前言
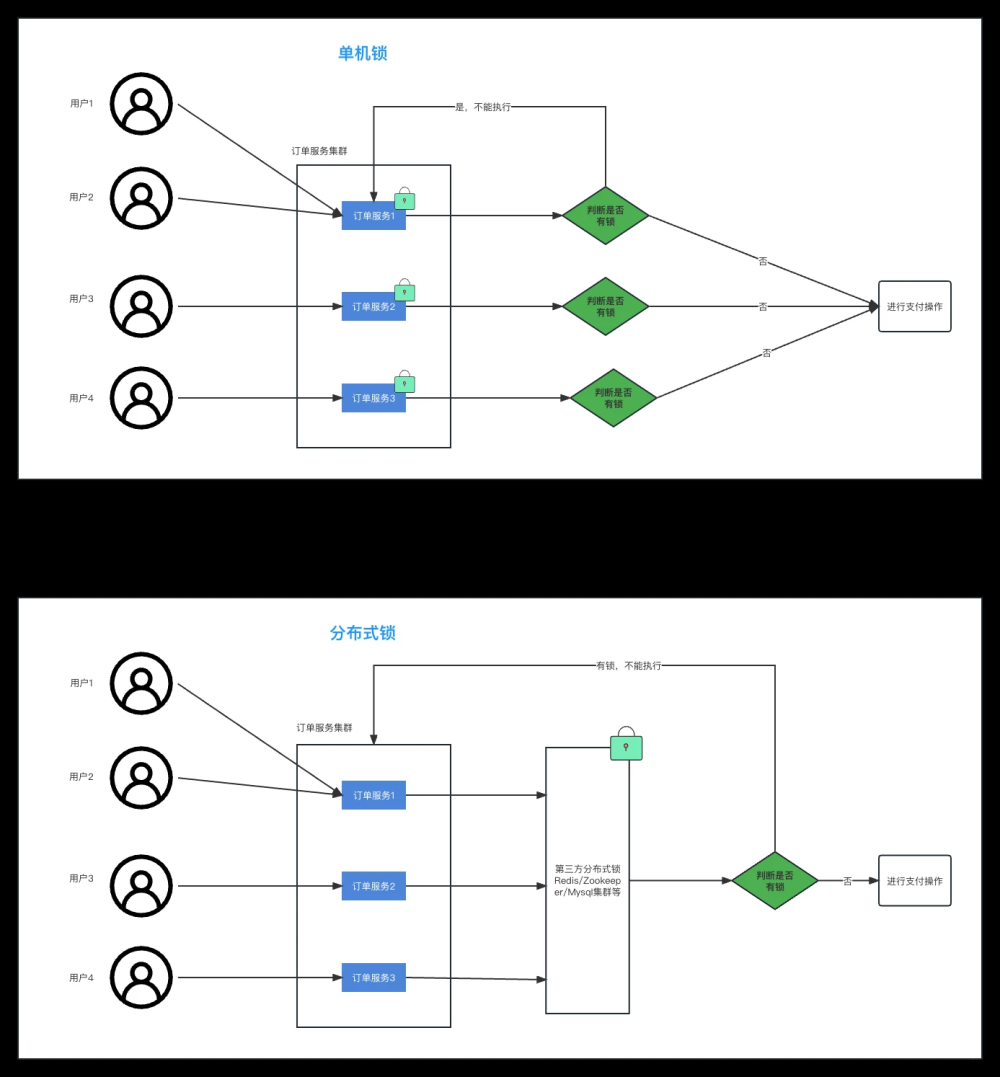
我们知道Redis 缓存可以使用setNx来作为分布式锁,但是我们直接使用setNx 需要考虑锁过期的问题;此时我们可以使用Redisson 的lock 来实现分布式锁,那么lock 内部帮我们做了哪些工作呢。
一、Redisson 分布式锁的实现:
1.1 引入redis 和 redisson jar
<!-- redis jar-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.9.1</version>
</dependency>
1.2 redis 客户端配置:
RedisConfig.java
package com.example.springredisms.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.apache.commons.pool2.impl.GenericObjectPoolConfig;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisPassword;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisStandaloneConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceClientConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettucePoolingClientConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${spring.redis.host:localhost}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.redis.port:6379}")
private int port;
@Value("${spring.redis.database:0}")
private int db;
@Value("${spring.redis.password:null}")
private String password;
/**
* 配置lettuce连接池
*
* @return
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.redis.lettuce.pool")
public GenericObjectPoolConfig redisPool() {
return new GenericObjectPoolConfig<>();
}
/**
* 配置第二个数据源
*
* @return
*/
public RedisStandaloneConfiguration redisConfig() {
RedisStandaloneConfiguration redisStandaloneConfiguration = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration(host, port);
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setDatabase(db);
if (password != null && !"".equals(password) && !"null".equals(password)){
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setPassword(RedisPassword.of(password));
}
return redisStandaloneConfiguration;
}
public LettuceConnectionFactory factory(GenericObjectPoolConfig redisPool, RedisStandaloneConfiguration redisConfig) {
LettuceClientConfiguration clientConfiguration = LettucePoolingClientConfiguration.builder().poolConfig(redisPool).build();
LettuceConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new LettuceConnectionFactory(redisConfig, clientConfiguration);
connectionFactory.afterPropertiesSet();
return connectionFactory;
}
/**
* 配置第一个数据源的RedisTemplate
* 注意:这里指定使用名称=factory 的 RedisConnectionFactory
*
* @param
* @return
*/
@Bean("redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate() {
RedisConnectionFactory factory1 = factory(redisPool(),redisConfig());
return redisTemplate(factory1);
}
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
// 使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer来序列化和反序列化redis的value值(默认使用JDK的序列化方式)
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> serializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object>(Object.class);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 指定要序列化的域,field,get和set,以及修饰符范围,ANY是都有包括private和public
objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
// 指定序列化输入的类型,类必须是非final修饰的,final修饰的类,比如String,Integer等会跑出异常
// objectMapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
serializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
// 配置连接工厂
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
//使用StringRedisSerializer来序列化和反序列化redis的key值
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 值采用json序列化
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(serializer);
// 设置hash key 和value序列化模式
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(serializer);
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
/***
* stringRedisTemplate默认采用的是String的序列化策略
* @param redisConnectionFactory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate = new StringRedisTemplate();
stringRedisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return stringRedisTemplate;
}
}
1.3 业务实现:
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redisson;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public String lockTest() {
