一、map和set是什么?
概念
Map和set是一种专门用来进行搜索的容器或者数据结构,其搜索的效率与其具体的实例化子类有关。以前常见的
搜索方式有:
- 直接遍历,时间复杂度为O(N),元素如果比较多效率会非常慢
- 二分查找,时间复杂度为 ,但搜索前必须要求序列是有序的
上述排序比较适合静态类型的查找,即一般不会对区间进行插入和删除操作了,而现实中的查找比如:
- 根据姓名查询考试成绩
- 通讯录,即根据姓名查询联系方式
- 不重复集合,即需要先搜索关键字是否已经在集合中
可能在查找时进行一些插入和删除的操作,即动态查找,那上述两种方式就不太适合了,本节介绍的Map和Set是一种适合动态查找的集合容器。
模型
一般把搜索的数据称为关键字(Key),和关键字对应的称为值(Value),将其称之为Key-value的键值对,所以
模型会有两种:
- 纯 key 模型,比如:有一个英文词典,快速查找一个单词是否在词典中快速查找某个名字在不在通讯录中
- Key-Value 模型,比如:
统计文件中每个单词出现的次数,统计结果是每个单词都有与其对应的次数:<单词,单词出现的次数>
梁山好汉的江湖绰号:每个好汉都有自己的江湖绰号而Map中存储的就是key-value的键值对,Set中只存储了Key。
我们可以发现map没有实现Iterable所以map不能使用迭代器去遍历,后面我们会说到,我们在想遍历map时,会将其转为set,然后去遍历。
二、Set
Set与Map主要的不同有两点:Set是继承自Collection的接口类,Set中只存储了Key。
1.无序,不重复,无索引
2.Set集合的方法基本上与Collection的API一致
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 把给定的对象添加到当前集合中 |
| void clear() | 清空集合中所有的元素 |
| boolean remove(E e) | 把对象在当前集合中删除 |
| boolean contains(Object obj) | 判断当前集合中是否包含给定的对象 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 判断当前集合是否为空 |
| int size() | 返回集合元素的个数 |
Set的特性
1. Set是继承自Collection的一个接口类
2. Set中只存储了key,并且要求key一定要唯一
我们可以发现add的返回值是boolean
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
System.out.println(set.add(1));
System.out.println(set.add(1));
}

set中没有key时返回true,有时返回false.
3. Set的底层是使用Map来实现的,其使用key与Object的一个默认对象作为键值对插入到Map中的
4. Set最大的功能就是对集合中的元素进行去重
5. 实现Set接口的常用类有TreeSet和HashSet,还有一个LinkedHashSet,LinkedHashSet是在HashSet的基础
上维护了一个双向链表来记录元素的插入次序。
6. Set中的Key不能修改,如果要修改,先将原来的删除掉,然后再重新插入
7. Set中不能插入null的key。
Set的三种遍历方法
1.迭代器
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
Iterator<Integer> it = set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(it.next()+" ");
}
}

2.for循环
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
for (Integer integer : set) {
System.out.print(integer+" ");
}
}

3.lambda表达式
我们来看一下这个参数

它是一个函数式接口
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.forEach(new Consumer<Integer>() {
@Override
public void accept(Integer key) {
System.out.print(key+" ");
}
});
}

三、Set的实现类
HashSet
HashSet集合底层采用的是哈希表存储数据
哈希表是一种对于增删查改性能都较好的结构
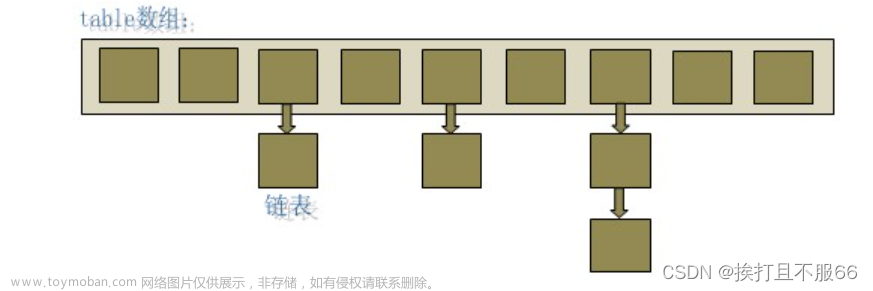
哈希表的组成:
JDK1.8之前: 数组 + 链表
JDK1.8开始: 数组 + 链表 + 红黑树

