阅读本文大约需要3分钟

主要内容:数据分析。
适用人群:Python初学者,数据分析师,或有志从事数据分析工作的人员。
准备软件:Anaconda(Spyder:代码编译)、Navicat Premium 12(数据库)。

从事IT项目管理这么多年,基本上已经遗弃编程技能,但从2019年开始接触Python,深深地迷上了这门语言,像硬件集成、数据分析,我都会用python来写。晓风想通过本文,让初学者们学会以下内容:
1、Pyecharts图表;
2、连接数据库;
3、大屏看板-监控中心。
今天,我们讲:3、大屏看板如何布局
首先,我们自己先拟个大屏的草稿(如上图),把大屏分割成8个部分(Part0-7)。

大屏内容设计好后,接上文,我们把图表的函数都用代码写出来
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Bar,Gauge,Pie,Page,Funnel,Geo,Scatter3D
import random
def bar(): #柱状图
cate = ['1月', '2月', '3月', '4月', '5月', '6月']
c = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(cate)
.add_yaxis("订单数", [random.randint(100, 200) for _ in cate])
.add_yaxis("完成数", [random.randint(50, 100) for _ in cate])
.set_series_opts(
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True,color="#2CB34A")
)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="2021年订单推移图",
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color="#2CB34A"),
pos_left="5%"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color="#2CB34A")),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(color="#2CB34A")),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(color="#2CB34A"))
)
.set_colors(["blue", "green"])
#.render("bar_stack0.html")
)
return c
def tab0(name,color): #标题
c = (Pie().
set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title=name,pos_left='center',pos_top='center',
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color=color,font_size=20))))
return c
def tab1(name,color): #标题
c = (Pie().
set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title=name,pos_left='center',pos_top='center',
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color=color,font_size=25))))
return c
def gau():#仪表图
c = (
Gauge(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width="400px", height="400px"))
.add(series_name="库位利用率", data_pair=[["", 90]])
.set_global_opts(
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False),
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(is_show=True, formatter="{a} <br/>{b} : {c}%"),
)
#.render("gauge.html")
)
return c
def radius():
cate = ['客户A', '客户B', '客户C', '客户D', '客户E', '其他客户']
data = [153, 124, 107, 99, 89, 46]
c=Pie()
c.add('', [list(z) for z in zip(cate, data)],
radius=["30%", "75%"],
rosetype="radius")
c.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="客户销售额占比", padding=[1,250],title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color="#FFFFFF")),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color="#FFFFFF"),type_="scroll",orient="vertical",pos_right="5%",pos_top="middle")
)
c.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {d}%"))
c.set_colors(['red',"orange", "yellow", "green", "Cyan", "purple"])
return c
def funnel():
cate = ['访问', '注册', '加入购物车', '提交订单', '付款成功']
data = [30398, 15230, 10045, 8109, 5698]
c = Funnel()
c.add("用户数", [list(z) for z in zip(cate, data)],
sort_='ascending',
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(position="inside"))
c.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title=""))
return c
def geo():
city_num = [('武汉',105),('成都',70),('北京',99),
('西安',80),('杭州',60),('贵阳',34),
('上海',65),('深圳',54),('乌鲁木齐',76),
('哈尔滨',47),('兰州',56),('信阳',85)]
start_end = [('宁波','成都'),('武汉','北京'),('武汉','西安'),
('长沙','杭州'),('武汉','贵阳'),('武汉','上海'),
('甘肃','深圳'),('北京','乌鲁木齐'),('上海','哈尔滨'),
('武汉','兰州'),('西藏','信阳')]
c = Geo()
c.add_schema(maptype='china',
itemstyle_opts=opts.ItemStyleOpts(color='#323c48', border_color='white'))
# 4.添加数据
c.add('', data_pair=city_num, color='white')
c.add('', data_pair=start_end, type_="lines",label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False),
effect_opts=opts.EffectOpts(symbol="arrow",
color='gold',
symbol_size=7))
c.set_global_opts(
title_opts = opts.TitleOpts(title=""))
return c
def scatter3D():
data = [(random.randint(0, 100), random.randint(0, 100), random.randint(0, 100)) for _ in range(80)]
c = (Scatter3D()
.add("", data)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(""),
)
)
接下来,我们引用Page函数,将所有图表堆积在一个页面中,代码如下
from pyecharts.charts import Page
page = Page()
page.add(
tab0("OFFICETOUCH","#2CB34A"),
bar(),
tab1("数据可视化大屏","#2CB34A"),
gau(),
radius(),
funnel(),
geo(),
scatter3D()
)
page.render("datacenter.html")
我们运行下上述两段代码,发现布局是按照从上到下一个个呈现的,到此我们完成了一半的编码

