优质博文:IT-BLOG-CN
一、题目
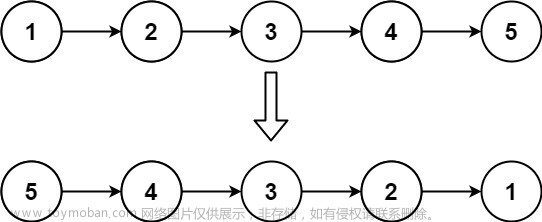
给你链表的头节点head,每k个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是k的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例2:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
二、代码
【1】先实现链表的反转功能
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head) {
// 1、第一个考查点:反转链表
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
// 用户暂时保存next的值;
ListNode nxt = null;
// 遍历链表进行翻转
while(cur != null) {
nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
// 在原链表上看,pre指向tail节点,cur指向pre下一个节点
return pre;
}
}
【2】实现指定长度数据的反转
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
// 主要作用:保留开始反转节点的上一个节点
ListNode headPre = new ListNode(0, head);
// 后面会不断更新,直至需要反转
ListNode p0 = headPre;
// 先遍历不反转的部分
for (int i = 1; i < left; i++) {
p0 = p0.next;
}
// 1、第一个考查点:反转链表
ListNode pre = null;
// 这里不再指向头节点,指向开始反转的节点
ListNode cur = p0.next;
// 用户暂时保存next的值;
ListNode nxt = null;
// 遍历链表进行翻转
for (int i = 0; i < right - left + 1; i++) {
if ( cur != null ) {
nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
}
// 在原链表上看,pre指向tail节点,cur指向pre下一个节点
// 将 pre节点放入 p0的next节点
p0.next.next = cur;
p0.next = pre;
return headPre;
}
}
【3】实现k位反转,不足k位不反转
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
// 1、计算中记录数
ListNode countList = head;
int count = 0;
while(countList != null) {
count++;
countList = countList.next;
}
// 主要作用:保留开始反转节点的上一个节点
ListNode dummp = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode p0 = dummp;
// 2、第一个考查点:反转链表
while (k <= count) {
// 循环推出条件
count -= k;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = p0.next;
// 遍历链表进行翻转
for(int i = 0; i<k; i++) {
// 用户暂时保存next的值;
ListNode nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
// 3、倒序后重新串联
ListNode p0Next = p0.next;
p0.next.next = cur;
p0.next = pre;
p0 = p0Next;
}
// 在原链表上看,pre指向tail节点,cur指向pre下一个节点
return dummp.next;
}
}
说明:自己尝试画图理解,否则不容易理解,附视频讲解
【3】模拟: 本题的目标非常清晰易懂,不涉及复杂的算法,但是实现过程中需要考虑的细节比较多,容易写出冗长的代码。主要考查面试者设计的能力。
我们需要把链表节点按照k个一组分组,所以可以使用一个指针head依次指向每组的头节点。这个指针每次向前移动k步,直至链表结尾。对于每个分组,我们先判断它的长度是否大于等于k。若是,我们就翻转这部分链表,否则不需要翻转。
接下来的问题就是如何翻转一个分组内的子链表但是对于一个子链表,除了翻转其本身之外,还需要将子链表的头部与上一个子链表连接,以及子链表的尾部与下一个子链表连接
因此,在翻转子链表的时候,我们不仅需要子链表头节点head,还需要有head的上一个节点pre,以便翻转完后把子链表再接回pre。
但是对于第一个子链表,它的头节点head前面是没有节点pre的。太麻烦了!难道只能特判了吗?答案是否定的。没有条件,我们就创造条件;没有节点,我们就创建一个节点。我们新建一个节点,把它接到链表的头部,让它作为pre的初始值,这样head前面就有了一个节点,我们就可以避开链表头部的边界条件。这么做还有一个好处,下面我们会看到。
反复移动指针head与pre,对head所指向的子链表进行翻转,直到结尾,我们就得到了答案。下面我们该返回函数值了。
有的同学可能发现这又是一件麻烦事:链表翻转之后,链表的头节点发生了变化,那么应该返回哪个节点呢?照理来说,前k个节点翻转之后,链表的头节点应该是第k个节点。那么要在遍历过程中记录第k个节点吗?但是如果链表里面没有k个节点,答案又还是原来的头节点。我们又多了一大堆循环和判断要写,太崩溃了!
等等!还记得我们创建了节点pre吗?这个节点一开始被连接到了头节点的前面,而无论之后链表有没有翻转,它的next指针都会指向正确的头节点。那么我们只要返回它的下一个节点就好了。至此,问题解决。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode hair = new ListNode(0);
hair.next = head;
ListNode pre = hair;
while (head != null) {
ListNode tail = pre;
// 查看剩余部分长度是否大于等于 k
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
tail = tail.next;
if (tail == null) {
return hair.next;
}
}
ListNode nex = tail.next;
ListNode[] reverse = myReverse(head, tail);
head = reverse[0];
tail = reverse[1];
// 把子链表重新接回原链表
pre.next = head;
tail.next = nex;
pre = tail;
head = tail.next;
}
return hair.next;
}
public ListNode[] myReverse(ListNode head, ListNode tail) {
ListNode prev = tail.next;
ListNode p = head;
while (prev != tail) {
ListNode nex = p.next;
p.next = prev;
prev = p;
p = nex;
}
return new ListNode[]{tail, head};
}
}
时间复杂度: O(n),其中n为链表的长度。head指针会在O(⌊nk⌋)个节点上停留,每次停留需要进行一次O(k)的翻转操作。
空间复杂度: O(1),我们只需要建立常数个变量。
【4】栈: 我们把k个数压入栈中,然后弹出来的顺序就是翻转的!剩下的链表个数够不够k个(因为不够k个不用翻转);已经翻转的部分要与剩下链表连接起来。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
Deque<ListNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<ListNode>();
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
while (true) {
int count = 0;
ListNode tmp = head;
while (tmp != null && count < k) {
stack.add(tmp);
tmp = tmp.next;
count++;
}
if (count != k) {
p.next = head;
break;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
p.next = stack.pollLast();
p = p.next;
}
p.next = tmp;
head = tmp;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
尾插法文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-805386.html
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode tail = dummy;
while (true) {
int count = 0;
while (tail != null && count != k) {
count++;
tail = tail.next;
}
if (tail == null) break;
ListNode head1 = pre.next;
while (pre.next != tail) {
ListNode cur = pre.next;
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next = tail.next;
tail.next = cur;
}
pre = head1;
tail = head1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
递归文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-805386.html
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while (cur != null && count != k) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
if (count == k) {
cur = reverseKGroup(cur, k);
while (count != 0) {
count--;
ListNode tmp = head.next;
head.next = cur;
cur = head;
head = tmp;
}
head = cur;
}
return head;
}
到了这里,关于K 个一组翻转链表(链表反转,固定长度反转)(困难)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!