目录
一、什么是哈希
二、哈希冲突
三、哈希函数
3.1、哈希函数设计原则
3.2、常见的哈希函数
四、哈希冲突解决
4.1、闭散列
4.2、开散列
五、哈希表的模拟实现
5.1、哈希表的功能模拟实现
5.2、测试模拟实现:
一、什么是哈希
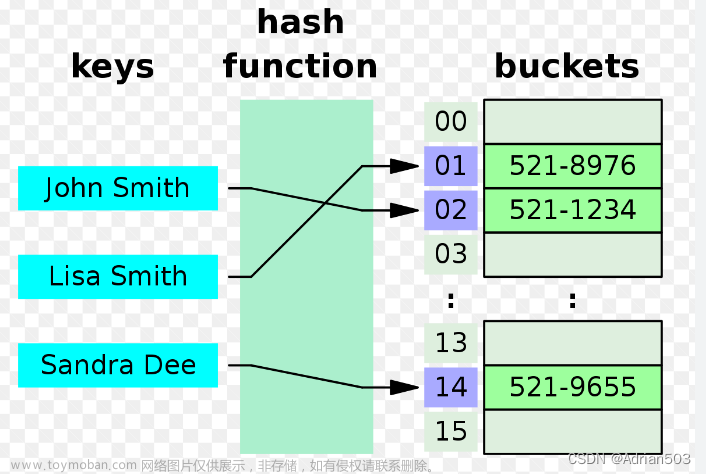
如果构造一种存储结构,可以通过某种函数 (hashFunc) 使元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间能够建立一对一的映射关系,那么在查找时通过该函数就可以很快找到该元素;当向该结构中:
插入元素时:根据待插入元素的关键码,以此函数计算出该元素的存储位置并按此位置进行存放;
搜索元素时:对元素的关键码进行同样的计算,把求得的函数值当做元素的存储位置,在结构中按此位置取元素比较,若关键码相等,则搜索成功。
该方法即为 哈希 (散列) 方法,哈希方法中使用的转换函数称为哈希 (散列) 函数,构造出来的结构称为哈希表 (Hash Table) (或者称散列表)。
特别注意:我们上面提到的不管是顺序搜索、平衡树搜索还是哈希搜索,其 key 值都是唯一的,也就是说,搜索树中不允许出现相同 key 值的节点,哈希表中也不允许出现相同 key 值的元素,我们下文所进行的所有操作也都是在这前提之上进行的。
二、哈希冲突
我们先来看一道题目:
现有数组{1,7,6,4,5,9};
哈希函数设置为:hash(key) = key % capacity; capacity为存储元素底层空间总的大小。

三、哈希函数
3.1、哈希函数设计原则
3.2、常见的哈希函数
2、 除留余数法--(常用)

四、哈希冲突解决
4.1、闭散列
比如我们上面举的例子:现在我们需要插入44这个元素,先通过哈希函数计算哈希地址,hashAddr为4, 因此44理论上应该插在该位置,但是该位置已经放了值为4的元素,即发生哈希冲突。
插入一个元素:
1、通过哈希函数获取待插入元素在哈希表中的位置
2、如果该位置中没有元素则直接插入新元素,如果该位置中有元素发生哈希冲突,使用线性探测找到下一个空位置,插入新元素。

删除一个元素:
// 哈希表每个空间给个标记
// EMPTY此位置空, EXIST此位置已经有元素, DELETE元素已经删除
enum State
{
EMPTY, //空
EXIST, //有元素
DELETE //删除了
};线性探测的实现:
//线性探测的实现
template<class K, class V>
class HashTable
{
struct Elem
{
pair<K, V> _val;
State _state;
};
public:
HashTable(size_t capacity = 3)
:_ht(capacity, _size(0))
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < capacity; ++i)
{
_ht[i]._state = EMPTY;
}
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& val)
{
size_t hashAddr = HashFunc(key);
while (_ht[hashAddr] != EMPTY)
{
if (_ht[hashAddr]._state == EXIST && _ht[hashAddr]._val.first == key)
return false;
hashAddr++;
if (hashAddr == _ht.capacty())
hashAddr = 0;
}
_ht[hashAddr]._state = EXIST;
_ht[hashAddr]._val = val;
_size++;
return true;
}
int Find(const K& key)
{
size_t hashAddr = HashFunc(key);
while (_ht[hashAddr]._state != EMPTY)
{
if (_ht[hashAddr]._state == EXIST && _ht[hashAddr]._val._first == key)
return hashAddr;
hashAddr++;
}
return hashAddr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
int index = Find(key);
if (index != -1)
{
_ht[index]._state = DELETE;
_size--;
return true;
}
return false;
}
private:
size_t HashFunc(const K& key)
return key % _ht.capacity();
private:
vector<Elem> _ht;
size_t _size;
};现在我们海奥面对一个问题:就是哈希表什么情况下需要扩容?怎样扩容?
