目录
一、卷积层—Convolution Layers
1.1 1d / 2d / 3d卷积
1.2 卷积—nn.Conv2d()
nn.Conv2d
1.3 转置卷积—nn.ConvTranspose
nn.ConvTranspose2d
二、池化层—Pooling Layer
(1)nn.MaxPool2d
(2)nn.AvgPool2d
(3)nn.MaxUnpool2d
三、线性层—Linear Layer
nn.Linear
四、激活函数层—Activate Layer
(1)nn.Sigmoid
(2)nn.tanh
(3)nn.ReLU
(4)nn.LeakyReLU
(5)nn.PReLU
(6)nn.RReLU
前期回顾:
Pytorch学习笔记(1):基本概念、安装、张量操作、逻辑回归
Pytorch学习笔记(2):数据读取机制(DataLoader与Dataset)
Pytorch学习笔记(3):图像的预处理(transforms)
Pytorch学习笔记(4):模型创建(Module)、模型容器(Containers)、AlexNet构建
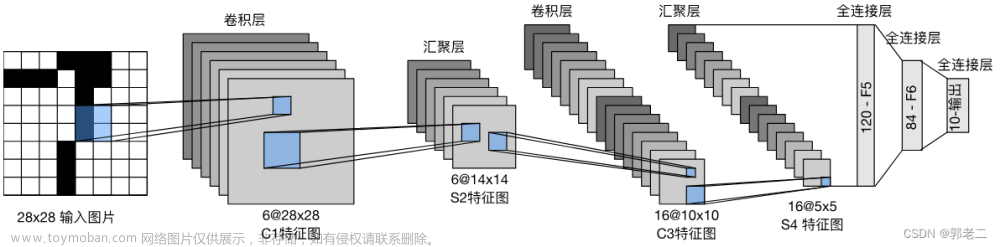
一、卷积层—Convolution Layers
卷积运算:卷积核在输入信号(图像)上滑动,相应位置上进行乘加。
卷积核:又称滤波器,过滤器,可认为是某种模式,某种特征。
卷积过程:类似于用一个模板去图像上寻找与它相似的区域,与卷积核模式越相似,激活值越高,从而实现特征提取。
1.1 1d / 2d / 3d卷积
卷积维度:一般情况下,卷积核在几个维度上滑动,就是几维卷积
(1)1d卷积示意

(2)2d卷积示意

(3)3d卷积示意

1.2 卷积—nn.Conv2d()
nn.Conv2d
功能:对多个二维信号进行二维卷积

主要参数:
- in_channels:输入通道数
- out_channels:输出通道数,等价于卷积核个数
- kernel_size:卷积核尺寸
- stride:步长
- padding:填充个数(一般用来保持输入输出尺寸一致)
- dilation:空洞卷积大小
- groups:分组卷积设置
- bias:偏置
尺寸计算方式:

Conv2d运算原理:
主要代码段如下:
(1)加载图片,将图片处理成张量的形式:
# ================================= load img ==================================
path_img = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)), "pig.jpeg")
print(path_img)
img = Image.open(path_img).convert('RGB') # 0~255
# convert to tensor
img_transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()])
img_tensor = img_transform(img)
# 添加 batch 维度
img_tensor.unsqueeze_(dim=0) # C*H*W to B*C*H*W(2) 进行卷积操作:
# =============== create convolution layer ==================
# ================ 2d
flag = 1
#flag = 0
if flag:
#定义一个卷积层
conv_layer = nn.Conv2d(3, 1, 3) # input:(i, o, size) weights:(o, i , h, w)
# 初始化卷积层权值
nn.init.xavier_normal_(conv_layer.weight.data)
# nn.init.xavier_uniform_(conv_layer.weight.data)
# 卷积运算
img_conv = conv_layer(img_tensor)
(3)运行并打印图片:
# ================================= visualization ==================================
print("卷积前尺寸:{}\n卷积后尺寸:{}".format(img_tensor.shape, img_conv.shape))
img_conv = transform_invert(img_conv[0, 0:1, ...], img_transform)
img_raw = transform_invert(img_tensor.squeeze(), img_transform)
plt.subplot(122).imshow(img_conv, cmap='gray')
plt.subplot(121).imshow(img_raw)
plt.show()我们来看一下效果,可以看到,卷积核对特征进行了提取:

我们再看一下图像尺寸的变化:

卷积前,图像尺寸是1000×1000, 卷积后, 图像尺寸是998×998。我们这里的卷积核设置, 输入通道3, 卷积核个数1, 卷积核大小3, 无padding,步长是1, 那么我们根据上面的公式, 输出尺寸:(1000−3)/1+1=998
我们继续随机初始化卷积核权重进行卷积后,则会出现以下效果:


1.3 转置卷积—nn.ConvTranspose
nn.ConvTranspose2d
功能:转置卷积实现上采样

主要参数:
- in_channels:输入通道数
- out_channels:输出通道数
- kernel_size:卷积核尺寸
- stride:步长
- padding:填充个数
- dilation:空洞卷积大小
- groups:分组卷积设置
- bias:偏置
转置卷积的尺寸计算(卷积运算的尺寸逆):

转置卷积代码如下:
# ================ transposed
flag = 1
# flag = 0
if flag:
conv_layer = nn.ConvTranspose2d(3, 1, 3, stride=2) # input:(input_channel, output_channel, size)
# 初始化网络层的权值
nn.init.xavier_normal_(conv_layer.weight.data)
# calculation
img_conv = conv_layer(img_tensor)转置卷积结果:

我们再看一下图像尺寸的变化:

我们发现,输入图像是1000的, 卷积核大小是3,stride=2, 所以输出尺寸:(1000−1)×2+3=2001
二、池化层—Pooling Layer
池化运算:对信号进行“收集”并“总结”, 类似水池收集水资源, 因而叫作池化层。
“收集”:多变少
“总结”:最大值 or 平均值
如图用2×2的窗口进行池化操作,最大池化用最大值代替这个窗口,平均池化用平均值代替这个窗口。

(1)nn.MaxPool2d
功能:对二维信号(图像)进行最大值池化

主要参数:
- kernel_size:卷积核尺寸
- stride:步长
- padding:填充个数
- dilation:池化间隔大小
- ceil_mode:尺寸向上取整,默认为False
- return_indices:记录池化像素索引
注意:stride一般设置的与窗口大小一致,以避免重叠
具体代码如下:
数据预处理:
set_seed(1) # 设置随机种子
# ================================= load img ==================================
path_img = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)), "pig.jpeg")
img = Image.open(path_img).convert('RGB') # 0~255
# convert to tensor
img_transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()])
img_tensor = img_transform(img)
img_tensor.unsqueeze_(dim=0) # C*H*W to B*C*H*W最大池化代码:
# ================ maxpool
flag = 1
#flag = 0
if flag:
maxpool_layer = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2), stride=(2, 2)) # input:(i, o, size) weights:(o, i , h, w)
img_pool = maxpool_layer(img_tensor)我们来看一下最大池化的效果:

输出尺寸变化:

我们可以发现,图像基本上没什么差别,但是图像的尺寸减少了一半, 所以池化层是可以帮助我们剔除一些冗余像素或减少后面计算量。
(2)nn.AvgPool2d
功能:对二维信号(图像)进行平均值池化

主要参数:
- kernel_size:卷积核尺寸
- stride:步长
- padding:填充个数
- dilation:池化间隔大小
- count_include_pad :填充值用于计算
- divisor_override:除法因子(自定义分母)
平均池化代码:
# ================ avgpool
flag = 1
#flag = 0
if flag:
avgpoollayer = nn.AvgPool2d((2, 2), stride=(2, 2)) # input:(i, o, size) weights:(o, i , h, w)
img_pool = avgpoollayer(img_tensor)我们来看一下平均池化的效果:

输出尺寸变化:

最大值池化和平均池化的差别:最大池化的亮度会稍微亮一些,毕竟它都是取的最大值,而平均池化是取平均值。
(3)nn.MaxUnpool2d
功能:对二维信号(图像)进行最大值池化上采样(反池化:将大尺寸图像变为小尺寸图像)

主要参数:
- kernel_size:卷积核尺寸
- stride:步长
- padding:填充个数
这里的参数与池化层是类似的。唯一的不同就是前向传播的时候我们需要传进一个indices, 我们的索引值,要不然不知道把输入的元素放在输出的哪个位置上。

反池化代码:
# ================ max unpool
flag = 1
#flag = 0
if flag:
# pooling
img_tensor = torch.randint(high=5, size=(1, 1, 4, 4), dtype=torch.float)
#最大值池化保留索引
maxpool_layer = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2), stride=(2, 2), return_indices=True)
img_pool, indices = maxpool_layer(img_tensor)
# unpooling
img_reconstruct = torch.randn_like(img_pool, dtype=torch.float)
#反池化操作
maxunpool_layer = nn.MaxUnpool2d((2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
img_unpool = maxunpool_layer(img_reconstruct, indices)
print("raw_img:\n{}\nimg_pool:\n{}".format(img_tensor, img_pool))
print("img_reconstruct:\n{}\nimg_unpool:\n{}".format(img_reconstruct, img_unpool))
输出结果:

三、线性层—Linear Layer
线性层又称为全连接层,其每个神经元与上一层所有神经元相连实现对前一层的线性组合,线性变换。

nn.Linear
功能:对一维信号(向量)进行线性组合

主要参数:
- in_features:输入结点数
- out_features:输出结点数
- bias:是否需要偏置
计算公式:y = 𝒙𝑾𝑻 + 𝒃𝒊𝒂𝒔
具体代码如下:
# ================ linear
flag = 1
# flag = 0
if flag:
inputs = torch.tensor([[1., 2, 3]])
linear_layer = nn.Linear(3, 4)
linear_layer.weight.data = torch.tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[2., 2., 2.],
[3., 3., 3.],
[4., 4., 4.]])
#设置偏置
linear_layer.bias.data.fill_(0)
output = linear_layer(inputs)
print(inputs, inputs.shape)
print(linear_layer.weight.data, linear_layer.weight.data.shape)
print(output, output.shape)运行结果:
偏置为0:

偏置为0.5:

四、激活函数层—Activate Layer
激活函数对特征进行非线性变换,赋予多层神经网络具有深度的意义
(1)nn.Sigmoid

代码:
m = nn.Sigmoid()
input = torch.randn(2)
output = m(input)
(2)nn.tanh

代码:
m = nn.Tanh()
input = torch.randn(2)
output = m(input)
(3)nn.ReLU

代码:
>>> m = nn.ReLU()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
(4)nn.LeakyReLU
- negative_slope:负半轴斜率
代码:
m = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
input = torch.randn(2)
output = m(input)
(5)nn.PReLU
- init:可学习斜率
代码:
m = nn.PReLU(3)
output = m(input)
print(output)(6)nn.RReLU
- lower:均匀分布下限
- upper:均匀分布上限

代码:
>>> m = nn.RReLU(0.1, 0.3)
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)本文参考:
系统学习Pytorch笔记五:nn的网络层介绍(卷积层,池化层,激活函数,全连接层等)文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-807955.html
[PyTorch 学习笔记] 3.3 池化层、线性层和激活函数层 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-807955.html
到了这里,关于Pytorch学习笔记(5):torch.nn---网络层介绍(卷积层、池化层、线性层、激活函数层)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!