Pre
Spring Boot - Application Events 的发布顺序_ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
概述
Spring Boot 的广播机制是基于观察者模式实现的,它允许在 Spring 应用程序中发布和监听事件。这种机制的主要目的是为了实现解耦,使得应用程序中的不同组件可以独立地改变和复用逻辑,而无需直接进行通信。
在 Spring Boot 中,事件发布和监听的机制是通过 ApplicationEvent、ApplicationListener 以及事件发布者(ApplicationEventPublisher)来实现的。其中,ApplicationEvent 是所有自定义事件的基础,自定义事件需要继承自它。
ApplicationListener 是监听特定事件并做出响应的接口,开发者可以通过实现该接口来定义自己的监听器。事件发布者(通常由 Spring 的 ApplicationContext 担任)负责发布事件。
在Spring框架中,ApplicationFailedEvent 是一个特殊的事件,它代表了应用程序在启动过程中遇到的失败情况。这个事件是在Spring的应用程序生命周期中,当应用程序启动失败时触发的。
ApplicationFailedEvent 事件通常包含了有关失败原因的信息,例如异常类型、异常消息、发生错误的类和方法、以及失败发生的时间等。这个事件是Spring事件机制的一部分,它允许开发者在应用程序中实现事件驱动的设计。
在Spring框架中,事件机制是基于观察者模式的实现。事件发布者和事件监听器通过事件进行通信。在Spring中,事件发布者通常是通过 ApplicationEventPublisher 接口来进行操作的,而事件监听器则通过实现 ApplicationListener 接口来定义。
当Spring应用程序启动时,它会经历多个阶段。如果在某个阶段发生了错误,比如在初始化数据源时出现了异常,Spring会发布 ApplicationFailedEvent 事件。事件监听器可以监听这个事件,并对事件进行处理,比如记录日志、发送警报或者进行补偿操作等。
在Spring Boot应用程序中,ApplicationFailedEvent 事件也可以被用来处理启动时的异常情况。Spring Boot提供了一种更简化的方式来监听这个事件,即使用 @EventListener 注解。这种方式可以让开发者更容易地编写事件监听器,而不需要实现复杂的接口。
例如,以下是一个简单的 @EventListener 注解的使用示例,用于监听 ApplicationFailedEvent 事件:
@Component
public class ApplicationFailedListener {
@EventListener
public void onApplicationFailedEvent(ApplicationFailedEvent event) {
Throwable throwable = event.getException();
// 对异常进行处理,比如记录日志
System.err.println("Application failed to start: " + throwable.getMessage());
}
}
当应用程序启动失败时,这个监听器会被触发,并可以执行相应的错误处理逻辑。这样,开发者可以更好地管理应用程序的启动过程,并在遇到失败时进行适当的响应。
Code
package com.artisan.event;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationFailedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
/**
* @author 小工匠
* @version 1.0
* @mark: show me the code , change the world
*/
public class ApplicationFailedListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationFailedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationFailedEvent event) {
System.out.println("--------------------> Handling ApplicationFailedEvent here!");
Throwable throwable = event.getException();
// 对异常进行处理,比如记录日志
System.err.println("Application failed to start: " + throwable.getMessage());
}
}
如何使用呢?
方式一:
@SpringBootApplication
public class LifeCycleApplication {
/**
* 除了手工add , 在 META-INF下面 的 spring.factories 里增加
* org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=自定义的listener 也可以
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(LifeCycleApplication.class);
springApplication.addListeners(new ApplicationFailedListener());
springApplication.run(args);
}
}
方式二: 通过spring.factories 配置

org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
com.artisan.event.ApplicationFailedListener
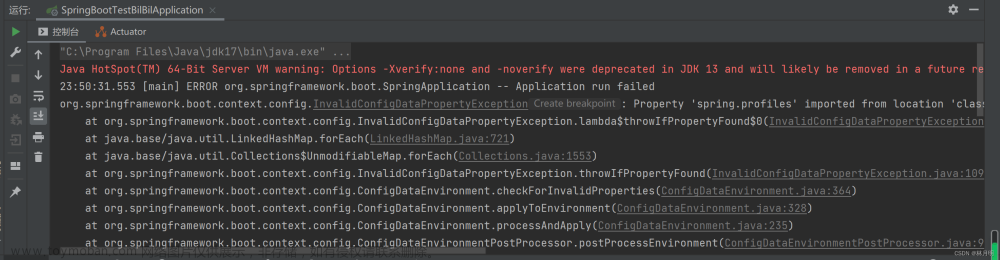
运行日志

源码分析
首先main方法启动入口
SpringApplication.run(LifeCycleApplication.class, args);
跟进去
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
继续
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
这里首先关注 new SpringApplication(primarySources)
new SpringApplication(primarySources)
/**
* Create a new {@link SpringApplication} instance. The application context will load
* beans from the specified primary sources (see {@link SpringApplication class-level}
* documentation for details. The instance can be customized before calling
* {@link #run(String...)}.
