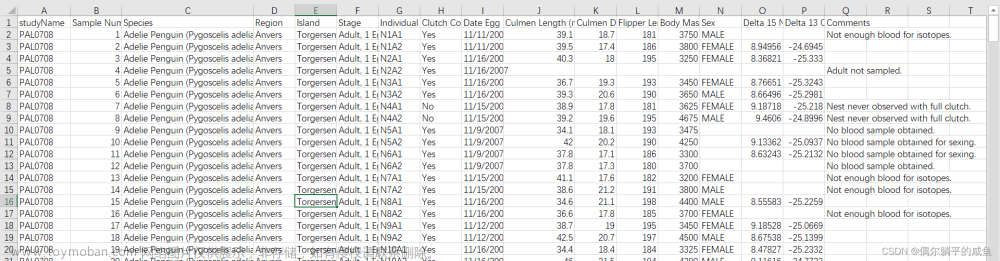
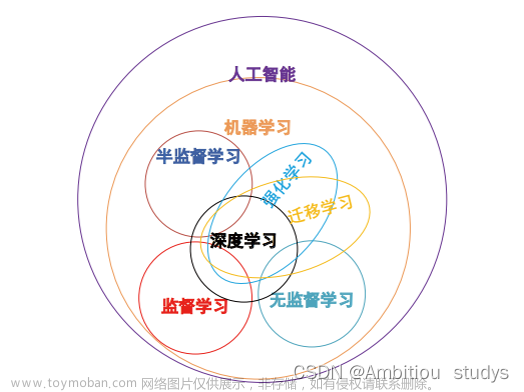
无监督学习(Unsupervised Learning)
机器学习的一种方法,没有给定事先标记过的训练示例,自动对输入的数据进行分类或分群。
方式一:站着或坐着
方式二:全身或半身
方式三:蓝眼球或不是蓝眼球
- 没有对与错
- 寻找数据的共同点
优点:
- 算法不受监督信息(偏见)的约束,可能考虑到新的信息
- 不需要标签数据,极大程度扩大数据样本
主要应用:聚类分析、关联规则、维度缩减
应用最广:聚类分析(clustering)
聚类分析
聚类分析又称为群分析,根据对象某些属性的相似度,将其自动化分为不同的类别
常用的聚类算法
KMeans聚类
- 根据数据与中心点距离划分类别
- 基于类别数据更新中心点
- 重复过程直到收敛
特点
- 实现简单,收敛快
- 需要指定类别数量
均值漂移聚类(Meanshift)
- 在中心点一定区域检索数据点
- 更新中心
- 重复流程到中心点稳定
特点
- 自动发现类别数量,不需要人工选择
- 需要选择区域半径
DBSCAN算法(基于密度的空间聚类算法)
- 基于区域点密度筛选有效数据
- 基于有效数据向周边扩张,直到没有新点加入
特点:
- 过滤噪音数据
- 不需要人为选择类别数量
- 数据密度不同时影响结果
K均值聚类(KMeans Analysis)
以空间中k个点为中心进行聚类,对最靠近他们的对象归类,是聚类算法中最为基础但也最为重要的算法。
算法流程:
- 选择聚类的个数k
- 确定聚类中心
- 根据点到聚类中心聚类确定各个点所属类别
- 根据各个类别数据更新聚类中心
- 重复以上步骤直到收敛(中心点不再变化)
优点:
- 原理简单、实现容易、收敛速度快
- 参数少、方便使用
缺点:
- 必须设置簇的数量
- 随机选择初始聚类中心、结果可能缺乏一致性
原始数据分布
随机选取聚类中心
根据距离聚类
根据聚类更新中心
根据新的距离更新聚类
中心不再变化
K近邻分类模型(KNN)
给定一个训练数据集,对新的输入实例,在训练数据集中找到与该实例最邻近的K个实例(也就是上面所说的K个邻居),这K个实例的多数属于某个类,就把该输入实例分类到这个类中
- 最简单的机器学习算法之一

均值漂移聚类
一种基于密度梯度上升的聚类算法(沿着密度上升方向寻找聚类中心点)
算法流程:
- 随机选择未分类点作为中心点
- 找出离中心点距离在带宽之内的点,记做集合S
- 计算从中心点到集合S中每个元素的偏移向量M
- 中心点以向量M移动
- 重复步骤2-4,直到收敛
- 重复1-5直到所有的点都被归类
- 分类:根据每个类,对每个点的访问频率,取访问频率最大的那个类,作为当前点集的所属类
实战准备
KMeans实现聚类
模型训练
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
KM = KMeans(n_clusters=3,random_state=0)
KM.fit(X)
获取模型确定的中心点
centers = KM.cluster_centers_
准确率计算
from sklearn.metrics import accuuracy_score
accuracy = accuracy_score(y,y_predict)
结果矫正
y_cal=[]
for i in y_predict:
if i==0:
y_cal.append(2)
elif i == 1:
y_cal.append(1)
else:
y_cal.append(0)
print(y_predict,y_cal)
Meanshift实现聚类
自动计算带宽(区域半径)
from sklearn.cluster import MeanShift,estimate_bandwidth
#detect bandwidth
bandwidth = estimate_bandwidth(X,n_samples=500)
模型建立与训练
ms = MeanShift(bandwidth=bandwidth)
ms.fit(X)
KNN实现分类
模型训练
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
KNN = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
KNN.fit(X,y)
实战:2D数据类别划分
- 采用Kmeans算法实现2D数据自动聚类,预测V1=80,V2=60数据类别
- 计算预测准确率,完成结果矫正
- 采用KNN、Meanshift算法,重复步骤1-2
导入类加载数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data=pd.read_csv('data.csv')
data.head()

