背景
HTTPS是在HTTP的基础上通过传输加密和身份认证保证了传输过程的安全性,安全基础为SSL(安全套接字协议),或者叫TLS。
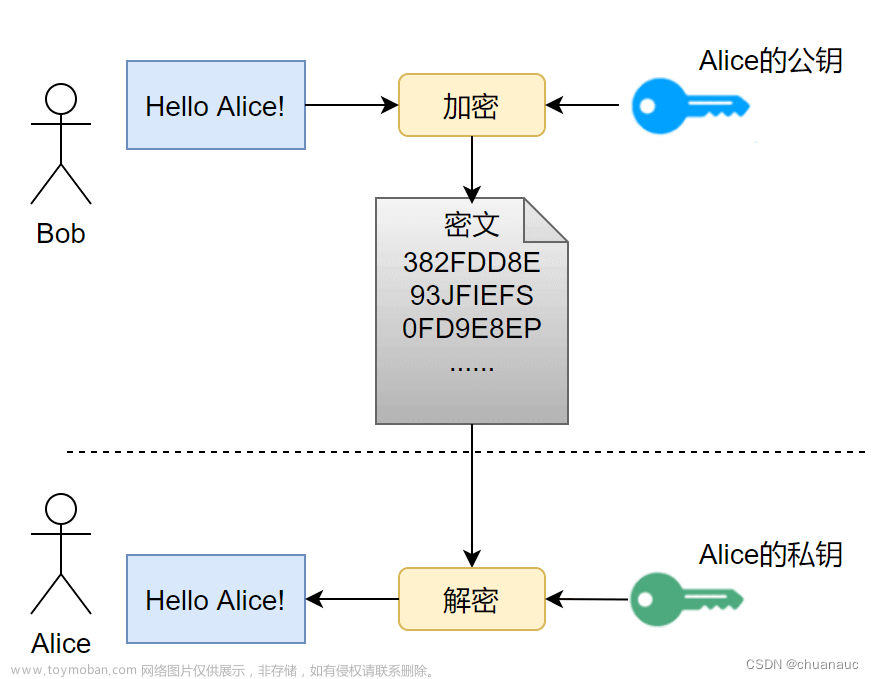
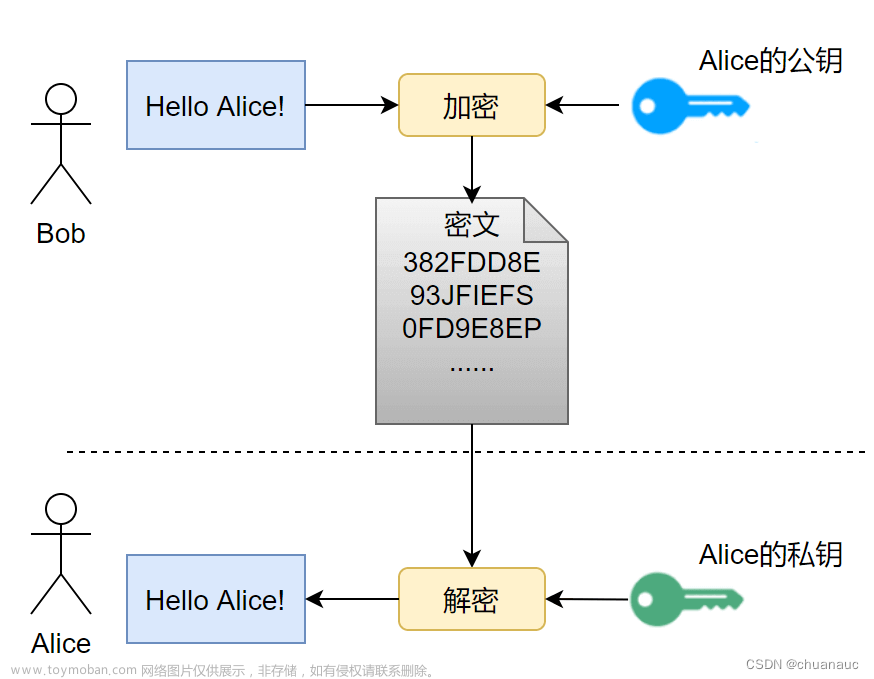
总的来说,先通过非对称加密传输密钥,之后用该密钥对数据进行对称加密。
- 客户端向服务器发起HTTPS请求,连接到服务器的443端口
- 服务器端有一个密钥对,即公钥和私钥,是用来进行非对称加密使用的,服务器端保存着私钥,不能泄露,公钥可以发送给任何人。服务器将自己的证书发送给客户端,证书中包含公钥。
- 客户端收到服务器端的证书之后,对证书进行检查,验证其合法性。如果公钥合格,那么客户端会生成一个随机值,这个随机值就是用于进行对称加密的密钥,我们将该密钥称之为client
key,即客户端密钥,这样在概念上和服务器端的密钥容易进行区分。然后用服务器的公钥对客户端密钥进行非对称加密,这样客户端密钥就变成密文了,至此,HTTPS中的第一次报文请求结束。 - 客户端发起HTTPS中的第二个报文请求,将加密之后的客户端密钥发送给服务器。
- 服务器接收到客户端发来的密文之后,用自己的私钥对其进行非对称解密,解密之后的明文就是客户端密钥,然后用客户端密钥对数据进行对称加密,这样数据就变成了密文。然后服务器将加密后的密文发送给客户端。
- 客户端收到服务器发送来的密文,用客户端密钥对其进行对称解密,得到服务器发送的数据。这样HTTPS中的第二个报文请求结束,整个HTTPS传输完成。
生成HTTPS证书
- 查看系统是否安装了openssl
openssl version -a
- 生成根证书的私钥
openssl genrsa -des3 -out server.key 2048
genrsa:产生rsa密钥
-out:输出文件名
2048:密钥的长度位数,默认为512
-
最后生成server.key文件
-
去除访问server.key每次输入密码的步骤
openssl rsa -in server.key -out server.key
- 生成服务器证书的申请文件
openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
- 主要填写内容如下
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:CN 国家
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:SH 省
Locality Name (eg, city) []:SH 市
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:SZZ 组织
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:SZZ 单位
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:SZZ 个人
Email Address []:szz@13.com 邮箱
Please enter the following ‘extra’ attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []: 密码
An optional company name []: 公司(可选)
最后生成server.csr文件
