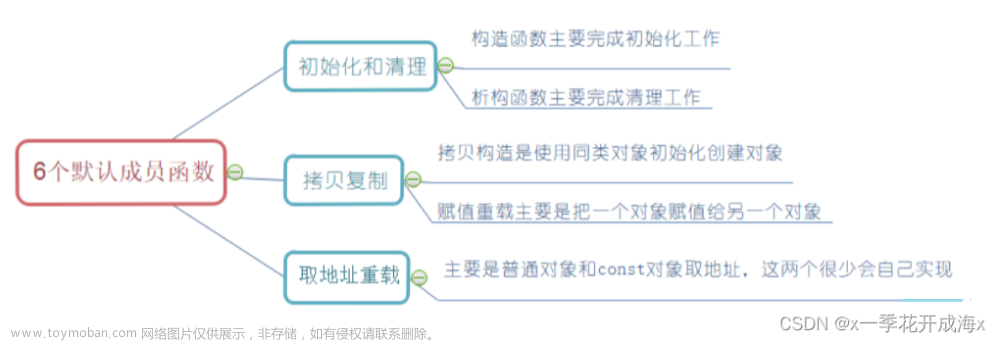
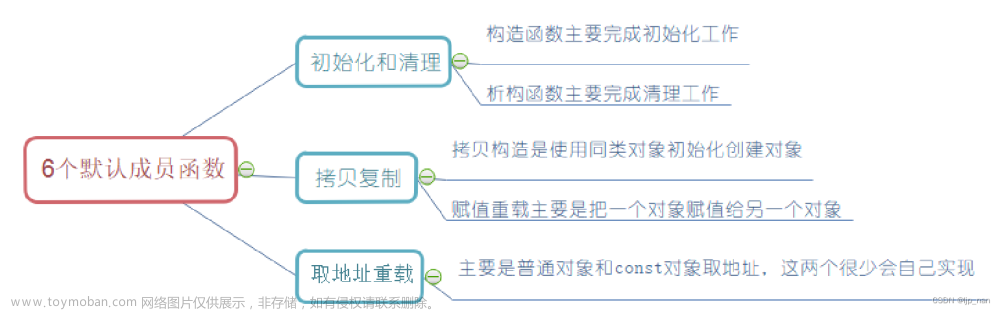
场景一:
与其过多叙述定义,不如在下面一个场景中来理解仿函数:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void bubbles_sort(T* arr,int size) //冒泡排序
{
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size - i-1; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[6] = { 1,3,2,5,7,4 };
bubbles_sort(arr,6);
for (auto a : arr)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
return 0;
}上面的代码是模板+冒泡函数对指定数组的排序,冒泡函数里面的交换条件是 > ,这样会使排序的结果为升序,如果我们要将冒泡函数的功能改为降序排序,那么只需要将 > 改为 < ,但是有没有办法能更好的封装这个冒泡函数,使得升序降序功能由调用函数时由使用者自己选择?
在C语言中,我们可以用函数指针来实现这个需求,定义两个不同的比较函数,在冒泡函数内部使用函数来比较两值的大小,在调用冒泡函数时实参可以传入不同的比较函数在内部进行比较。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void bubbles_sort(T* arr,int size,bool (*com)(T,T))//函数指针
{
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size - i-1; j++)
{
if (com(arr[j],arr[j+1]))//调用传入的函数
{
swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
template<class T>
bool compare_more(T a, T b)
{
return a > b;
}
template<class T>
bool compare_less(T a, T b)
{
return a < b;
}
int main()
{
int arr[6] = { 1,3,2,5,7,4 };
bubbles_sort(arr,6, compare_more);//当想要降序排序时,传入compare_less函数即可
for (auto a : arr)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
return 0;
}C++中如何实现这种需求呢?这里就需要用到仿函数,仿函数本质是利用类的运算符重载,传入函数不同的对象来实现不同的比较。看成果:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
struct Less
{
bool operator()(T a, T b)//重载()运算符
{
return a < b;
}
};
template<class T>
struct More
{
bool operator()(T a, T b)//重载()运算符
{
return a > b;
}
};
template<class T,class Compare>
void bubbles_sort(T* arr,int size, Compare com)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size - i-1; j++)
{
if (com(arr[j],arr[j+1]))//本质是com.operator(){a,b}
{
swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[6] = {1,3,2,5,7,4};
bubbles_sort(arr,6,More<int>());//当想要降序排序,传入Less()对象
for (auto a : arr)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
return 0;
}场景二:
再来设想一个场景,当一个容器中存放的是学生类的对象时,如何进行排序?
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Student
{
Student(string name,int age,string tele)
{
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
this->tele = tele;
}
string name;//姓名
int age;//年龄
string tele;//电话
};
int main()
{
vector<Student> v;
v.push_back(Student("张三", 18, "12345"));
v.push_back(Student("李四", 19, "12321"));
v.push_back(Student("张三", 15, "11234"));
sort(v.begin(),v.end());//这里会报错,因为学生类没有重载<,导致默认的less<Student>报错
for (auto stu : v)
{
cout << "姓名:" << stu.name << "年龄:" << stu.age << "电话:" << stu.tele<<endl;
}
return 0;
}上面的代码,直接调用算法库中的sort(),并没有指定学生对象排序是按照什么排序,默认sort函数会用less<Student>里面直接用< 运算符比较两个学生对象,但是学生类并没有重载 < 运算符,就会编译错误。
在这里,我们就可以自己创建一个比较的类,类里面重载()运算符来实现Student的比较方式,在把这个类的对象传入排序函数内部实现比较功能。或者在Student类中重载<运算符。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Student
{
Student(string name,int age,string tele)
{
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
this->tele = tele;
}
string name;//姓名
int age;//年龄
string tele;//电话
};
template<class T>
class Less
{
public:
bool operator()(T a, T b)//按年龄比较
{
return a.age < b.age;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<Student> v;
v.push_back(Student("张三", 18, "12345"));
v.push_back(Student("李四", 19, "12321"));
v.push_back(Student("张三", 15, "11234"));
sort(v.begin(),v.end(),Less<Student>());//传入对象,就可以按照自己定义的方式排序了
for (auto stu : v)
{
cout << "姓名:" << stu.name << "年龄:" << stu.age << "电话:" << stu.tele<<endl;
}
return 0;
}最后程序的结果是:(按照年龄排序)文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-803721.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-803721.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-803721.html
到了这里,关于C++六大组件之一:仿函数的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!