendByte(AT24C02_ADDRESS|0x01);
I2C_ReceiveAck();
Data=I2C_ReceiveByte();
I2C_SendAck(1);
I2C_Stop();
return Data;
}
AT21C02.h
#ifndef __AT24C02_H__
#define __AT24C02_H__
void AT24C02_WriteByte(unsigned char WordAddress,Data);
unsigned char AT24C02_ReadByte(unsigned char WordAddress);
#endif
二十八、单片机实操二十六:秒表(定时器扫描按键数码管)
1、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Timer0.h"
#include "Key.h"
#include "Nixie.h"
#include "Delay.h"
#include "AT24C02.h"
unsigned char KeyNum;
unsigned char Min,Sec,MiniSec;
unsigned char RunFlag;
void main()
{
Timer0_Init();
while(1)
{
KeyNum=Key();
if(KeyNum==1) //K1按键按下
{
RunFlag=!RunFlag; //启动标志位翻转
}
if(KeyNum==2) //K2按键按下
{
Min=0; //分秒清0
Sec=0;
MiniSec=0;
}
if(KeyNum==3) //K3按键按下
{
AT24C02_WriteByte(0,Min); //将分秒写入AT24C02
Delay(5);
AT24C02_WriteByte(1,Sec);
Delay(5);
AT24C02_WriteByte(2,MiniSec);
Delay(5);
}
if(KeyNum==4) //K4按键按下
{
Min=AT24C02_ReadByte(0); //读出AT24C02数据
Sec=AT24C02_ReadByte(1);
MiniSec=AT24C02_ReadByte(2);
}
Nixie_SetBuf(1,Min/10); //设置显示缓存,显示数据
Nixie_SetBuf(2,Min%10);
Nixie_SetBuf(3,11);
Nixie_SetBuf(4,Sec/10);
Nixie_SetBuf(5,Sec%10);
Nixie_SetBuf(6,11);
Nixie_SetBuf(7,MiniSec/10);
Nixie_SetBuf(8,MiniSec%10);
}
}
/**
* @brief 秒表驱动函数,在中断中调用
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void Sec_Loop(void)
{
if(RunFlag)
{
MiniSec++;
if(MiniSec>=100)
{
MiniSec=0;
Sec++;
if(Sec>=60)
{
Sec=0;
Min++;
if(Min>=60)
{
Min=0;
}
}
}
}
}
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1
{
static unsigned int T0Count1,T0Count2,T0Count3;
TL0 = 0x18; //设置定时初值
TH0 = 0xFC; //设置定时初值
T0Count1++;
if(T0Count1>=20)
{
T0Count1=0;
Key_Loop(); //20ms调用一次按键驱动函数
}
T0Count2++;
if(T0Count2>=2)
{
T0Count2=0;
Nixie_Loop();//2ms调用一次数码管驱动函数
}
T0Count3++;
if(T0Count3>=10)
{
T0Count3=0;
Sec_Loop(); //10ms调用一次数秒表驱动函数
}
}
Key.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
unsigned char Key_KeyNumber;
/**
* @brief 获取按键键码
* @param 无
* @retval 按下按键的键码,范围:0,1~4,0表示无按键按下
*/
unsigned char Key(void)
{
unsigned char Temp=0;
Temp=Key_KeyNumber;
Key_KeyNumber=0;
return Temp;
}
/**
* @brief 获取当前按键的状态,无消抖及松手检测
* @param 无
* @retval 按下按键的键码,范围:0,1~4,0表示无按键按下
*/
unsigned char Key_GetState()
{
unsigned char KeyNumber=0;
if(P31==0){KeyNumber=1;}
if(P30==0){KeyNumber=2;}
if(P32==0){KeyNumber=3;}
if(P33==0){KeyNumber=4;}
return KeyNumber;
}
/**
* @brief 按键驱动函数,在中断中调用
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void Key_Loop(void)
{
static unsigned char NowState,LastState;
LastState=NowState; //按键状态更新
NowState=Key_GetState(); //获取当前按键状态
//如果上个时间点按键按下,这个时间点未按下,则是松手瞬间,以此避免消抖和松手检测
if(LastState==1 && NowState==0)
{
Key_KeyNumber=1;
}
if(LastState==2 && NowState==0)
{
Key_KeyNumber=2;
}
if(LastState==3 && NowState==0)
{
Key_KeyNumber=3;
}
if(LastState==4 && NowState==0)
{
Key_KeyNumber=4;
}
}
Key.h
#ifndef __KEY_H__
#define __KEY_H__
unsigned char Key(void);
void Key_Loop(void);
#endif
Nixie.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
//数码管显示缓存区
unsigned char Nixie_Buf[9]={0,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10};
//数码管段码表
unsigned char NixieTable[]={0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,0x6D,0x7D,0x07,0x7F,0x6F,0x00,0x40};
/**
* @brief 设置显示缓存区
* @param Location 要设置的位置,范围:1~8
* @param Number 要设置的数字,范围:段码表索引范围
* @retval 无
*/
void Nixie_SetBuf(unsigned char Location,Number)
{
Nixie_Buf[Location]=Number;
}
/**
* @brief 数码管扫描显示
* @param Location 要显示的位置,范围:1~8
* @param Number 要显示的数字,范围:段码表索引范围
* @retval 无
*/
void Nixie_Scan(unsigned char Location,Number)
{
P0=0x00; //段码清0,消影
switch(Location) //位码输出
{
case 1:P24=1;P23=1;P22=1;break;
case 2:P24=1;P23=1;P22=0;break;
case 3:P24=1;P23=0;P22=1;break;
case 4:P24=1;P23=0;P22=0;break;
case 5:P24=0;P23=1;P22=1;break;
case 6:P24=0;P23=1;P22=0;break;
case 7:P24=0;P23=0;P22=1;break;
case 8:P24=0;P23=0;P22=0;break;
}
P0=NixieTable[Number]; //段码输出
}
/**
* @brief 数码管驱动函数,在中断中调用
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void Nixie_Loop(void)
{
static unsigned char i=1;
Nixie_Scan(i,Nixie_Buf[i]);
i++;
if(i>=9){i=1;}
}
Nixie.h
#ifndef __NIXIE_H__
#define __NIXIE_H__
void Nixie_SetBuf(unsigned char Location,Number);
void Nixie_Scan(unsigned char Location,Number);
void Nixie_Loop(void);
#endif
二十九、单片机实操二十七:DS18B20温度传感器与温度读取
1、DS18B20介绍