为了将图表按照我们的草稿布局,我们再引用HTML(from bs4 import BeautifulSoup)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
with open("datacenter.html", "r+", encoding='utf-8') as html:
html_bf = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
divs = html_bf.select('.chart-container')
divs[0]["style"] = "width:10%;height:10%;position:absolute;top:0;left:2%;"
divs[1]["style"] = "width:40%;height:40%;position:absolute;top:12%;left:0;"
divs[2]["style"] = "width:35%;height:10%;position:absolute;top:2%;left:30%;"
divs[3]["style"] = "width:40%;height:40%;position:absolute;top:10%;left:28%;"
divs[4]["style"] = "width:40%;height:35%;position:absolute;top:12%;left:55%;"
divs[5]["style"] = "width:30%;height:35%;position:absolute;top:60%;left:2%;"
divs[6]["style"] = "width:60%;height:50%;position:absolute;top:45%;left:15%;"
divs[7]["style"] = "width:35%;height:40%;position:absolute;top:50%;left:60%;"
body = html_bf.find("body")
body["style"] = "background-image: " # 背景颜色
html_new = str(html_bf)
html.seek(0, 0)
html.truncate()
html.write(html_new)
html.close()
代码中的divs[0][“style”] = “width:10%;height:10%;position:absolute;top:0;left:2%;” 即是我们对Part0的宽度、高度、位置、上边距、左边距的定义,这里我们用百分比以达到屏幕自适应的效果。
最后,我们还可以设置一张背景图,代码合起来如下
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Bar,Gauge,Pie,Page,Funnel,Geo,Scatter3D
import random
def bar(): #柱状图
cate = ['1月', '2月', '3月', '4月', '5月', '6月']
c = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(cate)
.add_yaxis("订单数", [random.randint(100, 200) for _ in cate])
.add_yaxis("完成数", [random.randint(50, 100) for _ in cate])
.set_series_opts(
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True,color="#2CB34A")
)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="2021年订单推移图",
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color="#2CB34A"),
pos_left="5%"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color="#2CB34A")),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(color="#2CB34A")),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(color="#2CB34A"))
)
.set_colors(["blue", "green"])
#.render("bar_stack0.html")
)
return c
def tab0(name,color): #标题
c = (Pie().
set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title=name,pos_left='center',pos_top='center',
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color=color,font_size=20))))
return c
def tab1(name,color): #标题
c = (Pie().
set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title=name,pos_left='center',pos_top='center',
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color=color,font_size=25))))
return c
def gau():#仪表图
c = (
Gauge(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width="400px", height="400px"))
.add(series_name="库位利用率", data_pair=[["", 90]])
.set_global_opts(
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False),
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(is_show=True, formatter="{a} <br/>{b} : {c}%"),
)
#.render("gauge.html")
)
return c
def radius():
cate = ['客户A', '客户B', '客户C', '客户D', '客户E', '其他客户']
data = [153, 124, 107, 99, 89, 46]
c=Pie()
c.add('', [list(z) for z in zip(cate, data)],
radius=["30%", "75%"],
rosetype="radius")
c.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="客户销售额占比", padding=[1,250],title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color="#FFFFFF")),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color="#FFFFFF"),type_="scroll",orient="vertical",pos_right="5%",pos_top="middle")