String lockKey ="good:123";
// 初始化 lock
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(lockKey);
// 阻塞获取锁
lock.lock();
// 获取锁成功执行扣减库存逻辑
try{
Thread.sleep(5000);
String stockKey ="good:stock:123";
int stock = (Integer) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(stockKey);
if (stock >0){
stock-=1;
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(stockKey,stock);
}else{
return "商品已经卖完了";
}
}catch (Exception ex){
}
finally {
// 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
return "success";
}
二、Redisson lock 实现原理
2.1 lock.lock():
lock.lock() 阻塞获取 redis 锁,获取到锁之后继续向下执行业务逻辑;
public void lock() {
try {
// 相应中断的获取锁
this.lockInterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException var2) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
lockInterruptibly():
public void lockInterruptibly(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
// tryAcquire 获取锁,如果获取成功 ttl 为null ,如果获取失败,说明当前有线程在持有锁,返回的是锁的剩余时间
Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl != null) {
// 当前线程没有获取到锁,订阅一个与锁相关联的 Redis 频道
// 当锁被释放时,持有锁的线程会向相关联的 Redis 频道发布一条消息。
// 那些订阅了这个频道并正在等待锁释放的线程会接收到这个消息,
// 并会再次尝试获取锁。这个机制使得等待锁的线程能立刻知道锁何时被释放。
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = this.subscribe(threadId);
this.commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
try {
while(true) {
// 循环去获取锁
ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
// 获取到锁直接返回
return;
}
// 如果锁的剩余时间还有很多
if (ttl >= 0L) {
// 尝试去获取锁,如果失败则加入到等待的双向链表节点中,同时park 挂起当前线程
this.getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
// 如果锁已经没有剩余时间了,锁到期了,则取获取锁
this.getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
}
}
} finally {
// 获取锁成功后 当前线程取消订阅这把锁
this.unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
}
}
tryAcquire() 尝试去获取锁 :
private Long tryAcquire(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
return (Long)this.get(this.tryAcquireAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId));
}
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId) {
if (leaseTime != -1L) {
// 如果 不需要进行锁续命则 直接尝试去获取锁
return this.tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else {
// 尝试去获取锁
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
ttlRemainingFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<Long>() {
public void operationComplete(Future<Long> future) throws Exception {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
Long ttlRemaining = (Long)future.getNow();
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
// 获取锁成功,开启一个定时任务 默认每隔10 s 完成一次锁续命
RedissonLock.this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
}
tryLockInnerAsync 获取锁:
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
this.internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return this.commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0)
then redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1);
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end;
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1)
then redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1);
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end;
return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.singletonList(this.getName()), new Object[]{this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId)});
}
这里完成了获取锁和重入锁的实现:
- 如果当前锁没有被线程占有,则设置当前当前线程 占有这把锁,并设置锁的过期时间为30s,返回null;
- 如果当前 锁已经存在,并且是相同线程占用,则 设置将锁的重入次数+1,并设置锁的过期时间为30ss,返回null;
- 如果锁已经被其它线程占有 ,则返回锁的过期时间;
scheduleExpirationRenewal :开启锁续命的定时任务
private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(final long threadId) {
if (!expirationRenewalMap.containsKey(this.getEntryName())) {
// 延迟 internalLockLeaseTime / 3L 默认值是 30/3 =10s 后开启任务
Timeout task = this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
// redis 锁续期
RFuture<Boolean> future = RedissonLock.this.renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
