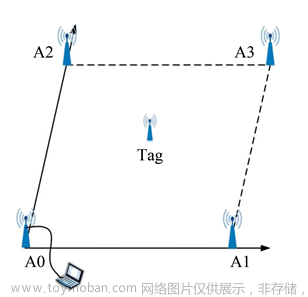
传统最小二乘空间定位原理
假设UWB定位系统里有n个基站。基站坐标设为
(
x
i
,
y
i
,
z
i
)
(x_{i},y_{i},z_{i})
(xi,yi,zi)(i=1,2,3…),标签坐标为(x,y,z),标签到基站的距离设为
d
i
(
i
=
1
,
2
,
3...
)
d_{i}(i=1,2,3...)
di(i=1,2,3...)可得以下关系式
{
(
x
−
x
1
)
2
+
(
y
−
y
1
)
2
+
(
z
−
z
1
)
2
=
d
1
2
(
x
−
x
2
)
2
+
(
y
−
y
2
)
2
+
(
z
−
z
2
)
2
=
d
2
2
⋯
(
x
−
x
n
)
2
+
(
y
−
y
n
)
2
+
(
z
−
z
n
)
2
=
d
n
2
\begin{cases}\left(x-x_1\right)^2+\left(y-y_1\right)^2+\left(z-z_1\right)^2=d_1^2\\\left(x-x_2\right)^2+\left(y-y_2\right)^2+\left(z-z_2\right)^2=d_2^2\\\cdots\\\left(x-x_n\right)^2+\left(y-y_n\right)^2+\left(z-z_n\right)^2=d_n^2\end{cases}
⎩
⎨
⎧(x−x1)2+(y−y1)2+(z−z1)2=d12(x−x2)2+(y−y2)2+(z−z2)2=d22⋯(x−xn)2+(y−yn)2+(z−zn)2=dn2
从第二式开始减去第一式,消去
x
2
,
y
2
,
z
2
x^2,y^2,z^2
x2,y2,z2可得
{
(
x
2
2
−
x
1
2
)
+
(
y
2
2
−
y
1
2
)
+
(
z
2
2
−
z
1
2
)
−
2
(
x
2
−
x
1
)
x
−
2
(
y
2
−
y
1
)
y
−
2
(
z
2
−
z
1
)
z
=
d
2
2
−
d
1
2
(
x
3
2
−
x
1
2
)
+
(
y
3
2
−
y
1
2
)
+
(
z
3
2
−
z
1
2
)
−
2
(
x
3
−
x
1
)
x
−
2
(
y
3
−
y
1
)
y
−
2
(
z
3
−
z
1
)
z
=
d
3
2
−
d
1
2
⋮
(
x
n
2
−
x
1
2
)
+
(
y
n
2
−
y
1
2
)
+
(
z
n
2
−
z
1
2
)
−
2
(
x
n
−
x
1
)
x
−
2
(
y
n
−
y
1
)
y
−
2
(
z
n
−
z
1
)
z
=
d
n
2
−
d
1
2
\begin{cases}({x_2}^2-{x_1}^2)+({y_2}^2-{y_1}^2)+({z_2}^2-{z_1}^2)-2(x_2-x_1)x-2(y_2-y_1)y-2(z_2-z_1)z={d_2}^2-{d_1}^2\\ ({x_3}^2-{x_1}^2)+({y_3}^2-{y_1}^2)+({z_3}^2-{z_1}^2)-2({x_3}-x_1)x-2({y_3}-y_1)y-2({z_3}-z_1)z={d_3}^2-{d_1}^2\\ \vdots\\ ({x_n}^2-{x_1}^2)+({y_n}^2-{y_1}^2)+({z_{n}}^2-{z_1}^2)-2({x_{n}}-{x_1})x-2({y_n}-{y_1})y-2({z_{n}}-z_1)z={d_n}^2-{d_1}^2\end{cases}
⎩
⎨
⎧(x22−x12)+(y22−y12)+(z22−z12)−2(x2−x1)x−2(y2−y1)y−2(z2−z1)z=d22−d12(x32−x12)+(y32−y12)+(z32−z12)−2(x3−x1)x−2(y3−y1)y−2(z3−z1)z=d32−d12⋮(xn2−x12)+(yn2−y12)+(zn2−z12)−2(xn−x1)x−2(yn−y1)y−2(zn−z1)z=dn2−d12
化成矩阵形式为AX=B
A
=
2
[
x
1
−
x
2
y
1
−
y
2
z
1
−
z
2
x
1
−
x
3
y
1
−
y
3
z
1
−
y
z
3
⋮
⋮
x
1
−
x
n
y
1
−
y
n
z
1
−
z
n
]
\left.A=2\left[\begin{matrix}x_1-x_2 & & y_1-y_2 & z_1-z_2\\ x_1-x_3 & & y_1-y_3 & z_1-yz_3\\ \vdots & & \vdots & \\ x_1-x_{n} & & y_1-y_{n} & z_1-z_{n}\end{matrix}\right.\right]
A=2
x1−x2x1−x3⋮x1−xny1−y2y1−y3⋮y1−ynz1−z2z1−yz3z1−zn
X
=
[
x
y
z
]
X=\begin{bmatrix}x\\y\\z\end{bmatrix}
X=
xyz
B
=
[
d
2
2
−
d
1
2
+
(
x
1
2
−
x
2
2
)
+
(
y
1
2
−
y
2
2
)
+
(
z
1
2
−
z
2
2
)
d
3
2
−
d
1
2
+
(
x
1
2
−
x
3
2
)
+
(
y
1
2
−
y
3
2
)
+
(
z
1
2
−
z
3
2
)
⋮
d
n
2
−
d
1
2
+
(
x
1
2
−
x
n
2
)
+
(
y
1
2
−
y
n
2
)
+
(
z
1
2
−
z
n
2
)
]