数据初始化
X=data.drop(['labels'],axis=1)
y=data.loc[:,'labels']
查看个类别数量
pd.value_counts(y)

数据可视化
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
fig1=plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'],X.loc[:,'V2'])
plt.title("un-labled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.show()

fig1=plt.figure()
label0=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.legend((label0,label1,label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
plt.show()

模型训练
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
KM = KMeans(n_clusters=3,random_state=0)
KM.fit(X)
查看聚类的中心点
KM.cluster_centers_

可视化中心点
centers = KM.cluster_centers_
fig3=plt.figure()
plt.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1])
plt.show()

centers = KM.cluster_centers_
fig3=plt.figure()
label0=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1])
plt.legend((label0,label1,label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
plt.show()

模型评估
y_predict_test = KM.predict([[80,60]])
y_predict=KM.predict(X)
print(pd.value_counts(y_predict),pd.value_counts(y))
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy = accuracy_score(y,y_predict)
print(accuracy)

fig4=plt.subplot(121)
label0=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict==0],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict==0])
label1=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict==1],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict==1])
label2=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict==2],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict==2])
plt.title("predicted data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1])
plt.legend((label0,label1,label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
fig4=plt.subplot(122)
label0=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1])
plt.legend((label0,label1,label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
plt.show()

模型矫正
y_corrected=[]
for i in y_predict:
if i==0:
y_corrected.append(1)
elif i==1:
y_corrected.append(2)
else:
y_corrected.append(0)
print(pd.value_counts(y_corrected))
print(pd.value_counts(y))

模块评估
print(accuracy_score(y,y_corrected))

可视化
fig4=plt.subplot(121)
label0=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_corrected==0],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_corrected==0])
label1=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_corrected==1],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_corrected==1])
label2=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_corrected==2],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_corrected==2])
plt.title("corrected data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1])
plt.legend((label0,label1,label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
fig4=plt.subplot(122)
label0=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1])
plt.legend((label0,label1,label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
plt.show()

KNN
模型训练
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
KNN = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
KNN.fit(X,y)
显示预测结果 评估模型
y_predict_knn_test=KNN.predict([[80,60]])
y_predict_knn=KNN.predict(X)
print(y_predict_knn_test)
print('knn accuracy',accuracy_score(y,y_predict_knn))

查看模型分布
print(pd.value_counts(y_predict_knn))
print(pd.value_counts(y))

可视化
fig5=plt.subplot(121)
label0=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict_knn==0],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict_knn==0])
label1=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict_knn==1],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict_knn==1])
label2=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict_knn==2],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict_knn==2])
plt.title("knn results")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1])
plt.legend((label0,label1,label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
fig6=plt.subplot(122)
label0=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1])
plt.legend((label0,label1,label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
plt.show()

meanshift
from sklearn.cluster import MeanShift,estimate_bandwidth
bw = estimate_bandwidth(X,n_samples=500)
模型训练
ms=MeanShift(bandwidth=bw)
ms.fit(X)
查看预测结果
y_predict_ms = ms.predict(X)
print(pd.value_counts(y_predict_ms))
print(pd.value_counts(y))

可视化
fig5=plt.subplot(121)
label0=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict_ms==0],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict_ms==0])
label1=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict_ms==1],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict_ms==1])
label2=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_predict_ms==2],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_predict_ms==2])
plt.title("ms results")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1])
plt.legend((label0,label1,label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
fig6=plt.subplot(122)
label0=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1])
plt.legend((label0,label1,label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
plt.show()

模型矫正
y_corrected_ms=[]
for i in y_predict_ms:
if i==0:
y_corrected_ms.append(2)
elif i==1:
y_corrected_ms.append(1)
else:
y_corrected_ms.append(0)
print(pd.value_counts(y_corrected_ms))
print(pd.value_counts(y))

可视化文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-810644.html
y_corrected_ms = np.array(y_corrected_ms)
fig5=plt.subplot(121)
label0=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_corrected_ms==0],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_corrected_ms==0])
label1=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_corrected_ms==1],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_corrected_ms==1])
label2=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y_corrected_ms==2],X.loc[:,'V2'][y_corrected_ms==2])
plt.title("ms corrected results")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1])
plt.legend((label0,label1,label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
fig6=plt.subplot(122)
label0=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==0],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==0])
label1=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==1],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==1])
label2=plt.scatter(X.loc[:,'V1'][y==2],X.loc[:,'V2'][y==2])
plt.title("labled data")
plt.xlabel('V1')
plt.ylabel('V2')
plt.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1])
plt.legend((label0,label1,label2),('label0','label1','label2'))
plt.show()
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-810644.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-810644.html
到了这里,关于机器学习之聚类-2D数据类别划分的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!