散列表的载荷因子定义为: = 填入表中的元素个数 / 散列表的长度
是散列表装满程度的标志因子,由于表长是定值,与“填入表中的元素个数”成正比,越大填入表中元素越多,产生冲突的可能性越大;反之,越小填入表中的元素越少,产生冲突的可能性就越小;实际上,散列表的平均查找长度是载荷因子的函数,只是不同处理冲突的方法有不同的函数;
对于开放定址法,载荷因子是特别重要因素,应严格限制在0.7-0.8以下;超过0.8,查表时cpu缓存不命中(cache missing)按照指数曲线上升,因此一些采用开放定址法的hash库,如Java的系统库限制了载荷因子为0.75,超过此值将resize散列表;
void CheckCapacity()
{
if (_size * 10 / _ht.capacity() >= 7)
{
HashTable(K, V, HF) newHt(GetNextPrime(ht.capacity));
for (size_t i = 0; i < _ht.capacity(); ++i)
{
if (_ht[i]._state == EXIST)
newHt.Insert(_ht[i]._val);
}
Swap(newHt);
}
}二次探测
性探测的缺陷时产生冲突的数据堆积在一块,这与其找下一个位置有关系,因为找空位置的方式就是挨个往后逐个查找的;二次探测就是为了避免该问题的,找下一个空位置的方法为,
(i=1,2,3...,是通过散列函数Hash(X)对元素的关键码key进行计算得到的位置,m表示表的大小);

研究表明,当表长度为质数且表转载因子不超过0.5时,新表项一定能够插入,而且任何一个位置都不会被探查两次,因此只要表中有一半的位置,就不会存在表满的问题,在搜索时可以不考虑表装满的情况,但在插入时必须确保表的装载因子不超过0.5,如超过需考虑增容;
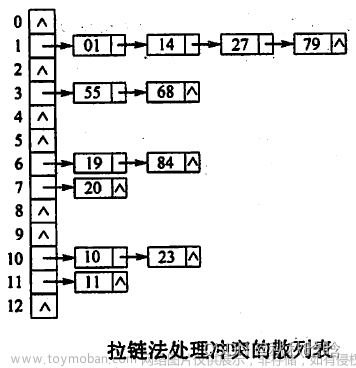
4.2、开散列

从上图可以看出,开散列中每个桶中放的都是发生哈希冲突的元素。
2、开散列的实现:
//开散列的实现
template<class V>
struct HashBucketNode
{
HashBucketNode(const V& data)
:_pNext(nullptr)
,_data(data)
{}
HashBucketNode<V>* _pNext;
V _data;
};
template<class V>
class HashBucket
{
typedef HashBucketNode<V> Node;
typedef Node* pNode;
public:
HashBucket(size_t capacity = 3)
:_size(0)
{
_ht.resize(GetNextPrime(capacity), nullptr);
}
pNode* Insert(const V& data)
{
size_t bucketNo = HashFunc(data);
pNode pCur = _ht[bucketNo];
while (pCur)
{
if (pCur->_data == data)
return pCur;
pCur = pCur->_pNext;
}
pCur = new Node(data);
pCur->_pNext = _ht[bucketNo];
_ht[bucketNo] = pCur;
_size++;
return pCur;
}
pNode* Erase(const V& data)
{
size_t bucketNo = HashFunc(data);
pNode pCur = _ht[bucketNo];
pNode pPrev = nullptr;
pNode pRet = nullptr;
while (pCur)
{
if (pCur->_data == data)
{
if (pCur == _ht[bucketNo])
_ht[bucketNo] = pCur->_pNext;
else
pPrev->_pNext = pCur->_pNext;
pRet = pCur->_pNext;
delete pCur;
_size--;
return pRet;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
pNode* Find(const V& data);
size_t Size()const;
bool Empty()const;
void Clear();
bool BucketCount()const;
void Swap(HashBucket<V, HF>& ht);
~HashBucket();
private:
size_t HashFunc(const V& data)
{
return data % _ht.capacity();
}
private:
vector<pNode*> _ht;
size_t _size;
};3、开散列的增容
void _CheckCapacity()
{
size_t bucketCount = BucketCount();
if (_size == bucketCount)
{
HashBucket<V, HF> newHt(bucketCount);
for (size_t bucketIdx = 0; bucketIdx < bucketCount; ++bucketIdx)
{
pNode pCur = _ht[bucketIdx];
while (pCur)
{
_ht[bucketIdx] = pCur->_pNext;
size_t bucketNo = newHt.HashFunc(pCur->_data);
pCur->_pNext = newHt._ht[bucketNo];
newHt._ht[bucketNo] = pCur;
pCur = _ht[bucketIdx];
}
}
newHt._size = _size;
this->Swap(newHt);
}
}4. 开散列的思考
1. 只能存储key为整形的元素,其他类型怎么解决?文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-797798.html
// 哈希函数采用处理余数法,被模的key必须要为整形才可以处理,此处提供将key转化为
整形的方法
// 整形数据不需要转化
template<class T>
class DefHashF
{
public:
size_t operator()(const T& val)
{
return val;
}
};
// key为字符串类型,需要将其转化为整形
class Str2Int
{
public:
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
const char* str = s.c_str();
unsigned int seed = 131; // 31 131 1313 13131 131313
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = hash * seed + (*str++);
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
};
// 为了实现简单,此哈希表中我们将比较直接与元素绑定在一起
template<class V, class HF>
class HashBucket
{
// ……
private:
size_t HashFunc(const V& data)
{
return HF()(data.first)%_ht.capacity();
}
};2. 除留余数法,最好模一个素数,如何每次快速取一个类似两倍关系的素数?文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-797798.html
size_t GetNextPrime(size_t prime)
{
const int PRIMECOUNT = 28;
static const size_t primeList[PRIMECOUNT] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,49157ul,
98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul,
25165843ul,50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul,
805306457ul,1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
size_t i = 0;
for (; i < PRIMECOUNT; ++i)