2、 引脚及应用电路

3、内部结构图

4、存储器结构

5、单总线介绍

6、单总线电路规范

7、单总线时序结构




8、DS18B20操作流程

9、DS18B20数据帧

10、温度存储格式
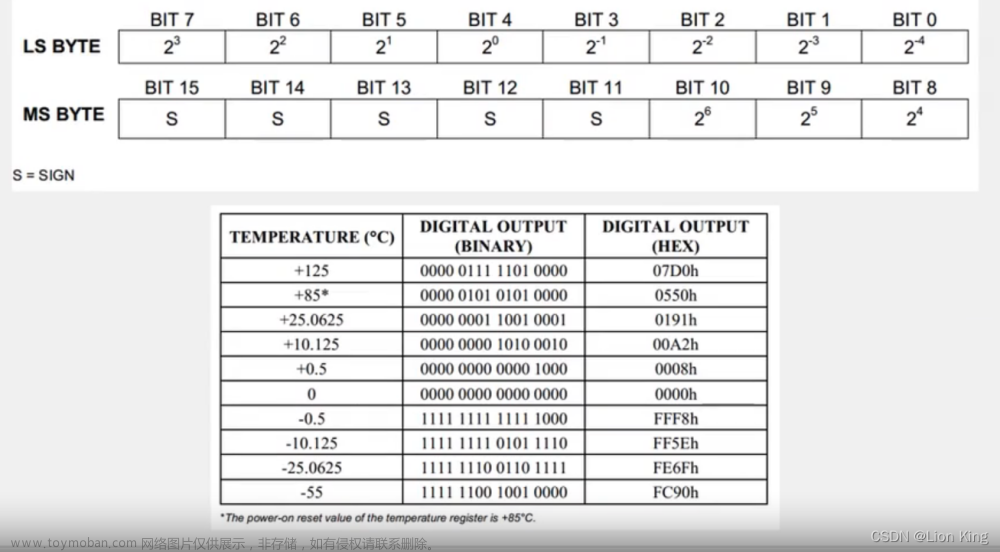
11、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "DS18B20.h"
#include "Delay.h"
#include "AT24C02.h"
#include "Key.h"
#include "Timer0.h"
float T,TShow;
char TLow,THigh;
unsigned char KeyNum;
void main()
{
DS18B20_ConvertT(); //上电先转换一次温度,防止第一次读数据错误
Delay(1000); //等待转换完成
THigh=AT24C02_ReadByte(0); //读取温度阈值数据
TLow=AT24C02_ReadByte(1);
if(THigh>125 || TLow<-55 || THigh<=TLow)
{
THigh=20; //如果阈值非法,则设为默认值
TLow=15;
}
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowString(1,1,"T:");
LCD_ShowString(2,1,"TH:");
LCD_ShowString(2,9,"TL:");
LCD_ShowSignedNum(2,4,THigh,3);
LCD_ShowSignedNum(2,12,TLow,3);
Timer0_Init();
while(1)
{
KeyNum=Key();
/*温度读取及显示*/
DS18B20_ConvertT(); //转换温度
T=DS18B20_ReadT(); //读取温度
if(T<0) //如果温度小于0
{
LCD_ShowChar(1,3,'-'); //显示负号
TShow=-T; //将温度变为正数
}
else //如果温度大于等于0
{
LCD_ShowChar(1,3,'+'); //显示正号
TShow=T;
}
LCD_ShowNum(1,4,TShow,3); //显示温度整数部分
LCD_ShowChar(1,7,'.'); //显示小数点
LCD_ShowNum(1,8,(unsigned long)(TShow*100)%100,2);//显示温度小数部分
/*阈值判断及显示*/
if(KeyNum)
{
if(KeyNum==1) //K1按键,THigh自增
{
THigh++;
if(THigh>125){THigh=125;}
}
if(KeyNum==2) //K2按键,THigh自减
{
THigh--;
if(THigh<=TLow){THigh++;}
}
if(KeyNum==3) //K3按键,TLow自增
{
TLow++;
if(TLow>=THigh){TLow--;}
}
if(KeyNum==4) //K4按键,TLow自减
{
TLow--;
if(TLow<-55){TLow=-55;}
}
LCD_ShowSignedNum(2,4,THigh,3); //显示阈值数据
LCD_ShowSignedNum(2,12,TLow,3);
AT24C02_WriteByte(0,THigh); //写入到At24C02中保存
Delay(5);
AT24C02_WriteByte(1,TLow);
Delay(5);
}
if(T>THigh) //越界判断
{
LCD_ShowString(1,13,"OV:H");
}
else if(T<TLow)
{
LCD_ShowString(1,13,"OV:L");
}
else
{
LCD_ShowString(1,13," ");
}
}
}
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1
{
static unsigned int T0Count;
TL0 = 0x18; //设置定时初值
TH0 = 0xFC; //设置定时初值
T0Count++;
if(T0Count>=20)
{
T0Count=0;
Key_Loop(); //每20ms调用一次按键驱动函数
}
}
OneWrite.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
//引脚定义
sbit OneWire_DQ=P3^7;
/**
* @brief 单总线初始化
* @param 无
* @retval 从机响应位,0为响应,1为未响应
*/
unsigned char OneWire_Init(void)
{
unsigned char i;
unsigned char AckBit;
OneWire_DQ=1;
OneWire_DQ=0;
i = 247;while (--i); //Delay 500us
OneWire_DQ=1;
i = 32;while (--i); //Delay 70us
AckBit=OneWire_DQ;
i = 247;while (--i); //Delay 500us
return AckBit;
}
/**
* @brief 单总线发送一位
* @param Bit 要发送的位
* @retval 无
*/
void OneWire_SendBit(unsigned char Bit)
{
unsigned char i;
OneWire_DQ=0;
i = 4;while (--i); //Delay 10us
OneWire_DQ=Bit;
i = 24;while (--i); //Delay 50us
OneWire_DQ=1;
}
/**
* @brief 单总线接收一位
* @param 无
* @retval 读取的位
*/
unsigned char OneWire_ReceiveBit(void)
{
unsigned char i;
unsigned char Bit;
OneWire_DQ=0;
