Top
NSD Operation DAY03
- 案例1:Nginx反向代理
- 案例2:Nginx的TCP/UDP调度器
- 案例3:Nginx常见问题处理
1 案例1:Nginx反向代理
1.1 问题
使用Nginx实现Web反向代理功能,实现如下功能:
- 后端Web服务器两台,可以使用httpd实现
- Nginx采用轮询的方式调用后端Web服务器
- 两台Web服务器的权重要求设置为不同的值
- 最大失败次数为2,失败超时时间为30秒
1.2 方案
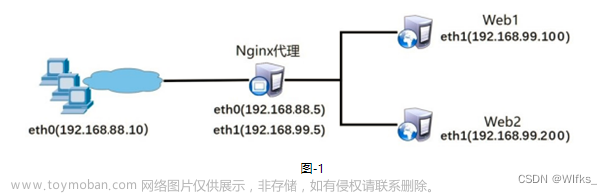
使用4台虚拟机,其中一台作为Nginx代理服务器,该服务器需要配置两块网卡,IP地址分别为192.168.88.5和192.168.99.5,两台Web服务器IP地址分别为192.168.99.100和192.168.99.200。客户端测试主机IP地址为192.168.88.10。如图-1所示。
1.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:部署实施后端Web服务器
环境准备,同网段要互通,检查yum
1)部署后端Web1服务器
后端Web服务器可以简单使用yum方式安装httpd实现Web服务,为了可以看出后端服务器的不同,可以将两台后端服务器的首页文档内容设置为不同的内容。
- [root@web1 ~]#yum -y install vim net-tools bash-completion psmisc httpd
- [root@web1 ~]# echo "web1" > /var/www/html/index.html
- [root@web1 ~]# systemctl restart httpd
- systemctl stop firewalld #关闭防火墙
2)部署后端Web2服务器
- [root@web2 ~]#yum -y install vim net-tools bash-completion psmisc httpd
- [root@web2 ~]# echo "web2" > /var/www/html/index.html
- [root@web2 ~]# systemctl restart httpd
- systemctl stop firewalld #关闭防火墙
3)到proxy主机测试
- [root@proxy nginx]# curl 192.168.99.100
- web1~~
- [root@proxy nginx]# curl 192.168.99.200
- web2~~
步骤二:配置Nginx服务器,添加服务器池,实现反向代理功能
如果需要可以先还原proxy主机的nginx
- [root@proxy nginx]# cd ~/lnmp_soft/
- [root@proxy lnmp_soft]# killall nginx
- [root@proxy lnmp_soft]# rm -rf /usr/local/nginx/
- [root@proxy lnmp_soft]# rm -rf nginx-1.17.6
- [root@proxy lnmp_soft]# tar -xf nginx-1.17.6.tar.gz
- [root@proxy lnmp_soft]# cd nginx-1.17.6/
- [root@proxy lnmp_soft]#yum -y install gcc make pcre-devel openssl-devel
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]# ./configure
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]#make
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]#make install
1)修改/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf配置文件
- [root@proxy ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- .. ..
- http {
- .. ..
- #使用upstream定义后端服务器集群,集群名称任意(如webserver)
- #使用server定义集群中的具体服务器和端口
- upstream webserver {
- server 192.168.99.100:80;
- server 192.168.99.200:80;
- }
- .. ..
- server {
- listen 80;
- server_name localhost;
- location / {
- #通过proxy_pass将用户的请求转发给webserver集群
- proxy_pass http://webserver;
- }
- }
- .. ..