{
if (primeList[i] > prime)
return primeList[i];
}
return primeList[i];
}五、哈希表的模拟实现
5.1、哈希表的功能模拟实现
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;
using std::pair;
using std::make_pair;
//选出key
template<class K, class V>
struct PairSelect1st
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv) { return kv.first; }
};
template<class K>
struct KSelect1st
{
const K& operator()(const K& k) { return k; }
};
//转成整型
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& val) { return val; }
};
//模板的特化
template<>
struct HashFunc<std::string>
{
size_t operator()(const std::string& s1)
{
size_t sum = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
sum = sum * 131 + s1[i];
}
return sum;
}
};
//比较判断
template<class K>
struct equal_to
{
bool operator()(const K& lval, const K& rval) { return lval == rval; }
};
template<>
//模板特化
struct equal_to<std::string>
{
bool operator()(const std::string& s1, const std::string& s2) { return s1 == s2; }
};
//素数表
const int PRIMECOUNT = 28;
const size_t primeList[PRIMECOUNT] = {
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul, 25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul, 805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
namespace OpenHash
{
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef HashNode<T>* pNode;
HashNode<T>* _next;
T _data;
public:
HashNode(const T& data = T())
:_next(nullptr)
,_data(data)
{}
};
template<class K, class V, class T, class Pred, class Select1st ,class HashFunc>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class V, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class Pred, class Select1st, class HashFunc>
struct Iterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, V, T, Pred, Select1st, HashFunc> HashTable;
typedef Iterator<K, V, T, Ref, Ptr, Pred, Select1st, HashFunc> self;
Node* _pnode;
HashTable* _pHT;
Iterator(Node* pnode = nullptr, HashTable* pHT = nullptr) : _pnode(pnode), _pHT(pHT) { }
Ref operator*() { return _pnode->_data; }
const Ref operator*()const { return _pnode->_data; }
Ptr operator->() { return &_pnode->_data; }
const Ptr operator->()const { return &_pnode->_data; }
self& operator++()
{
if (_pnode == nullptr)
return *this;
if (_pnode->_next != nullptr)
{
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return *this;
}
//_pnode->next == nullptr我们要去找现在的结点属于哪一个桶
size_t index = HashFunc()(Select1st()(_pnode->_data)) % _pHT->_table.size() + 1;
for (; index < _pHT->_table.size(); index++)
{
Node* cur = _pHT->_table[index];
if (cur != nullptr)
{
_pnode = cur;
return *this;
}
}
_pnode = nullptr;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
++(*this);
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const self& it)const { return _pnode != it._pnode; }
bool operator==(const self& it)const { return _pnode == it._pnode; }
};
template
<class K, class V, class T, class Pred = equal_to<std::string>,
class Select1st = PairSelect1st<K, V>, class HashFunc = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<T>* pNode;
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
template<class K, class V, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class Pred, class Select1st, class HashFunc>
friend struct Iterator;
private:
//存结点指针
vector<pNode> _table;
size_t _n;
public:
typedef Iterator<K, V, T, const T&, const T* ,Pred, Select1st, HashFunc> const_iterator;
typedef Iterator<K, V, T, T&, T*, Pred, Select1st, HashFunc> iterator;
HashTable() :_n(0) { }
void clear()
{
for (size_t index = 0; index < _table.size(); index++)
{
pNode cur = _table[index];
pNode prev = cur;
while (cur)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
delete prev;
}
}
}
~HashTable()
{
clear();
}
iterator begin()
{
size_t index = 0;
for (; index < _table.size(); index++)
{
pNode cur = _table[index];
if (cur != nullptr)
return iterator(cur,this);
}
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