i = 2;while (--i); //Delay 5us
OneWire_DQ=1;
i = 2;while (--i); //Delay 5us
Bit=OneWire_DQ;
i = 24;while (--i); //Delay 50us
return Bit;
}
/**
* @brief 单总线发送一个字节
* @param Byte 要发送的字节
* @retval 无
*/
void OneWire_SendByte(unsigned char Byte)
{
unsigned char i;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
OneWire_SendBit(Byte&(0x01<<i));
}
}
/**
* @brief 单总线接收一个字节
* @param 无
* @retval 接收的一个字节
*/
unsigned char OneWire_ReceiveByte(void)
{
unsigned char i;
unsigned char Byte=0x00;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
if(OneWire_ReceiveBit()){Byte|=(0x01<<i);}
}
return Byte;
}
OneWrite.h
#ifndef __ONEWIRE_H__
#define __ONEWIRE_H__
unsigned char OneWire_Init(void);
void OneWire_SendBit(unsigned char Bit);
unsigned char OneWire_ReceiveBit(void);
void OneWire_SendByte(unsigned char Byte);
unsigned char OneWire_ReceiveByte(void);
#endif
三十、单片机实操二十八:温度报警器
1、编写代码
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "DS18B20.h"
#include "Delay.h"
#include "AT24C02.h"
#include "Key.h"
#include "Timer0.h"
float T,TShow;
char TLow,THigh;
unsigned char KeyNum;
void main()
{
DS18B20_ConvertT(); //上电先转换一次温度,防止第一次读数据错误
Delay(1000); //等待转换完成
THigh=AT24C02_ReadByte(0); //读取温度阈值数据
TLow=AT24C02_ReadByte(1);
if(THigh>125 || TLow<-55 || THigh<=TLow)
{
THigh=20; //如果阈值非法,则设为默认值
TLow=15;
}
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowString(1,1,"T:");
LCD_ShowString(2,1,"TH:");
LCD_ShowString(2,9,"TL:");
LCD_ShowSignedNum(2,4,THigh,3);
LCD_ShowSignedNum(2,12,TLow,3);
Timer0_Init();
while(1)
{
KeyNum=Key();
/*温度读取及显示*/
DS18B20_ConvertT(); //转换温度
T=DS18B20_ReadT(); //读取温度
if(T<0) //如果温度小于0
{
LCD_ShowChar(1,3,'-'); //显示负号
TShow=-T; //将温度变为正数
}
else //如果温度大于等于0
{
LCD_ShowChar(1,3,'+'); //显示正号
TShow=T;
}
LCD_ShowNum(1,4,TShow,3); //显示温度整数部分
LCD_ShowChar(1,7,'.'); //显示小数点
LCD_ShowNum(1,8,(unsigned long)(TShow*100)%100,2);//显示温度小数部分
/*阈值判断及显示*/
if(KeyNum)
{
if(KeyNum==1) //K1按键,THigh自增
{
THigh++;
if(THigh>125){THigh=125;}
}
if(KeyNum==2) //K2按键,THigh自减
{
THigh--;
if(THigh<=TLow){THigh++;}
}
if(KeyNum==3) //K3按键,TLow自增
{
TLow++;
if(TLow>=THigh){TLow--;}
}
if(KeyNum==4) //K4按键,TLow自减
{
TLow--;
if(TLow<-55){TLow=-55;}
}
LCD_ShowSignedNum(2,4,THigh,3); //显示阈值数据
LCD_ShowSignedNum(2,12,TLow,3);
AT24C02_WriteByte(0,THigh); //写入到At24C02中保存
Delay(5);
AT24C02_WriteByte(1,TLow);
Delay(5);
}
if(T>THigh) //越界判断
{
LCD_ShowString(1,13,"OV:H");
}
else if(T<TLow)
{
LCD_ShowString(1,13,"OV:L");
}
else
{
LCD_ShowString(1,13," ");
}
}
}
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1
{
static unsigned int T0Count;
TL0 = 0x18; //设置定时初值
TH0 = 0xFC; //设置定时初值
T0Count++;
if(T0Count>=20)
{
T0Count=0;
Key_Loop(); //每20ms调用一次按键驱动函数
}
}
三十一、单片机实操二十九:LCD1602与功能函数代码
1、LCD1602介绍
2、引脚及应用电路