)
c.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {d}%"))
c.set_colors(['red',"orange", "yellow", "green", "Cyan", "purple"])
return c
def funnel():
cate = ['访问', '注册', '加入购物车', '提交订单', '付款成功']
data = [30398, 15230, 10045, 8109, 5698]
c = Funnel()
c.add("用户数", [list(z) for z in zip(cate, data)],
sort_='ascending',
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(position="inside"))
c.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title=""))
return c
def geo():
city_num = [('武汉',105),('成都',70),('北京',99),
('西安',80),('杭州',60),('贵阳',34),
('上海',65),('深圳',54),('乌鲁木齐',76),
('哈尔滨',47),('兰州',56),('信阳',85)]
start_end = [('宁波','成都'),('武汉','北京'),('武汉','西安'),
('长沙','杭州'),('武汉','贵阳'),('武汉','上海'),
('甘肃','深圳'),('北京','乌鲁木齐'),('上海','哈尔滨'),
('武汉','兰州'),('西藏','信阳')]
c = Geo()
c.add_schema(maptype='china',
itemstyle_opts=opts.ItemStyleOpts(color='#323c48', border_color='white'))
# 4.添加数据
c.add('', data_pair=city_num, color='white')
c.add('', data_pair=start_end, type_="lines",label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False),
effect_opts=opts.EffectOpts(symbol="arrow",
color='gold',
symbol_size=7))
c.set_global_opts(
title_opts = opts.TitleOpts(title=""))
return c
def scatter3D():
data = [(random.randint(0, 100), random.randint(0, 100), random.randint(0, 100)) for _ in range(80)]
c = (Scatter3D()
.add("", data)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(""),
)
)
return c
page = Page()
page.add(
tab0("OFFICETOUCH","#2CB34A"),
bar(),
tab1("数据可视化大屏","#2CB34A"),
gau(),
radius(),
funnel(),
geo(),
scatter3D()
)
page.render("datacenter.html")
#os.system("scatter.html")
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
with open("datacenter.html", "r+", encoding='utf-8') as html:
html_bf = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
divs = html_bf.select('.chart-container')
divs[0]["style"] = "width:10%;height:10%;position:absolute;top:0;left:2%;"
divs[1]["style"] = "width:40%;height:40%;position:absolute;top:12%;left:0;"
divs[2]["style"] = "width:35%;height:10%;position:absolute;top:2%;left:30%;"
divs[3]["style"] = "width:40%;height:40%;position:absolute;top:10%;left:28%;"
divs[4]["style"] = "width:40%;height:35%;position:absolute;top:12%;left:55%;"
divs[5]["style"] = "width:30%;height:35%;position:absolute;top:60%;left:2%;"
divs[6]["style"] = "width:60%;height:50%;position:absolute;top:45%;left:15%;"
divs[7]["style"] = "width:35%;height:40%;position:absolute;top:50%;left:60%;"
body = html_bf.find("body")
body["style"] = "background-image: url(bgd.jpg)" # 背景颜色
html_new = str(html_bf)
html.seek(0, 0)
html.truncate()
html.write(html_new)
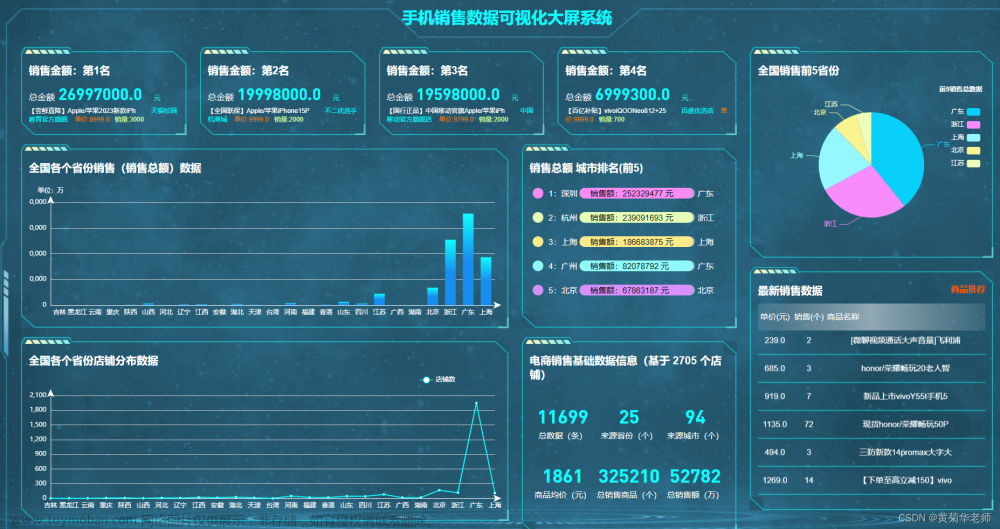
效果图如下:


学习到了这里,你是否能独立完成数据可视化的工作了啊?晓风终于不辱使命,向大家完整地介绍了如何使用Python绘制数据可视化大屏。晓风还会继续努力,为大家带来更多有趣、实用、简单地Python功能,愿我们一起成长!
另两篇教程,如下:
1、Python大屏看板最全教程之Pyecharts图表:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42341655/article/details/118078089
2、Python大屏看板最全教程之数据库连接https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42341655/article/details/118096691文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-789211.html
如果觉得有用的话,请帮忙点赞、关注、收藏哦,感谢您的支持!文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-789211.html
到了这里,关于Python数据可视化大屏最全教程(全)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!