list容器
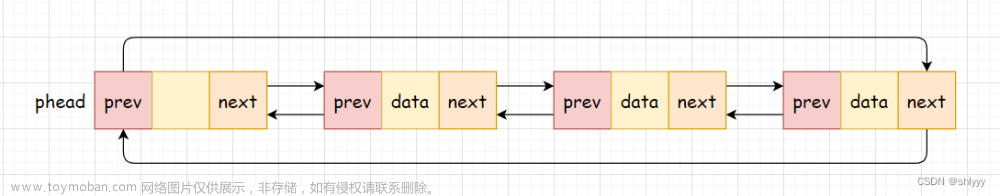
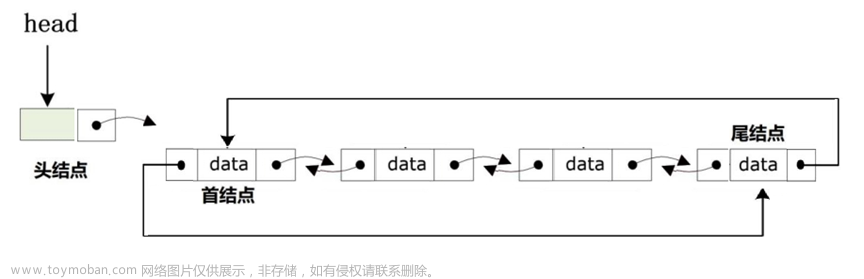
Go语言中list容器定义在"container/list"包中,实现了一个双向链表。本文第一部分总结源码包中的方法,第二部分展示使用list包的常见示例用法以及刷题时的用法。
食用指南:先看第二部分的常用示例用法然后再用到时在第一部分找对应的方法。
更多内容以及其他Go常用数据结构的实现在这里,感谢Star:https://github.com/acezsq/Data_Structure_Golang
1. list源码
- 基础方法
| 方法 | 所属类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| New() | list包函数 | 创建一个list |
| Next() *Element | Element | 获取当前结点的下一个结点 |
| Prev() *Element | Element | 获取当前结点的上一个结点 |
| Len() int | List | 获取链表长度 |
| Front() *Element | List | 获取链表第一个结点 |
| Back() *Element | List | 获取链表最后一个结点 |
- 插入方法
| 方法 | 所属类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| PushFront(v any) *Element | List | 在链表头部插入一个结点 |
| PushBack(v any) *Element | List | 在链表末尾插入一个结点 |
| insert(e, at *Element) *Element | List | 在一个结点之后插入一个新的结点 |
| insertValue(v any, at *Element) *Element | List | 在一个结点之后插入一个新的结点 |
| InsertBefore(v any, mark *Element) *Element | List | 在一个结点之前插入一个新的结点 |
| InsertAfter(v any, mark *Element) *Element | List | 在一个结点之后插入一个新的结点 |
- 移除移动方法
| 方法 | 所属类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| move(e, at *Element) | List | 将一个结点移动到另一个结点后面 |
| remove(e *Element) | List | 从链表移除一个结点 |
| Remove(e *Element) any | List | 从链表移除一个结点 |
| MoveToFront(e *Element) | List | 将一个结点移动到链表头部 |
| MoveToBack(e *Element) | List | 将一个结点移动到链表尾部 |
| MoveBefore(e, mark *Element) | List | 移动一个结点到另一个结点前面 |
| MoveAfter(e, mark *Element) | List | 移动一个结点到另一个结点后面 |
- 复制链表方法
| 方法 | 所属类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| PushBackList(other *List) | List | 将另一个链表复制到当前链表后面 |
| PushFrontList(other *List) | List | 将另一个链表复制到当前链表前面 |
Element类型定义了双向链表中的一个元素结点。next, prev分别表示当前节点指向下一个和上一个节点的指针,list表示当前节点属于哪个双向链表,而Value则表示当前结点存储的具体的值。
// Element is an element of a linked list.
type Element struct {
// Next and previous pointers in the doubly-linked list of elements.
// To simplify the implementation, internally a list l is implemented
// as a ring, such that &l.root is both the next element of the last
// list element (l.Back()) and the previous element of the first list
// element (l.Front()).
next, prev *Element
// The list to which this element belongs.
list *List
// The value stored with this element.
Value any
}
List类型定义了一个双向链表,空的List类型表示一个待使用的空链表。root是一个Element类型的字段,它代表了链表中的哨兵元素,哨兵元素是一个特殊的元素,它不存储任何实际的值,只是作为链表的起始和结束标记。len是一个整型字段,表示链表中当前的元素数量,不包括哨兵元素。
// List represents a doubly linked list.
