1 摘要
1.1 核心
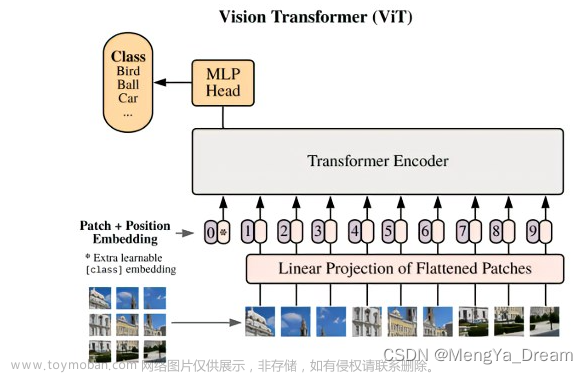
通过将图像切成patch线形层编码成token特征编码的方法,用transformer的encoder来做图像分类
2 模型架构
2.1 概览

2.2 对应CV的特定修改和相关理解
解决问题:
- transformer输入限制: 由于自注意力+backbone,算法复杂度为o(n²),token长度一般要<512才足够运算
解决:a) 将图片转为token输入 b) 将特征图转为token输入 c)√ 切patch转为token输入 - transformer无先验知识:卷积存在平移不变性(同特征同卷积核同结果)和局部相似性(相邻特征相似结果),
而transformer无卷积核概念,只有整个编解码器,需要从头学
解决:大量数据训练 - cv的各种自注意力机制需要复杂工程实现:
解决:直接用整个transformer模块 - 分类head:
解决:直接沿用transformer cls token - position编码:
解决:1D编码
pipeline:
224x224输入切成16x16patch进行位置编码和线性编码后增加cls token 一起输入的encoder encoder中有L个selfattention模块
输出的cls token为目标类别
3 代码
如果理解了transformer,看完这个结构感觉真的很简单,这篇论文也只是开山之作,没有特别复杂的结构,所以想到代码里看看。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-791085.html
import torch
from torch import nn
from einops import rearrange, repeat
from einops.layers.torch import Rearrange
# helpers
def pair(t):
return t if isinstance(t, tuple) else (t, t)
# classes
class FeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, hidden_dim, dropout = 0.):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.LayerNorm(dim),
nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, dim),
nn.Dropout(dropout)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.net(x)
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, heads = 8, dim_head = 64, dropout = 0.):
super().__init__()
inner_dim = dim_head * heads
project_out = not (heads == 1 and dim_head == dim)
self.heads = heads
self.scale = dim_head ** -0.5
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.attend = nn.Softmax(dim = -1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
# linear(1024 , 3072)
self.to_qkv = nn.Linear(dim, inner_dim * 3, bias = False)
self.to_out = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(inner_dim, dim),
nn.Dropout(dropout)
) if project_out else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
# [1, 65, 1024]
x = self.norm(x)
# [1, 65, 1024]
qkv = self.to_qkv(x).chunk(3, dim = -1)
# self.to_qkv(x) [1, 65, 3072]
# self.to_qkv(x).chunk(3,-1) [3, 1, 65, 1024]
q, k, v = map(lambda t: rearrange(t, 'b n (h d) -> b h n d', h = self.heads), qkv)
# q,k,v [1, 65, 1024] -> [1, 16, 65, 64]
# 把 65个1024的特征分为 heads个65个d维的特征 然后每个heads去分别有自己要处理的隐藏层,对不同的特征建立不同学习能力
dots = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-1, -2)) * self.scale
# [1, 16, 65, 64] * [1, 16, 64, 65] -> [1, 16, 65, 65]
# scale 保证在softmax前所有的值都不太大
attn = self.attend(dots)
# softmax [1, 16, 65, 65]
attn = self.dropout(attn)
# dropout [1, 16, 65, 65]
out = torch.matmul(attn, v)
# out [1, 16, 65, 64]
out = rearrange(out, 'b h n d -> b n (h d)')
# out [1, 65, 1024]
return self.to_out(out)
# out [1, 65, 1024]
class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, depth, heads, dim_head, mlp_dim, dropout = 0.):
super().__init__()
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([])
for _ in range(depth):
self.layers.append(nn.ModuleList([
Attention(dim, heads = heads, dim_head = dim_head, dropout = dropout),
FeedForward(dim, mlp_dim, dropout = dropout)
]))
def forward(self, x):
# [1, 65, 1024]
for attn, ff in self.layers:
# [1, 65, 1024]
x = attn(x) + x
# [1, 65, 1024]
x = ff(x) + x
# [1, 65, 1024]
return self.norm(x)
# shape不会改变
class ViT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, *, image_size, patch_size, num_classes, dim, depth, heads, mlp_dim, pool = 'cls', channels = 3, dim_head = 64, dropout = 0., emb_dropout = 0.):
super().__init__()
image_height, image_width = pair(image_size)
patch_height, patch_width = pair(patch_size)
assert image_height % patch_height == 0 and image_width % patch_width == 0, 'Image dimensions must be divisible by the patch size.'
