目录
1.环境准备
2.ES JAVA API
3.Spring Boot操作ES
1.环境准备
本文是作者ES系列的第三篇文章,关于ES的核心概念移步:
https://bugman.blog.csdn.net/article/details/135342256?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
关于ES的下载安装教程以及基本使用,移步:
https://bugman.blog.csdn.net/article/details/135342256?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
在前文中,我们已经搭建好了一个es+kibana的基础环境,本文将继续使用该环境,演示JAVA操作es。
2.ES JAVA API
Elasticsearch Rest High Level Client 是 Elasticsearch 官方提供的一个 Java 客户端库,用于与 Elasticsearch 进行交互。这个客户端库是基于 REST 风格的 HTTP 协议,与 Elasticsearch 进行通信,提供了更高级别的抽象,使得开发者可以更方便地使用 Java 代码与 Elasticsearch 进行交互。
依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>7.17.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.17.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.10.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.fastjson2</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson2</artifactId>
<version>2.0.45</version>
</dependency>
其实Rest High Level Client的使用逻辑一共就分散步:
- 拼json
- 创建request
- client执行request
创建client:
RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("127.0.0.1",9200,"http")));创建索引:
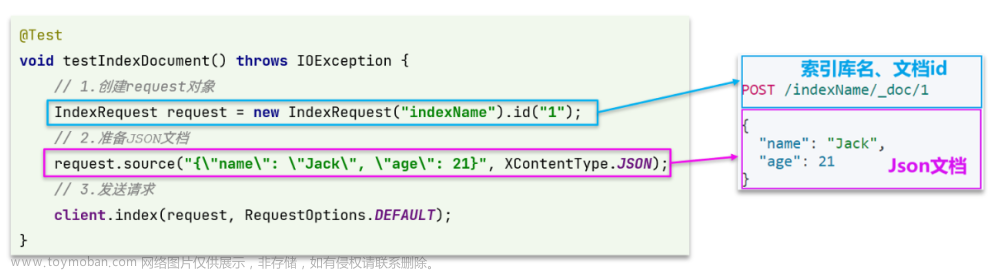
@Test
public void createIndex() throws IOException {
//1.拼json
//settings
Settings.Builder settings = Settings.builder()
.put("number_of_shards", 3)
.put("number_of_replicas", 1);
//mappings
XContentBuilder mappings = JsonXContent.contentBuilder().
startObject().
startObject("properties").
startObject("name").
field("type", "text").
endObject().
startObject("age").
field("type", "integer").
endObject().
endObject().
endObject();
//2.创建request
CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest = new CreateIndexRequest("person").settings(settings).mapping(mappings);
//3.client执行request
restHighLevelClient.indices().create(createIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}创建文档:
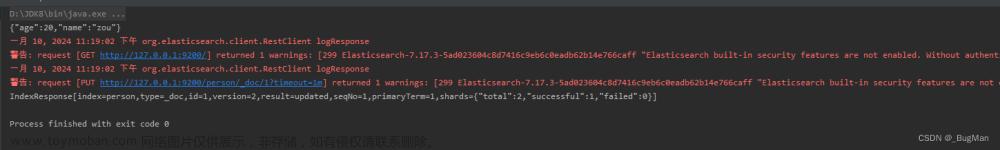
@Test
public void createDoc() throws IOException {
Person person=new Person("1","zou",20);
JSONObject json = JSONObject.from(person);
System.out.println(json);
IndexRequest request=new IndexRequest("person",null,person.getId().toString());
request.source(json, XContentType.JSON);
IndexResponse response = restHighLevelClient.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response);
}响应结果:
修改文档:
@Test
public void updateDoc() throws IOException {
HashMap<String, Object> doc = new HashMap();
doc.put("name","张三");
String docId="1";
UpdateRequest request=new UpdateRequest("person",null,docId);
UpdateResponse response = restHighLevelClient.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.getResult().toString());
}删除文档:
@Test
public void deleteDoc() throws IOException {
DeleteRequest request=new DeleteRequest("person",null,"1");
DeleteResponse response = restHighLevelClient.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.getResult().toString());
}响应结果:
搜索示例:
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.common.unit.TimeValue;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.search.builder.SearchSourceBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ElasticsearchSearchExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 RestHighLevelClient 实例,连接到 Elasticsearch 集群
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(
RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http"))
);
// 构建搜索请求
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("your_index"); // 替换为实际的索引名称
// 构建查询条件
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery()); // 查询所有文档
// 设置一些可选参数
searchSourceBuilder.from(0); // 设置起始索引,默认为0
searchSourceBuilder.size(10); // 设置返回结果的数量,默认为10
searchSourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(5000)); // 设置超时时间,默认为1分钟
// 将查询条件设置到搜索请求中
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
try {
// 执行搜索请求
SearchResponse searchResponse = client.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 处理搜索响应
System.out.println("Search took: " + searchResponse.getTook());
// 获取搜索结果
SearchHits hits = searchResponse.getHits();
System.out.println("Total hits: " + hits.getTotalHits().value);
// 遍历搜索结果
for (SearchHit hit : hits.getHits()) {
System.out.println("Document ID: " + hit.getId());
System.out.println("Source: " + hit.getSourceAsString());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// 处理异常
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 关闭客户端连接
client.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// 处理关闭连接异常
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
请注意,上述示例中的 your_index 应该替换为你实际的 Elasticsearch 索引名称。这个示例使用了简单的 matchAllQuery,你可以根据实际需求构建更复杂的查询条件。在搜索响应中,你可以获取到搜索的结果以及相关的元数据。
3.Spring Boot操作ES
在 Spring Boot 中操作 Elasticsearch 通常使用 Spring Data Elasticsearch,以标准的JPA的模式来操作ES。
依赖:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.x</version> <!-- 选择一个与Elasticsearch 7.17.3兼容的Spring Boot版本 -->
</parent><dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Starter Web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency><!-- Spring Data Elasticsearch -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency><!-- Spring Boot Starter Test (for testing) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
application.properties配置:
spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-nodes=localhost:9200
实体类:
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Field;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.FieldType;
import java.util.Date;
@Document(indexName = "blogpost_index")
public class BlogPost {
@Id
private String id;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text)
private String title;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text)
private String content;
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String author;
@Field(type = FieldType.Date)
private Date publishDate;
// 构造函数、getter和setter
public BlogPost() {
}
public BlogPost(String id, String title, String content, String author, Date publishDate) {
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
this.author = author;
this.publishDate = publishDate;
}
// 省略 getter 和 setter 方法
}
dao层:
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.ElasticsearchRepository;
public interface BlogPostRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<BlogPost, String> {
// 你可以在这里定义自定义查询方法
}
service层:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-824450.html
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
@Service
public class BlogPostService {
private final BlogPostRepository blogPostRepository;
@Autowired
public BlogPostService(BlogPostRepository blogPostRepository) {
this.blogPostRepository = blogPostRepository;
}
public BlogPost save(BlogPost blogPost) {
return blogPostRepository.save(blogPost);
}
public Optional<BlogPost> findById(String id) {
return blogPostRepository.findById(id);
}
public List<BlogPost> findAll() {
return (List<BlogPost>) blogPostRepository.findAll();
}
public void deleteById(String id) {
blogPostRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-824450.html
到了这里,关于【elastic search】JAVA操作elastic search的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!