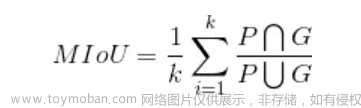Dice
理论
Dice用来衡量预测结果pred和标签label的相似度,公式如下图所示,即两个集合的交集/并集。
注意:对于多分类的分割任务,网络的输出结果是多通道的,使用Dice计算准确度需要将标签转换为多通道的one_hot形式。
代码
def dice_acc(predict, label):
"""
计算多个batch的dicc
@param predict: 模型预测值,Shape:[B, C, W, H]
@param label: one_hot形式的标签,Shape:[B, C, W, H]
"""
batch_num, class_num = predict.shape[0: 2]
assert predict.size() == label.size(), "the size of predict and target must be equal."
# 计算交集
intersection = (predict * label).reshape((batch_num, class_num, -1)).sum(dim=2)
# 计算并集
union = (predict + label).reshape((batch_num, class_num, -1)).sum(dim=2)
dice = (2. * intersection + 1) / (union + 1)
dice = dice.mean()
# loss = 1 - dice
return dice
- 如果需要计算
dice loss,只需要1- dice_acc即可。 - 可以借助
torch.nn.functional.one_hot()函数将标签转化为one_hot形式。 - 以上代码传入的
predict和label都是tensor,需要调用dice.item()只返回数值。
MIou
理论
为了计算MIoU,我们需要先引入混淆矩阵的概念。所谓混淆矩阵,就是真实结果和预测结果所组成的矩阵,将整个结果集划分为TP,TN,FP,FN四类。
- TP:True Positive 真正的正类,即label是正标签,predict也是正标签。
- FN:False Negative 假的负类,即label是正标签,predict却预测是负标签。
- FP:False Positive 假的正类,即label是负标签,predict却预测是正标签。
- TN:True Negative 真正的负类,即label是负标签,predict也是负标签。
有了混淆矩阵后,我们可以在此基础上计算各种评价指标:
查准率 precison

查全率 recall

MIoU 平均交并比

上面的公式对应到混淆矩阵A上为 A(i, i) / A(i, : ) + A(:, j) - A(i, j),即对角线元素比上(对角线元素所在行和列的元素和 - 对角线元素)。
注意:为了计算
MIoU,我们需要把多通道的预测结果通过torch.argmax()函数转化为单通道的预测类别,然后和单通道的label计算交并比。
代码
为了计算MIoU,这里提供两种方式,一种是比较高效的矩阵运算,另一种是常规的好理解的但效率不高的方式,两者都可以用。
高效的矩阵运算
def miou(predict, label, class_num=3):
"""
计算多个batch的moiu
@param predict: 模型预测值,Shape:[B, W, H]
@param label: 标签,Shape:[B, W, H]
"""
batch = label.shape[0]
predict, label = predict.flatten(), label.flatten()
# 忽略背景的话就 >0
k = (predict >= 0) & (predict < class_num)
# 计算混淆矩阵
hist = torch.bincount(class_num * predict[k].type(torch.int32) + label[k], minlength=batch * (class_num ** 2)).reshape(batch, class_num, class_num)
# 将多个batch合并为一个,如果传入的参数没有batch这个维度,可以注释掉这句话
hist = hist.sum(0)
# 计算各个类的iou
miou = torch.diag(hist) / torch.maximum((hist.sum(1) + hist.sum(0) - torch.diag(hist)), torch.tensor(1))
# 计算平均值miou
return miou.mean()
低效的好理解的
def IOU(pred, target, n_classes = 3 ):
"""
计算miou
@param predict: 模型预测值,Shape:[W, H]
@param label: 标签,Shape:[W, H]
"""
ious = []
# 从1开始,即忽略背景
# 依次计算每个类
for cls in range(1, n_classes):
pred_inds = pred == cls
target_inds = target == cls
# 计算两个集合在该类上的交集
intersection = (pred_inds[target_inds]).sum()
# 计算并集
union = pred_inds.sum() + target_inds.sum() - intersection
if union == 0:
ious.append(float('nan')) # If there is no ground truth,do not include in evaluation
else:
ious.append(float(intersection.item()) / float(max(union.item(), 1)))
# 计算多类的平均值
return torch.mean(torch.tensor(ious))
注意,这种的传入的参数是二维的,不能有batch维度。
计算混淆矩阵
这里提供一个计算混淆矩阵的快速实现,但很低效,仅供看看,实际还是要用上面torch.bincount计算混淆矩阵快。
# TP predict 和 label 同时为1
TP = ((pred1 == 1) & (label == 1)).cpu().sum()
# TN predict 和 label 同时为0
TN = ((pred1 == 0) & (label == 0)).cpu().sum()
# FN predict 0 label 1
FN = ((pred1 == 0) & (label == 1)).cpu().sum()
# FP predict 1 label 0
FP = ((pred1 == 1) & (label == 0)).cpu().sum()
Dice和MIoU两者的关系
对于二分类的任务来说,二者思想都是交集/并集,但dice并不是在分母上减去交集,而是将交集在分子上算了两次。
对于多分类来说,Dice是将预测结果转为了多通道,而MIoU只在一个通道上计算。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-787942.html
参考链接
https://www.jianshu.com/p/42939bf83b8a
https://blog.csdn.net/Pierce_KK/article/details/96505691
https://blog.csdn.net/lipengfei0427/article/details/109556985文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-787942.html
到了这里,关于图像分割评价指标:Dice和MIoU的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!