执行顺序探究
新建一个对象用于测试
@Component
public class Student implements InitializingBean {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/**
* InitializingBean 提供的在属性设置之后执行的方法
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("====== Student afterPropertiesSet");
}
/**
* 初始化方法用于配置 bean inti
*/
public void init() {
System.out.println("====== afterPropertiesSet init");
}
/**
* PostConstruct
*/
@PostConstruct
public void post() {
System.out.println("====== Student PostConstruct");
}
}
新建一个TestBeanPostProcessor 实现 BeanPostProcessor
@Component
public class TestBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println("======== Student postProcessAfterInitialization");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("=============Student postProcessBeforeInitialization");
return bean;
}
}
通过注解的 方式进行测试
@Test
public void test3() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.liyong.learn");
Student bean = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(String.format("ben is name{%s} age is {%s}", bean.getName(), bean.getAge()));
}
得到的结果如下: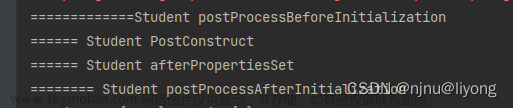
总结PostProcessBeforeInitialization -> PostConstruct -> InitializingBean -> PostProcessAfterInitialization
通过Bean.xml的方式文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-806513.html
<bean id="student" class="com.liyong.learn.Student" init-method="init">
<property name="name" value="english"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="testBeanPostProcessor" class="com.liyong.learn.TestBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
@Test
public void test () {
// 指定XML路径
String path = "beans.xml";
// 创建DefaultListableBeanFactory工厂,这也就是Spring的基本容器
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
// 创建BeanDefinition阅读器
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// 进行BeanDefinition注册流程
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(path);
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor((BeanPostProcessor) beanFactory.getBean("testBeanPostProcessor"));
// Bean实例创建流程
Student student = (Student) beanFactory.getBean("student");
System.out.println(String.format("bean attrs name {%s} age {%s}", student.getName(), student.getAge()));
}
执行结果如下:
总结PostProcessBeforeInitialization -> InitializingBean -> initMethod -> PostProcessAfterInitialization 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-806513.html
到了这里,关于Spring-BeanPostProcessor PostConstruct init InitializingBean 执行顺序的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!




![[Spring5.3.2] Servlet[springmvc]的Servlet.init()引发异常, 解析类文件失败](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/431312-1.png)




