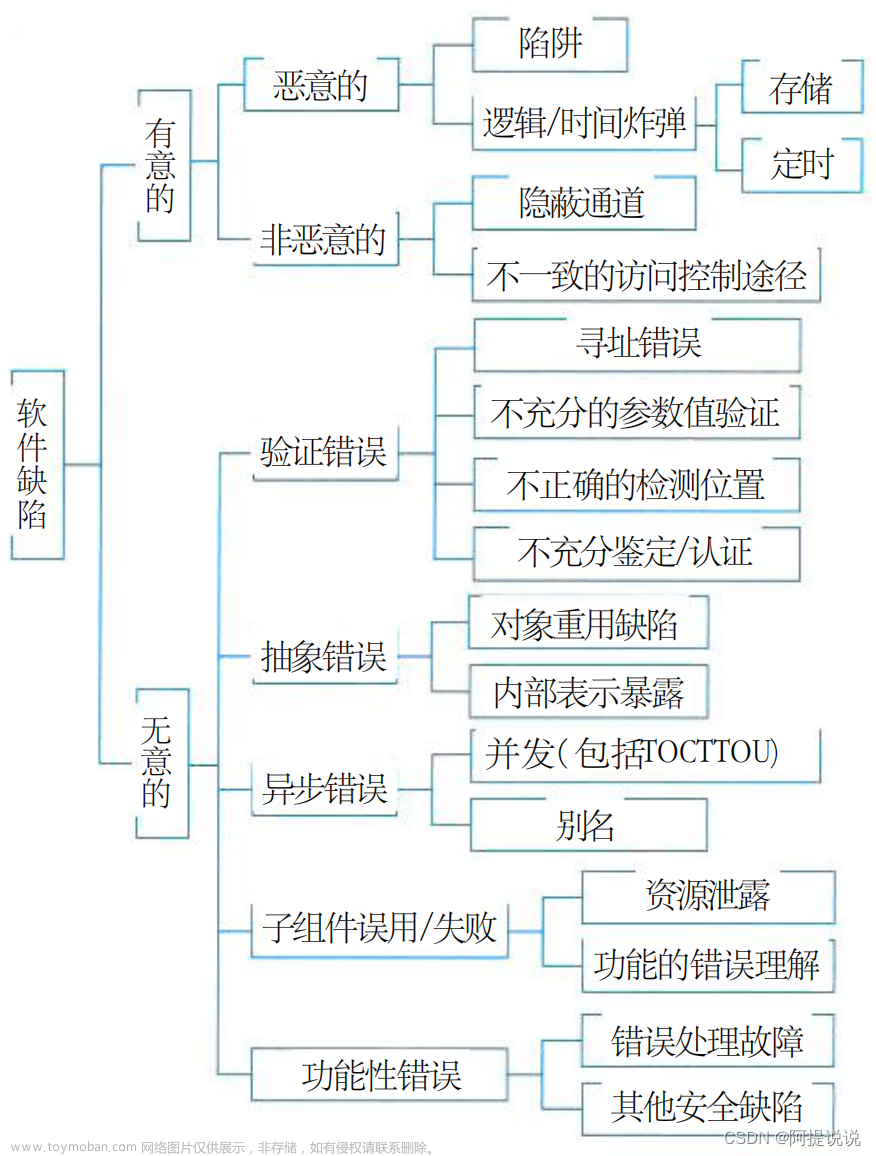
元空间就是从C堆中划出来的一片完整的区域,为了提升元数据的内存分配效率,又把元空间按若干个chunk内存块管理起来,其中chunk块又分为已使用和空间两种类型,并分别用VirtualSpaceList和ChunkManager来管理,chunk内存块之间以链表的形式关联起来,同时为了满足不同元数据占用内存大小的内存分配,chunk内存块也是有多种不同大小的chunk,如SpecializedChunk, SmallChunk, MediumChunk,分别表示128B、512B、8K大小。本章要做的工作就是在实际分配内存存放元数据前的一切准备工作。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-791086.html
18.1 metaspace.cpp
18.1.1 Metaspace::global_initialize
void Metaspace::global_initialize() {
// 这一步就是给_capacity_until_GC参数赋值为最大元空间大小:_capacity_until_GC = MaxMetaspaceSize;表示当空间到_capacity_until_GC的值时,就会触发GC操作
MetaspaceGC::initialize();
// 初始化共享空间的对齐大小,实际上vm_allocation_granularity()里面就是去拿page size(页大小4*k)
int max_alignment = os::vm_allocation_granularity();
size_t cds_total = 0;
// 设置空间对齐值
MetaspaceShared::set_max_alignment(max_alignment);
/* DumpSharedSpaces 表示共享空间转储到文件,默认是不开启的,为了减少HotSpot源码的复杂性,这个也按默认false处理,这条线也不走。
JVM可以在多个Java进程之间共享公共类元数据,以减少内存使用并缩短启动时间。该共享类数据存储在共享空间。实际生产中也不会这么做,所以可以忽略。如果想开启,可以按如下命令执行:
java -XX:+DumpSharedSpaces -XX:SharedArchiveFile=yourSharedSpaces.jsa -jar yourApplication.jar
*/
if (DumpSharedSpaces) {
#if INCLUDE_CDS
MetaspaceShared::estimate_regions_size();
SharedReadOnlySize = align_size_up(SharedReadOnlySize, max_alignment);
SharedReadWriteSize = align_size_up(SharedReadWriteSize, max_alignment);
SharedMiscDataSize = align_size_up(SharedMiscDataSize, max_alignment);
SharedMiscCodeSize = align_size_up(SharedMiscCodeSize, max_alignment);
// the min_misc_code_size estimate is based on MetaspaceShared::generate_vtable_methods()
uintx min_misc_code_size = align_size_up(
(MetaspaceShared::num_virtuals * MetaspaceShared::vtbl_list_size) *
(sizeof(void*) + MetaspaceShared::vtbl_method_size) + MetaspaceShared::vtbl_common_code_size,
max_alignment);
if (SharedMiscCodeSize < min_misc_code_size) {
report_out_of_shared_space(SharedMiscCode);
}
// Initialize with the sum of the shared space sizes. The read-only
// and read write metaspace chunks will be allocated out of this and the
// remainder is the misc code and data chunks.
cds_total = FileMapInfo::shared_spaces_size();
cds_total = align_size_up(cds_total, _reserve_alignment);
_space_list = new VirtualSpaceList(cds_total/wordSize);