future.addListener(new FutureListener<Boolean>() {
public void operationComplete(Future<Boolean> future) throws Exception {
RedissonLock.expirationRenewalMap.remove(RedissonLock.this.getEntryName());
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
// 当前线程没有获取获取到锁,进行延期则直接报错
RedissonLock.log.error("Can't update lock " + RedissonLock.this.getName() + " expiration", future.cause());
} else {
// 续期成功后,继续进行下一次调用
if ((Boolean)future.getNow()) {
RedissonLock.this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
}
});
}
}, this.internalLockLeaseTime / 3L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (expirationRenewalMap.putIfAbsent(this.getEntryName(), new ExpirationEntry(threadId, task)) != null) {
task.cancel();
}
}
}
renewExpirationAsync 锁续期:
protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
return this.commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1)
then redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]);
return 1; end; return 0;",
Collections.singletonList(this.getName()), new Object[]{this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId)});
}
- 如果这把锁还存在,则设置过期时间(默认值是30s)并且返回true
- 这把锁不存在返回false;
2.2 锁释放 lock.unlock():
在业务执行完毕之后 通过lock.unlock(); 释放锁
public void unlock() {
try {
// 释放 锁
this.get(this.unlockAsync(Thread.currentThread().getId()));
} catch (RedisException var2) {
if (var2.getCause() instanceof IllegalMonitorStateException) {
throw (IllegalMonitorStateException)var2.getCause();
} else {
throw var2;
}
}
}
unlockAsync 释放锁:
public RFuture<Void> unlockAsync(final long threadId) {
final RPromise<Void> result = new RedissonPromise();
// 释放锁
RFuture<Boolean> future = this.unlockInnerAsync(threadId);
future.addListener(new FutureListener<Boolean>() {
public void operationComplete(Future<Boolean> future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
RedissonLock.this.cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);
result.tryFailure(future.cause());
} else {
//
Boolean opStatus = (Boolean)future.getNow();
if (opStatus == null) {
IllegalMonitorStateException cause = new IllegalMonitorStateException("attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: " + RedissonLock.this.id + " thread-id: " + threadId);
result.tryFailure(cause);
} else {
if (opStatus) {
// 释放锁成功 则取消锁延期
RedissonLock.this.cancelExpirationRenewal((Long)null);
}
result.trySuccess((Object)null);
}
}
}
});
return result;
}
unlockInnerAsync 释放锁:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-824435.html
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return this.commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0)
then redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); return 1; end;
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then return nil;end;
local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1);
if (counter > 0) then redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); return 0;
else redis.call('del', KEYS[1]);
redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); return 1; end;
return nil;", Arrays.asList(this.getName(), this.getChannelName()), new Object[]{LockPubSub.unlockMessage, this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId)});
}
- 如果当前锁已经不存在,则发布锁释放消息,让其他阻塞的现车去抢占锁,返回true;
- 如果锁还存在,则将锁的重入次数-1 后返回锁的重入次数;
- 如果重入次数大于0 说明当前线程还需要绩效持有锁,重新设置锁的过期时间,返回false;
- 如果重入次数等于0 ,则删除这个key 相当于是否了锁,然后发布锁释放消息,让其他阻塞的现车去抢占锁,返回true;
总结
锁过期自动续时的触发条件是tryLock设置的锁到期时间leaseTime == -1;自动续时原理就是创建一个定时任务,每internalLockLeaseTime / 3时间触发一次,如果发现持有锁未释放,就把锁过期时间更新为internalLockLeaseTime(internalLockLeaseTime的值取得是lockWatchdogTimeout默认是30s);过期时间更新成功后,再次递归调用renewExpiration(),创建下一次定时任务;默认每次都延期30s;
这种机制主要是为了避免在没来得及解锁的情况下系统就挂了,导致该锁在redis中一直都被占用,其他线程永远都无法获取锁,也就是死锁的情况;文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-824435.html
到了这里,关于源码篇--Redisson 分布式锁lock的实现的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!