* @param resourceLoader the resource loader to use
* @param primarySources the primary bean sources
* @see #run(Class, String[])
* @see #setSources(Set)
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
this.bootstrappers = new ArrayList<>(getSpringFactoriesInstances(Bootstrapper.class));
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
聚焦 setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
run
继续run
// 开始启动Spring应用程序
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); // 创建一个计时器
stopWatch.start(); // 开始计时
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext(); // 创建引导上下文
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; // Spring应用上下文,初始化为null
configureHeadlessProperty(); // 配置无头属性(如:是否在浏览器中运行)
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); // 获取运行监听器
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass); // 通知监听器启动过程开始
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); // 创建应用参数
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments); // 预备环境
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); // 配置忽略BeanInfo
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); // 打印Banner
context = createApplicationContext(); // 创建应用上下文
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup); // 设置应用启动状态
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); // 准备上下文
refreshContext(context); // 刷新上下文,执行Bean的生命周期
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); // 刷新后的操作
stopWatch.stop(); // 停止计时
if (this.logStartupInfo) { // 如果需要记录启动信息
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); // 记录启动信息
}
listeners.started(context); // 通知监听器启动完成
callRunners(context, applicationArguments); // 调用Runner
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners); // 处理运行失败
throw new IllegalStateException(ex); // 抛出异常
}
try {
listeners.running(context); // 通知监听器运行中
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null); // 处理运行失败
throw new IllegalStateException(ex); // 抛出异常
}
return context; // 返回应用上下文
}
我们重点看
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners); // 处理运行失败
继续
private void handleRunFailure(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners) {
try {
try {
handleExitCode(context, exception);
if (listeners != null) {
listeners.failed(context, exception);
}
}
finally {
reportFailure(getExceptionReporters(context), exception);
if (context != null) {
context.close();
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Unable to close ApplicationContext", ex);
}
ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(exception);
}
继续 listeners.failed(context, exception);
void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.failed",
(listener) -> callFailedListener(listener, context, exception), (step) -> {
step.tag("exception", exception.getClass().toString());
step.tag("message", exception.getMessage());
});
}
继续 callFailedListener;
private void callFailedListener(SpringApplicationRunListener listener, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
Throwable exception) {
try {
listener.failed(context, exception);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (exception == null) {
ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(ex);
}
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.log.error("Error handling failed", ex);
}
else {
String message = ex.getMessage();
message = (message != null) ? message : "no error message";
this.log.warn("Error handling failed (" + message + ")");
}
}
}
@Override
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
ApplicationFailedEvent event = new ApplicationFailedEvent(this.application, this.args, context, exception);
if (context != null && context.isActive()) {
// Listeners have been registered to the application context so we should
// use it at this point if we can
context.publishEvent(event);
}
else {
// An inactive context may not have a multicaster so we use our multicaster to
// call all of the context's listeners instead
if (context instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : ((AbstractApplicationContext) context)
.getApplicationListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
this.initialMulticaster.setErrorHandler(new LoggingErrorHandler());
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(event);
}
}
context.publishEvent(event);
@Override
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
ApplicationFailedEvent event = new ApplicationFailedEvent(this.application, this.args, context, exception);
if (context != null && context.isActive()) {
// Listeners have been registered to the application context so we should
// use it at this point if we can
context.publishEvent(event);
}
else {
// An inactive context may not have a multicaster so we use our multicaster to
// call all of the context's listeners instead
if (context instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : ((AbstractApplicationContext) context)
.getApplicationListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
this.initialMulticaster.setErrorHandler(new LoggingErrorHandler());
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(event);
}
}
继续this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(event);
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
继续
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
// 如果eventType不为null,则直接使用它;否则,使用resolveDefaultEventType方法来解析事件的默认类型。
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
// 获取一个线程池执行器,它用于异步执行监听器调用。
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// 获取所有对应该事件类型的监听器。
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
// 如果执行器不为null,则使用它来异步执行监听器调用;
// 否则,直接同步调用监听器。
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
继续
/**
* 调用一个事件监听器的方法。
*
* @param listener 要调用的监听器
* @param event 要处理的事件
*/
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
// 直接调用监听器的onApplicationEvent方法
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
// 如果消息为null或者消息匹配事件类的预期类型,则忽略异常并记录debug日志
if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass())) {
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
// 否则,抛出异常
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
继续 就会调到我们自己的业务逻辑了文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-795312.html
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationFailedEvent event) {
System.out.println("--------------------> Handling ApplicationFailedEvent here!");
Throwable throwable = event.getException();
// 对异常进行处理,比如记录日志
System.err.println("Application failed to start: " + throwable.getMessage());
}
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-795312.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-795312.html
到了这里,关于Spring Boot - Application Events 的发布顺序_ApplicationFailedEvent的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!