目录
前言
1 话题简介
2 常用指令
3 RCLCPP实现实现话题
3.1 创建工作空间
3.2 代码编写
3.2.1 发布端编写
3.2.2 发布端编写
前言
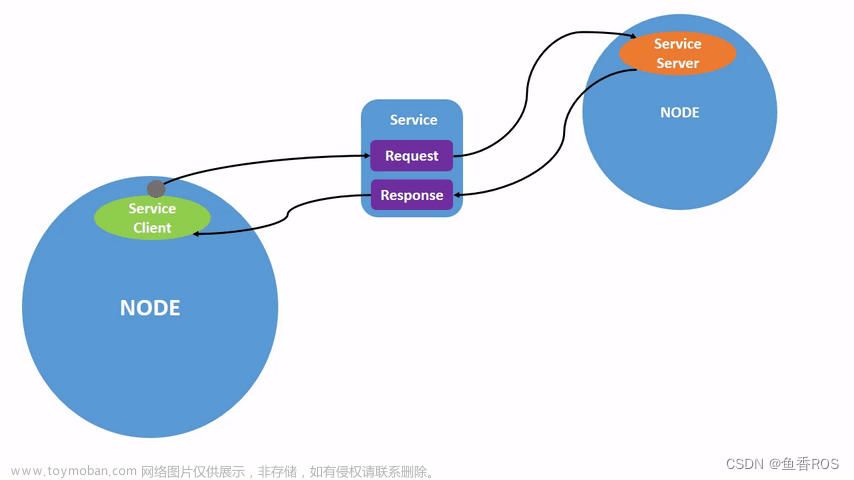
ROS2中的一个重要概念是话题(Topic)。话题是一种通过发布者和订阅者之间进行异步通信的机制。发布者(Publisher)将消息发布到特定的话题上,而订阅者(Subscriber)则可以选择订阅感兴趣的话题,并接收发布者发送的消息。
话题可以用来传递各种类型的消息,例如传感器数据、机器人状态、控制指令等。每个话题有一个唯一的名称,并且可以有多个发布者和订阅者。
ROS2提供了一套API来操作话题。开发者可以使用语言(如C++和Python)来编写发布者和订阅者节点,并在运行时将它们连接到ROS2系统中。
使用话题,开发者可以实现多个节点之间的解耦和灵活性。不同的节点可以以不同的速度发布和接收消息,可以动态地增加或删除节点,而不会影响其他节点的运行。
总结来说,ROS2中的话题机制提供了一种灵活和可扩展的通信方式,可以方便地实现不同节点之间的消息传递和协作。它是ROS2中重要的基础组件之一,为构建机器人应用提供了强大的功能和便利的开发体验。
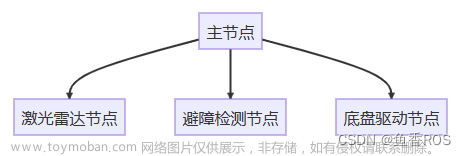
1 话题简介
支持1对1,1对多,多对1,多对多。
为了方便发送者和接收者进行数据的交换,ROS2帮我们在数据传递时做好了消息的序列化和反序列化,而且ROS2的消息序列化与反序列化通信是可以做到跨编程语言、跨平台和跨设备之间的。
一个节点发布数据到某个话题上,另外一个节点就可以通过订阅话题拿到数据。

2 常用指令
首先运行一个发布节点:
ros2 run demo_nodes_cpp talker查看上面发布节点的话题信息:
查看话题列表
ros2 topic list -t打印话题
ros2 topic echo /chatter查看topic信息
ros2 topic info /chatter查看消息类型
ros2 interface show std_msgs/msg/String手动发布命令
ros2 topic pub /chatter std_msgs/msg/String 'data: "123"'图形化查看节点信息
rqt_graph查看话题频率
ros2 topic hz /chatter
3 RCLCPP实现实现话题
3.1 创建工作空间
cd project/
mkdir -p project/
cd project/
ros2 pkg create cpp_topic --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp
touch cpp_topic/src/publisher.cpp3.2 代码编写
调用Node的成员函数create_publisher并传入对应的参数即可。通过文档可以看出,至少需要传入消息类型(msgT)、话题名称(topic_name)和 服务质量(qos)。
官方rclcpp文档地址:rclcpp: rclcpp: ROS Client Library for C++

