算法思想及流程:

代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include"gdal_priv.h"
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
/// <summary>
/// 先通过GDAL库读入数据,再将数据其转为Mat类
/// </summary>
/// <param name="src"></param>
/// <param name="fileName"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
int readMat(Mat& src, string fileName)
{
GDALDataset* poDataset;
GDALAllRegister();//注册所有的驱动
poDataset = (GDALDataset*)GDALOpen(fileName.c_str(), GA_ReadOnly);//读取影像
if (poDataset == NULL)
{
cout << "read failed" << endl;
return -1;
}
int width = poDataset->GetRasterXSize();//图像宽度(列数)
int height = poDataset->GetRasterYSize();//图像高度(行数)
Mat gdal_mat1(height, width, CV_8UC1, Scalar(0));
Mat gdal_mat2(height, width, CV_8UC1, Scalar(0));
Mat gdal_mat3(height, width, CV_8UC1, Scalar(0));
Mat gdal_mat4(height, width, CV_8UC1, Scalar(0));
Mat gdal_mat5(height, width, CV_8UC1, Scalar(0));
Mat gdal_mat6(height, width, CV_8UC1, Scalar(0));
Mat gdal_mat7(height, width, CV_8UC1, Scalar(0));
poDataset->GetRasterBand(1)->RasterIO(GF_Read, 0, 0, width, height, gdal_mat1.data, width, height, GDT_Byte, 0, 0);
poDataset->GetRasterBand(2)->RasterIO(GF_Read, 0, 0, width, height, gdal_mat2.data, width, height, GDT_Byte, 0, 0);
poDataset->GetRasterBand(3)->RasterIO(GF_Read, 0, 0, width, height, gdal_mat3.data, width, height, GDT_Byte, 0, 0);
poDataset->GetRasterBand(4)->RasterIO(GF_Read, 0, 0, width, height, gdal_mat4.data, width, height, GDT_Byte, 0, 0);
poDataset->GetRasterBand(5)->RasterIO(GF_Read, 0, 0, width, height, gdal_mat5.data, width, height, GDT_Byte, 0, 0);
poDataset->GetRasterBand(6)->RasterIO(GF_Read, 0, 0, width, height, gdal_mat6.data, width, height, GDT_Byte, 0, 0);
poDataset->GetRasterBand(7)->RasterIO(GF_Read, 0, 0, width, height, gdal_mat7.data, width, height, GDT_Byte, 0, 0);
merge(vector<Mat>{ gdal_mat1, gdal_mat2, gdal_mat3, gdal_mat4, gdal_mat5, gdal_mat6, gdal_mat7}, src);
return 1;
}
int KMeans(Mat& src, Mat& classify, int K, double* band1Center, double* band2Center, double* band3Center,
double* band4Center, double* band5Center, double* band6Center, double* band7Center)
{
int f = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < src.rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < src.cols; j++)
{
double* dO = new double[K];
for (int k = 0; k < K; k++)//求与第k类中心的距离
{
double d[7];
d[0] = (int)src.at<Vec<uchar, 7>>(i, j)[0] - band1Center[k];
d[1] = (int)src.at<Vec<uchar, 7>>(i, j)[1] - band2Center[k];
d[2] = (int)src.at<Vec<uchar, 7>>(i, j)[2] - band3Center[k];
d[3] = (int)src.at<Vec<uchar, 7>>(i, j)[3] - band4Center[k];
d[4] = (int)src.at<Vec<uchar, 7>>(i, j)[4] - band5Center[k];
d[5] = (int)src.at<Vec<uchar, 7>>(i, j)[5] - band6Center[k];
d[6] = (int)src.at<Vec<uchar, 7>>(i, j)[6] - band7Center[k];
dO[k] = sqrt(d[0] * d[0] + d[1] * d[1] + d[2] * d[2] + d[3] * d[3] + d[4] * d[4] + d[5] * d[5] + d[6] * d[6]);
double dmin = 999999;
int dminK;
for (int l = 0; l < K; l++)
if (dO[l] < dmin)
{
dmin = dO[l];
dminK = l;
}
classify.at<int>(i, j) = dminK;//对像元分类
}
delete[] dO;
}
double* sum = new double[7];
int classNum;//每个类像元个数
for (int k = 0; k < K; k++)//求每个类的中心
{
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)//重置sum
sum[i] = 0;
classNum = 0;//重置classNum
for (int i = 0; i < src.rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < src.cols; j++)