// The zero value for List is an empty list ready to use.
type List struct {
root Element // sentinel list element, only &root, root.prev, and root.next are used
len int // current list length excluding (this) sentinel element
}
获取一个结点的前后结点。
// Next returns the next list element or nil.
func (e *Element) Next() *Element {
if p := e.next; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
return p
}
return nil
}
// Prev returns the previous list element or nil.
func (e *Element) Prev() *Element {
if p := e.prev; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
return p
}
return nil
}
创建结点。
// Init initializes or clears list l.
func (l *List) Init() *List {
l.root.next = &l.root
l.root.prev = &l.root
l.len = 0
return l
}
// New returns an initialized list.
func New() *List { return new(List).Init() }
package main
import "container/list"
func main() {
list1 := list.New()
// TODO
}
获取双向链表的长度,时间复杂度时O(1)
// Len returns the number of elements of list l.
// The complexity is O(1).
func (l *List) Len() int { return l.len }
获取当前链表的第一个和最后一个结点。
// Front returns the first element of list l or nil if the list is empty.
func (l *List) Front() *Element {
if l.len == 0 {
return nil
}
return l.root.next
}
// Back returns the last element of list l or nil if the list is empty.
func (l *List) Back() *Element {
if l.len == 0 {
return nil
}
return l.root.prev
}
实现对List类型的延迟初始化。具体来说,它用于在第一次访问List对象时,检查是否已经进行了初始化,如果没有,则执行初始化操作。
// lazyInit lazily initializes a zero List value.
func (l *List) lazyInit() {
if l.root.next == nil {
l.Init()
}
}
在一个结点之后插入一个新的结点,输入是结点类型对象。另外需要修改指针以及新节点归属的链表以及链表的长度。
// insert inserts e after at, increments l.len, and returns e.
func (l *List) insert(e, at *Element) *Element {
e.prev = at
e.next = at.next
e.prev.next = e
e.next.prev = e
e.list = l
l.len++
return e
}
添加一个结点,但是输入的时结点的值信息。
// insertValue is a convenience wrapper for insert(&Element{Value: v}, at).
func (l *List) insertValue(v any, at *Element) *Element {
return l.insert(&Element{Value: v}, at)
}
从链表中删除一个结点,输入是结点类型对象。
// remove removes e from its list, decrements l.len
func (l *List) remove(e *Element) {
e.prev.next = e.next
e.next.prev = e.prev
e.next = nil // avoid memory leaks
e.prev = nil // avoid memory leaks
e.list = nil
l.len--
}
移动一个结点到另一个结点后面。
// move moves e to next to at.
func (l *List) move(e, at *Element) {
if e == at {
return
}
e.prev.next = e.next
e.next.prev = e.prev
e.prev = at
e.next = at.next
e.prev.next = e
e.next.prev = e
}
从链表中移除一个结点并返回该结点的值。
// Remove removes e from l if e is an element of list l.
// It returns the element value e.Value.
// The element must not be nil.
func (l *List) Remove(e *Element) any {
if e.list == l {
// if e.list == l, l must have been initialized when e was inserted
// in l or l == nil (e is a zero Element) and l.remove will crash
l.remove(e)
}
return e.Value
}
在链表头或者尾部插入一个结点,输入时结点中存储具体的值。
// PushFront inserts a new element e with value v at the front of list l and returns e.
func (l *List) PushFront(v any) *Element {
l.lazyInit()
return l.insertValue(v, &l.root)
}
// PushBack inserts a new element e with value v at the back of list l and returns e.
func (l *List) PushBack(v any) *Element {
l.lazyInit()
return l.insertValue(v, l.root.prev)
}
在一个结点前和在一个结点后面插入一个结点,输入是结点的值。
// InsertBefore inserts a new element e with value v immediately before mark and returns e.
// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
// The mark must not be nil.
func (l *List) InsertBefore(v any, mark *Element) *Element {
if mark.list != l {
return nil
}
// see comment in List.Remove about initialization of l
return l.insertValue(v, mark.prev)
}
// InsertAfter inserts a new element e with value v immediately after mark and returns e.
// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
// The mark must not be nil.
func (l *List) InsertAfter(v any, mark *Element) *Element {
if mark.list != l {
return nil
}
// see comment in List.Remove about initialization of l
return l.insertValue(v, mark)
}
将一个结点移动到链表头尾,某个结点前后。
// MoveToFront moves element e to the front of list l.
// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
// The element must not be nil.
func (l *List) MoveToFront(e *Element) {
if e.list != l || l.root.next == e {
return
}
// see comment in List.Remove about initialization of l
l.move(e, &l.root)
}
// MoveToBack moves element e to the back of list l.
// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
// The element must not be nil.
func (l *List) MoveToBack(e *Element) {
if e.list != l || l.root.prev == e {
return
}
// see comment in List.Remove about initialization of l
l.move(e, l.root.prev)
}
// MoveBefore moves element e to its new position before mark.