num_patches = (image_height // patch_height) * (image_width // patch_width)
patch_dim = channels * patch_height * patch_width
assert pool in {'cls', 'mean'}, 'pool type must be either cls (cls token) or mean (mean pooling)'
# num_patches 64
# patch_dim 3072
# dim 1024
self.to_patch_embedding = nn.Sequential(
#Rearrange是einops中的一个方法
# einops:灵活和强大的张量操作,可读性强和可靠性好的代码。支持numpy、pytorch、tensorflow等。
# 代码中Rearrage的意思是将传入的image(3,224,224),按照(3,(h,p1),(w,p2))也就是224=hp1,224 = wp2,接着把shape变成b (h w) (p1 p2 c)格式的,这样把图片分成了每个patch并且将patch拉长,方便下一步的全连接层
# 还有一种方法是采用窗口为16*16,stride 16的卷积核提取每个patch,然后再flatten送入全连接层。
Rearrange('b c (h p1) (w p2) -> b (h w) (p1 p2 c)', p1 = patch_height, p2 = patch_width),
nn.LayerNorm(patch_dim),
nn.Linear(patch_dim, dim),
nn.LayerNorm(dim),
)
self.pos_embedding = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, num_patches + 1, dim))
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, 1, dim))
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(emb_dropout)
self.transformer = Transformer(dim, depth, heads, dim_head, mlp_dim, dropout)
self.pool = pool
self.to_latent = nn.Identity()
self.mlp_head = nn.Linear(dim, num_classes)
def forward(self, img):
# 1. [1, 3, 256, 256] 输入img
x = self.to_patch_embedding(img)
# 2. [1, 64, 1024] patch embd
b, n, _ = x.shape
# 3. [1, 1, 1024] cls_tokens
cls_tokens = repeat(self.cls_token, '1 1 d -> b 1 d', b = b)
# 4. [1, 65, 1024] cat [cls_tokens, x]
x = torch.cat((cls_tokens, x), dim=1)
# 5. [1, 65, 1024] add [x] [pos_embedding]
x += self.pos_embedding[:, :(n + 1)]
# 6. [1, 65, 1024] dropout
x = self.dropout(x)
# 7. [1, 65, 1024] N * transformer
x = self.transformer(x)
# 8. [1,1024] cls_x output
x = x.mean(dim = 1) if self.pool == 'mean' else x[:, 0]
# 9. [1,1024] cls_x output mean
x = self.to_latent(x)
# 10.[1,1024] nn.Identity()不改变输入和输出 占位层
return self.mlp_head(x)
# 11.[1,cls] mlp_cls_head
4 总结
multihead和我原有的理解偏差修正。
我以为的是QKV会有N块相同的copy(),每一份去做后续的linear等操作。
代码里是直接用linear将QKV分为一整个大块,用permute/rearrange的操作切成了N块,f(Q,K)之后再恢复成一整个大块,很强。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-791085.html
到了这里,关于论文阅读 Vision Transformer - VIT的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!