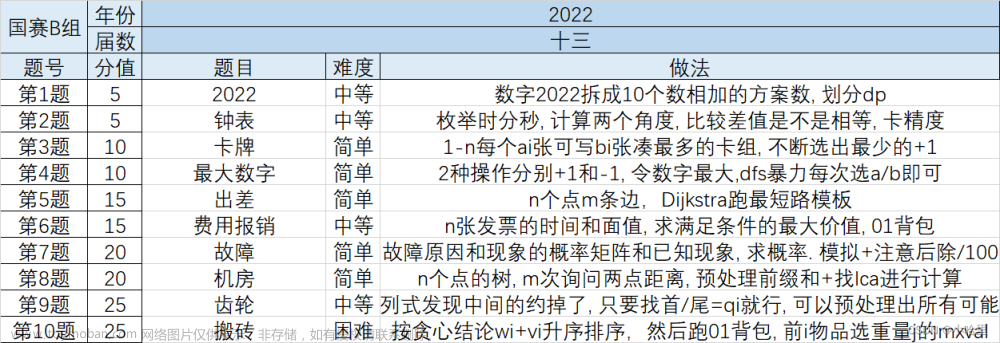
1.左移右移
1.题目描述
小蓝有一个长度为 N N N 的数组, 初始时从左到右依次是 1 , 2 , 3 , … N 1,2,3, \ldots N 1,2,3,…N 。
之后小蓝对这个数组进行了 M M M 次操作, 每次操作可能是以下 2 种之一:
-
左移 x x x, 即把 x x x 移动到最左边。
-
右移 x x x, 即把 x x x 移动到最右边。
请你回答经过 M M M 次操作之后, 数组从左到右每个数是多少?
2.输入格式
第一行包含 2 个整数, N N N 和 M M M 。以下 M M M 行每行一个操作, 其中 “ L x Lx Lx "表示左移 x x x ," R x Rx Rx "表示右移 x x x 。
3.输出格式
输出 N N N 个数, 代表操作后的数组。
4.样例输入
5 3
L 3
L 2
R 1
5.样例输出
2 3 4 5 1
6.数据范围
1 ≤ N , M ≤ 200000 , 1 ≤ x ≤ N . 1≤N,M≤200000,1≤x≤N. 1≤N,M≤200000,1≤x≤N.
6.原题链接
左移右移
2.解题思路
题目的含义非常简单,如果按照朴素的方式遍历寻找 x x x,然后直接进行插入操作,在 n n n的级别在 2 e 5 2e5 2e5的范围这时间复杂度显然是不可接受的。想要解决此题我们需要思考两个点:
- 如何高效地进行插入和删除操作
- 如何快速地找到某个点所在的位置
对于第一点,我们应该快速地想到链表这个数据结构,由于题目需要在左端点和右端点都进行插入操作,所以我们应该联想到 双链表 。它可以在
O
(
1
)
O(1)
O(1)的时间范围内对元素进行插入和删除,这显然是我们需要的数据结构。
当然,双链表并不支持高效地查找,所以我们如何快速找到
x
x
x 的位置呢?这时候我们应该联想到 哈希表,因为我们需要手动实现双链表,所以每个链表结点都对应一个值,同时它也是一个对象,我们可以使用哈希表,以值为
k
e
y
key
key,以这个链表结点对象为
v
a
l
u
e
value
value。这样我们就可以快速获得这个结点,然后再进行常规的双链表插入删除操作。
考虑一个更简单的做法,由于每次都将某个数要么变为最大,要么变为最小,那么我们可以记录每个数的权值大小。假设此时最小的数权值为 l l l ,最大的数权值为 r r r ,若要将 x x x 挪到最左边,将其权值赋值为 l − 1 l-1 l−1 ,若要将其移动最右边则将其赋值为 r + 1 r+1 r+1,同时更新 l , r l,r l,r。每个数最开始的权值等于其自身,当操作完毕后,按照权值排序得到的序列即是答案。
3.Ac_code
Java文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-788366.html
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static Map<Integer,Node> map=new HashMap<>();
static PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int m=sc.nextInt();
//双链表的头结点和尾结点
Node head=new Node(-1,null,null);
Node last=new Node(-1,null,null);
Node pre=head;
//构建双链表
for (int i = 1; i <=n; i++) {
pre.next=new Node(i,pre,null);
pre=pre.next;
map.put(i,pre);
}
last.pre=pre;
pre.next=last;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
char c=sc.next().charAt(0);
int x=sc.nextInt();
//先将x对应的结点在双链表中删除
Node node=map.get(x);
node.pre.next=node.next;
node.next.pre=node.pre;
if (c=='L'){
//将其插入到左端点
node.next=head.next;
head.next.pre=node;
head.next=node;
node.pre=head;
}else{
//将其插入到右端点
node.pre=last.pre;
last.pre.next=node;
node.next=last;
last.pre=node;
}
}
pre=head.next;
while (pre!=last){
out.print(pre.v+" ");
pre=pre.next;
}
out.flush();
}
static class Node{
int v;
Node pre;
Node next;
public Node(int v, Node pre, Node next) {
this.v = v;
this.pre = pre;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
C++文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-788366.html
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define pb(s) push_back(s);
#define SZ(s) ((int)s.size());
#define ms(s,x) memset(s, x, sizeof(s))
#define all(s) s.begin(),s.end()
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
const int N = 200010;
int n, m;
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m;
std::vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
a[i] = i;
}
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
string op;
int x;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
cin >> op >> x;
x--;
if (op == "L") a[x] = --l;
else a[x] = ++r;
}
std::vector<PII> b(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
b[i] = {a[i], i};
}
sort(all(b));
for (auto [x, y]: b) cout << y + 1 << " ";
}
int main()
{
ios_base :: sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
到了这里,关于第十三届蓝桥杯Java B 组国赛 C 题——左移右移(AC)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!