if (classify.at<int>(i, j) == k)
{
for (int l = 0; l < 7; l++)
sum[l] = sum[l] + (int)src.at<Vec<uchar, 7>>(i, j)[l];
classNum++;
}
double bandCenterD;//聚类中心移动距离
bandCenterD = fabs(sum[0] / classNum - band1Center[k]);
if (bandCenterD > 0)//若聚类中心移动距离大于阈值
f = 1;
bandCenterD = fabs(sum[1] / classNum - band2Center[k]);
if (bandCenterD > 0)
f = 1;
bandCenterD = fabs(sum[2] / classNum - band3Center[k]);
if (bandCenterD > 0)
f = 1;
bandCenterD = fabs(sum[3] / classNum - band4Center[k]);
if (bandCenterD > 0)
f = 1;
bandCenterD = fabs(sum[4] / classNum - band5Center[k]);
if (bandCenterD > 0)
f = 1;
bandCenterD = fabs(sum[5] / classNum - band6Center[k]);
if (bandCenterD > 0)
f = 1;
bandCenterD = fabs(sum[6] / classNum - band7Center[k]);
if (bandCenterD > 0)
f = 1;
band1Center[k] = sum[0] / classNum;//计算新的聚类中心
band2Center[k] = sum[1] / classNum;
band3Center[k] = sum[2] / classNum;
band4Center[k] = sum[3] / classNum;
band5Center[k] = sum[4] / classNum;
band6Center[k] = sum[5] / classNum;
band7Center[k] = sum[6] / classNum;
}
return f;
}
int main()
{
Mat src;
string fileName = "E:\\show\\4\\before.img";
if (readMat(src, fileName) == -1)//读入数据
return -1;
int K;
cout << "请输入要分为几类" << endl;
cin >> K;
Mat classify = Mat_<int>(src.rows, src.cols);//(Size(src.cols, src.rows), CV_8U);
double* band1Center = new double[K];
double* band2Center = new double[K];
double* band3Center = new double[K];
double* band4Center = new double[K];
double* band5Center = new double[K];
double* band6Center = new double[K];
double* band7Center = new double[K];
RNG rng1;
for (int k = 0; k < K; k++)//初始聚类中心为随机均匀分布
{
band1Center[k] = rng1.uniform(int(0), int(255));
band2Center[k] = rng1.uniform(int(0), int(255));
band3Center[k] = rng1.uniform(int(0), int(255));
band4Center[k] = rng1.uniform(int(0), int(255));
band5Center[k] = rng1.uniform(int(0), int(255));
band6Center[k] = rng1.uniform(int(0), int(255));
band7Center[k] = rng1.uniform(int(0), int(255));
}
int I = 1;
while (KMeans(src, classify, K, band1Center, band2Center, band3Center, band4Center, band5Center, band6Center, band7Center))
{
cout << "第" << I << "次迭代" << endl;
I++;
}
Mat classifyed(Size(src.cols, src.rows), CV_8UC3);
int* rR = new int[K];
int* rG = new int[K];
int* rB = new int[K];
RNG rng2;
for (int k = 0; k < K; k++)
{
rR[k] = rng2.uniform(int(0), int(255));
rG[k] = rng2.uniform(int(0), int(255));
rB[k] = rng2.uniform(int(0), int(255));
}
for (int i = 0; i < src.rows; i++)//设置每一类的颜色
for (int j = 0; j < src.cols; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < K; k++)
if (classify.at<int>(i, j) == k)
classifyed.at<Vec3b>(i, j) = { (uchar)rB[k],(uchar)rG[k],(uchar)rR[k] };
namedWindow("Classification", CV_WINDOW_FREERATIO);
imshow("Classification", classifyed);
cout << "Classification complete" << endl;
waitKey(0);
return 0;
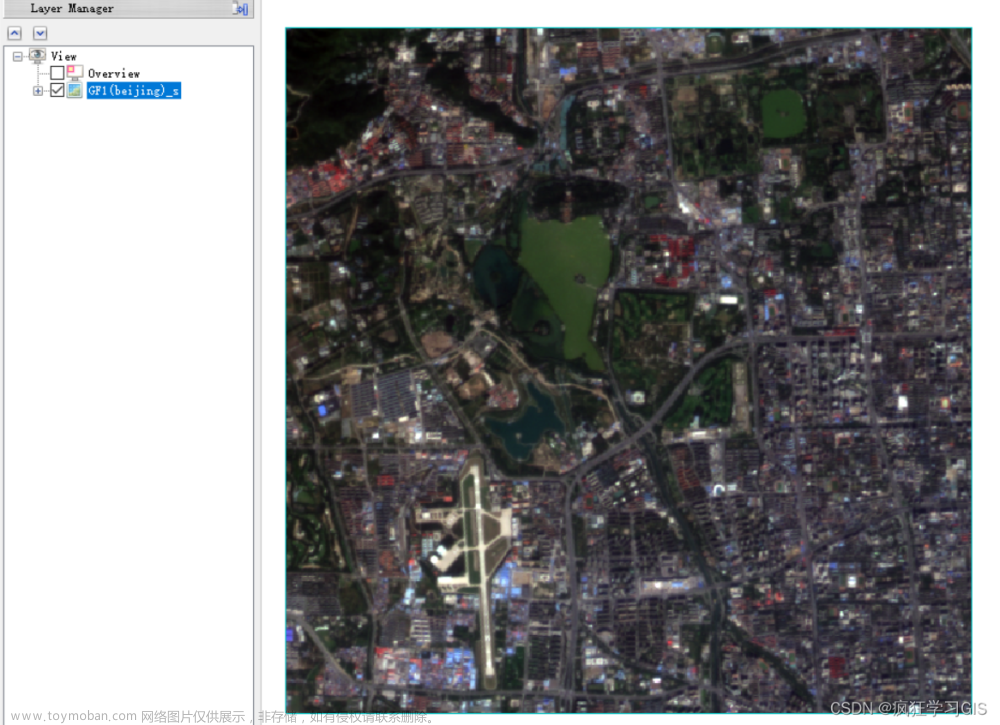
}原图像(3、2、1波段):

分类后(输入分类数K=4):


代码已能实现简单的分类。但受限于本人水平,该代码仍有许多不足,初始聚类中心的选择尚需改进,存储聚类中心的方式不够简洁文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-799420.html
注:当前代码只能读入img格式图像文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-799420.html
到了这里,关于C++实现K-均值算法非监督分类(opencv2.4.9、gdal2.1.2)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!




![[软件工具]opencv-svm快速训练助手教程解决opencv C++ SVM模型训练与分类实现任务支持C# python调用](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/741619-1.png)