_chunk_manager_metadata = new ChunkManager(SpecializedChunk, SmallChunk, MediumChunk);
if (!_space_list->initialization_succeeded()) {
vm_exit_during_initialization("Unable to dump shared archive.", NULL);
}
#ifdef _LP64
if (cds_total + compressed_class_space_size() > UnscaledClassSpaceMax) {
vm_exit_during_initialization("Unable to dump shared archive.",
err_msg("Size of archive (" SIZE_FORMAT ") + compressed class space ("
SIZE_FORMAT ") == total (" SIZE_FORMAT ") is larger than compressed "
"klass limit: " SIZE_FORMAT, cds_total, compressed_class_space_size(),
cds_total + compressed_class_space_size(), UnscaledClassSpaceMax));
}
// Set the compressed klass pointer base so that decoding of these pointers works
// properly when creating the shared archive.
assert(UseCompressedOops && UseCompressedClassPointers,
"UseCompressedOops and UseCompressedClassPointers must be set");
Universe::set_narrow_klass_base((address)_space_list->current_virtual_space()->bottom());
if (TraceMetavirtualspaceAllocation && Verbose) {
gclog_or_tty->print_cr("Setting_narrow_klass_base to Address: " PTR_FORMAT,
_space_list->current_virtual_space()->bottom());
}
Universe::set_narrow_klass_shift(0);
#endif // _LP64
#endif // INCLUDE_CDS
} else {
#if INCLUDE_CDS
/*
UseSharedSpaces:启用共享存档,这个空间主要是针对热点数据的存储,比如包含元数据、字节码和其他相关信息的共享存档文件。开启命令如下:
java -Xshare:dump -XX:SharedArchiveFile=yourSharedArchive.jsa -jar yourApplication.jar
这块默认是开启的,该文档用于存放CDS数据(类共享数据),该数据用于缩短Java应用程序的启动时间并减少内存占用。CDS的想法是创建一个包含预先计算的数据结构、类元数据和字节码的共享存档文件。该存档可以内存映射mmap到多个Java进程地址空间,允许它们共享公共类和资源(这样省去了JVM启动时对公共类的加载、分配内存等时间和内存空间)。
*/
address cds_address = NULL;
if (UseSharedSpaces) {
// 找到那个存档文件,并封装成FileMapInfo
FileMapInfo* mapinfo = new FileMapInfo();
// map_shared_spaces()函数,将存档文件映射到当前Java进程的内存地址空间
if (mapinfo->initialize() && MetaspaceShared::map_shared_spaces(mapinfo)) {
cds_total = FileMapInfo::shared_spaces_size();
cds_address = (address)mapinfo->region_base(0);
} else {
assert(!mapinfo->is_open() && !UseSharedSpaces,
"archive file not closed or shared spaces not disabled.");
}
}
#endif // INCLUDE_CDS
#ifdef _LP64 // 64位机器不在考虑范围内
// If UseCompressedClassPointers is set then allocate the metaspace area
// above the heap and above the CDS area (if it exists).