消息接口是ROS2通信时必须的一部分,通过消息接口ROS2才能完成消息的序列化和反序列化。ROS2为定义好了常用的消息接口,并生成了相应的C++和Python的依赖文件,通过脚本直接导入。
通过ros2 pkg指令创建的功能包目录结构如下:
$ tree -a
.
└── cpp_topic
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── include
│ └── cpp_topic
├── package.xml
└── src
└── publisher.cpp
3.2.1 发布端编写
publisher.cpp
/*****ros2官方demo*******/
#include <chrono>
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "std_msgs/msg/string.hpp"
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
/* This example creates a subclass of Node and uses std::bind() to register a
* member function as a callback from the timer. */
class MinimalPublisher : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
MinimalPublisher()
: Node("minimal_publisher"), count_(0)
{
publisher_ = this->create_publisher<std_msgs::msg::String>("topic", 10);
timer_ = this->create_wall_timer(
500ms, std::bind(&MinimalPublisher::timer_callback, this));
}
private:
void timer_callback()
{
auto message = std_msgs::msg::String();
message.data = "Hello, world! " + std::to_string(count_++);
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Publishing: '%s'", message.data.c_str());
publisher_->publish(message);
}
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
rclcpp::Publisher<std_msgs::msg::String>::SharedPtr publisher_;
size_t count_;
};
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
rclcpp::spin(std::make_shared<MinimalPublisher>());
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(cpp_topic)
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
# find dependencies
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
find_package(std_msgs REQUIRED)
add_executable(pulisher src/publisher.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(pulisher rclcpp std_msgs)
install(TARGETS
pulisher
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME})
if(BUILD_TESTING)
find_package(ament_lint_auto REQUIRED)
# the following line skips the linter which checks for copyrights
# comment the line when a copyright and license is added to all source files
set(ament_cmake_copyright_FOUND TRUE)
# the following line skips cpplint (only works in a git repo)
# comment the line when this package is in a git repo and when
# a copyright and license is added to all source files
set(ament_cmake_cpplint_FOUND TRUE)
ament_lint_auto_find_test_dependencies()
endif()
ament_package()
package.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-model href="http://download.ros.org/schema/package_format3.xsd" schematypens="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"?>
<package format="3">
<name>cpp_topic</name>
<version>0.0.0</version>
<description>TODO: Package description</description>
<maintainer email="xxxxx@xxx.com">linux</maintainer>
<license>TODO: License declaration</license>
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend>
<depend>rclcpp</depend>
<depend>std_msgs</depend>
<test_depend>ament_lint_auto</test_depend>
<test_depend>ament_lint_common</test_depend>
<export>
<build_type>ament_cmake</build_type>
</export>
</package>在project目录运行如下编译指令
colcon build --packages-select cpp_topic编译完成后目录如下:

运行
source install/setup.bash
ros2 run cpp_topic pulisher

此时可以通过命令订阅该topic

3.2.2 发布端编写
上面过程中是通过ros2自动的命令进行话题的订阅,下面使用c++代码实现话题订阅。
创建订阅节点文件
touch cpp_topic/src/subscriber.cppsubscriber.cpp:
/*****ros2官方demo*******/
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "std_msgs/msg/string.hpp"
using std::placeholders::_1;
class MinimalSubscriber : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
MinimalSubscriber()
: Node("minimal_subscriber")
{
subscription_ = this->create_subscription<std_msgs::msg::String>(
"topic", 10, std::bind(&MinimalSubscriber::topic_callback, this, _1));
}
private:
void topic_callback(const std_msgs::msg::String & msg) const
{
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "I heard: '%s'", msg.data.c_str());
}
rclcpp::Subscription<std_msgs::msg::String>::SharedPtr subscription_;
};
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
rclcpp::spin(std::make_shared<MinimalSubscriber>());
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}CMakeLists.txt增加如下代码
add_executable(subscriber src/subscriber.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(subscriber rclcpp std_msgs)
install(TARGETS
subscriber
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME})在project目录运行如下编译指令
colcon build --packages-select cpp_topic在project目录先运行上面的发布节点
source install/setup.bash
ros2 run cpp_topic pulisher新开一个终端进入到project目录,运行订阅节点
source install/setup.bash
ros2 run cpp_topic subscriber
无论你是初学者还是有经验的开发者,希望我的博客能对你的学习之路有所帮助。如果你觉得这篇文章有用,不妨点击点赞、收藏,或者留下你的评论分享你的见解和经验,也欢迎你对我博客的内容提出建议和问题。每一次的点赞、评论、分享和关注都是对我的最大支持,也是对我持续分享和创作的动力。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-806972.html
阅读我的CSDN主页,解锁更多精彩内容:Tech Embedded-CSDN博客文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-806972.html
到了这里,关于ROS2学习笔记三:话题Topic的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!