// If e or mark is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
// The element and mark must not be nil.
func (l *List) MoveBefore(e, mark *Element) {
if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
return
}
l.move(e, mark.prev)
}
// MoveAfter moves element e to its new position after mark.
// If e or mark is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
// The element and mark must not be nil.
func (l *List) MoveAfter(e, mark *Element) {
if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
return
}
l.move(e, mark)
}
将一个链表复制到另一个链表的后面或者前面。
// PushBackList inserts a copy of another list at the back of list l.
// The lists l and other may be the same. They must not be nil.
func (l *List) PushBackList(other *List) {
l.lazyInit()
for i, e := other.Len(), other.Front(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Next() {
l.insertValue(e.Value, l.root.prev)
}
}
// PushFrontList inserts a copy of another list at the front of list l.
// The lists l and other may be the same. They must not be nil.
func (l *List) PushFrontList(other *List) {
l.lazyInit()
for i, e := other.Len(), other.Back(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Prev() {
l.insertValue(e.Value, &l.root)
}
}
2. 使用示例
- 创建链表,添加结点,遍历链表
package main
import (
"container/list"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
// 创建一个新的链表
l := list.New()
// 在链表尾部添加元素
l.PushBack(1)
l.PushBack(2)
l.PushBack(3)
// 在链表头部添加元素
l.PushFront(0)
// 遍历链表并打印元素值
for e := l.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next() {
fmt.Println(e.Value) // 0 1 2 3
}
// 获取链表长度
fmt.Println("Length:", l.Len()) // 4
// 删除指定元素
elementToRemove := l.Front().Next()
l.Remove(elementToRemove)
// 在指定元素之前插入元素
elementToInsertBefore := l.Back()
l.InsertBefore(4, elementToInsertBefore)
// 在指定元素之后插入元素
elementToInsertAfter := l.Front()
l.InsertAfter(5, elementToInsertAfter)
// 遍历链表并打印元素值
for e := l.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next() {
fmt.Println(e.Value) // 0 5 2 4 3
}
// 清空链表
l.Init()
// 遍历链表并打印元素值
for e := l.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next() {
fmt.Println(e.Value) //
}
}
- 使用反射获取结点中存储的值
从下面Element类型的定义中可以看到Value的类型时any类型,也就是空接口类型。所以在获取到结点的Value时需要通过反射获取具体的值类型用于后续任务。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-806179.html
// Element is an element of a linked list.
type Element struct {
// Next and previous pointers in the doubly-linked list of elements.
// To simplify the implementation, internally a list l is implemented
// as a ring, such that &l.root is both the next element of the last
// list element (l.Back()) and the previous element of the first list
// element (l.Front()).
next, prev *Element
// The list to which this element belongs.
list *List
// The value stored with this element.
Value any
}
比如LeetCode上的LFU这道题中使用双链表完成时,e := node.Value.(*entry)这行代码通过反射获取到结点值的具体的类型,这样才能使得后续使用e时是*entry类型。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-806179.html
type entry struct {
key, value, freq int
}
type LFUCache struct {
capacity int
minFreq int
keyToNode map[int]*list.Element
freqToList map[int]*list.List
}
func Constructor(capacity int) LFUCache {
return LFUCache{
capacity: capacity,
keyToNode: map[int]*list.Element{},
freqToList: map[int]*list.List{},
}
}
func (c *LFUCache) pushfront(e *entry) {
if _, ok := c.freqToList[e.freq]; !ok {
c.freqToList[e.freq] = list.New()
}
c.keyToNode[e.key] = c.freqToList[e.freq].PushFront(e)
}
func (c *LFUCache) getEntry(key int) *entry {
node := c.keyToNode[key]
if node == nil {
return nil
}
e := node.Value.(*entry)
lst := c.freqToList[e.freq]
lst.Remove(node)
if lst.Len()==0 {
delete(c.freqToList,e.freq)
if c.minFreq == e.freq {
c.minFreq++
}
}
e.freq++
c.pushfront(e)
return e
}
func (c *LFUCache) Get(key int) int {
if e:=c.getEntry(key); e!=nil {
return e.value
} else {
return -1
}
}
func (c *LFUCache) Put(key int, value int) {
if e := c.getEntry(key); e!=nil {
e.value = value
return
}
if len(c.keyToNode) == c.capacity {
lst := c.freqToList[c.minFreq]
delete(c.keyToNode,lst.Remove(lst.Back()).(*entry).key)
if lst.Len()==0 {
delete(c.freqToList,c.minFreq)
}
}
c.pushfront(&entry{key,value,1})
c.minFreq = 1
}
/**
* Your LFUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor(capacity);
* param_1 := obj.Get(key);
* obj.Put(key,value);
*/
到了这里,关于Go语言数据结构(一)双向链表的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!