我们每个Key在哈希表存储的位置为 :(数组长度 - 1) & 哈希值。
哈希值是什么?
1.根据hashCode方法计算出来的Int类型的整数
2.该方法定义在Object类中,所有类都可以调用,默认使用地址值进行计算。
3.一般情况下,会重写hashCode方法,利用对象内部的属性值计算哈希值。
如果没有重写hashCode方法,不同对象计算出来的哈希值是不同的。
如果重写了hashCode方法,不同的对象只要属性相同,计算出来的哈希值就是一样的。
在小部分情况下,不同的属性值或者不同的地址值计算出来的哈希值也有可能一样。(哈希碰撞)
HashSet底层原理:
1.创建一个默认长度为16,默认加载因子为0.75的数组
2.根据元素的哈希值跟数组的长度计算出应该存入的位置
3.判断当前位置是否为null,如果是null直接存入
4.如果不为null,调用equals方法比较属性值
5.一样 不存
JDK1.8之前不一样:存入数组,老元素挂在新元素下面
JDK1.8之后不一样:存入数组,新元素挂在老元素下面
当链表长度大于8数组长度大于64时,链表自动转为红黑树
如果集合中存储的是自定义对象,必须重写hashCode和equals方法
HashSet三大问题
1.为什么存和取的顺序不一样?
因为我们存的时候:(数组长度 - 1) & 哈希值 是按照这公式存的。
2.HashSet为什么没有索引?
因为HashSet底层是由数组 + 链表 + 红黑树组成 无法统一
3.HashSet是利用什么机制保证数据去重的?
HashCode方法 和 equals方法
LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet继承HashSet,方法参照HashSet即可
有序,不重复,无索引
这里的有序指的是保证存储和取出的元素顺序一致
底层仍然是哈希表,只是每个元素多了一个双链表用来记录存储的顺序。
TreeSet
不重复,无索引,可排序
可排序: 按照元素的默认规则排序
底层原理: 是基于红黑树的数据结构,增删查改性能都比较好
class student {
int age;
String name;
public student(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<student> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add(new student(18,"张三"));
}

因为我们的TreeSet是可排序的,在传入自定义类型时,需要指定比较方式,这里我们有两种解决办法:
1.实现Comparable接口
class student implements Comparable<student>{
int age;
String name;
public student(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(student o) {
return this.age - o.age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "student{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<student> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add(new student(18,"张三"));
set.add(new student(16,"李四"));
System.out.println(set);
}

2.传入比较器
class student {
int age;
String name;
public student(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "student{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<student> set = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<student>() {
@Override
public int compare(student o1, student o2) {
return o1.age - o2.age;
}
});
set.add(new student(18,"张三"));
set.add(new student(16,"李四"));
System.out.println(set);
}

四、Map
Map是一个接口类,该类没有继承自Collection,该类中存储的是<K,V>结构的键值对,并且K一定是唯一的,不能重复。
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| V put(k key,V value) | 添加元素 |
| V remove(Object key) | 根据键删除键值对元素 |
| void clear() | 移除所有的键值对元素 |
| boolean containsKey(Object Key) | 判断集合是否包含指定的键 |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | 判断集合是否包含指定的值 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 判断集合是否为空 |
| int size() | 集合的长度,键值对的个数 |
Map的特性
1. Map是一个接口,不能直接实例化对象,如果要实例化对象只能实例化其实现类TreeMap或者HashMap
2. Map中存放键值对的Key是唯一的,value是可以重复的
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("aaa",1);
map.put("bbb",2);
map.put("ccc",3);
System.out.println(map);
map.put("bbb",4);
System.out.println(map);
}

我们可以发现当我们放入相同Key的时候,会将之前的value覆盖。
我们来探究一下put的返回值是什么?
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("aaa",1);
map.put("bbb",2);
map.put("ccc",3);
System.out.println(map.put("bbb", 4));
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("aaa",1);
map.put("bbb",2);
map.put("ccc",3);
System.out.println(map.put("ddd", 4));
}

我们可以总结一下,put时如果Map中没有key则返回Null,否则返回覆盖的value.
3. Map中的Key可以全部分离出来,存储到Set中来进行访问(因为Key不能重复)。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("aaa",1);
map.put("bbb",2);
map.put("ccc",3);
Set<String> set = map.keySet();
for (String s : set) {
System.out.print(s+" ");
}
}