\left.B=\left[\begin{matrix}{{d}_{2}}^2-{{d}_{1}}^2+({x_{1}}^2-{x_{2}}^2)+({y_{1}}^2-{y_{2}}^2)+({z_1}^2-{z_2}^2) & \\ {{d}_{3}}^2-{{d}_{1}}^2+({x_{1}}^2-{x_{3}}^2)+({y_{1}}^2-{y_{3}}^2)+({z_1}^2-{z_3}^2) & \\ \vdots & \\ {{d}_{n}}^2-{{d}_{1}}^2+({x_{1}}^2-{x_{n}}^2)+({y_{1}}^2-{y_{n}}^2)+({z_1}^2-{z_{n}}^2) & \end{matrix}\right.\right]
B=
d22−d12+(x12−x22)+(y12−y22)+(z12−z22)d32−d12+(x12−x32)+(y12−y32)+(z12−z32)⋮dn2−d12+(x12−xn2)+(y12−yn2)+(z12−zn2)
要求X可得
[
x
y
z
]
=
1
2
(
A
T
A
)
−
1
A
T
B
\begin{bmatrix}x\\ y\\ z\end{bmatrix}=\dfrac{1}{2}\Big(A^{T}A\Big)^{-1}A^{T}B
xyz
=21(ATA)−1ATB
要求三维坐标至少四个基站文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-827184.html
python算法模拟:
这里先模拟二维的,使用最小二乘法求解时,会因基站z轴坐标差值小导致误差较大,相较与水平坐标,z坐标不可靠,故采用其他方法获取z值文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-827184.html
import tkinter as tk
import numpy as np
import math
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class MapApp:
def __init__(self, master):
self.master = master
self.master.title("UWB Emulation")
self.master.geometry("800x600")
self.num_base_stations = 4
self.base_stations = [(random.randint(50, 550), random.randint(50, 550)) for _ in range(self.num_base_stations)]
self.noise_mean = 0
self.noise_stddev = 1
self.canvas = tk.Canvas(self.master, width=600, height=600, bg="white")
self.canvas.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
self.label = tk.Label(self.master, text="")
self.label.pack()
self.mouse_marker = None
self.distance_circles = []
self.create_widgets()
# 鼠标移动时进行一次计算
self.canvas.bind("<Motion>", self.show_mouse_position)
def create_widgets(self):
self.create_base_stations()
self.create_noise_slider()
def create_base_stations(self):
i=0
for station in self.base_stations:
x, y = station
self.canvas.create_oval(x - 5, y - 5, x + 5, y + 5, fill="red")
# 在标签中显示每个基站的坐标
station_label = tk.Label(self.master, text=f"Base Station {i+1}: ({x}, {y})")
station_label.pack()
i = i+1
def calculate_distance(self, x, y):
distances = [math.sqrt((x - station[0])**2 + (y - station[1])**2) + random.gauss(self.noise_mean, self.noise_stddev) for station in self.base_stations]
return distances
def draw_distance_circles(self, x, y, distances):
for i, station in enumerate(self.base_stations):
x0, y0 = station
radius = distances[i]
circle = self.canvas.create_oval(x0 - radius, y0 - radius, x0 + radius, y0 + radius, outline="blue")
self.distance_circles.append(circle)
#最小二乘法
def uwb_LeastQusare(self, distance_vector):
