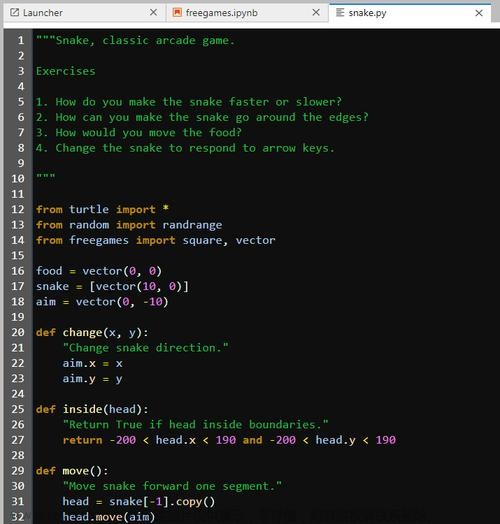
链栈是采用链式存储结构实现的栈,通常用单链表来表示。链栈的优点是不存在栈满上溢的情况(只有在内存溢出时才会出现栈满,通常不考虑)。链栈的栈顶是链表的第一个结点,栈底是链表的最后一个结点,一个链栈可以由栈顶指针唯一确定。链栈的每个结点都包含两个域,数据域和指针域,与单链表的结点结构一样。链栈只能在栈顶进行入栈或出栈操作,类似于一个只能进行头插法或尾插法的单链表。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-790132.html
1.链栈的初始化
Lsnode *InitStack(Lsnode *top)//初始化栈
{ top=(Lsnode *)malloc(sizeof(Lsnode));
top->next=NULL;
printf("Stack is NULL.\n");
return top;
}
2.插入一个元素
void Push(Lsnode *top, ElemType x)//插入一个元素
{Lsnode *p;
p=(Lsnode *)malloc(sizeof(Lsnode));
p->data=x;
p->next=top->next;
top->next=p;
}3.删除一个元素
ElemType Pop(Lsnode *top) //删除一个元素
{ElemType x; Lsnode *p;
if(top->next!=NULL)
{ p=top->next; top->next=p->next;
x=p->data; free(p); return x;
}
else
{ printf("Stack null! \n");
exit(1);
}
}
4.取栈顶元素
ElemType GetTop(Lsnode *top) //取栈顶元素
{ElemType x; Lsnode *p;
if(top->next!=NULL)
{ p=top->next;
x=p->data; return x;
}
else
{ printf("Stack null! \n");
exit(1);
}
}
5.输出链栈
void OutStack(Lsnode *top)//输出链栈
{ElemType x;Lsnode *p;
p=top->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
x=p->data; printf(" %d ",x);
p=p->next;
}
} 6.完整代码
#include"stdio.h"
#include"stdlib.h"
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct Lsnode
{ElemType data;
struct Lsnode *next;
} Lsnode;
void OutStack(Lsnode *p);
Lsnode *InitStack(Lsnode *p);
void Push(Lsnode *p,ElemType x);
ElemType Pop(Lsnode *p);
ElemType GetTop(Lsnode *p);
Lsnode *q;
int main()
{
ElemType y,cord;ElemType a;
do { printf("\n");
printf("\n 主菜单\n");
printf("\n 1 初始化栈\n");
printf("\n 2 插入一个元素\n");
printf("\n 3 删除栈顶元素\n");
printf("\n 4 取栈顶元素\n");
printf("\n 5 结束程序运行\n");
printf("\n---------------\n");
printf("请输入您的选择(1.2.3.4.5)"); scanf("%d",&cord);
switch(cord)
{case 1:q=InitStack(q);OutStack(q);
break;
case 2:{printf("\n请输入要插入的数据:");scanf("%d",&a);
Push(q,a);OutStack(q);
}break;
case 3:{a=Pop(q);printf("\n删除的是 %d\n",a);
OutStack(q);
}break;
case 4:{y=GetTop(q);printf("\n 栈顶=%d\n",y);
OutStack(q);
}break;
case 5:exit(1);
}
}while(cord<=5);
}
Lsnode *InitStack(Lsnode *top)//初始化栈
{ top=(Lsnode *)malloc(sizeof(Lsnode));
top->next=NULL;
printf("Stack is NULL.\n");
return top;
}
void Push(Lsnode *top, ElemType x)//插入一个元素
{Lsnode *p;
p=(Lsnode *)malloc(sizeof(Lsnode));
p->data=x;
p->next=top->next;
top->next=p;
}
ElemType Pop(Lsnode *top) //删除一个元素
{ElemType x; Lsnode *p;
if(top->next!=NULL)
{ p=top->next; top->next=p->next;
x=p->data; free(p); return x;
}
else
{ printf("Stack null! \n");
exit(1);
}
}
ElemType GetTop(Lsnode *top) //取栈顶元素
{ElemType x; Lsnode *p;
if(top->next!=NULL)
{ p=top->next;
x=p->data; return x;
}
else
{ printf("Stack null! \n");
exit(1);
}
}
void OutStack(Lsnode *top)//输出链栈
{ElemType x;Lsnode *p;
p=top->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
x=p->data; printf(" %d ",x);
p=p->next;
}
} 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-790132.html
到了这里,关于数据结构:链栈(含完整代码,可复制)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!