目录
前言
一、Yolov8环境搭建
二、配置RealSense-ros功能包
1.安装ROS-humble
2.安装Intel RealSense SDK 2.0
编辑 3.克隆ROS功能包
三、物体距离检测代码实现
1.算法流程:
2.代码示例:
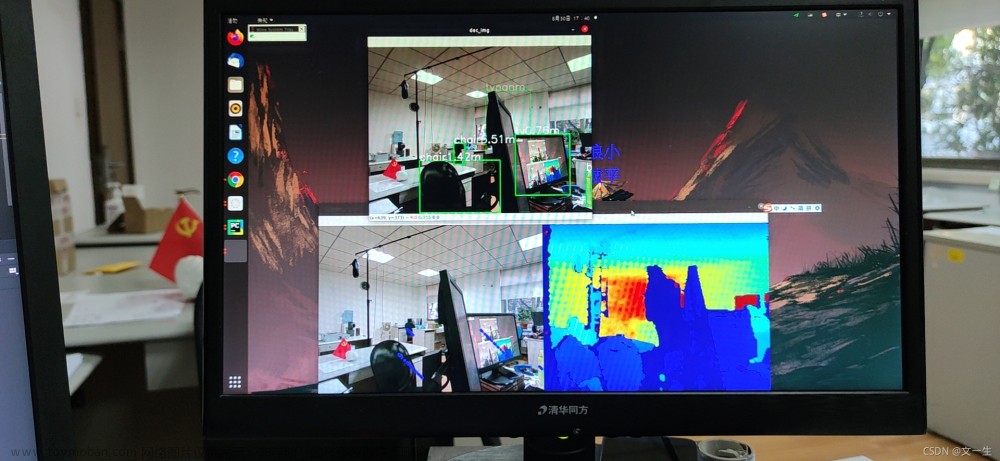
3.效果展示:
前言
要基于YOLOv8和RealsenseD455相机实现物体距离检测,可以按照以下步骤进行操作:
-
准备环境:
- 安装YOLOv8:可以使用开源框架如Darknet或PyTorch实现YOLOv8模型。
- 安装Realsense SDK:根据相机型号和操作系统,下载并安装相机的SDK。
-
获取相机数据:
- 使用Realsense SDK连接并获取相机数据。
- 通过相机获取的RGB图像作为输入,传递给YOLOv8模型。
-
物体检测:
- 使用YOLOv8模型对输入的图像进行物体检测,获取物体的边界框和类别。
-
距离估计:
- 根据Realsense相机的深度图像,对检测到的物体进行距离估计。
- 使用相机的深度图像,可以通过计算像素与实际距离的关系来获取物体的距离。
-
结果显示:
- 将检测到的物体类别、边界框和距离信息进行显示或保存。
一、Yolov8环境搭建
YOLOv8是一种基于深度学习的目标检测算法,可以实现实时的物体检测、分割、分类等操作。
官方网址:
https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
基本环境要求:Python>=3.8 Pytorch>=1.8
以第三方库的形式安装Yolov8:
pip install ultralytics安装完毕后,通过以下命令测试是否安装成功:
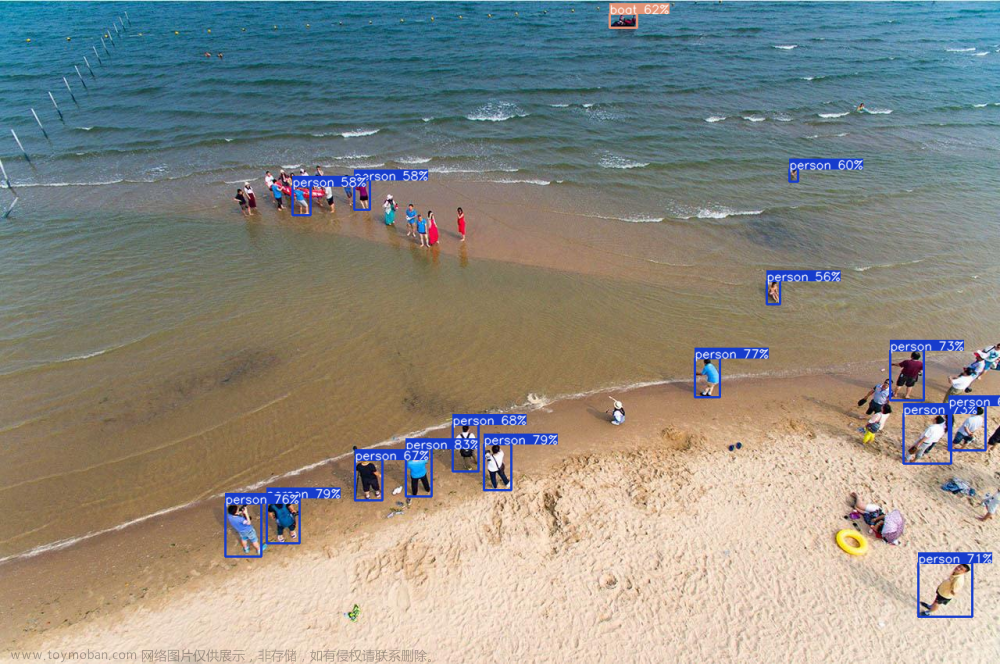
yolo predict model=yolov8n.pt source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'命令执行完毕后,将在同级目录下得到runs目录,内容为示例图的检测结果。

得到示例图片说明Yolo模型运行正常。
如果由于网络问题,下载资源速度很慢,可以选择直接下载网盘中链接到当前目录进行测试。

网盘链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1txVCeJ0eBOEv2DF4evzftg 提取码: hnnp
二、配置RealSense-ros功能包
1.安装ROS-humble
官方安装手册:
Installation — ROS 2 Documentation: Humble documentation
2.安装Intel RealSense SDK 2.0
GitHub - IntelRealSense/realsense-ros: Intel(R) RealSense(TM) ROS Wrapper for Depth Camera
sudo apt install ros-humble-librealsense2*可以选择安装realsense viewer进行相机调试,Intel提供两种安装方法,第一种是通过build好的package安装,第二种是通过源码自己build安装,为了方便,本文直接使用第一种方法。
step1:注册服务器的公钥
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-key F6E65AC044F831AC80A06380C8B3A55A6F3EFCDE || sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv-key F6E65AC044F831AC80A06380C8B3A55A6F3EFCDE
step2:将服务器加入到repo列表