3、内部结构框图
 4、存储器结构
4、存储器结构

5、时序结构

6、LS1602指令集

7、LCD1602操作流程

8、编写代码
详见LCD1602模块。
三十二、单片机实操三十:直流电机驱动(PWM)与LED呼吸灯
1、直流电机介绍

2、电机驱动电路

3、PWM介绍

4、产生PWM的方法

5、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
sbit LED=P2^0;
void Delay(unsigned int t)
{
while(t--);
}
void main()
{
unsigned char Time,i;
while(1)
{
for(Time=0;Time<100;Time++) //改变亮灭时间,由暗到亮
{
for(i=0;i<20;i++) //计次延时
{
LED=0; //LED亮
Delay(Time); //延时Time
LED=1; //LED灭
Delay(100-Time); //延时100-Time
}
}
for(Time=100;Time>0;Time--) //改变亮灭时间,由亮到暗
{
for(i=0;i<20;i++) //计次延时
{
LED=0; //LED亮
Delay(Time); //延时Time
LED=1; //LED灭
Delay(100-Time); //延时100-Time
}
}
}
}
三十三、单片机实操三十一:直流电机调速
1、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
#include "Key.h"
#include "Nixie.h"
#include "Timer0.h"
sbit Motor=P1^0;
unsigned char Counter,Compare; //计数值和比较值,用于输出PWM
unsigned char KeyNum,Speed;
void main()
{
Timer0_Init();
while(1)
{
KeyNum=Key();
if(KeyNum==1)
{
Speed++;
Speed%=4;
if(Speed==0){Compare=0;} //设置比较值,改变PWM占空比
if(Speed==1){Compare=50;}
if(Speed==2){Compare=75;}
if(Speed==3){Compare=100;}
}
Nixie(1,Speed);
}
}
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1
{
TL0 = 0x9C; //设置定时初值
TH0 = 0xFF; //设置定时初值
Counter++;
Counter%=100; //计数值变化范围限制在0~99
if(Counter<Compare) //计数值小于比较值
{
Motor=1; //输出1
}
else //计数值大于比较值
{
Motor=0; //输出0
}
}
三十四、单片机实操三十二:AD/DA之AD模数转换
1、AD/DA介绍