生成根证书
openssl req -new -x509 -key server.key -out ca.crt -days 3650
-new:表示生成一个新证书签署请求
-x509:专用于CA生成自签证书,如果不是自签证书则不需要此项
-key:用到的私钥文件
-out:证书的保存路径
-days:证书的有效期限,单位是天
最后生成ca.crt文件
生成服务器证书
生成默认的V1.0版本的证书
openssl x509 -req -days 3650 -in server.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey server.key -CAcreateserial -out server.crt
生成V3版本的证书
openssl x509 -req -days 3650 -in server.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey server.key -CAcreateserial -out server.crt -extensions v3_req -extensions v3_ca -extfile ./openssl.conf
关键点在于
- -extensions v3_req 指定 X.509 v3版本
- -extensions v3_ca 生成CA扩展名
- -extfile ./openssl.conf 指定特殊的配置文件
其中openssl.conf文件的内容看文章末尾
最后生成ca.srl,server.crt两个文件,此时一共生成了server.key,server.csr,ca.srl,ca.crt,server.crt 5个文件。其中server.crt就是最终需要发送给客户端使用的证书了。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-797578.html
查看证书内容
openssl x509 -in cert.pem -noout -text
openssl.conf
tsa_policy2 = 1.2.3.4.5.6
tsa_policy3 = 1.2.3.4.5.7
####################################################################
[ ca ]
default_ca = CA_default # The default ca section
####################################################################
[ CA_default ]
dir = ./demoCA # Where everything is kept
certs = $dir/certs # Where the issued certs are kept
crl_dir = $dir/crl # Where the issued crl are kept
database = $dir/index.txt # database index file.
#unique_subject = no # Set to 'no' to allow creation of
# several ctificates with same subject.
new_certs_dir = $dir/newcerts # default place for new certs.
