本系列文章记录本人硕士阶段YOLO系列目标检测算法自学及其代码实现的过程。其中算法具体实现借鉴于ultralytics YOLO源码Github,删减了源码中部分内容,满足个人科研需求。
本系列文章主要以YOLOv5为例完成算法的实现,后续修改、增加相关模块即可实现其他版本的YOLO算法。
文章地址:
YOLOv5算法实现(一):算法框架概述
YOLOv5算法实现(二):模型加载
YOLOv5算法实现(三):数据集加载
YOLOv5算法实现(四):正样本匹配与损失计算
YOLOv5算法实现(五):预测结果后处理
YOLOv5算法实现(六):评价指标及实现
YOLOv5算法实现(七):模型训练
YOLOv5算法实现(八):模型验证
YOLOv5算法实现(九):模型预测
引言
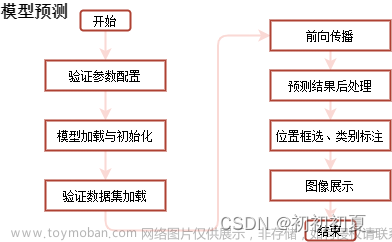
本篇文章综合之前文章中的功能,实现模型的预测。模型预测的逻辑如图1所示。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-812213.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-812213.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-812213.html
模型预测(predict.py)
def predice():
img_size = 640 # 必须是32的整数倍 [416, 512, 608]
file = "yolov5s"
cfg = f"cfg/models/{file}.yaml" # 改成生成的.cfg文件
weights_path = f"weights/{file}/{file}.pt" # 改成自己训练好的权重文件
json_path = "data/dataset.json" # json标签文件
img_path = "test.jpg"
save_path = f"results/{file}/test_result8.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(cfg), "cfg file {} dose not exist.".format(cfg)
assert os.path.exists(weights_path), "weights file {} dose not exist.".format(weights_path)
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "json file {} dose not exist.".format(json_path)
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "image file {} dose not exist.".format(img_path)
with open(json_path, 'r') as f:
class_dict = json.load(f)
category_index = {str(v): str(k) for k, v in class_dict.items()}
input_size = (img_size, img_size)
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
device = torch.device("cpu")
model = Model(cfg, ch=3, nc=3)
weights_dict = torch.load(weights_path, map_location='cpu')
weights_dict = weights_dict["model"] if "model" in weights_dict else weights_dict
model.load_state_dict(weights_dict, strict=False)
model.to(device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# init
img = torch.zeros((1, 3, img_size, img_size), device=device)
model(img)
img_o = cv2.imread(img_path) # BGR
assert img_o is not None, "Image Not Found " + img_path
img = letterbox(img_o, new_shape=input_size, auto=True, color=(0, 0, 0))[0]
# Convert
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, to 3x416x416
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device).float()
img /= 255.0 # scale (0, 255) to (0, 1)
img = img.unsqueeze(0) # add batch dimension
t1 = torch_utils.time_synchronized()
pred = model(img)[0] # only get inference result
t2 = torch_utils.time_synchronized()
print("inference time: {}s".format(t2 - t1))
print('model: {}'.format(file))
pred = utils.non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres=0.1, iou_thres=0.6, multi_label=True)[0]
t3 = time.time()
print("post-processing time: {}s".format(t3 - t2))
# process detections
pred[:, :4] = utils.scale_coords(img.shape[2:], pred[:, :4], img_o.shape).round()
bboxes = pred[:, :4].detach().cpu().numpy()
scores = pred[:, 4].detach().cpu().numpy()
classes = pred[:, 5].detach().cpu().numpy().astype(np.int) + 1
pil_img = Image.fromarray(img_o[:, :, ::-1])
plot_img = draw_objs(pil_img,
bboxes,
classes,
scores,
category_index=category_index,
box_thresh=0.2,
line_thickness=3,
font='arial.ttf',
font_size=30)
plt.imshow(plot_img)
plt.show()
# 保存预测的图片结果
plot_img.save(save_path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
predict()
到了这里,关于【目标检测】YOLOv5算法实现(九):模型预测的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!