2、硬件电路模型

3、硬件电路

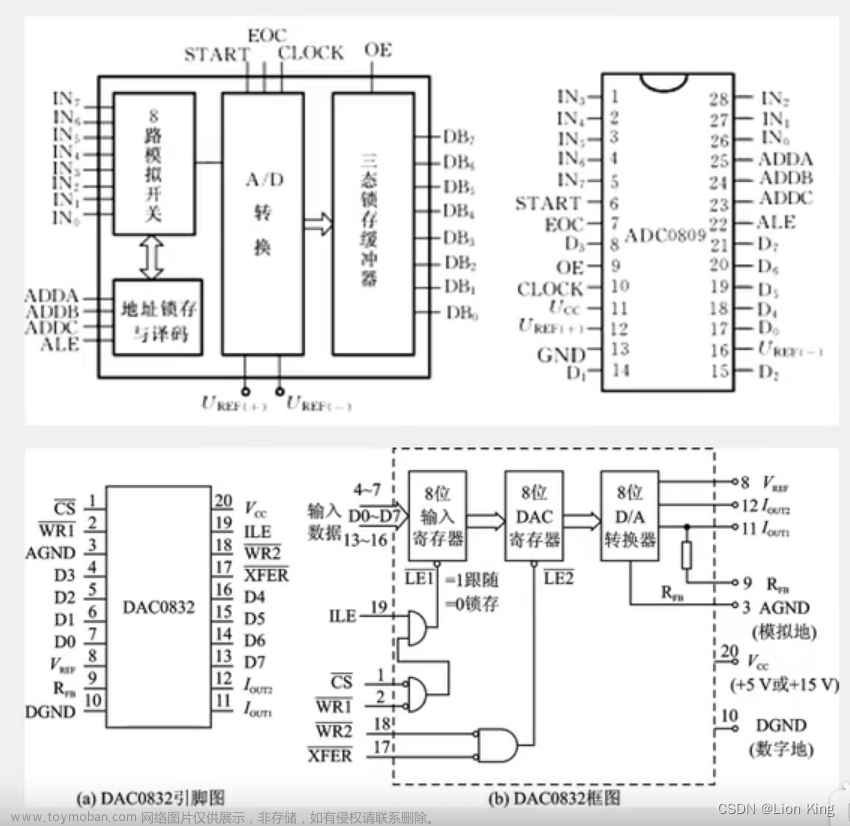
4、运算放大器

5、运放电路


6、DA原理


7、AD原理
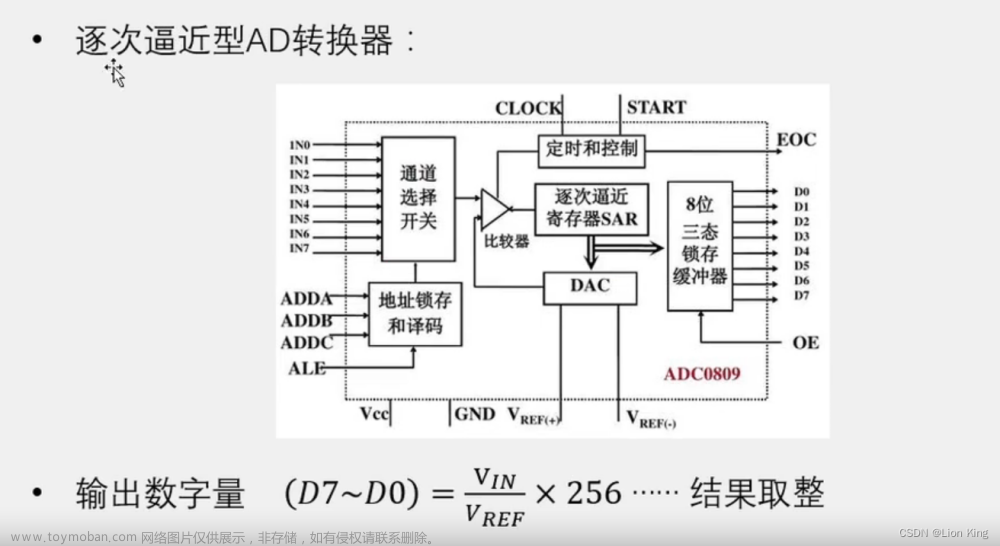
8、AD/DA性能指标

9、XPT2046功能说明

10、 XPT2046时序

11、开发板原理图

8、编写代码
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "XPT2046.h"
unsigned int ADValue;
void main(void)
{
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowString(1,1,"ADJ NTC GR");
while(1)
{
ADValue=XPT2046_ReadAD(XPT2046_XP); //读取AIN0,可调电阻
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,ADValue,3); //显示AIN0
ADValue=XPT2046_ReadAD(XPT2046_YP); //读取AIN1,热敏电阻
LCD_ShowNum(2,6,ADValue,3); //显示AIN1
ADValue=XPT2046_ReadAD(XPT2046_VBAT); //读取AIN2,光敏电阻
LCD_ShowNum(2,11,ADValue,3); //显示AIN2
Delay(100);
}
}
XPT2046.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include <INTRINS.H>
//引脚定义
sbit XPY2046_DIN=P3^4;
sbit XPY2046_CS=P3^5;
sbit XPY2046_DCLK=P3^6;
sbit XPY2046_DOUT=P3^7;
/**
* @brief ZPT2046读取AD值
* @param Command 命令字,范围:头文件内定义的宏,结尾的数字表示转换的位数
* @retval AD转换后的数字量,范围:8位为0~255,12位为0~4095
*/
unsigned int XPT2046_ReadAD(unsigned char Command)
{
unsigned char i;
unsigned int Data=0;
XPY2046_DCLK=0;
XPY2046_CS=0;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
XPY2046_DIN=Command&(0x80>>i);
XPY2046_DCLK=1;
XPY2046_DCLK=0;
}
for(i=0;i<16;i++)
{
XPY2046_DCLK=1;
XPY2046_DCLK=0;
if(XPY2046_DOUT){Data|=(0x8000>>i);}
}
XPY2046_CS=1;
return Data>>8;
}
XPT2046.h
#ifndef __XPT2046_H__
#define __XPT2046_H__
#define XPT2046_VBAT 0xAC
#define XPT2046_AUX 0xEC
#define XPT2046_XP 0x9C //0xBC
#define XPT2046_YP 0xDC
unsigned int XPT2046_ReadAD(unsigned char Command);
#endif
三十五、单片机实操三十三:DA数模转换
1、编写代码
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
#include "Timer0.h"
sbit DA=P2^1;
unsigned char Counter,Compare; //计数值和比较值,用于输出PWM
unsigned char i;
void main()
{
Timer0_Init();
while(1)
{
for(i=0;i<100;i++)
{
Compare=i; //设置比较值,改变PWM占空比
Delay(10);
}
for(i=100;i>0;i--)
{
Compare=i; //设置比较值,改变PWM占空比
Delay(10);
}
}
}
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1
{
TL0 = 0x9C; //设置定时初值
TH0 = 0xFF; //设置定时初值
Counter++;
Counter%=100; //计数值变化范围限制在0~99
if(Counter<Compare) //计数值小于比较值
{
DA=1; //输出1
}
else //计数值大于比较值
{
DA=0; //输出0
}
}
三十六、单片机实操三十四:红外遥控与外部中断
1、红外遥控简介