sudo add-apt-repository "deb https://librealsense.intel.com/Debian/apt-repo $(lsb_release -cs) main" -u
step3:安装realsense-viewer的libraries
sudo apt-get install librealsense2-dev
sudo apt-get install librealsense2-dbg
step4: 打开realsense viewer查看图像是否正常(注意打开软件中RGB开关)
realsense-viewer3.克隆ROS功能包
1.克隆到workspace/src目录下:
git clone https://github.com/IntelRealSense/realsense-ros.git -b ros2-development2.安装相关依赖项:
回到当前工作空间目录下
sudo apt-get install python3-rosdep -y
sudo rosdep init
rosdep update
rosdep install -i --from-path src --rosdistro $ROS_DISTRO --skip-keys=librealsense2 -y如果发生rosdep失败可以下载使用国内版rosdepc替代。
3.编译当前工作空间:
colcon build4.节点启动命令:
ros2 launch realsense2_camera rs_launch.py

三、物体距离检测代码实现
1.算法流程:
将相机输出的深度图像信息与RGB图像对齐处理,滤除深度值大于阈值的背景图像,在将背景去除后的图像送入Yolo模型进行处理,得到对应物体的类别信息与蒙板信息。使用简化的KNN算法对蒙板对应的深度值进行筛选,取出边缘点和极端数据。最后均值处理得到物体的三维坐标信息。
2.代码示例:
源码链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1M2_yx7Cu9UXm3u0VwzLELQ 提取码: ai64
物体测距节点:
obj_detect.py:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Basic ROS2
# Author:Jin Xiangyv
# 2024.1.2
#System imports
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from rclpy.qos import qos_profile_sensor_data
from rclpy.qos import ReliabilityPolicy, QoSProfile
# Executor and callback imports
from rclpy.callback_groups import MutuallyExclusiveCallbackGroup
from rclpy.executors import MultiThreadedExecutor
# ROS2 interfaces
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image, CameraInfo
from std_msgs.msg import String
# Image msg parser
from cv_bridge import CvBridge
# Vision model
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Others
import numpy as np
import time, json, torch
class Yolov8Node(Node):
'''
Work:
a class based on the visual recognition moudle of YOLOv8
which can obtain the object's category and position.