iterator end() { return iterator(nullptr, this); }
const_iterator cbegin()
{
size_t index = 0;
for (; index < _table.size(); index++)
{
pNode cur = _table[index];
if (cur != nullptr)
return const_iterator(cur, this);
}
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const_iterator cend() { return const_iterator(nullptr, this); }
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const T& data)
{
//如果为空,则开空间
if (!_table.size())
_table.resize(53ul);
//挑选key
Select1st st1;
//转换整型
HashFunc hf;
//判断是否冗余
iterator ret = find(data);
if (ret._pnode != nullptr)
return std::make_pair(iterator(nullptr,this), false);
//判断是否需要扩容
if ((double)_n / (double)_table.size() >= 1)
{
vector<pNode> new_table(GetNextPrime(_table.size()));
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
pNode cur = _table[i];
if (cur != nullptr)
{
pNode next = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
next = cur->_next;
size_t new_index = (hf(st1(cur->_data))) % new_table.size();
//头插
cur->_next = new_table[new_index];
new_table[new_index] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
//不推荐,插入的时候重新创建结点,浪费
/*while(e != nullptr)
{
tmp.insert(e->_kv);
e = e->_next;
}*/
}
new_table.swap(_table);
}
//计算hashbucket的下标
size_t index = hf(st1(data)) % _table.size();
pNode newNode = new Node(data);
//头插
newNode->_next = _table[index];
_table[index] = newNode;
_n++;
return std::make_pair(iterator(newNode,this), true);
}
iterator find(const T& data)
{
HashFunc hf;
Select1st slt;
if (_table.size() == 0)
return iterator(nullptr,this);
size_t index = hf(slt(data)) % _table.size();
pNode cur = _table[index];
while (cur)
{
if (Pred()(slt(cur->_data), slt(data)))
return iterator(cur,this);
else
cur = cur->_next;
}
return iterator(nullptr,this);
}
bool erase(const T& data)
{
Select1st st1;
size_t index = HashFunc()(st1(data)) % _table.size();
pNode cur = _table[index];
pNode prev = cur;
while (cur)
{
if (Pred()(st1(cur->_data) , st1(data)))
{
//找到了
if (cur == _table[index])
{
_table[index] = cur->_next;
_n--;
delete cur;
return true;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
_n--;
delete cur;
return true;
}
}
else//没找到
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return false;
}
size_t GetNextPrime(size_t prime)
{
size_t i = 0;
for (; i < PRIMECOUNT; i++)
{
if (primeList[i] > prime)
return primeList[i];
}
return primeList[i];
}
size_t size() const{ return _n; }
};
}
5.2、测试模拟实现:
//OpenHash(开散列)
void Test_KV2()//KV模型
{
OpenHash::HashTable<string, string, pair<string, string>> hts;
pair<string, string> arr[] = {
make_pair("left", "左边") ,make_pair("right", "右边"),make_pair("up", "向上")
,make_pair("down", "向下"),make_pair("left","左边"),make_pair("eat","吃")
,make_pair("sleep","睡觉"),make_pair("run","跑"),make_pair("jump","跳")};
for (auto e : arr)
hts.insert(e);
//非const迭代器
OpenHash::HashTable<string, string, pair<string, string>>::iterator it = hts.begin();
while (it != hts.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
it++;
}
cout << endl;
hts.erase(make_pair("sleep", "睡觉"));
hts.erase(make_pair("left", "左边"));
hts.erase(make_pair("up", "向上"));
//const类型
OpenHash::HashTable<string, string, pair<string, string>>::const_iterator cit = hts.cbegin();
while (cit != hts.cend())
{
cout << cit->first << ":" << cit->second << endl;
cit++;
}
cout << endl;
}
void Test_K2()//K模型
{
OpenHash::HashTable<string, string, string, equal_to<string>, KSelect1st<string>, HashFunc<string>> hts;
string arr[] = {
"left", "左边" ,"right", "右边","up", "向上"
,"down", "向下","left","左边","eat","吃"
,"sleep","睡觉","run","跑","jump","跳" };
for (auto e : arr)
hts.insert(e);
OpenHash::HashTable<string, string, string, equal_to<string>, KSelect1st<string>, HashFunc<string>>::iterator it = hts.begin();
while (it != hts.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
}
到了这里,关于哈希(hash)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!