2、 硬件电路
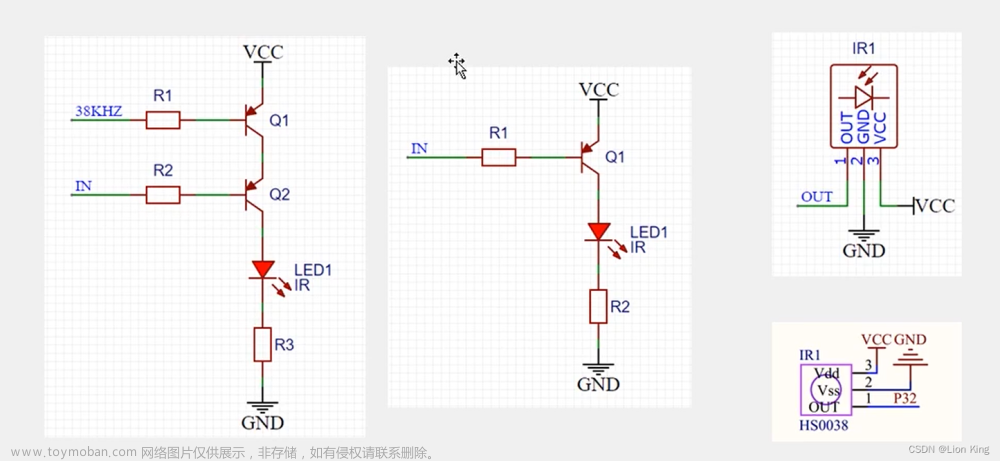
3、基本发送与接收

4、NEC编码


5、 遥控器键码

6、51单片机的外部中断

7、外部中断寄存器
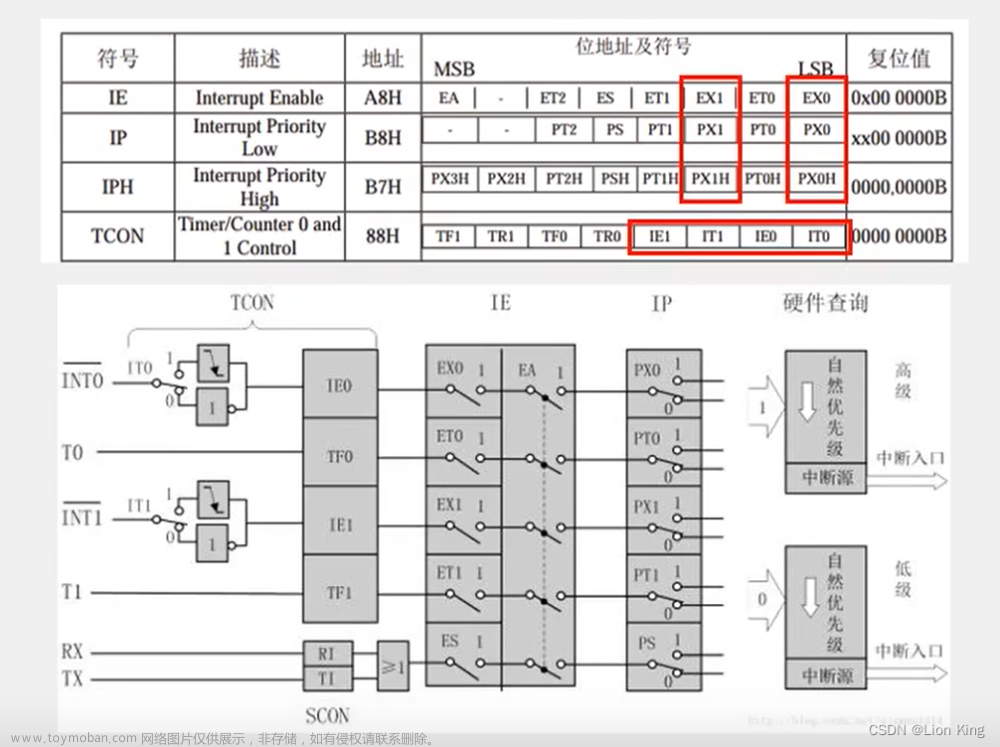
8、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "IR.h"
unsigned char Num;
unsigned char Address;
unsigned char Command;
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowString(1,1,"ADDR CMD NUM");
LCD_ShowString(2,1,"00 00 000");
IR_Init();
while(1)
{
if(IR_GetDataFlag() || IR_GetRepeatFlag()) //如果收到数据帧或者收到连发帧
{
Address=IR_GetAddress(); //获取遥控器地址码
Command=IR_GetCommand(); //获取遥控器命令码
LCD_ShowHexNum(2,1,Address,2); //显示遥控器地址码
LCD_ShowHexNum(2,7,Command,2); //显示遥控器命令码
if(Command==IR_VOL_MINUS) //如果遥控器VOL-按键按下
{
Num--; //Num自减
}
if(Command==IR_VOL_ADD) //如果遥控器VOL+按键按下
{
Num++; //Num自增
}
LCD_ShowNum(2,12,Num,3); //显示Num
}
}
}
IR.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Timer0.h"
#include "Int0.h"
unsigned int IR_Time;
unsigned char IR_State;
unsigned char IR_Data[4];
unsigned char IR_pData;
unsigned char IR_DataFlag;
unsigned char IR_RepeatFlag;
unsigned char IR_Address;
unsigned char IR_Command;
/**
* @brief 红外遥控初始化
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void IR_Init(void)
{
Timer0_Init();
Int0_Init();
}
/**
* @brief 红外遥控获取收到数据帧标志位
* @param 无
* @retval 是否收到数据帧,1为收到,0为未收到
*/
unsigned char IR_GetDataFlag(void)
{
if(IR_DataFlag)
{
IR_DataFlag=0;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief 红外遥控获取收到连发帧标志位
* @param 无
* @retval 是否收到连发帧,1为收到,0为未收到
*/
unsigned char IR_GetRepeatFlag(void)
{
if(IR_RepeatFlag)
{
IR_RepeatFlag=0;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief 红外遥控获取收到的地址数据
* @param 无
* @retval 收到的地址数据
*/
unsigned char IR_GetAddress(void)
{
return IR_Address;
}
/**
* @brief 红外遥控获取收到的命令数据
* @param 无
* @retval 收到的命令数据
*/
unsigned char IR_GetCommand(void)
{
return IR_Command;
}
//外部中断0中断函数,下降沿触发执行
void Int0_Routine(void) interrupt 0
{
if(IR_State==0) //状态0,空闲状态
{
Timer0_SetCounter(0); //定时计数器清0
Timer0_Run(1); //定时器启动
IR_State=1; //置状态为1
}
else if(IR_State==1) //状态1,等待Start信号或Repeat信号
{
IR_Time=Timer0_GetCounter(); //获取上一次中断到此次中断的时间
Timer0_SetCounter(0); //定时计数器清0
//如果计时为13.5ms,则接收到了Start信号(判定值在12MHz晶振下为13500,在11.0592MHz晶振下为12442)
if(IR_Time>12442-500 && IR_Time<12442+500)
{
IR_State=2; //置状态为2
}
//如果计时为11.25ms,则接收到了Repeat信号(判定值在12MHz晶振下为11250,在11.0592MHz晶振下为10368)
else if(IR_Time>10368-500 && IR_Time<10368+500)
{
IR_RepeatFlag=1; //置收到连发帧标志位为1
Timer0_Run(0); //定时器停止