- }
2)重新加载配置
- [root@proxy ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
- #请先确保nginx是启动状态,否则运行该命令会报错,报错信息如下:
- #[error] open() "/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid" failed (2: No such file or directory)
3)客户端使用火狐浏览器或curl多次访问proxy主机可以看到网站的轮询效果
步骤二:配置upstream服务器集群池属性
1)设置权重
weight可以设置后台服务器的权重,权重越大任务的分配量就越大
- [root@proxy ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- upstream webserver {
- server 192.168.99.100 weight=2;
- server 192.168.99.200;
- }
重新加载配置并访问,可以看到web1的任务量增加
设置健康检查,max_fails可以设置后台服务器的失败次数,fail_timeout可以设置后台服务器的失败超时时间。
- [root@proxy ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- upstream webserver {
- server 192.168.99.100;
- server 192.168.99.200 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30;
- }
重新加载配置并访问,
sbin/nginx -s reload
测试时,先将web2的httpd服务关闭,回到proxy访问集群页面curl 192.168.99.5
只会显示web1的页面,此时即使将web2的httpd服务开启也无效,因为要等
待30秒
步骤三:配置upstream服务器集群的调度算法
1)设置相同客户端访问相同Web服务器
- [root@proxy ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- upstream webserver {
- ip_hash;
- server 192.168.99.100 ;
- server 192.168.99.200 ;
- }
2)重新加载配置
- [root@proxy ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
客户端使用浏览器访问代理服务器测试只会见到一个页面
步骤四:添加down标记
down标记可以让集群主机暂时不参与集群活动
- [root@proxy ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- upstream webserver {
- server 192.168.99.100 ;
- server 192.168.99.200 down;
- }
重新加载配置
- [root@proxy ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
客户端使用浏览器访问代理服务器测试只会见到99.100
2 案例2:Nginx的TCP/UDP调度器
2.1 问题
使用Nginx实现TCP/UDP调度器功能,实现如下功能:
- 后端SSH服务器两台
- Nginx编译安装时需要使用--with-stream,开启ngx_stream_core_module模块
- Nginx采用轮询的方式调用后端SSH服务器
2.2 方案
使用4台虚拟机,其中一台作为Nginx代理服务器,该服务器需要配置两块网卡,IP地址分别为192.168.88.5和192.168.99.5,两台SSH服务器IP地址分别为192.168.99.100和192.168.99.200。客户端测试主机IP地址为192.168.88.10。如图-2所示。

2.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:部署支持4层TCP/UDP代理的Nginx服务器
1)部署nginx服务器
编译安装必须要使用--with-stream参数开启4层代理模块。
- [root@proxy nginx]# cd ~/lnmp_soft/nginx-1.17.6/
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]# killall nginx
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]# rm -rf /usr/local/nginx/
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]# ./configure \
- > --with-stream #开启4层代理功能
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]# make && make install #编译并安装
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V #查看安装模块情况
步骤二:配置Nginx服务器,添加服务器池,实现TCP/UDP代理功能
1)修改/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf配置文件
- [root@proxy ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- stream {
- upstream backend {
- server 192.168.99.100:22; #后端SSH服务器的IP和端口
- server 192.168.99.200:22;
- }
- server {
- listen 12345; #Nginx监听的端口
- proxy_pass backend;
- }
- }
- http {
- .. ..
- }
2)重新加载配置
- [root@proxy ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
- #请先确保nginx是启动状态,否则运行该命令会报错,报错信息如下:
- #[error] open() "/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid" failed (2: No such file or directory)
3)客户端使用访问代理服务器测试轮询效果
- [root@client ~]# ssh 192.168.88.5 -p 12345 #使用该命令多次访问查看效果
注意:如果配置没有错误,但无法反复登陆web1与web2,可以按下列方式解决
- rm -rf ~/.ssh/known_hosts #在proxy中删除记录文件
- ssh 192.168.99.5 -p 12345 #再次尝试登录,会连接到另外一台集群主机
3 案例3:Nginx常见问题处理
3.1 问题
本案例要求对Nginx服务器进行适当优化,解决如下问题,以提升服务器的处理性能:
- 如何自定义返回给客户端的404错误页面
- 如何查看服务器状态信息
- 如果客户端访问服务器提示“Too many open files”如何解决
- 如何解决客户端访问头部信息过长的问题
- 如何让客户端浏览器缓存数据
客户机访问此Web服务器验证效果:
- 使用ab压力测试软件测试并发量
- 编写测试脚本生成长头部信息的访问请求
- 客户端访问不存在的页面,测试404错误页面是否重定向
3.2 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:自定义报错页面
HTTP常见状态码列表:
200 正常
301 & 302 重定向
400 请求语法错误
401 访问被拒绝
403 禁止访问
404 资源找不到
414 请求URI头部太长
500 服务器内部错误
502 代理服务器无法正常获取下一个服务器正常的应答
1)优化前,客户端使用浏览器访问不存在的页面,会提示404文件未找到
2)修改Nginx配置文件,自定义报错页面
- [root@proxy ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- .. ..
- charset utf-8; #仅在需要中文时修改该选项
- error_page 404 /test.jpg; #自定义错误页面为一张图片,图片可以从真机拷入
- .. ..
