1 常见IOU汇总
| classification loss | 分类损失 |
|---|---|
| localization loss, | 定位损失(预测边界框与GT之间的误差) |
| confidence loss | 置信度损失(框的目标性 objectness of the box) |
总的损失函数: classification loss + localization loss + confidence loss
YOLOv5使用二元交叉熵损失函数计算类别 概率和目标置信度得分 的损失。
YOLOv5使用 CIOU Loss作为bounding box回归的损失。
多标签分类:
- 大多数分类器假设输出标签是互斥的。 如果输出是互斥的目标类别,则确实如此。 因此,YOLO应用softmax函数将得分转换为总和为1的概率。 而YOLOv3/v4/v5使用多标签分类。 例如,输出标签可以是“行人”和“儿童”,它们不是非排他性的。 (输出的总和可以大于1)
- YOLOv3/v4/v5用多个独立的逻辑(logistic)分类器替换softmax函数,以计算输入属于特定标签的可能性。
- 在计算分类损失进行训练时,YOLOv3/v4/v5对每个标签使用二元交叉熵损失。 这也避免使用softmax函数而降低了计算复杂度。
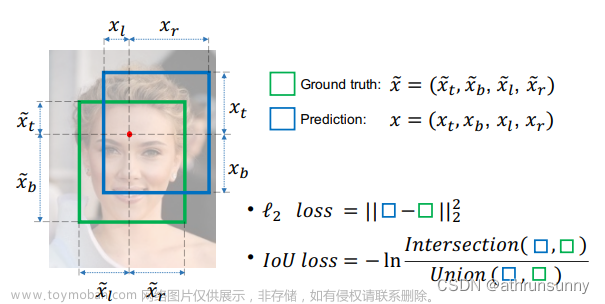
1.1 IOU(Intersection over Union)


这里有两个问题:
- 如果两个物体不重叠,则IoU值将为零,并且不会反映两个形状彼此之间的距离;且将IoU用作损失,则其梯度将为零并且无法进行优化。
- IoU无法区分两个对象之间不同的对齐方式。 (如下图)

1.2 GIOU(Generalized-IoU)

C是包含A和B的最小的面积。
C
GIOU作为loss函数时,Loss=1-GIOU,当A、B两框不相交时A∪B值不变,最大化GIOU就是就小化C,这样就会促使两个框不断靠近。

1.3 DIOU(Distance-IoU)
 根据GIoU损失(第一行)和DIoU损失(第二行)的边界框回归步骤。绿色和黑色分别表示目标框和锚框。蓝色和红色分别表示GIoU损失和DIoU损失的预测框。GIoU损耗一般增大Bounding box的尺寸以与目标框重叠,而DIoU损耗则直接使中心点归一化距离最小化。
根据GIoU损失(第一行)和DIoU损失(第二行)的边界框回归步骤。绿色和黑色分别表示目标框和锚框。蓝色和红色分别表示GIoU损失和DIoU损失的预测框。GIoU损耗一般增大Bounding box的尺寸以与目标框重叠,而DIoU损耗则直接使中心点归一化距离最小化。
在这些情况 (C=A∪B) 下,GIoU损失降级为IoU损失,而我们的DIoU损失仍然是可区分的。绿色和红色分别表示目标框和预测框。

其中B_gt = (xgt, ygt, wgt, hgt) 为ground-truth,B = (x, y, w, h) 为预测框。
bounding box回归的DIoU损失,其中心点之间的归一化距离可以直接最小化。
C是覆盖两个盒子的最小围盒的对角线长度,d = ρ(b, b_GT) 是两个盒子中心点的距离。


IoU损失在非重叠情况下有很大的误差,GIoU损失在水平和垂直情况下有很大的误差,我们的DIoU损失在任何地方回归误差都非常小。
1.4 CIOU(Complete-IoU)

根据GIoU损失(第一行)和CIoU损失(第二行)优化的不同迭代后bounding box的更新。绿色和黑色分别表示目标框和锚框。蓝色和红色分别表示GIoU损失和CIoU损失的预测框。GIoU损失只考虑重叠面积,并倾向于通过增大预测框的尺寸来增加GIoU。
得益于这三种几何因素(中心点距离、重叠面积和高宽比),CIoU损失中归一化中心点距离的最小可以使算法快速收敛,重叠面积和高宽比的一致性有助于更好地匹配两个框。
可以看到,对于非重叠情况,IoU损失有很大的误差。对于水平和垂直情况,GIoU损失有很大的误差。而我们的CIoU损失在任何场景下都有很小的回归误差。


