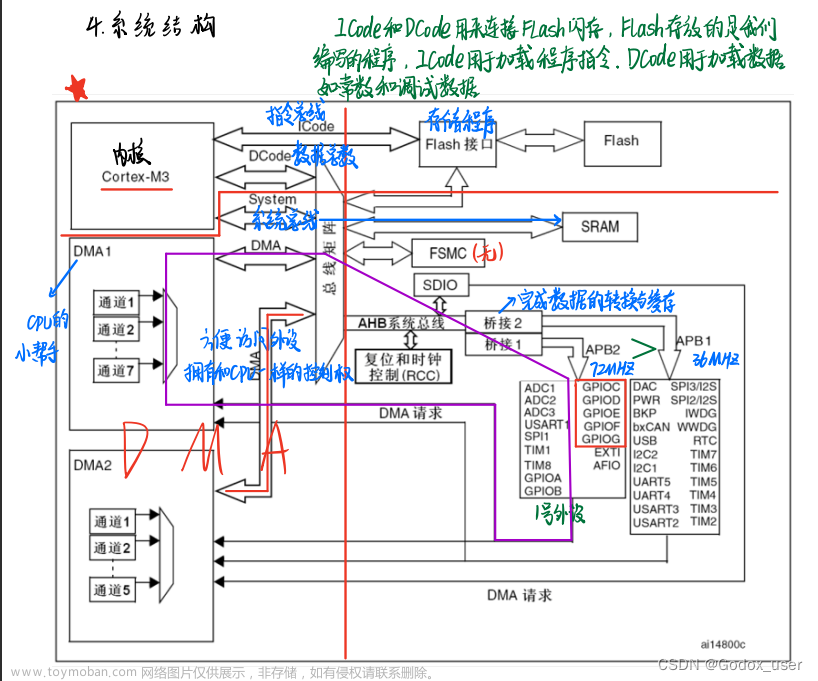
一、八段码数码管
数码管:实际上是多个LED按照一定顺序排列,并加上遮罩所构成的元件。
八段码一般会引出9个引脚,其中7个引脚显示数字(或某些字母),1个显示小数点,1个作为片选端。
根据连接方式的不同,数码管分为共阳和共阴。
共阳在这端输出低电平时点亮,高电平时会熄灭,共阴则相反。
为了便于编程,设计者将数码管的8个LED按照一点规则编号并设置了独特的名称,如下图示:

编码
共阴和共阳互为对方的按位取反
编码示意图 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-818634.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-818634.html
二、效果展示
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-818634.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-818634.html
三、代码
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#include "led.h"
#define time_m 1000
#define time_n 500
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
void Delay(int m,int n) //延时函数
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<m;i++) {
for(j=0;j<n;j++);
}
}
void seg_0();
void seg_1();
void seg_2();
void seg_3();
void seg_4();
void seg_5();
void seg_6();
void seg_7();
void seg_8();
void seg_9();
int main(void)
{
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOC, ENABLE);
//八段码初始-灭
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_1);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_3);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_4);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_5);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_6);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8);
while (1)
{
seg_0();
Delay(time_m,time_n);
seg_1();
Delay(time_m,time_n);
seg_2();
Delay(time_m,time_n);
seg_3();
Delay(time_m,time_n);
seg_4();
Delay(time_m,time_n);
seg_5();
Delay(time_m,time_n);
seg_6();
Delay(time_m,time_n);
seg_7();
Delay(time_m,time_n);
seg_8();
Delay(time_m,time_n);
seg_9();
Delay(time_m,time_n);
}//while(1)
}
void seg_0()
{
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_1);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_3);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_4);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_5);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_6);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8);
}
void seg_1()
{
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_1);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_3);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_4);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_5);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_6);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8);
}
void seg_2()
{
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_1);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_3);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_4);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_5);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_6);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8);
}
void seg_3()
{
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_1);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_3);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_4);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_5);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_6);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8);
}
void seg_4()
{
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_1);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_3);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_4);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_5);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_6);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8);
}
void seg_5()
{
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_1);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_3);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_4);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_5);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_6);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8);
}
void seg_6()
{
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_1);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_3);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_4);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_5);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_6);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8);
}
void seg_7()
{
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_1);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_3);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_4);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_5);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_6);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8);
}
void seg_8()
{
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_1);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_3);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_4);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_5);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_6);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8);
}
void seg_9()
{
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_1);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_3);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_4);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_5);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_6);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_7);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8);
}
到了这里,关于STM32单片机学习4--STM32控制八段码的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!