- [root@proxy ~]# nginx -s reload
3)优化后,客户端再次使用浏览器访问不存在的页面,会看到图片
步骤二:如何查看服务器状态信息(非常重要的功能)
编译安装时使用--with-http_stub_status_module开启状态页面模块
如果要添加模块,但不想删除之前nginx数据,可以将nginx源码目录下的objs目录中的nginx文件拷贝到nginx的sbin目录下替代现有主程序,然后killall nginx 再重启即可
- [root@proxy nginx]# cd ~/lnmp_soft/nginx-1.17.6/
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]# ./configure \
- > --with-stream #开启4层代理模块
- > --with-http_stub_status_module #开启status状态页面
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]# make #编译
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]# killall nginx
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]# cp objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ #覆盖原文件
- [root@proxy nginx-1.17.6]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx #开启nginx
2)修改Nginx配置文件,定义状态页面
- [root@proxy ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- … …
- location /status {
- stub_status on;
- #allow IP地址;
- #deny all;
- }
- … …
- [root@proxy ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
4)优化后,查看状态页面信息
- [root@proxy ~]# curl http://192.168.99.5/status
- Active connections: 1
- server accepts handled requests
- 10 10 3
- Reading: 0 Writing: 1 Waiting: 0
Active connections:当前活动的连接数量。
Accepts:已经接受客户端的连接总数量。
Handled:已经处理客户端的连接总数量。
Requests:客户端发送的请求数量。
Reading:当前服务器正在读取客户端请求头的数量。
Writing:当前服务器正在写响应信息的数量。
Waiting:当前多少客户端在等待服务器的响应。
步骤三:优化Nginx并发量
1)优化前使用ab高并发测试,使用web1或proxy自己作为海量客户(防火墙与selinux都关闭
- [root@proxy ~]# ab -n 100 -c 100 http://192.168.99.5/ #-n任务量,-c是连接数
- ...
- ...
- 100% #成功
- [root@proxy ~]# ab -n 2000 -c 2000 http://192.168.99.5/
- Benchmarking 192.168.99.5 (be patient)
- socket: Too many open files (24) #失败
2)修改Nginx配置文件,增加并发量
- [root@proxy ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- .. ..
- worker_processes 2; #与CPU核心数量一致
- events {
- worker_connections 50000; #每个worker最大并发连接数
- }
- .. ..
- [root@proxy ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
3)优化Linux内核参数(最大文件数量)
- [root@proxy ~]# ulimit -n #查看最大文件数量
- [root@proxy ~]# ulimit -n 100000 #临时设置最大文件数量
- [root@proxy ~]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf
- .. ..
- * soft nofile 100000
- * hard nofile 100000
- #该配置文件分4列,分别如下:
- #用户或组 硬限制或软限制 需要限制的项目 限制的值
4)优化后测试服务器并发量
- [root@proxy ~]# ab -n 2000 -c 2000 http://192.168.99.5/
步骤四:优化Nginx数据包头缓存,支持超长地址
优化前,使用脚本测试超长头部请求是否能获得响应
默认情况下nginx无法支持长地址栏,会报414错误
- [root@proxy ~]# cat lnmp_soft/buffer.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- URL=http://192.168.99.5/index.html?
- for i in {1..5000}
- do
- URL=${URL}v$i=$i
- done
- curl $URL #经过5000次循环后,生成一个超长的URL地址
- [root@proxy ~]# ./buffer.sh
- .. ..
- <center><h1>414 Request-URI Too Large</h1></center> #访问失败
2)修改Nginx配置文件,增加数据包头部缓存大小
- [root@proxy ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- .. ..
- http {
- client_header_buffer_size 200k; #请求包头信息的缓存大小 35
- large_client_header_buffers 4 200k; #大请求包头部信息的缓存个数与容量 36 -44444444444
- .. ..
- }
- [root@proxy ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload

3)优化后,使用脚本测试超长头部请求是否能获得响应
- [root@proxy ~]# ./buffer.sh
步骤五:浏览器本地缓存静态数据
1)使用Firefox浏览器查看缓存
以Firefox浏览器为例,在Firefox地址栏内输入about:cache将显示Firefox浏览器的缓存信息,如图-3所示,点击List Cache Entries可以查看详细信息。

2)清空firefox本地缓存数据,如图-4所示。
3)修改Nginx配置文件,定义对静态页面的缓存时间
- [root@proxy ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- server {
- listen 80;
- server_name localhost;
- location / {
- root html;
- index index.html index.htm;
- }
- location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|gif|png|css|js|ico|xml)$ {
- expires 30d; #定义客户端缓存时间为30天
- }
- }
- [root@proxy ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
4)优化后,使用Firefox浏览器访问图片,再次查看缓存信息
http://192.168.99.5/day.jpg文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-810726.html
在firefox地址栏内输入about:cache,查看本地缓存数据,查看是否有图片以及过期时间是否正确。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-810726.html
到了这里,关于Nginx代理服务器、HTTP调度、TCP/UDP调度、Nginx优化、HTTP错误代码、状态页面、压力测试的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!