certificate = $dir/cacert.pem # The CA certificate
serial = $dir/serial # The current serial number
crlnumber = $dir/crlnumber # the current crl number
# must be commented out to leave a V1 CRL
crl = $dir/crl.pem # The current CRL
private_key = $dir/private/cakey.pem# The private key
RANDFILE = $dir/private/.rand # private random number file
x509_extensions = usr_cert # The extentions to add to the cert
# Comment out the following two lines for the "traditional"
# (and highly broken) format.
name_opt = ca_default # Subject Name options
cert_opt = ca_default # Certificate field options
# Extension copying option: use with caution.
# copy_extensions = copy
# Extensions to add to a CRL. Note: Netscape communicator chokes on V2 CRLs
# so this is commented out by default to leave a V1 CRL.
# crlnumber must also be commented out to leave a V1 CRL.
# crl_extensions = crl_ext
default_days = 365 # how long to certify for
default_crl_days= 30 # how long before next CRL
default_md = default # use public key default MD
preserve = no # keep passed DN ordering
# A few difference way of specifying how similar the request should look
# For type CA, the listed attributes must be the same, and the optional
# and supplied fields are just that :-)
policy = policy_match
# For the CA policy
[ policy_match ]
countryName = match
stateOrProvinceName = match
organizationName = match
organizationalUnitName = optional
commonName = supplied
emailAddress = optional
# For the 'anything' policy
# At this point in time, you must list all acceptable 'object'
# types.
[ policy_anything ]
countryName = optional
stateOrProvinceName = optional
localityName = optional
organizationName = optional
organizationalUnitName = optional
commonName = supplied
emailAddress = optional
####################################################################
[ req ]
default_bits = 1024
default_keyfile = privkey.pem
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
attributes = req_attributes
x509_extensions = v3_ca # The extentions to add to the self signed cert
# Passwords for private keys if not present they will be prompted for
# input_password = secret
# output_password = secret
# This sets a mask for permitted string types. There are several options.
# default: PrintableString, T61String, BMPString.
# pkix : PrintableString, BMPString (PKIX recommendation before 2004)
# utf8only: only UTF8Strings (PKIX recommendation after 2004).
# nombstr : PrintableString, T61String (no BMPStrings or UTF8Strings).
# MASK:XXXX a literal mask value.
# WARNING: ancient versions of Netscape crash on BMPStrings or UTF8Strings.
string_mask = utf8only
req_extensions = v3_req # The extensions to add to a certificate request
[ req_distinguished_name ]
countryName = Country Name (2 letter code)
countryName_default = CN
countryName_min = 2
countryName_max = 2
stateOrProvinceName = State or Province Name (full name)
stateOrProvinceName_default = BeiJing
localityName = Locality Name (eg, city)
0.organizationName = Organization Name (eg, company)
0.organizationName_default = myca
# we can do this but it is not needed normally :-)
#1.organizationName = Second Organization Name (eg, company)
#1.organizationName_default = World Wide Web Pty Ltd
organizationalUnitName = Organizational Unit Name (eg, section)
#organizationalUnitName_default =
commonName = Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name)
commonName_max = 64
emailAddress = Email Address
emailAddress_max = 64
# SET-ex3 = SET extension number 3
[ req_attributes ]
challengePassword = A challenge password
challengePassword_min = 4
challengePassword_max = 20
unstructuredName = An optional company name
[ usr_cert ]
# These extensions are added when 'ca' signs a request.
# This goes against PKIX guidelines but some CAs do it and some software
# requires this to avoid interpreting an end user certificate as a CA.
basicConstraints=CA:FALSE
# Here are some examples of the usage of nsCertType. If it is omitted
# the certificate can be used for anything *except* object signing.
# This is OK for an SSL server.
# nsCertType = server
# For an object signing certificate this would be used.
# nsCertType = objsign
# For normal client use this is typical
# nsCertType = client, email
# and for everything including object signing:
nsCertType = client, email, objsign
# This is typical in keyUsage for a client certificate.
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
# This will be displayed in Netscape's comment listbox.
nsComment = "OpenSSL Generated Certificate"
# PKIX recommendations harmless if included in all certificates.
subjectKeyIdentifier=hash
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer
# This stuff is for subjectAltName and issuerAltname.
# Import the email address.
# subjectAltName=email:copy
# An alternative to produce certificates that aren't
# deprecated according to PKIX.
# subjectAltName=email:move
# Copy subject details
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
#nsCaRevocationUrl = http://www.domain.dom/ca-crl.pem
#nsBaseUrl
#nsRevocationUrl
#nsRenewalUrl
#nsCaPolicyUrl
#nsSslServerName
# This is required for TSA certificates.
# extendedKeyUsage = critical,timeStamping
[ svr_cert ]
