一、栈
1.栈的概念及结构
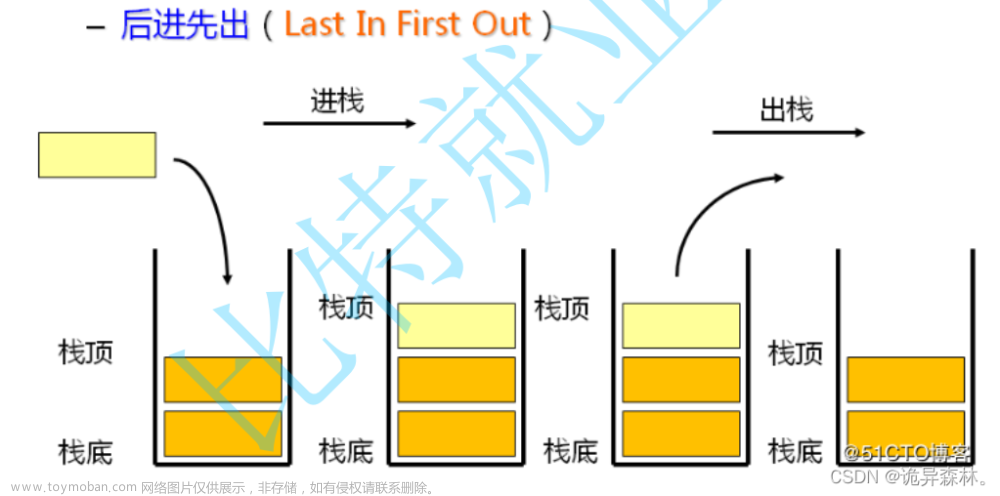
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作,进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈,出数据也在栈顶。
栈既可以用链表实现,也可以用顺序表实现,也就是我们所说的数组
实现方式
1.数组 2.链表
1.相当于之前顺序表的尾插,尾插用尾去做了栈顶,非常适合
/唯一缺陷就是:空间不够需要增容
2.如果用尾插作栈顶,就用双向链表。如果用单链表,就用首插作为栈顶,这样入栈和出栈效率都是O(1)
2.栈的定义
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;//动态栈,如果是数组的话就是静态栈
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
3.栈的初始化和栈的销毁
//初始化
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType)*4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->top = 0;//top是指向栈顶数据的下一个数据
//投top如果给0就表示栈顶数据的下一个数据,如果给-1就表示栈顶的数据
ps->capacity = 4;
}
//销毁
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
4.压栈和出栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//满了->增容
if (ps->capacity == ps->top)
{
STDataType* newnode = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(STDataType));
if (newnode==NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
ps->a = newnode;
ps->capacity = ps->capacity * 2;
}
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
//出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//空栈不能继续删
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
}
5.返回栈顶元素和判断栈的大小以及判断是否为空栈
//返回栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//栈为空时不能调用Top
assert(ps->top);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
//判断栈的大小
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
//判断是否为空
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
6.测试函数
#include "stack.h"
int main()
{
ST st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
StackPush(&st, 4);
StackPush(&st, 5);
while (!StackEmpty(&st))
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
}
StackDestory(&st);
return 0;
}
注意:由于栈是特殊的线性表,所以对于栈来说不能遍历,只能从栈顶开始取数据,所以取出一个数据销毁一个数据,就像上面while循环一样
二、队列
1.队列的概念及结构
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端程序进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出的特点
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
对于队列来说,不管是中途出队列还是最后出队列,都不会印象其顺序
队列的实现
队列也可以数组和链表实现,使用链表结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
2.队列的定义
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
注意:为了方便找到队头和队尾,所以创建一个结构体指向队头和队尾
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
3.队列的初始化和销毁
//队列初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//销毁队列
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
4.进队列和出队列
//进队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
//出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
//一个节点
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//多个节点
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}
5.取队尾和取队头
//取队头
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
//取队尾
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->tail->data;
}
6.判断队列大小和判断队列是否为空
//队列大小
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
cur = cur->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
7.测试函数
注:队列和栈的性质相似,由于队列是先进先出,所以也不能进行队列的遍历,也只能进行,从队头取数据。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-802265.html
#include "Queue.h"
void TestQueue()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
QueuePush(&q, 5);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
QueueDestory(&q);
}
int main()
{
TestQueue();
}
三、总结
栈和队列相较于链表和顺序表来说,不是很难,只要,前面的顺序表和链表的操作掌握了,队列和栈基本都没啥问题。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-802265.html
到了这里,关于数据结构---栈和队列的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!