if (using_class_space()) {
if (UseSharedSpaces) {
#if INCLUDE_CDS
char* cds_end = (char*)(cds_address + cds_total);
cds_end = (char *)align_ptr_up(cds_end, _reserve_alignment);
allocate_metaspace_compressed_klass_ptrs(cds_end, cds_address);
#endif
} else {
char* base = (char*)align_ptr_up(Universe::heap()->reserved_region().end(), _reserve_alignment);
allocate_metaspace_compressed_klass_ptrs(base, 0);
}
}
#endif // _LP64
// 下面的操作都是内存分配钱的大小对齐和确定
_first_chunk_word_size = InitialBootClassLoaderMetaspaceSize / BytesPerWord;
_first_chunk_word_size = align_word_size_up(_first_chunk_word_size);
_first_class_chunk_word_size = MIN2((size_t)MediumChunk*6,
(CompressedClassSpaceSize/BytesPerWord)*2);
_first_class_chunk_word_size = align_word_size_up(_first_class_chunk_word_size);
size_t word_size = VIRTUALSPACEMULTIPLIER * _first_chunk_word_size;
word_size = align_size_up(word_size, Metaspace::reserve_alignment_words());
// 创建VirtualSpaceList来管理已使用的chunk,细节看`章节18.1.2`
_space_list = new VirtualSpaceList(word_size);
// 创建ChunkManager来管理空闲的chunk,这一步的操作看`章节18.1.3`
_chunk_manager_metadata = new ChunkManager(SpecializedChunk, SmallChunk, MediumChunk);
if (!_space_list->initialization_succeeded()) {
vm_exit_during_initialization("Unable to setup metadata virtual space list.", NULL);
}
}
_tracer = new MetaspaceTracer();
}
18.1.2 VirtualSpaceList::VirtualSpaceList
VirtualSpaceList::VirtualSpaceList(size_t word_size) :
_is_class(false), // 各字段的初始化工作
_virtual_space_list(NULL),
_current_virtual_space(NULL),
_reserved_words(0),
_committed_words(0),
_virtual_space_count(0) {
MutexLockerEx cl(SpaceManager::expand_lock(),
Mutex::_no_safepoint_check_flag);
create_new_virtual_space(word_size); // 实际做事的函数
}
bool VirtualSpaceList::create_new_virtual_space(size_t vs_word_size) {
assert_lock_strong(SpaceManager::expand_lock());
// 上面初始化时,已经设置_is_class = false,所以这条逻辑不会走
if (is_class()) {
assert(false, "We currently don't support more than one VirtualSpace for"
" the compressed class space. The initialization of the"
" CCS uses another code path and should not hit this path.");
return false;
}
// 大小不能为0
if (vs_word_size == 0) {
assert(false, "vs_word_size should always be at least _reserve_alignment large.");
return false;
}
// 求得对齐后,要分配的字节大小
size_t vs_byte_size = vs_word_size * BytesPerWord;
assert_is_size_aligned(vs_byte_size, Metaspace::reserve_alignment());
// 创建并分配VirtualSpaceNode对象,看下面VirtualSpaceNode::VirtualSpaceNode函数
VirtualSpaceNode* new_entry = new VirtualSpaceNode(vs_byte_size);
// 创建完后,要对字段进行初始化,看下面VirtualSpaceNode::initialize函数
if (!new_entry->initialize()) {
delete new_entry;
return false;
} else {
assert(new_entry->reserved_words() == vs_word_size,
"Reserved memory size differs from requested memory size");
// ensure lock-free iteration sees fully initialized node
OrderAccess::storestore();
link_vs(new_entry);
return true;
}
}
VirtualSpaceNode::VirtualSpaceNode(size_t bytes) : _top(NULL), _next(NULL), _rs(), _container_count(0) {
assert_is_size_aligned(bytes, Metaspace::reserve_alignment());
#if INCLUDE_CDS
// This allocates memory with mmap. For DumpSharedspaces, try to reserve
// configurable address, generally at the top of the Java heap so other
// memory addresses don't conflict.