IR_State=0; //置状态为0
}
else //接收出错
{
IR_State=1; //置状态为1
}
}
else if(IR_State==2) //状态2,接收数据
{
IR_Time=Timer0_GetCounter(); //获取上一次中断到此次中断的时间
Timer0_SetCounter(0); //定时计数器清0
//如果计时为1120us,则接收到了数据0(判定值在12MHz晶振下为1120,在11.0592MHz晶振下为1032)
if(IR_Time>1032-500 && IR_Time<1032+500)
{
IR_Data[IR_pData/8]&=~(0x01<<(IR_pData%8)); //数据对应位清0
IR_pData++; //数据位置指针自增
}
//如果计时为2250us,则接收到了数据1(判定值在12MHz晶振下为2250,在11.0592MHz晶振下为2074)
else if(IR_Time>2074-500 && IR_Time<2074+500)
{
IR_Data[IR_pData/8]|=(0x01<<(IR_pData%8)); //数据对应位置1
IR_pData++; //数据位置指针自增
}
else //接收出错
{
IR_pData=0; //数据位置指针清0
IR_State=1; //置状态为1
}
if(IR_pData>=32) //如果接收到了32位数据
{
IR_pData=0; //数据位置指针清0
if((IR_Data[0]==~IR_Data[1]) && (IR_Data[2]==~IR_Data[3])) //数据验证
{
IR_Address=IR_Data[0]; //转存数据
IR_Command=IR_Data[2];
IR_DataFlag=1; //置收到连发帧标志位为1
}
Timer0_Run(0); //定时器停止
IR_State=0; //置状态为0
}
}
}
IR.h
#ifndef __IR_H__
#define __IR_H__
#define IR_POWER 0x45
#define IR_MODE 0x46
#define IR_MUTE 0x47
#define IR_START_STOP 0x44
#define IR_PREVIOUS 0x40
#define IR_NEXT 0x43
#define IR_EQ 0x07
#define IR_VOL_MINUS 0x15
#define IR_VOL_ADD 0x09
#define IR_0 0x16
#define IR_RPT 0x19
#define IR_USD 0x0D
#define IR_1 0x0C
#define IR_2 0x18
#define IR_3 0x5E
#define IR_4 0x08
#define IR_5 0x1C
#define IR_6 0x5A
#define IR_7 0x42
#define IR_8 0x52
#define IR_9 0x4A
void IR_Init(void);
unsigned char IR_GetDataFlag(void);
unsigned char IR_GetRepeatFlag(void);
unsigned char IR_GetAddress(void);
unsigned char IR_GetCommand(void);
#endif
Int0.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
/**
* @brief 外部中断0初始化
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void Int0_Init(void)
{
IT0=1;
IE0=0;
EX0=1;
EA=1;
PX0=1;
}
/*外部中断0中断函数模板
void Int0_Routine(void) interrupt 0
{
}
*/
Int0.h
#ifndef __INT0_H__
#define __INT0_H__
void Int0_Init(void);
#endif
Timer0.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
/**
* @brief 定时器0初始化
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void Timer0_Init(void)
{
TMOD &= 0xF0; //设置定时器模式
TMOD |= 0x01; //设置定时器模式
TL0 = 0; //设置定时初值
TH0 = 0; //设置定时初值
TF0 = 0; //清除TF0标志
TR0 = 0; //定时器0不计时
}
/**
* @brief 定时器0设置计数器值
* @param Value,要设置的计数器值,范围:0~65535
* @retval 无
*/
void Timer0_SetCounter(unsigned int Value)
{
TH0=Value/256;
TL0=Value%256;
}
/**
* @brief 定时器0获取计数器值
* @param 无
* @retval 计数器值,范围:0~65535
*/
unsigned int Timer0_GetCounter(void)
{
return (TH0<<8)|TL0;
}
/**