4. Map中的value可以全部分离出来,存储在Collection的任何一个子集合中(value可能有重复)。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("aaa",1);
map.put("bbb",2);
map.put("ccc",2);
Collection<Integer> collection = map.values();
for (Integer integer : collection) {
System.out.print(integer+" ");
}
}

5. Map中键值对的Key不能直接修改,value可以修改,如果要修改key,只能先将该key删除掉,然后再来进行重新插入。
TreeSet和HashSet的区别
区别:
1、HashMap中元素是没有顺序的;TreeMap中所有元素都是有某一固定顺序的。2、HashMap继承AbstractMap类,是基于hash表实现的;TreeMap继承SortedMap类,是基于红黑树实现的。
在数组中是通过数组下标来对 其内容进行索引的,而Map是通过对象来对 对象进行索引的,用来 索引的对象叫键key,其对应的对象叫值value;
1、HashMap是通过hashcode()对其内容进行快速查找的;HashMap中的元素是没有顺序的;
TreeMap中所有的元素都是有某一固定顺序的,如果需要得到一个有序的结果,就应该使用TreeMap;
2、HashMap和TreeMap都不是线程安全的;
3、HashMap继承AbstractMap类;覆盖了hashcode() 和equals() 方法,以确保两个相等的映射返回相同的哈希值;
TreeMap继承SortedMap类;他保持键的有序顺序;
4、HashMap:基于hash表实现的;使用HashMap要求添加的键类明确定义了hashcode() 和equals() (可以重写该方法);为了优化HashMap的空间使用,可以调优初始容量和负载因子;
TreeMap:基于红黑树实现的;TreeMap就没有调优选项,因为红黑树总是处于平衡的状态;
5、HashMap:适用于Map插入,删除,定位元素;
TreeMap:适用于按自然顺序或自定义顺序遍历键(key);
Map的三种遍历方式
1.键找值
我们可以简单理解为把key放入set中
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("aaa",1);
map.put("bbb",2);
map.put("ccc",3);
Set<String> set = map.keySet();
for (String s : set) {
System.out.println(s+" = "+map.get(s));
}
}

2.键值对(entry)

我们可以发现调用entry方法返回的是一个set对象,不过set存放的是键值对
我们可以发现为什么我们要加上map.键值对
我们可以发现Enrty是Map下的一个接口,所以我们需要用map.或者导入相应的包即可。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("aaa",1);
map.put("bbb",2);
map.put("ccc",3);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+" = "+entry.getValue());
}
}

3.lambda表达式


我们可以发现它的参数是一个函数式接口。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("aaa",1);
map.put("bbb",2);
map.put("ccc",3);
map.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public void accept(String key, Integer value) {
System.out.println(key+" = "+value);
}
});
}
这里我们先用匿名内部类实现,等我下一篇lambda表达式博客总结好,大家在进行简化。
五、Map的实现类
HashMap
1.HashMap是Map里面的一个实现类
2.直接使用Map里面的方法即可
3.由键值决定:无序,不重复,无索引
4.HashMap跟HashSet的底层原理是一样的,都是哈希表结构
HashMap是根据键值来确定在哈希表的位置的,所以保证了键值的唯一。
如果键存储的是自定义对象,需要重写hashCode 和 equals方法。
LinkedHashMap
由键决定: 有序,不重复,无索引
这里的有序指的是保证存储和取出的元素顺序一致
底层仍然是哈希表,只是每个元素多了一个双链表用来记录存储的顺序。
TreeMap
TreeMap跟TreeSet底层一样,都是红黑树结构的
由键决定特性: 不重复,无索引,可排序
可排序:对键排序
自定义类型为键值时两种排序方式:
1.实现Comparable接口
2.传入比较器参数
六、小试牛刀
1.统计10w个数据中不重复的数据(多个出现只保留一个)
public static void func(int[] arr) {
//hashSet是天然去重的集合
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
set.add(arr[i]);
}
System.out.println(set);
}
2、统计10W个数据当中,第一个重复的数据?文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-799484.html
public static void func1(int[] arr) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (set.contains(arr[i])) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
break;
} else {
set.add(arr[i]);
}
}
}
3、统计10W个数据当中,每个数据出现的次数? 对应的关系文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-799484.html
public static void func2(int[] arr) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(map.containsKey(arr[i])) {
map.put(arr[i],map.get(arr[i]) + 1);
}else {
map.put(arr[i],1);
}
}
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : entries) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " = " + entry.getValue());
}
}
到了这里,关于万字详解map与set的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!


![[数据结构]-map和set](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/764611-1.png)