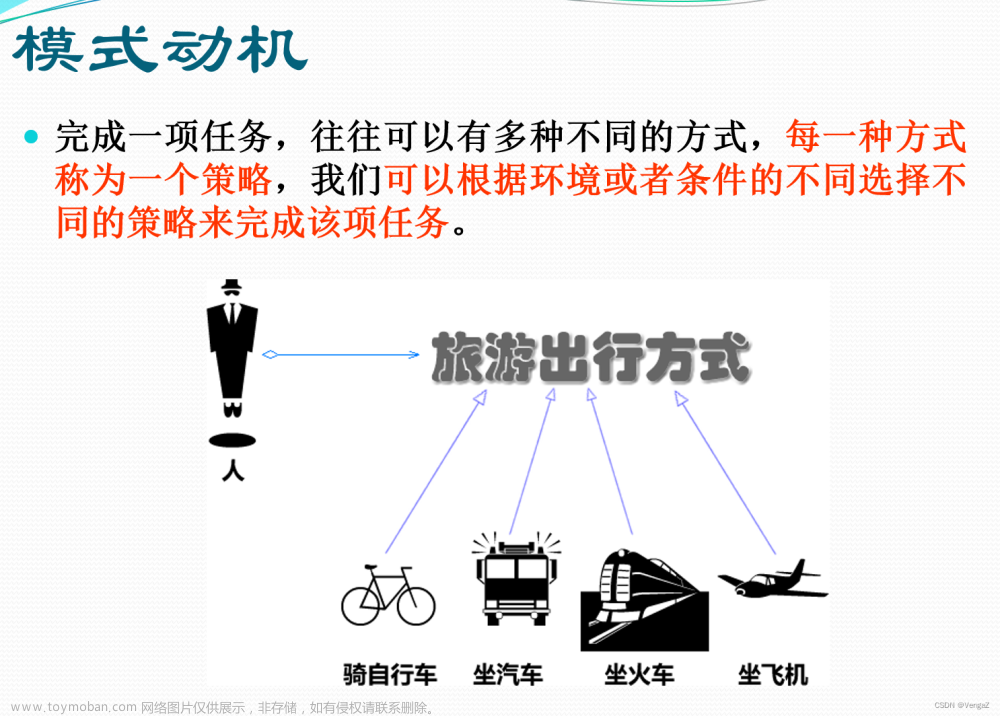
它允许在运行时根据需要选择算法的行为。该模式通过将算法封装成独立的类,使得它们可以相互替换,而不影响使用算法的客户端代码。
策略模式主要包含以下角色:
- 环境(Context):环境对象持有一个策略对象的引用,它提供了一个接口用于执行具体的算法。
- 抽象策略(Strategy):定义了策略类的统一接口,用于约束具体策略类的行为。
- 具体策略(Concrete Strategy):实现了抽象策略定义的接口,具体实现算法逻辑。
下面以一个简单的支付系统为例来说明策略模式的应用:
// 抽象策略类
public interface PaymentStrategy {
void pay(double amount);
}
// 具体策略类
public class AliPayStrategy implements PaymentStrategy {
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("使用支付宝支付:" + amount + "元");
// 具体的支付逻辑
}
}
public class WeChatPayStrategy implements PaymentStrategy {
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("使用微信支付:" + amount + "元");
// 具体的支付逻辑
}
}
// 环境类
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class PaymentContext {
private PaymentStrategy strategy;
public void pay(double amount) {
strategy.pay(amount);
}
}
在上述示例中,我们定义了一个抽象策略类PaymentStrategy,并有两个具体的策略类AliPayStrategy和WeChatPayStrategy分别实现了支付宝支付和微信支付的具体逻辑。
环境类PaymentContext持有一个策略对象的引用,并提供了设置策略和支付方法。客户端通过设置不同的策略对象来实现不同的支付方式。这样,客户端代码与具体的支付算法解耦,可以动态地在运行时切换支付策略。
下面是使用策略模式实现的客户端代码:
javaCopy Codepublic class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PaymentContext context = new PaymentContext();
// 使用支付宝支付
PaymentStrategy aliPayStrategy = new AliPayStrategy();
context.setPaymentStrategy(aliPayStrategy);
context.pay(100.0);
// 使用微信支付
PaymentStrategy weChatPayStrategy = new WeChatPayStrategy();
context.setPaymentStrategy(weChatPayStrategy);
context.pay(200.0);
}
}
运行上述客户端代码,输出如下:
Copy Code 使用支付宝支付:100.0 元
使用微信支付:200.0 元
通过策略模式,我们可以轻松地在运行时切换不同的支付方式,而不需要改动客户端代码。策略模式将算法的选择和使用进行了解耦,提高了代码的灵活性和可维护性。同时,策略模式也符合开闭原则,当需要新增一种支付方式时,只需要添加新的具体策略类即可,无需修改原有代码逻辑。
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double price = 100.0;
String type = "normal";
double discount = 1.0;
// 根据商品类型设置折扣率
if (type.equals("vip")) {
discount = 0.9;
} else if (type.equals("member")) {
discount = 0.95;
} else if (type.equals("promotion")) {
discount = 0.8;
}
double actualPrice = price * discount;
System.out.println("商品的实际价格为:" + actualPrice);
}
}
上述代码中,我们根据商品类型手动设置相应的折扣率,然后计算实际价格。这样的代码虽然简单,但存在以下问题:
- 客户端代码与具体的折扣算法高度耦合,如果需要更改算法,例如新增一种商品类型,就需要修改客户端代码,这会导致代码的可维护性变差。
- 没有遵循开闭原则,当需要新增一种商品类型时,就需要修改原有代码逻辑,这样会影响到其他代码的稳定性。
因此,采用策略模式能更好地解决这些问题,实现代码的松耦合和可维护性。
public class CeLue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double price = 100.0;
String type = "vip";