# 创建A矩阵
x_1, y_1 = self.base_stations[0]
a = np.array([[x_1 - station[0], y_1 - station[1]] for station in self.base_stations[1:]])
# 创建B矩阵
d_1 = distance_vector[0]
# print('test')
# print(distance_vector[1]**2 - d_1**2)
# print(distance_vector[1]**2 - d_1**2 + (x_1**2 - self.base_stations[1][0]**2))
# print(distance_vector[1]**2 - d_1**2 + (x_1**2 - self.base_stations[1][0]**2) + (y_1**2 - self.base_stations[1][1]**2))
b = np.array([[distance_vector[i]**2 - d_1**2 + (x_1**2 - station[0]**2) + (y_1**2 - station[1]**2)] for i, station in enumerate(self.base_stations[1:],start=1)])
X = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(np.dot(np.transpose(a), a)), np.dot(np.transpose(a), b)) * 0.5
# print('aa:')
# print(a)
# print('bb:')
# print(b)
# print('cc')
# print(X)
return X;
def show_mouse_position(self, event):
if self.mouse_marker:
self.canvas.delete(self.mouse_marker)
true_val = event.x, event.y
x, y = event.x, event.y
distances = self.calculate_distance(x, y)
distance_text = "\n".join([f"Base Station {i+1}: {dist:.2f}" for i, dist in enumerate(distances)])
self.label.config(text=f"Mouse Position: ({x}, {y})\nDistances to Base Stations:\n{distance_text}")
#最小二乘法求解
result = self.uwb_LeastQusare(distances)
Err_val = (true_val[0]-result[0])**2 + (true_val[1]-result[1])**2
print('result'+' '+str(result))
print(Err_val)
self.mouse_marker = self.canvas.create_oval(x - 3, y - 3, x + 3, y + 3, fill="green")
for circle in self.distance_circles:
self.canvas.delete(circle)
self.distance_circles = []
self.draw_distance_circles(x, y, distances)
def create_noise_slider(self):
noise_frame = tk.Frame(self.master)
noise_frame.pack()
noise_label = tk.Label(noise_frame, text="Noise Level:")
noise_label.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
noise_slider = tk.Scale(noise_frame, from_=0, to=100, resolution=0.1, orient=tk.HORIZONTAL, command=self.update_noise_level)
noise_slider.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
def update_noise_level(self, value):
self.noise_stddev = float(value)
def get_distance_values(self):
# 获取显示在窗口上的距离值
return self.label["text"]
def main():
root = tk.Tk()
app = MapApp(root)
root.mainloop()
# 获取显示在窗口上的距离值
distance_values = app.get_distance_values()
print("Distance Values:", distance_values)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
到了这里,关于uwb最小二乘空间定位+python模拟的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!