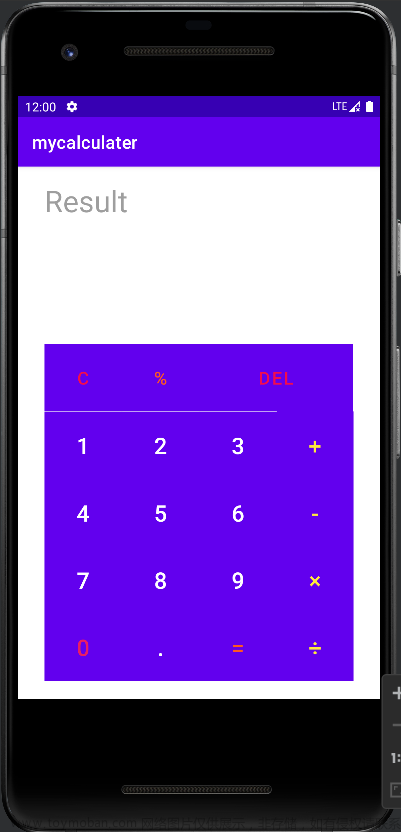
一.实验要求
结合所学内容利用Android studio来设计一个开发实例,这里去我选择做一个简易的计算器,可以初步实现加减乘除。
二.实验功能
该计算器与我们平常手机上的计算器一样,可以进行加减乘除操作。
三.实验过程
1.首先是关于计算器的布局
在layout文件下的drawable文件中新建四个xml文件:
button_bg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<!-- 背景色 -->
<solid android:color="#FFB400"/>
<corners
android:radius="5dp"/>
</shape>
这是一个用于定义 Android 形状的 XML 文件。这个文件定义了一个背景色为黄色(#FFB400)的形状,并设置了圆角半径为5dp。
gray.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<corners
android:radius="5dp"/>
<solid
android:color="#ffDEDEDE"/>
</shape>
这是一个用于定义 Android 形状的 XML 文件。这个文件定义了一个背景色为灰色(#ffDEDEDE)的形状,并设置了圆角半径为5dp。
white.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<corners
android:radius="5dp"/>
<solid
android:color="#ffffffff"/>
</shape>
这是一个用于定义 Android 形状的 XML 文件。这个文件定义了一个背景色为白色(#ffffffff)的形状,并设置了圆角半径为5dp。
selector.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<item android:drawable="@drawable/gray"
android:state_pressed="true"/>
<item android:drawable="@drawable/white"/>
</selector>
这是一个用于定义状态选择器的 XML 文件。在这个文件中,当控件处于被按下的状态时(state_pressed=true),会显示gray.xml所定义的样式,否则显示white.xml所定义的样式。
然后就是关于activity_main.xml文件的设计,由于代码较多在这里只展示一部分,具体代码放在源码链接。
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_input"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:background="@drawable/white"
android:editable="false"
android:paddingBottom="5dp"
android:textSize="30sp" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:gravity="center_horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_clr"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:text="C"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:paddingRight="15sp"
android:paddingBottom="15sp"
android:background="@drawable/selector"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_del"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:text="⬅"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:paddingRight="15sp"
android:paddingBottom="15sp"
android:background="@drawable/selector"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_div"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:text="÷"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:paddingRight="15sp"
android:paddingBottom="15sp"
android:background="@drawable/selector"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_mul"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:text="×"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:paddingRight="15sp"
android:paddingBottom="15sp"
android:background="@drawable/selector"/>
</LinearLayout>2.关于MainActivity
在onCreate方法中,我们首先通过findViewById方法获取到布局中定义的各个按钮和文本框的引用,并为它们设置点击事件监听器(this),这里我只显示一部分因为内容大致一样。
btn_0 = findViewById(R.id.btn_0);
btn_1 = findViewById(R.id.btn_1);
btn_2 = findViewById(R.id.btn_2);btn_0.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_1.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_2.setOnClickListener(this);在onClick方法中,我们根据点击的按钮的id进行不同的处理:
- 如果点击的按钮是数字或小数点按钮,则将相应的字符追加到当前输入的字符串后面,并更新显示在文本框中。
- 如果点击的按钮是加、减、乘、除按钮,则在当前输入的字符串后面添加一个空格和相应的运算符,并更新显示在文本框中。
- 如果点击的按钮是清除按钮,则清空当前输入的字符串,并清空文本框的显示。
- 如果点击的按钮是删除按钮,则删除当前输入字符串的最后一个字符,并更新显示在文本框中。
- 如果点击的按钮是等号按钮,则调用getResult方法进行计算,并将结果显示在文本框中。
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String str = et_input.getText().toString();
if (v.getId() == R.id.btn_0 || v.getId() == R.id.btn_1 || v.getId() == R.id.btn_2 ||