* @brief 定时器0启动停止控制
* @param Flag 启动停止标志,1为启动,0为停止
* @retval 无
*/
void Timer0_Run(unsigned char Flag)
{
TR0=Flag;
}
Timer0.h
#ifndef __TIMER0_H__
#define __TIMER0_H__
void Timer0_Init(void);
void Timer0_SetCounter(unsigned int Value);
unsigned int Timer0_GetCounter(void);
void Timer0_Run(unsigned char Flag);
#endif
三十七、单片机实操三十五:红外遥控电机调速
1、编写程序
main.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Delay.h"
#include "Key.h"
#include "Nixie.h"
#include "Motor.h"
#include "IR.h"
unsigned char Command,Speed;
void main()
{
Motor_Init();
IR_Init();
while(1)
{
if(IR_GetDataFlag()) //如果收到数据帧
{
Command=IR_GetCommand(); //获取遥控器命令码
if(Command==IR_0){Speed=0;} //根据遥控器命令码设置速度
if(Command==IR_1){Speed=1;}
if(Command==IR_2){Speed=2;}
if(Command==IR_3){Speed=3;}
if(Speed==0){Motor_SetSpeed(0);} //速度输出
if(Speed==1){Motor_SetSpeed(50);}
if(Speed==2){Motor_SetSpeed(75);}
if(Speed==3){Motor_SetSpeed(100);}
}
Nixie(1,Speed); //数码管显示速度
}
}
Time1.c
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
/**
* @brief 定时器1初始化,100us@12.000MHz
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void Timer1_Init(void)
{
TMOD &= 0x0F; //设置定时器模式
TMOD |= 0x10; //设置定时器模式
TL1 = 0x9C; //设置定时初值
TH1 = 0xFF; //设置定时初值
TF1 = 0; //清除TF1标志
TR1 = 1; //定时器1开始计时
ET1=1;
EA=1;
PT1=0;
}
/*定时器中断函数模板
void Timer1_Routine() interrupt 3
{
static unsigned int T1Count;
TL1 = 0x9C; //设置定时初值
TH1 = 0xFF; //设置定时初值
T1Count++;
if(T1Count>=1000)
{
T1Count=0;
}
}
*/
Time1.h
#ifndef __TIMER1_H__
#define __TIMER1_H__
void Timer1_Init(void);
#endif
Motor.c文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-777610.html
#include <STC89C5xRC.H>
#include "Timer1.h"
//引脚定义
sbit Motor=P1^0;
unsigned char Counter,Compare;
/**
* @brief 电机初始化
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void Motor_Init(void)
{
Timer1_Init();
}
/**
* @brief 电机设置速度
* @param Speed 要设置的速度,范围0~100
* @retval 无
*/
void Motor_SetSpeed(unsigned char Speed)
{
Compare=Speed;
}
//定时器1中断函数
void Timer1_Routine() interrupt 3
{
TL1 = 0x9C; //设置定时初值
TH1 = 0xFF; //设置定时初值
Counter++;
Counter%=100; //计数值变化范围限制在0~99
if(Counter<Compare) //计数值小于比较值
{
Motor=1; //输出1
}
else //计数值大于比较值
{
Motor=0; //输出0
}
}
Motor.h文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-777610.html
#ifndef __MOTOR_H__
#define __MOTOR_H__
void Motor_Init(void);
void Motor_SetSpeed(unsigned char Speed);
#endif
到了这里,关于C语言:51单片机看这一篇就够了的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!