Param:
model:neural network model
device:use GPU accelerationn or use CPU
depth_threshold:background remove
threshold:reserved parameter
enable_yolo:use YOLO or not
'''
def __init__(self):
super().__init__("yolov8_node")
rclpy.logging.set_logger_level('yolov8_node', rclpy.logging.LoggingSeverity.INFO)
## Declare parameters for node
self.declare_parameter("model", "yolov8n-seg.pt")
self.declare_parameter("device", "cuda:0")
self.declare_parameter("depth_threshold", 0.6)
self.declare_parameter("threshold", 0.3)
self.declare_parameter("enable_yolo", True)
## Transmit parameters
model = self.get_parameter("model").get_parameter_value().string_value
self.device = self.get_parameter("device").get_parameter_value().string_value
self.depth_threshold = self.get_parameter("depth_threshold").get_parameter_value().double_value
self.threshold = self.get_parameter("threshold").get_parameter_value().double_value
self.enable_yolo = self.get_parameter("enable_yolo").get_parameter_value().bool_value
## Camera correction matrix
self.tf_world_to_camera = np.array([[1.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000],
[0.000, 1.000, 0.000, 0.000],
[0.000, 0.000, 1.000, 0.000],
[0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 1.000]])
self.tf_camera_to_optical = np.array([[385.591, 0.000, 324.346, 0.000],
[ 0.000, 385.137, 244.673, 0.000],
[ 0.000, 0.000, 1.000, 0.000]])
self.tf_world_to_optical = np.matmul(self.tf_camera_to_optical, self.tf_world_to_camera)
## Multithread processing
self.group_img_sub = MutuallyExclusiveCallbackGroup()
self.group_timer = MutuallyExclusiveCallbackGroup()
## Others init
self.cv_bridge = CvBridge()
self.yolo = YOLO("yolov8n-seg.pt")
self.yolo.fuse()
'''
Conv2d and BatchNorm2d Layer Fusion:
Conv2d layers are often followed by BatchNorm2d layers in deep neural networks.
Fusing these layers means combining the operations of the convolutional layer and the batch normalization layer into a single operation.
This can reduce the computational cost and improve inference speed.
'''
self.color_image_msg = None
self.depth_image_msg = None
self.camera_intrinsics = None
self.pred_image_msg = Image()
self.result_img = None
# Set clipping distance for background removal
depth_scale = 0.001
self.depth_threshold = self.depth_threshold/depth_scale
# Publishers
self._item_dict_pub = self.create_publisher(String, "/yolo/prediction/item_dict", 10)
self._pred_pub = self.create_publisher(Image, "/yolo/prediction/image", 10)
self._bg_removed_pub = self.create_publisher(Image, "/yolo/bg_removed", 10)
self._test = self.create_publisher(Image, "/yolo/test", 10)
# Subscribers
self._color_image_sub = self.create_subscription(Image, "/camera/camera/color/image_raw", self.color_image_callback, qos_profile_sensor_data, callback_group=self.group_img_sub)
self._depth_image_sub = self.create_subscription(Image, "/camera/camera/depth/image_rect_raw", self.depth_image_callback, qos_profile_sensor_data, callback_group=self.group_img_sub)
self._camera_info_subscriber = self.create_subscription(CameraInfo, '/camera/camera/color/camera_info', self.camera_info_callback, QoSProfile(depth=1,reliability=ReliabilityPolicy.RELIABLE), callback_group=self.group_img_sub)
# Timers
self._vision_timer = self.create_timer(0.04, self.object_segmentation, callback_group=self.group_timer) # 25 hz
def color_image_callback(self, msg):
self.color_image_msg = msg
def depth_image_callback(self, msg):
self.depth_image_msg = msg
def camera_info_callback(self, msg):
pass
def clsuter_select(self, num_list, threshold):
"""
parameters
num_list: original number list
threshold: retention rate
returns
new number list
Works by removing singularity in original number list
"""
n = len(num_list)
n_threshold = n*(1-threshold)
new_list = []
out_list = []
for i in num_list:
if i != 0:
new_list.append(i)
for num in new_list:
fit_num = 0
