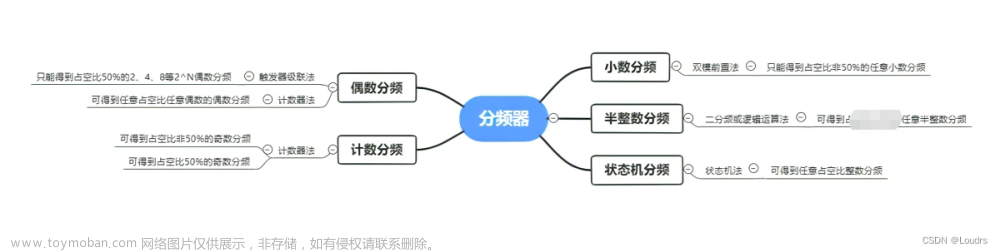
分频器简介
实现分频一般有两种方法,一种方法是直接使用 PLL 进行分频,比如在 FPGA 或者 ASIC 设计中,都可以直接使用 PLL 进行分频。但是这种分频有时候受限于 PLL 本身的特性,无法得到频率很低的时钟信号,比如输入 100Mhz 时钟,很多PLL 都无法得到 1Mhz 以下的时钟信号。另外一种方法是直接使用 Verilog 代码来实现分频。
注意:
使用 Verilog 代码分频得到的时钟信号尽量不要当做其他模块的输入时钟信号,因为通过 Verilog 代码分频得到的时钟信号默认不会连接到 FPGA 的时钟网络上,这样会导致时钟出现偏移和抖动,在高频电路中会影响电路稳定性,这种分频方式一般用于产生外部低速总线的参考时钟,如SPI、I2C的参考时钟。
偶数分频器和奇数分频器
根据分频器的分频比例是偶数还是奇数,可以将其分为偶数分频器和奇数分频器。
- 偶数分频:就是分频前的频率和分频后的频率比值是偶数,比如一个 50Mhz 的晶振时钟,进行二分频后,就是 50Mhz/2=25Mhz
- 奇数分频:就是分配前的频率和分频后的频率比值是奇数。比如一个 50Mhz 的晶振时钟,进行三分频后,就是 50Mhz/3=16.667Mhz
偶数分频实现
假设 N(N为偶数)分频,只需计数到 N/2-1,然后时钟翻转、计数器清零,如此循环就可以得到 N 分频。举个例子,比如晶振时钟是 100Mhz 时钟,想得到一个 25Mhz 的时钟,那么这个是一个 100/25=4 的四分频设计,按照我们刚说的计数到 4/2-1=1,然后时钟翻转、计数器清零,就可以得到一个 25Mhz 的时钟。
偶数分频 Verilog 代码
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module divider4(
input sys_clk,
input sys_rst_n,
output reg out_clk
);
//分频计数器
reg [2:0] count;
//分频计数器,按分频比/2-1进行计数
always @(posedge sys_clk) begin
if(!sys_rst_n)
count <= 2'd0;
else if(count < 2'd1)
count <= count + 2'd1;
else
count <= 2'd0;
end
//翻转输出时钟
always @(posedge sys_clk) begin
if(!sys_rst_n)
out_clk<= 1'b0;
else if(count == 2'd1)
out_clk <= ~out_clk;
end
endmodule
奇数分频器实现
同样假设 N(N为奇数)分频,计数器需要计数到 N-1,当计数器为0时输出时钟1在输入时钟的上升沿拉低,当计数器计数到 N/2 取整时输出时钟1在输入时钟的上升沿进行拉高,同时当计数器为0时输出时钟2在输入时钟的下降沿拉低,当计数器计数到 N/2 取整时输出时钟2在输入时钟的下降沿进行拉高,将输出时钟1和输出时钟2相与即可得到真正的输出时钟。 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-825175.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-825175.html
奇数分频 Verilog 代码
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module divider5(
input sys_clk,
input sys_rst_n,
output out_clk
);
//分频计数器
reg [2:0] count;
//上升沿跳变的中间时钟
reg out_clk1;
//下降沿跳变的中间时钟
reg out_clk2;
//分频计数器,按分频比-1进行计数
always @(posedge sys_clk) begin
if(!sys_rst_n)
count <= 3'd0;
else if(count < 3'd4)
count <= count + 3'd1;
else
count <= 3'd0;
end
//输出时钟1
always @(posedge sys_clk) begin
if(!sys_rst_n)
out_clk1 <= 1'b0;
else if(count == 3'd0)
out_clk1 <= 1'b0;
else if(count == 3'd2)
out_clk1 <= 1'b1;
end
//输出时钟2
always @(negedge sys_clk) begin
if(!sys_rst_n)
out_clk2 <= 1'b0;
else if(count == 3'd0)
out_clk2 <= 1'b0;
else if(count == 3'd2)
out_clk2 <= 1'b1;
end
//输出分频后的时钟
assign out_clk = out_clk1 & out_clk2;
endmodule
任意分频器实现
在实现任意分频器时可以利用条件生成语句,当模块例化时传入的参数为偶数则生成偶数分频的代码,否则生成奇数分频的代码,有关生成语句相关的内容参考03 Verilog HDL 语法。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-825175.html
任意分频 Verilog 代码
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module divider #(
//参数列表
parameter COUNT_WIDTH = 3, //内部分频计数器宽度
parameter DIV = 5 //分频系数
)
(
input sys_clk,
input sys_rst_n,
output reg out_clk
);
//分频计数器
reg [COUNT_WIDTH-1:0] count;
generate
if((DIV % 2) == 0) begin
//偶数分频
//按分频比/2-1进行计数
always @(posedge sys_clk) begin
if(!sys_rst_n)
count <= 0;
else if(count < (DIV / 2 -1))
count <= count + 1;
else
count <= 0;
end
//翻转输出时钟
always @(posedge sys_clk) begin
if(!sys_rst_n)
out_clk <= 1'b0;
else if(count == (DIV / 2 -1))
out_clk <= ~out_clk;
end
end
else begin
//奇数分频
//上升沿跳变的中间时钟
reg out_clk1;
//下降沿跳变的中间时钟
reg out_clk2;
//按分频比-1进行计数
always @(posedge sys_clk) begin
if(!sys_rst_n)
count <= 0;
else if(count < (DIV -1))
count <= count + 1;
else
count <= 0;
end
//输出时钟1
always @(posedge sys_clk) begin
if(!sys_rst_n)
out_clk1 <= 1'b0;
else if(count == 0)
out_clk1 <= 1'b0;
else if(count == (DIV / 2))
out_clk1 <= 1'b1;
end
//输出时钟2
always @(negedge sys_clk) begin
if(!sys_rst_n)
out_clk2 <= 1'b0;
else if(count == 0)
out_clk2 <= 1'b0;
else if(count == (DIV / 2))
out_clk2 <= 1'b1;
end
//输出分频后的时钟
always @(*) begin
out_clk = out_clk1 & out_clk2;
end
end
endgenerate
endmodule
到了这里,关于06 分频器设计的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!