PayStrategy conType = getPayStrategy(type);
PayContext payContext = new PayContext(conType);
payContext.pay(price);
}
private static PayStrategy getPayStrategy(String type) {
switch (type) {
case "vip":
return new VipType();
default:
return new NormalType();
}
}
}
interface PayStrategy {
void pay(double amount);
}
class NormalType implements PayStrategy {
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("普通支付" + amount + "元");
}
}
class VipType implements PayStrategy {
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("vip支付" + amount * 0.9 + "元");
}
}
class PayContext {
private PayStrategy payStrategy;
public PayContext(PayStrategy payStrategy) {
this.payStrategy = payStrategy;
}
public void pay(double amount) {
payStrategy.pay(amount);
}
}
分享一个案例:统一认证登录
认证接口类 AuthService
public interface AuthService {
UserExt execute(AuthParamsDto authParamsDto);
}
它的实现类 可以是密码登录PasswordAuthServiceImpl 手机号登录PhoneAuthServiceImpl 微信登录WxAuthServiceImpl 等,获取前缀,拼接bean名称,Spring上下文拿到bean文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-807833.html
调用,我用的是SpringsSecurity框架并重写了 UserDetailsService文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-807833.html
@Autowired
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
//传入的是AuthParamsDto的json串
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
AuthParamsDto authParamsDto = null;
try {
//将认证参数转为AuthParamsDto类型
authParamsDto = JSON.parseObject(s, AuthParamsDto.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("认证请求不符合项目要求:{}",s);
throw new RuntimeException("认证请求数据格式不对");
}
//认证方式
String authType = authParamsDto.getAuthType();
//从spring容器中拿具体的认证bean实例
AuthService authService = applicationContext.getBean(authType + "_authservice", AuthService.class);
//开始认证,认证成功拿到用户信息
XcUserExt xcUserExt = authService.execute(authParamsDto);
return getUserPrincipal(xcUserExt);
}
@Data
public class AuthParamsDto {
private String username; //用户名
private String password; //域 用于扩展
private String cellphone;//手机号
private String checkcode;//验证码
private String checkcodekey;//验证码key
private String authType; // 认证的类型 password:用户名密码模式类型 sms:短信模式类型
private Map<String, Object> payload = new HashMap<>();//附加数据,作为扩展,不同认证类型可拥有不同的附加数据。如认证类型为短信时包含smsKey : sms:3d21042d054548b08477142bbca95cfa; 所有情况下都包含clientId
}
到了这里,关于【设计模式 行为型】策略模式的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!