CIoU Loss定义为:
1.5 损失函数总结
IoU系列(IoU, GIoU, DIoU, CIoU)
下图为上面博客的引用! 博主总结的非常好!文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-804860.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-804860.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-804860.html
2 YOLOv5损失函数
def bbox_iou(box1, box2, xywh=True, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, eps=1e-7):
# Returns Intersection over Union (IoU) of box1(1,4) to box2(n,4)
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
if xywh: # transform from xywh to xyxy
(x1, y1, w1, h1), (x2, y2, w2, h2) = box1.chunk(4, 1), box2.chunk(4, 1)
w1_, h1_, w2_, h2_ = w1 / 2, h1 / 2, w2 / 2, h2 / 2
b1_x1, b1_x2, b1_y1, b1_y2 = x1 - w1_, x1 + w1_, y1 - h1_, y1 + h1_
b2_x1, b2_x2, b2_y1, b2_y2 = x2 - w2_, x2 + w2_, y2 - h2_, y2 + h2_
else: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1.chunk(4, 1)
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2.chunk(4, 1)
w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, b1_y2 - b1_y1
w2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, b2_y2 - b2_y1
# Intersection area
inter = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \
(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)
# Union Area
union = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + eps
# IoU
iou = inter / union
if CIoU or DIoU or GIoU:
cw = torch.max(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.min(b1_x1, b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) width
ch = torch.max(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.min(b1_y1, b2_y1) # convex height
if CIoU or DIoU: # Distance or Complete IoU https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287v1
c2 = cw ** 2 + ch ** 2 + eps # convex diagonal squared
rho2 = ((b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) ** 2 + (b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) ** 2) / 4 # center dist ** 2
if CIoU: # https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-SSD-pytorch/blob/master/utils/box/box_utils.py#L47
v = (4 / math.pi ** 2) * torch.pow(torch.atan(w2 / (h2 + eps)) - torch.atan(w1 / (h1 + eps)), 2)
with torch.no_grad():
alpha = v / (v - iou + (1 + eps))
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + v * alpha) # CIoU
return iou - rho2 / c2 # DIoU
c_area = cw * ch + eps # convex area
return iou - (c_area - union) / c_area # GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdf
return iou # IoU
class ComputeLoss:
sort_obj_iou = False
# Compute losses
def __init__(self, model, autobalance=False):
device = next(model.parameters()).device # get model device
h = model.hyp # hyperparameters
# Define criteria
BCEcls = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=torch.tensor([h['cls_pw']], device=device))
BCEobj = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=torch.tensor([h['obj_pw']], device=device))
# Class label smoothing https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.04103.pdf eqn 3
self.cp, self.cn = smooth_BCE(eps=h.get('label_smoothing', 0.0)) # positive, negative BCE targets
# Focal loss
g = h['fl_gamma'] # focal loss gamma
if g > 0:
BCEcls, BCEobj = FocalLoss(BCEcls, g), FocalLoss(BCEobj, g)
m = de_parallel(model).model[-1] # Detect() module
self.balance = {3: [4.0, 1.0, 0.4]}.get(m.nl, [4.0, 1.0, 0.25, 0.06, 0.02]) # P3-P7
self.ssi = list(m.stride).index(16) if autobalance else 0 # stride 16 index
self.BCEcls, self.BCEobj, self.gr, self.hyp, self.autobalance = BCEcls, BCEobj, 1.0, h, autobalance
self.na = m.na # number of anchors
self.nc = m.nc # number of classes
self.nl = m.nl # number of layers
self.anchors = m.anchors
self.device = device
def __call__(self, p, targets): # predictions, targets
lcls = torch.zeros(1, device=self.device) # class loss
lbox = torch.zeros(1, device=self.device) # box loss
lobj = torch.zeros(1, device=self.device) # object loss
tcls, tbox, indices, anchors = self.build_targets(p, targets) # targets
# Losses
for i, pi in enumerate(p): # layer index, layer predictions
b, a, gj, gi = indices[i] # image, anchor, gridy, gridx
tobj = torch.zeros(pi.shape[:4], dtype=pi.dtype, device=self.device) # target obj
n = b.shape[0] # number of targets
if n:
# pxy, pwh, _, pcls = pi[b, a, gj, gi].tensor_split((2, 4, 5), dim=1) # faster, requires torch 1.8.0
pxy, pwh, _, pcls = pi[b, a, gj, gi].split((2, 2, 1, self.nc), 1) # target-subset of predictions
# Regression
pxy = pxy.sigmoid() * 2 - 0.5
pwh = (pwh.sigmoid() * 2) ** 2 * anchors[i]
pbox = torch.cat((pxy, pwh), 1) # predicted box
iou = bbox_iou(pbox, tbox[i], CIoU=True).squeeze() # iou(prediction, target)
lbox += (1.0 - iou).mean() # iou loss
# Objectness
iou = iou.detach().clamp(0).type(tobj.dtype)
if self.sort_obj_iou:
j = iou.argsort()
b, a, gj, gi, iou = b[j], a[j], gj[j], gi[j], iou[j]
if self.gr < 1:
iou = (1.0 - self.gr) + self.gr * iou
tobj[b, a, gj, gi] = iou # iou ratio
# Classification
if self.nc > 1: # cls loss (only if multiple classes)
t = torch.full_like(pcls, self.cn, device=self.device) # targets
t[range(n), tcls[i]] = self.cp
lcls += self.BCEcls(pcls, t) # BCE
# Append targets to text file
# with open('targets.txt', 'a') as file:
# [file.write('%11.5g ' * 4 % tuple(x) + '\n') for x in torch.cat((txy[i], twh[i]), 1)]
obji = self.BCEobj(pi[..., 4], tobj)
lobj += obji * self.balance[i] # obj loss
if self.autobalance:
self.balance[i] = self.balance[i] * 0.9999 + 0.0001 / obji.detach().item()
if self.autobalance:
self.balance = [x / self.balance[self.ssi] for x in self.balance]
lbox *= self.hyp['box']
lobj *= self.hyp['obj']
lcls *= self.hyp['cls']
bs = tobj.shape[0] # batch size
return (lbox + lobj + lcls) * bs, torch.cat((lbox, lobj, lcls)).detach()
到了这里,关于【目标检测算法】IOU、GIOU、DIOU、CIOU与YOLOv5损失函数的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!