if (DumpSharedSpaces) {
bool large_pages = false; // No large pages when dumping the CDS archive.
char* shared_base = (char*)align_ptr_up((char*)SharedBaseAddress, Metaspace::reserve_alignment());
_rs = ReservedSpace(bytes, Metaspace::reserve_alignment(), large_pages, shared_base, 0);
if (_rs.is_reserved()) {
assert(shared_base == 0 || _rs.base() == shared_base, "should match");
} else {
// Get a mmap region anywhere if the SharedBaseAddress fails.
_rs = ReservedSpace(bytes, Metaspace::reserve_alignment(), large_pages);
}
MetaspaceShared::set_shared_rs(&_rs);
} else
#endif
{
bool large_pages = should_commit_large_pages_when_reserving(bytes);
// 直接看这一行,这里创建一个ReservedSpace对象句柄,同时创建指定大小的内存区域,里面用的是mmap映射方式,细节在前面的章节`章节17.4.3.2`和`章节17.4.3.3`中有描述,可以返回去看,总之,这里才是真正给元空间mmap映射了一块内存区域
_rs = ReservedSpace(bytes, Metaspace::reserve_alignment(), large_pages);
}
if (_rs.is_reserved()) {
assert(_rs.base() != NULL, "Catch if we get a NULL address");
assert(_rs.size() != 0, "Catch if we get a 0 size");
assert_is_ptr_aligned(_rs.base(), Metaspace::reserve_alignment());
assert_is_size_aligned(_rs.size(), Metaspace::reserve_alignment());
MemTracker::record_virtual_memory_type((address)_rs.base(), mtClass);
}
}
bool VirtualSpaceNode::initialize() {
// 由上一步VirtualSpaceNode::VirtualSpaceNode函数映射的内存区域用ReservedSpace对象来持有,命名为_rs,该对象创建的内存is_reserved()一定是返回true,否则return false退出函数
if (!_rs.is_reserved()) {
return false;
}
// 断言验证_rs的base和size值都是对齐后的值
assert_is_ptr_aligned(_rs.base(), Metaspace::commit_alignment());
assert_is_size_aligned(_rs.size(), Metaspace::commit_alignment());
// 由前面创建_rs得知_rs.special()返回的是false,所以这里pre_committed_size就是0
size_t pre_committed_size = _rs.special() ? _rs.size() : 0;
// 这一步也是做一初始值设置工作或赋值操作
bool result = virtual_space()->initialize_with_granularity(_rs, pre_committed_size,
Metaspace::commit_alignment());
if (result) {
assert(virtual_space()->committed_size() == virtual_space()->actual_committed_size(),
"Checking that the pre-committed memory was registered by the VirtualSpace");
// 设置top值,也就是内存空间的限制界线值
set_top((MetaWord*)virtual_space()->low());
// 设置reserved的值,其实就是上面_rs的值再通过MemRegion来包装
set_reserved(MemRegion((HeapWord*)_rs.base(),
(HeapWord*)(_rs.base() + _rs.size())));
assert(reserved()->start() == (HeapWord*) _rs.base(),
err_msg("Reserved start was not set properly " PTR_FORMAT
" != " PTR_FORMAT, reserved()->start(), _rs.base()));
assert(reserved()->word_size() == _rs.size() / BytesPerWord,
err_msg("Reserved size was not set properly " SIZE_FORMAT
" != " SIZE_FORMAT, reserved()->word_size(),
_rs.size() / BytesPerWord));
}
// 返回结果
return result;
}
18.1.3 ChunkManager构造函数
ChunkManager(size_t specialized_size, size_t small_size, size_t medium_size)
: _free_chunks_total(0), _free_chunks_count(0) {
// 上面提到过chunk块大小有多种,各不一样,这里分别对元空间涉及的3种chunk块设置成_free_chunks数组中的元素,_free_chunks数组指向的是FreeList类型的链表,用于链接所包含的所有chunk块,这里的size是指FreeList链表中每个chunk的大小,千万不要误认为是FreeList链表的总大小
_free_chunks[SpecializedIndex].set_size(specialized_size);
_free_chunks[SmallIndex].set_size(small_size);
_free_chunks[MediumIndex].set_size(medium_size);
}
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-791086.html
到了这里,关于Hotspot源码解析-第十八章-元空间的创建与分配的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!