# These extensions are added when 'ca' signs a request.
# This goes against PKIX guidelines but some CAs do it and some software
# requires this to avoid interpreting an end user certificate as a CA.
basicConstraints=CA:FALSE
# Here are some examples of the usage of nsCertType. If it is omitted
# the certificate can be used for anything *except* object signing.
# This is OK for an SSL server.
nsCertType = server
# For an object signing certificate this would be used.
# nsCertType = objsign
# For normal client use this is typical
# nsCertType = client, email
# and for everything including object signing:
# nsCertType = client, email, objsign
# This is typical in keyUsage for a client certificate.
# digitalSignature nonRepudiation keyEncipherment dataEncipherment
# keyAgreement keyCertSign cRLSign encipherOnly decipherOnly
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment, keyAgreement
# This will be displayed in Netscape's comment listbox.
#nsComment = "OpenSSL Generated Certificate"
# PKIX recommendations harmless if included in all certificates.
subjectKeyIdentifier=hash
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer
# This stuff is for subjectAltName and issuerAltname.
# Import the email address.
# subjectAltName=email:copy
# An alternative to produce certificates that aren't
# deprecated according to PKIX.
# subjectAltName=email:move
# Copy subject details
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
#nsCaRevocationUrl = http://www.domain.dom/ca-crl.pem
#nsBaseUrl
#nsRevocationUrl
#nsRenewalUrl
#nsCaPolicyUrl
#nsSslServerName
# This is required for TSA certificates.
extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth,clientAuth
[ v3_req ]
# Extensions to add to a certificate request
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
[ v3_ca ]
# Extensions for a typical CA
# PKIX recommendation.
subjectKeyIdentifier=hash
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid:always,issuer
# This is what PKIX recommends but some broken software chokes on critical
# extensions.
#basicConstraints = critical,CA:true
# So we do this instead.
basicConstraints = CA:true
# Key usage: this is typical for a CA certificate. However since it will
# prevent it being used as an test self-signed certificate it is best
# left out by default.
# keyUsage = cRLSign, keyCertSign
# Some might want this also
# nsCertType = sslCA, emailCA
# Include email address in subject alt name: another PKIX recommendation
# subjectAltName=email:copy
# Copy issuer details
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
# DER hex encoding of an extension: beware experts only!
# obj=DER:02:03
# Where 'obj' is a standard or added object
# You can even override a supported extension:
# basicConstraints= critical, DER:30:03:01:01:FF
[ crl_ext ]
# CRL extensions.
# Only issuerAltName and authorityKeyIdentifier make any sense in a CRL.
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid:always
[ proxy_cert_ext ]
# These extensions should be added when creating a proxy certificate
# This goes against PKIX guidelines but some CAs do it and some software
# requires this to avoid interpreting an end user certificate as a CA.
basicConstraints=CA:FALSE
# Here are some examples of the usage of nsCertType. If it is omitted
# the certificate can be used for anything *except* object signing.
# This is OK for an SSL server.
# nsCertType = server
# For an object signing certificate this would be used.
# nsCertType = objsign
# For normal client use this is typical
# nsCertType = client, email
# and for everything including object signing:
# nsCertType = client, email, objsign
# This is typical in keyUsage for a client certificate.
# keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
# This will be displayed in Netscape's comment listbox.
nsComment = "OpenSSL Generated Certificate"
# PKIX recommendations harmless if included in all certificates.
subjectKeyIdentifier=hash
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer
# This stuff is for subjectAltName and issuerAltname.
# Import the email address.
# subjectAltName=email:copy
# An alternative to produce certificates that aren't
# deprecated according to PKIX.
# subjectAltName=email:move
# Copy subject details
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
#nsCaRevocationUrl = http://www.domain.dom/ca-crl.pem
#nsBaseUrl
#nsRevocationUrl
#nsRenewalUrl
#nsCaPolicyUrl
#nsSslServerName
# This really needs to be in place for it to be a proxy certificate.
proxyCertInfo=critical,language:id-ppl-anyLanguage,pathlen:3,policy:foo
####################################################################
[ tsa ]
default_tsa = tsa_config1 # the default TSA section
[ tsa_config1 ]
# These are used by the TSA reply generation only.
dir = ./demoCA # TSA root directory
serial = $dir/tsaserial # The current serial number (mandatory)
crypto_device = builtin # OpenSSL engine to use for signing
signer_cert = $dir/tsacert.pem # The TSA signing certificate
# (optional)
certs = $dir/cacert.pem # Certificate chain to include in reply
# (optional)
signer_key = $dir/private/tsakey.pem # The TSA private key (optional)
default_policy = tsa_policy1 # Policy if request did not specify it
# (optional)
other_policies = tsa_policy2, tsa_policy3 # acceptable policies (optional)
digests = md5, sha1 # Acceptable message digests (mandatory)
accuracy = secs:1, millisecs:500, microsecs:100 # (optional)
clock_precision_digits = 0 # number of digits after dot. (optional)
ordering = yes # Is ordering defined for timestamps?
# (optional, default: no)
tsa_name = yes # Must the TSA name be included in the reply?
# (optional, default: no)
ess_cert_id_chain = no # Must the ESS cert id chain be included?
# (optional, default: no)
参考
链接: Linux下生成免费HTTPS证书.
链接: openssl生成V3 CA 证书.文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-797578.html
到了这里,关于【使用openssl生成https v3版本证书】的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!