current = num
for item in new_list:
flag = abs(current - item)
if flag < 200*threshold:
fit_num = fit_num + 1
if fit_num > n_threshold:
out_list.append(num)
return out_list
def bg_removal(self, color_img_msg: Image, depth_img_msg: Image):
"""
parameters
color_img_msg: Message class 'Image'--RGB image
depth_img_msg: Message class 'Image'--Z16 image
returns
Backgroung removed image
Works by removing background in original image
"""
if self.color_image_msg is not None and self.depth_image_msg is not None:
# Convert color image msg
cv_color_image = self.cv_bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(color_img_msg, desired_encoding='bgr8')
np_color_image = np.array(cv_color_image, dtype=np.uint8)
# Convert depth image msg
cv_depth_image = self.cv_bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(depth_img_msg, desired_encoding='passthrough')
np_depth_image = np.array(cv_depth_image, dtype=np.uint16)
self.test_msg = self.cv_bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(np_depth_image, encoding='16UC1')
self._test.publish(self.test_msg)
# background removal
grey_color = 153
depth_image_3d = np.dstack((np_depth_image, np_depth_image, np_depth_image)) # depth image is 1 channel, color is 3 channels
# bg_removed = np.where((depth_image_3d > self.depth_threshold) | (depth_image_3d != depth_image_3d), grey_color, np_color_image)
bg_removed = np.where((depth_image_3d > 10000) | (depth_image_3d != depth_image_3d), grey_color, np_color_image)
return bg_removed, np_color_image, np_depth_image
self.get_logger().error("Background removal error, color or depth msg was None")
def filter_depth_object_img(self, img, starting_mask, deviation): #TODO: I need explanation from alfredo -Dreez
"""
parameters
img: np depth image
deviation: the deviation allowed
returns
filteref image
Works by removing pixels too far from the median value
"""
mdv = np.median(img[starting_mask]) #median depth value
u_lim = mdv + mdv*deviation #upper limit
uidx = (img >= u_lim)
#we stack the two masks and then takes the max in the new axis
out_img = img
zero_img = np.zeros_like(img)
out_img[uidx] = zero_img[uidx]
return out_img
def object_segmentation(self):
if self.enable_yolo and self.color_image_msg is not None and self.depth_image_msg is not None:
self.get_logger().debug("Succesfully acquired color and depth image msgs")
# Remove background
bg_removed, np_color_image, np_depth_image = self.bg_removal(self.color_image_msg, self.depth_image_msg)
self.get_logger().debug("Succesfully removed background")
self._bg_removed_pub.publish(self.cv_bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(bg_removed, encoding='bgr8'))
# Predict on image "bg_removed"
results = self.yolo(source=bg_removed,device='0')
self.get_logger().debug("Succesfully predicted")
# Go through detections in prediction results
for detection in results:
# Extract image with yolo predictions
pred_img = detection.plot()
self.result_img = pred_img
self.pred_image_msg = self.cv_bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(pred_img, encoding='bgr8')
self._pred_pub.publish(self.pred_image_msg)
# Get number of objects in the scene
object_boxes = detection.boxes.xyxy.cpu().numpy()
n_objects = object_boxes.shape[0]
try:
masks = detection.masks
except AttributeError:
continue
self.get_logger().debug("Succesfully extracted boxes and masks")
# Declare variables used later
objects_median_center = []
objects_median_center_transform = []
detection_class = detection.boxes.cls.cpu().numpy()
detection_conf = detection.boxes.conf.cpu().numpy()
for i in range(n_objects):
# Get mask for the i'th object
single_selection_mask = np.array(masks.xyn[i])
single_object_box = object_boxes[i]
center_x = int(0.5*(single_object_box[0] + single_object_box[2]))
center_y = int(0.5*(single_object_box[1] + single_object_box[3]))
depth = []
sum = 0
dict = 0
for point in single_selection_mask:
p_x = int(point[0]*480)
p_y = int(point[1]*640)
if np_depth_image.item(p_x, p_y)!= 0:
depth.append(np_depth_image.item(p_x, p_y))
print("original")
print(depth)
print(len(depth))
selected_depth = self.clsuter_select(depth, 0.8)
selected_depth = self.clsuter_select(selected_depth, 0.8)
print("selected")
print(selected_depth)
print(len(selected_depth))
for dep in selected_depth:
sum = sum + dep
if len(selected_depth) != 0:
dict = sum/len(selected_depth)
else:
dict = 0
dict = dict/1024
print("end")
print("class:" + str(detection.names[detection_class[i]]))
print(dict)
a = self.tf_world_to_optical[:,3]
obj_center = [dict*center_x - a[0],dict*center_y - a[1], dict*1 - a[2]]
obj_transformed = np.linalg.solve(self.tf_world_to_optical[:,[0,1,2]], obj_center)
objects_median_center.append(obj_center)
objects_median_center_transform.append(obj_transformed)
# Item dict creation
item_dict = {}
for item, n, median_tf in zip(detection_class, range(n_objects), objects_median_center_transform):
item_dict[f'item_{n}'] = {'class': detection.names[item],'position': median_tf.tolist()}
self.item_dict = item_dict
self.item_dict_str = json.dumps(self.item_dict)
print(self.item_dict)
self.get_logger().info(f"Yolo detected items: {[detection.names[item] for item in detection_class]}")
item_dict_msg = String()
item_dict_msg.data = self.item_dict_str
self._item_dict_pub.publish(item_dict_msg)
self.get_logger().debug("Item dictionary succesfully created and published")
def shutdown_callback(self):
self.get_logger().warn("Shutting down...")
##Main funtion
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
# Instansiate node class
vision_node = Yolov8Node()
# Create executor
executor = MultiThreadedExecutor()
executor.add_node(vision_node)
try:
# Run executor
executor.spin()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
finally:
# Shutdown executor
vision_node.shutdown_callback()
executor.shutdown()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()图像可视化节点:
video_player.py:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Basic ROS2
# Author:Jin Xiangyv
# 2024.1.2
import rclpy
import message_filters
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image
from cv_bridge import CvBridge
import cv2
class Video_player(Node):
def __init__(self, name):
super().__init__(name)
self.version_info()
self.get_logger().info("Wait for video source......")
self.subcriber_1 = message_filters.Subscriber(self,Image,'/yolo/prediction/image')
self.subcriber_2 = message_filters.Subscriber(self,Image,'/yolo/bg_removed')
self.sync = message_filters.ApproximateTimeSynchronizer([self.subcriber_1,
self.subcriber_2],\
10,0.5,allow_headerless=True)
self.sync.registerCallback(self.multi_callback)
self.cv_bridge = CvBridge()
def multi_callback(self,stream_1,stream_2):
self.get_logger().info("Image received:")
prediction_img = self.cv_bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(stream_1,'bgr8')
background_removal_img = self.cv_bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(stream_2,'bgr8')
cv2.imshow("prediction_img",prediction_img)
cv2.imshow("background_removal_img",background_removal_img)
cv2.waitKey(10)
def version_info(self):
self.get_logger().info("VERSION 1.2.0")
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
node = Video_player("video_player")
rclpy.spin(node)
node.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown() 3.效果展示:
ros2 launch realsense2_camera rs_launch.py
ros2 run vision_pkg_python obj_detectros2 run vision_pkg_python video_player 

查看物体位置信息:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-798437.html
ros2 topic echo /yolo/prediction/item_dict
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-798437.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-798437.html
到了这里,关于基于YOLOv8和RealsenseD455相机实现物体距离检测的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!