v.getId() == R.id.btn_3 || v.getId() == R.id.btn_4 || v.getId() == R.id.btn_5 ||
v.getId() == R.id.btn_6 || v.getId() == R.id.btn_7 || v.getId() == R.id.btn_8 ||
v.getId() == R.id.btn_9 || v.getId() == R.id.btn_pt) {
// 处理数字和小数点按钮的点击事件
if (clr_flag) {
clr_flag = false;
str = "";
et_input.setText("");
}
et_input.setText(str + ((Button) v).getText());
} else if (v.getId() == R.id.btn_add || v.getId() == R.id.btn_sub ||
v.getId() == R.id.btn_mul || v.getId() == R.id.btn_div) {
// 处理运算符按钮的点击事件
if (clr_flag) {
clr_flag = false;
str = "";
et_input.setText("");
}
if (str.contains("+") || str.contains("-") || str.contains("×") || str.contains("÷")) {
str = str.substring(0, str.indexOf(" "));
}
et_input.setText(str + " " + ((Button) v).getText() + " ");
} else if (v.getId() == R.id.btn_clr) {
// 处理清除按钮的点击事件
if (clr_flag)
clr_flag = false;
str = "";
et_input.setText("");
} else if (v.getId() == R.id.btn_del) {
// 处理删除按钮的点击事件
if (clr_flag) {
clr_flag = false;
str = "";
et_input.setText("");
} else if (str != null && !str.equals("")) {
et_input.setText(str.substring(0, str.length() - 1));
}
} else if (v.getId() == R.id.btn_eq) {
// 处理等号按钮的点击事件
getResult();
}
}当输入数据之后就需要输出结果了,这里定义了getResult方法来输出结果。getResult方法用于计算当前输入的表达式,并将结果显示在文本框中。它首先判断表达式中是否包含运算符,如果不包含则直接返回。然后根据运算符的类型进行相应的运算,并将结果显示在文本框中。
private void getResult() {
String exp=et_input.getText().toString();
if(exp==null||exp.equals("")) return ;
//因为没有运算符所以不用运算
if(!exp.contains(" ")){
return ;
}
if(clr_flag){
clr_flag=false;
return;
}
clr_flag=true;
//截取运算符前面的字符串
String s1=exp.substring(0,exp.indexOf(" "));
//截取的运算符
String op=exp.substring(exp.indexOf(" ")+1,exp.indexOf(" ")+2);
//截取运算符后面的字符串
String s2=exp.substring(exp.indexOf(" ")+3);
double cnt=0;
if(!s1.equals("")&&!s2.equals("")){
double d1=Double.parseDouble(s1);
double d2=Double.parseDouble(s2);
if(op.equals("+")){
cnt=d1+d2;
}
if(op.equals("-")){
cnt=d1-d2;
}
if(op.equals("×")){
cnt=d1*d2;
}
if(op.equals("÷")){
if(d2==0) cnt=0;
else cnt=d1/d2;
}
if(!s1.contains(".")&&!s2.contains(".")&&!op.equals("÷")) {
int res = (int) cnt;
et_input.setText(res+"");
}else {
et_input.setText(cnt+"");}
}
//如果s1是空 s2不是空 就执行下一步
else if(!s1.equals("")&&s2.equals("")){
double d1=Double.parseDouble(s1);
if(op.equals("+")){
cnt=d1;
}
if(op.equals("-")){
cnt=d1;
}
if(op.equals("×")){
cnt=0;
}
if(op.equals("÷")){
cnt=0;
}
if(!s1.contains(".")) {
int res = (int) cnt;
et_input.setText(res+"");
}else {
et_input.setText(cnt+"");}
}
//如果s1是空 s2不是空 就执行下一步
else if(s1.equals("")&&!s2.equals("")){
double d2=Double.parseDouble(s2);
if(op.equals("+")){
cnt=d2;
}
if(op.equals("-")){
cnt=0-d2;
}
if(op.equals("×")){
cnt=0;
}
if(op.equals("÷")){
cnt=0;
}
if(!s2.contains(".")) {
int res = (int) cnt;
et_input.setText(res+"");
}else {
et_input.setText(cnt+"");}
}
else {
et_input.setText("");
}
}结果如下:

加法:

减法:
 c
c
乘法:

除法:

四.实验总结
这次内容具体包括:通过一个启动Activity布置4个按钮,每个按钮分别触发加、减、乘、除的Activity;然后在打开的Activity中实现与实验一类似的页面,以一个按钮触发计算输出。但是在这次实验中我首先用的是switch case语句来记录用户所点击的按钮。但是所有的case语句都报错了,经过查看资料发现问题是由于switch语句的case标签不是常量表达式引起的。在Java中,case标签必须是一个常量表达式,例如整数或字符常量,枚举常量等。如果case语句包含变量或函数调用等非常量表达式,则会引发"Constant expression required"错误。于是我将switch语句替换成了if语句,结果顺利进行。
五.代码仓库文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-781197.html
xushijie/移动开发计算器文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-781197.html
到了这里,关于移动开发作业三:使用Android studio来实现简单的计算器的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!